A Study on the Factors that Contribute Towards the Downfall of New Enterprises within Their First Year of Operation: A Case Study on Nigeria
ABSTRACT
Background
This present paper proposes for a research study to be conducted on the factors that contribute towards the downfall of new enterprises within their first year of operation. The study proposes that Nigeria be used as a representative of emerging nations and that it is equally used as the data collection centre.
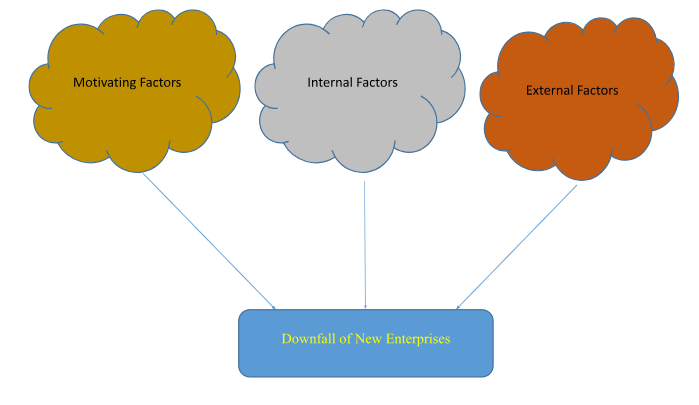
The unique proposition that the study will present is drawing a link between factors that motivate someone to establish an enterprise, factors that are internal or within the control of the entrepreneur and external factors that are beyond the control of the entrepreneur and how they collectively contribute towards the downfall of the new enterprises.
The significant contribution this study intends to make is by proposing possible remedies or solutions that can protect new enterprises from collapsing within their first year of operation.
INTRODUCTIONw
The background/motivation for the study
By a simple walk along a business district or rather an area populated with many small and medium enterprises one would note over a period of time that either most of the old shops have closed down and there are new business in the same location or there is a sign at the door that reads ‘under new management.’ Having being accustomed to these observation here in the United Kingdom as well as back home in Nigeria , there is a conviction that there are a host of factors that pose a grievous threat or challenge to new entrepreneurs to an extent that very few are unable to last over a longer period of time. Seeking business dissertation help becomes critical for the ones who aim to navigate through all these challenges and establish a sustainable system.

This observation is equally shared by Hyder & Lussier (2016), Wagner (2013), and Schaefer (2011), who collectively stated that an average of 80% of new start-ups fail within their first 12 to 18 months, while some of the surviving enterprises basically survive on hand-to-mouth basis i.e. they are not making any substantial profit but rather are making enough to cover for their expenses (breaking-even). This experience is so common that it is a norm for every successful entrepreneur to have a fair share of failures, however, this begs the question on whether there is no sure way of doing things the right way in the first instance especially considering the amount of financial literature and even documented dos and don’ts for new entrepreneurs. To further give this problem a panorama view and evoke more thoughts for discussion is the fact that even well-established business and economies at times end up failing leaving so many unanswered question considering the financial, infrastructural, and human resources that were at its disposal but it still fail. For example, despite of all the financial expertise economies of first-World countries such as the UK, US, and Germany among others went through an economic recession from 2007 to 2009 (Grusky et al 2011). Secondly, a company such as Nokia, which was a pioneer in the mobile phone industry of which at one point it had the biggest share of the market, still failed to live up to competition from new entrants like Samsung and Apple, eventually it was bought-out in 2014 by Microsoft Inc. (Singh, 2014). Thirdly, Yahoo Inc. is also a case example of a company with financial, infrastructural, and human resources that has failed to live up to its expectation so much so that it recently sold its core business, which include internet operations and land holdings to Verizon Communication mid last year (Solomon, 2016).

Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to A case study of Aramco.
The focus of this research study will be on the failure of start-ups rather than well-established businesses that have been in operation for many years. It is imperative to focus on start-ups since there are higher probabilities on their failure compared to well-established businesses. Secondly, focus on start-ups is also motivated by the fact that a big percentage of the population are presently enchanted to venture into entrepreneurship because of the allure that has been attached to it i.e. freedom and the possibility of making more money than in formal employment. Consequently, this means more and more people are likely to suffer similar fate experienced by start-up entrepreneurs who were forced to close down resulting in wasted time, financial resources, and most cases indebtedness.
Research Aim
The aim of this study is to identify the main factors that contribute towards the downfall or failure of new enterprises within their first year of operation.
