Evaluating the success of Government
Introduction
Unemployment and inflation are the major factor to understand the economic growth of the country and it is the responsibility of the government to tackle the unemployment and inflation rate in the economy to stabile the financial activities, international trade and exchange rate in the international market (Argy and Nevile, 2016). The study focuses on analysing the government’s initiative and the policies in the economy to tackle the unemployment rate as well as the rate of inflation to stabilise the economy and ensure future sustainable development of the country. The paper is effective to discuss the theories of managing unemployment rate and inflation rate as well as identify the government policies and practice to reduce both the rate of unemployment and inflation in the economy, so that the country can be represented internationally with high economic growth and social development, thus providing valuable insights for those seeking economics dissertation help.

Policies of government to tackle unemployment and inflation rate
Unemployment rate is defined as the percentage of unemployed workers in the total work force in the economy and it indicates the spare capacity and unused resources of the economy. There are different theories of managing unemployment rate where the government of the country takes different policies to tackle the unemployment rate and try to reduce it for stabilising the labour market and providing job opportunity to the people in the economy. There are demand side policies and supply side policies to reduce the demand deficient unemployment as well as reduce the structural unemployment (Argy and Nevile, 2016). The major supply side policies are such as providing supply side training and development program to the employees to resolve the occupational immobility, giving geographical subsidies to help the workers and firms to move faster and manage the supply of the employees in the market and apart from that there is removal of employment rules and market regulations to increase flexibility in the labour market (Clark, 2016). The other supply side policies are such as giving employment subsidies to encourage the firms to take the long term unemployed so that the employment rate can be increased in long run. In order to reduce the real wage unemployment, it is also necessity to reduce the power of trade union and increase the minimum wage bar in the market. Hereby, the rules of minimum wage and the flexibility at the labour market need to be changed where the employees can get the opportunity to be employed in the economy (Bhattarai, 2016).
Figure 1: Policies to tackle unemployment rate
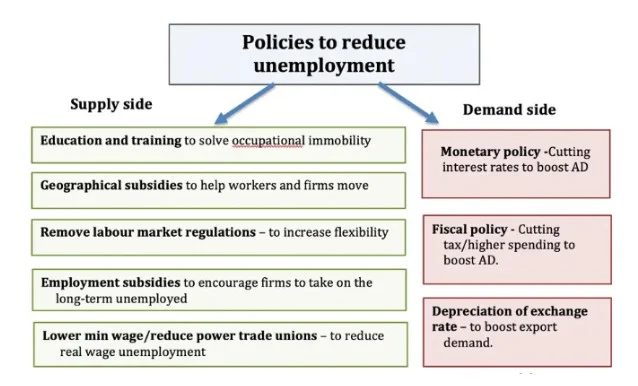
On the other hand, there are demand side policies, including the fiscal policy, monetary policy and depreciation of exchange rate in the economy. These are the major policies and practice, through which the government aims at reducing the rate of unemployment in the market. Through the fiscal and monetary policies, the government of the economy aim to manage the unemployment rate and reduce it in long run. The fiscal and monetary policies will be analysed where the theory of managing unemployment rate in the economy can be evaluated further for understanding the initiative of the government of the economy for reduction of the rate of unemployment in the country (Bhattarai, 2016).
Fiscal policy to reduce unemployment rate:
Fiscal policy is effective to reduce the unemployment rate in the economy, where increasing the aggregate demand and the rate of economic growth can manage the issue of unemployment in the country. The government in this regard the expansionary fiscal policy where the aggregate demand curve will shift in a rightward direction to improve the activities in the economy where the tax cutting an increasing government spending in the economy will be able to reduce the unemployment rate (Piore, 2017). In this regard, lower tax rate increases the disposable income of the households and it further boosts the consumption, leading to higher aggregate demand. With an increase in aggregate demand, there will be an increase in real Gross Domestic Product (GDP), where the firms are able to produce more and contribute positively in expanding the activities if international trade influencing strong economic growth (Odo et al., 2017).
