Evolution and Amine Oxidase Activity
Introduction
The protein science is poised to enter a new era with a promise of unlocking several cells’ inner working mystery. The sequencing of next generation is on the brink of transformation related to the way DNA information is accessed. The protein assay variety can have linkages to a RNA or DNA and whose read-out is growing; the protein information is gaining at an increased rate. For instance, the experiments of ribosomal profiling are telling of where and when ribosomes bind to translate while CRAC and CHIP-seq provides information on the RNA and DNA that binds the protein properties. The new insights are gained in the mechanics of proteins’ large assemblies through strides that are incredible being made in the technology of electron microscopy. However, this vast molecular data is not worth much without its availability and the scientific community interpreting it. For those working on biomedical research, seeking biomedical science dissertation help can be invaluable in managing and making sense of this complex data.

How information in biological macro-molecules, such as DNA and protein can be represented inan electronical format
UniProt is a database collection for long, enabling the scientist to be navigating the huge amount of functional information and sequences available for proteins. The UniProtKB (UniProt Knowledgebase) can be considered as the central resource combining UniProtKB/TrEMBL and UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot. UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot have with it more than 550 000 sequences created by the expertise of the biocuration team. With the help of these entries, experimental information is extractable from the summarized and organized and the literature greatly eases the access of the scientists to the information of the protein.
DNA and protein sequences from related organisms are influenced by a common evolutionary
Mammalian blood plasma is contained with significant activity of amine oxidase (AOC) which contains soluble copper. AOC is referred to as serum amine oxidase (SAO) or plasma. The origin and identity of SAO had been under investigation on the basis of recently done characterization of AOC genes of four porcine with AOC3 vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1), AOC2 retina-specific amine oxidase (RAO), AOC1 encoding diamine oxidase (DAO), and AOC4 a VAP-1 homologue expression mainly in liver and having a sequence of signal peptide instead of a domain of transmembrane at the N-terminus. The characterization and the purification of a major activity of amine oxidase from the porcine serum have shown that it is an AOC4 gene product. It is intriguing that all mammals that possess a functional AOC4 gene are expected to be exhibiting high plasma amine oxidase activity (Thompson et al., 2011). The rodents and the humans have been lacking a functional AOC4 gene having a comparatively low plasma amine oxidase activity derivable from the release of the partial proteolytic of the AOC3 gene product VAP-1 having association with membrane.
Application of several alternative programs for MSA
MSA (Multiple sequence alignment) methods have the reference to algorithmic solution series for the evolutionary alignment in relation to the sequences, while considering the events of evolution such as rearrangements, deletions, insertions, and mutations under certain conditions. These methods have applications to RNA, DNA or protein sequences. Nature has conducted a study revealing the MSA in becoming the one of the models that has been widely used in biology. A large volume of in silico analyses is dependent on the methods of MSA. This includes motif finding, phylogenetic reconstruction, and domain analysis and a wide array of other applications (Edgar and Batzoglou, 2006).
MSA is a very useful tool for evolutionary and molecular biology and there have been a number of algorithms and programs available for this purpose. Although the studies conducted earlier have done comparison of the accuracy of the alignment of various MSA programs, the memory usage and computational time have not been evaluated systematically. Given the production of unprecedented data by the deep sequencing platforms of the next generation, and increased demand for the data analysis of large scale; it has imperativeness for the optimization of software application. Thus, the balance between the computational cost and the alignment accuracy has turned out to be a critical indicator and the MSA program that is most suitable. The comparison is done of both cost and accuracy of 9 popular MSA programs, namely T-Coffee, Probcons, Probalign, POA, MUSCLE, MAFFT, DIALIGN-TX, CLUSTAL OMEGA, and CLUSTALW and discussion done about the relevance of a few embedded implementations in the algorithm of each program. The alignment’s accuracy has been calculated with the two standard scoring functions having provision to BAliBASE, the total-column scores and sum-of-pairs, and the determination of the computational costs has been by the collection of the peak memory usage and the execution time.
Searches for sequence and structure data from the publicly available databases, such as GenBank, UniProt and PDB
GenBank
GenBank is a genetic sequence database of NIH, which is the publicly available DNA sequences’ annotated collection. GenBank has been the element of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration, comprising of the GenBank, European Nucleotide Archive (ENA), and DDBJ (DNA DataBank of Japan). These three organizations have purported in exchanging data in day to day basis (Altschul et al., 1997).