Research Objectives
To establish the motivating factors for new start-ups/enterprises.
To identify the internal and external factors that cause new enterprises to fold-up within their first year of operation.
To establish the possible remedies or solutions to avert failure of new enterprises within their first year of operation.
Dig deeper into A Study into the Motivating Factors with our selection of articles.
LITERATURE REVIEW
A discussion of previous (empirical) studies on the topic area
In order to understand why new start-up fail within their first year of operation it is pivotal to first establish what motivates entrepreneurs to set-up shop. According to Greene (2012), an entrepreneur by definition should be someone who is motivated to venture into entrepreneurship by the desire to fill an existing gap within the market i.e. to supply what is missing in the market or the current supply of the product and/or services is unable to satisfy the existing demand. However, Reinders & Freijsen (2012) states that media has hyped entrepreneurship to an extent that it seems more fashionable than formal employment more so by focusing on success stories of entrepreneurs who have achieved tremendous success, which affords them a life full of luxury. As a result Stokes & Wilson (2010), states that most of new entrepreneurs are inspired by the allure of freedom attached with self-employment whereby one gets to be his/her own boss and thus able to work at preferred hours. Secondly, some of the new entrepreneurs perceive entrepreneurship to be an easy avenue to grow rich faster unlike formal employment where it takes a longer period and attainment of additional qualifications in order to earn a higher salary. Thirdly, a portion of new entrepreneurs establish start-ups just as side hustles that could possibly complement their salaries, which means it is not their fulltime engagement. Latha & Murthy (2009) on their part added that some entrepreneurs are inspired to establish a business to simply pursue the commercial gains attached to their passion, which could be in drawing/painting, music, reading, or swimming.
Rajavel (2013) in his writings stated that most entrepreneurs fail because they go into entrepreneurship for the wrong reason, which blinded their mind and thoughts to what was critical to the survival and success of their businesses. According to Amel & Akkari (2012), the primary reason start-ups fold-up within their first year of operation is because of liquidity crunch, which makes it impossible to cover operational costs and hence they reach a point they do not have any inventory to sell. On this point, Willebrands et al (2012) stated that in a country such as Nigeria, start-ups fail within their first year because of financial burden accrued from servicing the loan, which was obtained to complement the owner’s capital. Whilst start-ups require regular inflow of cash, the burden of credit capital means the new businesses make cash withdrawal contrary to the proven business practice of cash reinjection into the business within the first months or years of operation that is necessary to accelerate growth and ensure success of the business. In essence, this argument attributes the failure of new business within their first year of operation to financial responsibilities that are attached to it in a time when it needs regular cash injection.
In the studies conducted by Hyder & Lussier (2016), which applied the use of Lussier Model of business failure and success, 143 small business in Pakistan were sampled and it was noted that failure of a business can be linked to lack of the following requirements; initial business planning, qualified workforce, adequate capital inflows, and partnerships. Kraybill et al (2011) conducted a study to establish the source of success for Amish enterprises in North America, which had recorded 90% success rate and it was noted that the success or failure of a small business in Amish communities is determined by five forms of socio-cultural capital that comprise of human, social, cultural, symbolic, and religious capitals. In a study conducted by Cant et al (2014) focusing on South Africa, it was noted that 5 out of 7 small businesses fail within first twelve months of operation and this mainly because of lack of
financial support. From those interviewed in the study 56.9% stated they had received financial support from bank through loans while only 1.7% had received financial support from the government and this meant that collectively 58.6% of the respondents were under the pressure of loan repayment whilst their businesses were still in need of regular capital injections. Ropega (2011) conducted a unique study by focusing on the sources and process of failure for small and medium enterprises. The findings of this study showed that SMEs collapse because the management fail to take note of the business’ dire situation at the opportune time, which results in delay of implementation of corrective measures subsequently leading to the collapse of the business.
Identification of Gap
Previous discussion on the factors that contribute to the downfall of new enterprises within their first year of operation have failed to adopt a common and holistic approach to the analysis, which looks at the internal and external factors that are responsible for the failure. Evidently, from the above discussion it is hard to extrapolate the specific internal factors that are even associated with the motivation to venture into entrepreneurship and the external factors, which are responsible for the downfall of new start-ups within their first year of operation. However, lack of adequate financial resources stands out as the common factor but exiting literature has failed to explore this factor from a holistic perspective whereby entrepreneurs’ financial literacy and initial business planning are linked to this common cause of downfall for new start-ups within their first year of operation.