Figure 2: Impacts of higher aggregate demand in the economy

Monetary policy to reduce unemployment rate:
The monetary policy is also effective to tackle the issue of unemployment in the economy and in this regard, cutting the interest rate in the economy is one of the effective strategic initiatives of the government to reduce unemployment rate. Lower rates decrease the cost of borrowing and it further encourages the people to spend and invest more for better return on investment. It is the goal of the government to stabilise the labour market and the major policies of the government are managing money supply, reducing interest rate to boost aggregate demand and stabilise the prices and wage in the economy (Odo et al., 2017).
In addition to this, inflation rate is also one of the major factor for enhancing the economic growth and social development of the country and in this regard, inflation is a quantitative measure of the rate at which the average price level of the baskets of goods and services in an economy increases over a period of time. Hyperinflation is the phase where the real value of the economy becomes lower as the value of local currency decreases with the rise of prices of the goods and services. Primary policy to tackle the inflation rate in the economy is monetary policy where rising interest rate can reduce the inflation rate in the market. Other polices of managing inflation rate are such as fiscal policy by higher tax rate, and the supply side policies including wage control, appreciation in the exchange rate and the control of money supply in the economy (Okoye et al., 2016).
Fiscal policy to reduce inflation rate:
The tight fiscal policy to stabilise the inflation rate is higher income tax or lower the spending of the government in the country which in turn helps to reduce the aggregate demand and leading to lower growth and less demand pull inflation. Fiscal policy of changing tax rate and government spending level is effective for managing inflation rate in the economy, where it reduces the inflationary pressure by reducing aggregate demand and of the economy (Seguino, 2019). Fiscal policy can also reduce government borrowing which shifts the aggregate demand curve towards left and this is effective policy by the government to stabilise the economy.
Figure 3: Impacts of lower aggregate demand in the economy
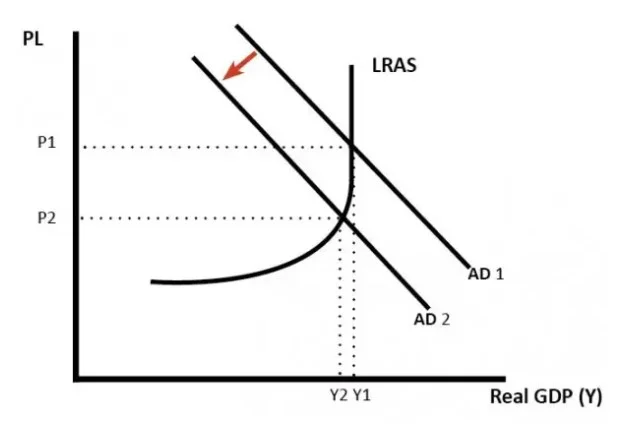
Monetary policy to reduce inflation rate:
the monetary policy of the government higher interest rate is the policy where the government can stabilise the rate of inflation as higher rate of interest further increases the cost if the borrowing and discourage spending in the economy. This leads to lower economic growth and lower inflation (Seguino, 2019).
Unemployment and inflation rate in the UK
Unemployment rate of the UK is decreasing over the years, where the government plays a crucial role to reduce the unemployment rate and provide different opportunities to the labour market to stabilise the employment in the market. In the UK, during the year 2009, the inflation rate is high and the rate is 5.7%. The government aims at reducing the unemployment rate to stabilise the economy and take corrective actions for managing proper employment in the economy. In this regard, the government of the UK is successful to reduce the unemployment rate where from 2017; the rate is decreasing over the years where ore job opportunities created in the economy. In 2012, it was at its peak with 8.1%, but in 2015, it was 5.4%. In the last year, 2019, the unemployment rate was 3.8%, where the government took effective measures to manage the unemployment rate in the economy (Statista, 2019a).
Figure 4: Unemployment rate in the UK

On the other hand, considering the inflation rate, the UK is successful to stabilise the inflation rate. In 2009, it was 2.2%, but in 2011, it was 4.5% which was high. Government if the UK aims at reducing the rate of inflation to stabilise the economy, where it started to decrease the rate from 2013. However, after 2015, it was increasing over the years and after 2017, it again started to deteriorate due to the government intervention in the economy. In 2019, the inflation rate was 1.8%, where it is possible to maintain the rate under 2% to improve the economic value and the value for the local currency in the international market (Statista, 2019b).
Figure 5: Inflation rate in the UK

Government initiative in the UK:
UK is successful to reduce the unemployment rate after the recession 2008-2009 where the fiscal policy can decrease the rate of unemployment by helping the aggregate demand to boost contributing positively for economy growth. The government of the UK took expansionary fiscal policy to reduce the unemployment rate and encourage more employments opportunities in the market. In this regard, there are other supply side policies of the UK to promote employment in the market. The government through the use of Federal Reserve aims at reducing the unemployment rate for economic growth and in this regard the expansionary monetary policy will help the country to reduce the rate of unemployment. Reducing the federal funds rate is the monetary policy to reduce the unemployment rate. In this regard, the other strategic initiative of the government of the UK is investment on education and training, giving employments subsidies and improves labour market flexibility. The government of the UK is collaborative and aim at improving flexibility in the labour market so that it is possible for the government to reduce unemployment and boost the employments opportunities in the market. In addition to this, the government takes initiatives to pen the training and educational programs and introduce it in the market for improving the knowledge and capabilities of the employees. After the recession, the government takes serious account for reduction of the unemployment rate (Pettinger, 2019a).
On the other hand, the inflation rate of the UK is also decreasing over time and it is possible for the government to reduce it fewer than 2% which stabilise the economy and improve the foreign trade. In the UK, the monetary policy is set by the MPC and the Bank of England where the targets the inflation rate within 2% and above -1%. The UK government aims to increase the rate of interest which may reduce the aggregate demand influencing to deteriorate the rate of inflation in the economy. In addition to this, the government also focuses on supply side policies to control the inflation rate. According to the supply side polices, long term competitiveness and the productivity may reduce the rate of inflation. It is possible to increase the productivity of the firms by deregulating the company and improving privatisation. The government of the UK is efficient to privatise the organisations and enhance competitiveness and productivity of the firm and this intern helps to reduce the inflation rate in the UK. Exchange rate policy is another strategic move of the government of the UK to tackle the inflation rate and in this regard, in 1980, UK joined ERM as means of controlling inflation. Keeping the value of the pound high will help to reduce the inflationary pressures on the economy and in this regard the stringer pound makes import cheaper and lower cost push inflation. This is an effective strategy to increase import and on the other hand, stringer pound means reduction of domestic demand and it lead to less demand pull inflation. A stringer pound also creates incentive for the firms to cut the cost of production in order to enhance competitiveness. In order to maintain the value of pound, the interest rate is approximately 15% to contribute positively in recession and enhance the economic growth and social development (Pettinger, 2019b).
Unemployment and inflation rate in the USA
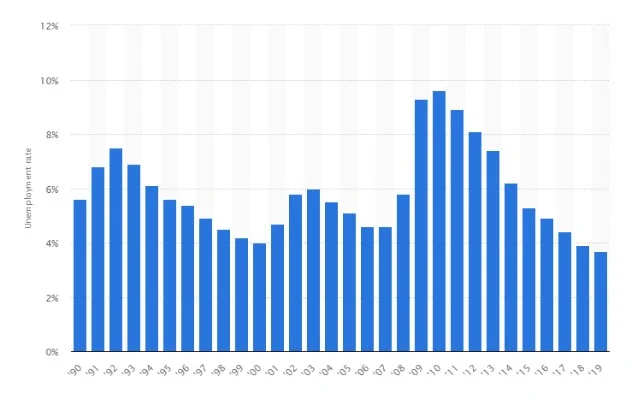
USA is also another effective country, where the government is efficient to manage the unemployment and inflation rate in order to enhance economic growth and represent the economy efficiently in the international market. In this regard, the unemployment rate of the economy in 2009 was 9.3% and it has increased during 2010 and 2011. However, after that, it started to reduce where the government took corrective initiative to control the unemployment rate and enhance the economic growth by boosting the aggregate demand in the economy. In the year of 2018, it was 3.9% and in 2019, it was 3.7% and thus it can be stated that the unemployment rate of the economy started to decrease at a rapid rate which influence the economic growth and social development where the employees can have the opportunity for employment (Statista, 2019c).