Statement of Problem
There is a need to establish the link between motivating factors (reasons to start a new enterprise) for new entrepreneurs, internal factors (within the purview of the entrepreneur) and external factors (outside the purview of the entrepreneur) and how they all collectively contribute to the downfall of new enterprises within their first year of operation.
Theoretical Framework
This proposed research study will be based on the grounded theory, meaning it will aim at developing a theory that explain what factors contribute towards the downfall of new enterprises within their first year of operation. As envisioned from the problem statement, the theoretical framework of this proposed study needs to draw a link between motivating factors, internal factors and external factors, and how they all contribute towards the downfall of new enterprises. This is illustrated in the image below.
Research questions
What are some of the factors that motivate people to venture into entrepreneurship?
What are the internal and external factors that cause new enterprises to fold up within their first year of operation?
What are the possible remedies or solutions that can be applied to avert the downfall of new enterprises within their first year of operation?
PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
Research Design
In the writings by Godwill (2015), it is noted that there are three different types of research approaches that comprise of the deductive, inductive, and abductive approaches. The deductive approach is applied in the test of assumptions; the inductive approach is applied in the development of new theories, while abductive approach is applied when seeking to explain puzzles. Considering this proposed study will be based on the grounded theory it means the pertinent approach is the inductive approach. Hegde (2015) further notes that inductive approach is appropriate in studies that have clearly formulated research aim, questions, and objectives same as this proposed study. As earlier stated through the theoretical framework, this proposed study intends to develop a theory that links motivating factors, internal factors, and external factors to the downfall of new enterprises within their first year of operation. The image below is an illustration of the inductive process, which starts with observation of the factors, followed by establishing a pattern between the factors and downfall of enterprises, and lastly, formulation of a theory.
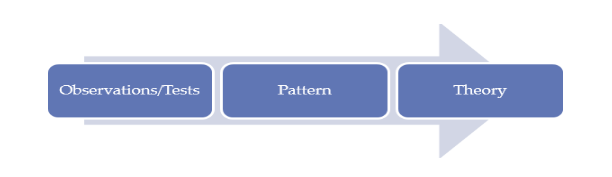
Figure 2: The Inductive Process
Source: Bryman & Bell (2015)
As for research strategy, the study will apply the pragmatic approach or mixed method whereby both qualitative and quantitative methods are applied (Barnham, 2015). The qualitative strategy will be applied because the proposed study is exploratory in nature i.e. it will seek to explore the factors that contribute towards the downfall of new enterprises within their first year of operation. Quantitative strategy will be applied since surveys will used in the data collection process.
Sample type
The proposed study will be based in Nigeria, which will be used as a representation of emerging economies. Ergo, the study will be keen on establishing the factors that contribute towards the downfall of enterprises within their first year of operation in emerging economies with specific emphasis on the Nigerian economy. It is important to note, Nigeria was selected as the data collection centre the researcher has favourable access to enterprises that are located there as compared to other emerging economies.
The suitable sample type of research participants will be Nigerian entrepreneurs who were forced to close down their start-ups/ enterprises within their first year of operation. Considering it will be hard to walk around and randomly access this unique set of sample participants, the purposive sampling will be applied, which will entail accessing appropriate participants through judgemental basis (Bryant, 2015). To be specific the researcher will visit the Lagos county offices and request for the list of business that failed to renewed their operating licenses for the current financial year of 2017 after only one year of operation. In essence, the researcher will be looking for small and medium enterprises that only operated in the year 2016 and never renewed their license in 2017 meaning they close shop within their first year of operation. Once the list is obtained the researcher will proceed to call each individual entrepreneur to seek their consent to participate in the research study. The researcher will aim at recruiting 30 entrepreneurs who closed their business after operating in 2016 Other participants who will also be incorporated into the study include Business Development Manager from at least five different banks that deal will banking of small and medium enterprises.
Data collection methods
Data will be collected through telephone or face-to-face interviews with the Nigerian entrepreneurs who closed shop within the first year of operation. As for Banks’ Business Development Managers they will be issued with questionnaires that seek to gather their perspective on factors that contribute towards the downfall of enterprises within their first year of operation.
Data analysis methods
Data collected from the entrepreneurs will be analysed through thematic content analysis while data collected from the Business Development Managers will be analysed through statistical approximation on Microsoft Excel and/or IBM SPSS.