Figure 6: Unemployment rate in the USA
Inflation rate of the USA is also effective where the government took efficient step including fiscal and monetary policy to reduce the inflation rate under 2% and boost the economy successfully. In 2009, it was negative at -4% and in 2011, it was high at 3.2%, after that it started to decrease. However, in 2018, it was high at 2.4% and in 2019; it becomes lower at 1.8%. Hereby, the inflation rate is fluctuating in the USA and the government to strong policy and procedure to reduce the inflation rate to increase the value of the currency in the global market (Statista, 2019d).
Figure 7: Inflation rate in the USA

Government initiative in the USA:
In order to tackle the unemployment rate in the USA, the government took active initiative where the expansionary fiscal policy is effective in which the government raises spending in the economy. there are investment in the educational training as well as the regulations have been changed under new rules and employment regulations, in which the government of the UK focuses on reducing the power of trade unions, giving equal opportunity to the labour force, managing minimum wage of the economy and improving labour market flexibility to boost the mobility of the employees. Unemployment benefit in the market and reducing the trade union’s power are effective to boost employment in the economy. Strict benefit requirement and improved geographical mobility further boosts the employment rate in the market. On the other hand, the inflation rate of the economy is also under control and it is under 2%, which is stabilising in terms of economic growth and social development. The government raises the interested rate to stabilise the inflation rate and enhance the activities in international trade. Wage control strategy is another effective policy, where the reduction of minimum wage may reduce the inflation rate and deteriorate the inflationary pressure on the economy. Cost push inflationary control mechanism is also adopted by the USA government where the cost of other production is controlled to improve efficiency and manage the CPI under 2%. Hereby, it is possible for the government to predict the future inflation and take corrective actions immediate to boost the economic growth and social development and managing the value of their currency through inflation control and exchange rate stability (Pettinger, 2019c).
Evaluation and analysis
It is necessary for the government of the countries to take corrective initiative to tackle the inflation rate and the rate of unemployment as these are effective for boosting economic growth and enhance social development. As per the above analysis, it can be stated that, the counties, the UK and USA are effective to control the unemployment rate and inflation rate to foster growth and manage aggregate demand in the economy. Both the fiscal and monetary policy are effective to control the unemployment where rise in government spending and the high interest rate in the rte in the economy give employment opportunities and scope to invest more for high return investment. The fiscal policy of rising aggregate demand is effective for reducing unemployment rate and on the other hand reduction on aggregate demand is effective for reducing the inflation rate and stabilises the economy (Pettinger, 2019a).
Continue your exploration of Evolution Of Industrial Growth with our related content.
On the other hand, the monetary policy is also effective where the government control monetary supply and manage the interest rate to control the inflation rate and also the rate of unemployment in the economy. Decreasing the money supply can control the inflation rate in the economy and it further helps to control the interest rate and circulation of money in the economy. there are also supply side policies which are effective to control the unemployment rate and in this regard the unemployment rate of both the nations are also controlled efficiently by the government, where the government aims at investing more on educational training, reducing the power of trade union and manage the regulations and minimum wage to improve flexibility in the labour market. Hereby, it is effective for the government of both the countries to tackle the inflation and unemployment rate in the economy and enhance the economic growth and social development in long run (Pettinger, 2019b).

Conclusion
The inflation and unemployment rate needs to control under the government intervention, where both the fiscal and monetary policies and practice are effective to control the rate and reduce it at lower to stabilise the economy. Reduction of interest rate and boosting aggregate demand in the economy for both the countries, UK and USA are effective to improve employment and reduce the rate of unemployment. On the other hand, the tight fiscal policy of higher income tax and lower government spending in the economy as well as the monetary policy of high interest rate are also effective for the countries to tackle the issue of unemployment and inflation rate and lower the rate of unemployment and inflation in long run. As per the analysis, it can be stated that, the governments of both the countries, UK and USA are successful to reduce the unemployment rate at 3.8% and 3.7% respectively and stabilise the economy by reducing the inflation rate under 2%.
Reference List
Argy, V.E. and Nevile, J., 2016. Inflation and Unemployment: Theory, Experience and Policy Making. London: Routledge.
Bhattarai, K., 2016. Unemployment–inflation trade-offs in OECD countries. Economic modelling, 58, pp.93-103.
Clark, P.B., 2016. 11 Inflation and Unemployment in the United States: Recent Experience and Policies. Inflation and Unemployment: Theory, Experience and Policy Making, p.221.
Odo, S.I., Elom-Obed, F.O., Okoro, T.O. and Nwachukwu, J.O., 2017. Understanding the Relationship between Unemployment and Inflation in Nigeria. Journal of Poverty, Investment and Development, 35, pp.55-64.
Okoye, L.U., Evbuomwan, G.O., Modebe, N.J. and Ezeji, F.N., 2016. Macroeconomic performance and government fiscal deficits-Evidence from Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Management Technology & Development, 7(2).
Piore, M., 2017. Unemployment and inflation: institutionalist and structuralist views. London: Routledge.
Seguino, S., 2019. Tools of macroeconomic policy: fiscal, monetary and macroprudential approaches. Gender Equality and Inclusive Growth: Economic Policies to Achieve Sustainable Development.
Dig deeper into Evaluating The Efficacy of Public Cctv Systems with our selection of articles.
Bibliography
Ayogueze, N.F. and Anidiobu, G.A., 2017. Assessment of impact of government budget deficits on unemployment rate in Nigeria. Journal of Economics and Finance, 8(6), pp.18-26.
Bar-Yam, Y., Langlois-Meurinne, J., Kawakatsu, M. and Garcia, R., 2017. Preliminary steps toward a universal economic dynamics for monetary and fiscal policy. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.06285.
Buba, S. and Aljadi, S., 2017. Inflation and Unemployment in Nigeria: An ARDL Approach. World Journal of Economic and Finance, 32, pp.69-74.
Carvalho, A.C. and Carvalho, D.F., 2019. The performance of the brazilian economy: The development of inflation, growth and unemployment. Revista galega de economía: Publicación Interdisciplinar da Facultade de Ciencias Económicas e Empresariais, 28(1), pp.91-101.
Gaffard, J.L., Napoletano, M. and Battiston, S., 2018. Some reflections on inflation targeting, monetary–fiscal policy interactions, and unconventional monetary policies. European Journal of Economics and Economic Policies: Intervention, 15(2), pp.132-138.
Hongo, D.O., Li, F., Ssali, M.W., Nyaranga, M.S., Musamba, Z.M. and Lusaka, B.N., 2019. Inflation, unemployment and subjective wellbeing: nonlinear and asymmetric influences of economic growth.
Mohseni, M. and Jouzaryan, F., 2016. Examining the effects of inflation and unemployment on economic growth in Iran (1996-2012). Procedia Economics and Finance, 36, pp.381-389.
Moura, A., 2019. Monetary and fiscal policy in Portugal before and after the Euro adoption (Doctoral dissertation).
O'Connell, J., 2016. On Keynes on inflation and unemployment. The European Journal of the History of Economic Thought, 23(1), pp.82-101.
Rieger, B., 2018. Making Britain work again: unemployment and the remaking of British social policy in the Eighties. The English Historical Review, 133(562), pp.634-666.
Sasongko, G. and Huruta, A.D., 2019. The causality between inflation and unemployment: the Indonesian evidence. Business: Theory and Practice, 20, pp.1-10.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