CONTRIBUTION
This proposed research study will enrich the body of knowledge on entrepreneurship by developing a theory, which explains why start-ups or new enterprises failing within their first year of operation. More importantly, this study inform on the possible remedies or solutions that can be applied by entrepreneurs in Nigeria, other emerging economies as well as in developed nations to avoid the downfall of enterprises within the initial months or year of operation.
CONCLUSION
It is a common norm that not all enterprises established within the same time will be able to survive through the first 12 to 18 months. This means that there are outstanding factors that limit the survival and success of some enterprises. Of great importance is to explore possible remedies or solutions that can be applied to avert the downfall of new enterprises, which will save entrepreneurs the agony of wasting time, financial resources and the burden of debt resulting from failed ventures
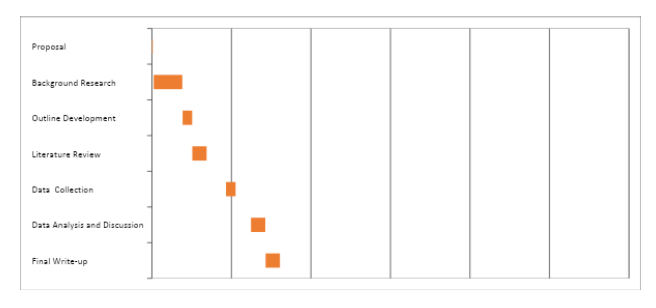
PROPOSED TIME FRAME FOR PhD STUDY

The table and chart below shows that this research study starts from 20th January, 2017 and it ends by 5th August 2019

REFERENCES
Amel, D. H., & Akkari, I. (2012). The entrepreneurial failure: Exploring links between the main causes of failure and the company life cycle. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 3(4)
Barnham, C. (2015). Quantitative and Qualitative Research. International Journal of Market Research. Vol. 57 (6), p837-854
Bryant, L. (2015). Critical and Creative Research Methodologies in Social Work. Farnham, Surrey: Routledge
Bryman, A. & Bell, E. (2015) “Business Research Methods” (4th Ed) Oxford: Oxford University Publishe
Greene, C. L., (2012). Entrepreneurship: Ideas in action. Mason, OH: South-Western Cengage Learning
Grusky, D. B., Western, B., & Wimer, C. (2011). The great recession. New York: Russell Sage Foundation
Godwill, E. (2015) Fundamentals of Research Methodology: A Holistic Guide for Research Completion, Management, Validation and Ethics. New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
Hegde, D. (2015) Essays on Research Methodology. New Delhi: Springer
Latha, L. & Murthy, B. (2009). The motives of small scale entrepreneurs: An exploratory study. South Asian Journal of Management, 16(2), 91-108.
Rajavel, N. (2013). A STUDY ON CAUSES FOR BUSINESS FAILURE: AN EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS. International Journal of Entrepreneurship & Business Environment Perspectives, 2(4), 605-612
Reinders, A., & Freijsen, M. (2012). The E-Factor: The 10 Highly Effective Habits. Dallas: BenBella Books, Inc
Schaefer, P. (2011) The Seven Pitfalls of Business Failure and How to Avoid Them. Business Know-How. [Online] retrieved from https://www.businessknowhow.com/startup/business-failure.htm [accessed on 23 January 2017]
Singh, N. P. (2014). Microsoft Acquired Nokia In Unipolar Operating System Market. Independent Journal of Management & Production, 5(3), 598-622.
Stokes, D., & Wilson, N. (2010). Small Business Management and Entrepreneurship. Andover: Cengage Learnin
Solomon, B. (2016) Yahoo Sells To Verizon In Saddest $5 Billion Deal in Tech History. Forbes. [Online] retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/briansolomon/2016/07/25/yahoo-sells-to-verizon-for-5-billion-marissa-mayer/#7ed4760571b4 [accessed on 24 January 2017]
Wagner, E. (2013) Five Reasons 8 Out of 10 Businesses Fail. Forbes. [Online] retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/ericwagner/2013/09/12/five-reasons-8-out-of-10-businesses-fail/#14cec39c5e3c [accessed on 24 January 2017]
Willebrands, D. Lammers, J. & Hartog, J.A. (2012) A Successful Businessman is Not a Gambler. Risk Attitude and Business Performance among Small Enterprises in Nigeria. Journal of Economic Psychology, 342-354
Take a deeper dive into A Study into the Motivating Factors with our additional resources.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