Accessing GenBank
There are a number of ways for searching and retrieving data from GenBank.
Searching GenBank for the annotations and sequence identifiers with Entrez Nucleotide
GenBank sequences are searched and aligned with a query sequence with the use of Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). There is independent searching by BLAST of dbGSS, dbEST, and CoreNucleotide
Searching, linking, and downloading of the sequences programmatically with the use of NCBI e-utilities.
UniProt
UniProt consortium produces UniProt, where UniProt consortium is partnership between Protein Information Resource (PIR), the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB) and European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI).
UniProt is contained with high quality manually non-redundant and annotated protein sequence records. Manual annotation is comprised of comparison, analysis, and merging of all sequences available for a given protein, along with a critical review of associated predicted and experimental data. The biological information is extracted from the UniProt curators from the literature and various computational analyses are performed.
PDB
An international repository to process and distribute the protein structures is the PDB (Altschul et al., 1997). The PDB structures have been subject to determination in an experimental way by electron microscopy, NMR, and X-ray crystallography etc. From the PDB, there is removal of the theoretical models. The PDB is also contained with some nucleotides and chemical ligand structures. The representation of each PDB entry is by a four-character identifier (PDB ID), the first character is the integer from 0 to 9.
Top 2 Software Tools for the Generation of Sequence Logos
kpLogo
kpLogo has been an integrated framework for the visualization and sensitive detection of the ultra-short motifs which are position specific from either unweighted or weighted sequences particularly aimed for high-throughput studies like vitro selection. There is free availability of the source code for download. kpLogo also have the availability for Galaxy tool.
Gene Slider
The entropy can be visualized by the Gene Slider and it can converse protein sequences and the long DNA. To view the entire sequence or the details, it has zoom function. Its availability is also on an app implementable in Processing and Java Script. Additionally, there is availability of the source code under GNU GPLv2 license.
Phylogenetic Tree-based approach to select phylogenomics’ orthologous sequences
Phylogenomics is describable for the usage of several concatenated orthologous sequences derivable from transcriptome or genome data for the reconstruction of phylogeny. As the high-throughput cost sequencing has continuity in decreasing, the target genes are rapidly replaced by the phylogenomics by PCR based methods, as data of larger sets can be considered of bearing on evolutionary questions while they require lesser amount of time in the laboratory and usually at a lower cost. There are many studies having the demonstration of the phylogenomics’ utility to address the organismal phylogeny with the outstanding questions (Dunn et al., 2008).
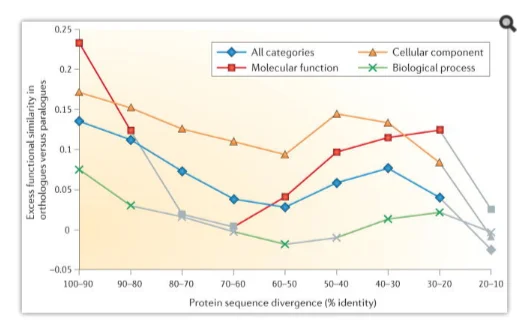
Implications of evolutionary and functional gene orthology
The concept of paralogy and orthology was introduced by Walter Fitch (Fitch, 2000) for distinguishing between distinct types of homologous relationships that are fundamentally distinct between genes as per the descent mode from their common ancestor. Orthologues are genes derivable by specification, and on the other hand paralogues are the genes that have undergone duplication to evolve. The orthologous relationships through clear delineation between genes have indispensability to reconstruct the evolution species and the genomes. The species phylogenies, indeed, is aimed to represent the past speciation events’ course and therefore only amongst the orthologous genes’ are the relationships expected in serving that purpose.

Biological function of a gene or protein
Paralogy and orthology as terms and concepts are fundamental to the functional and comparative genomics owing to a number of major, biologically key implications. The original definitions are directly followed by some of the implications, where it is the additional observations that others rely on, such as functional divergence and association of gene duplications (Koonin, 2011).
References
- Altschul, S. F., Madden, T. L., Schaffer, A. A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W. and Lipman, D. J. (1997) ‘Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs’, Nucl Acids Res., 25:3389–3402.
- Dunn, C. W., Hejnol, A., Matus, D. Q., et al. (2008) ‘Broad phylogenomic sampling improves resolution of the animal tree of life’, Nature, 452(7188):745–9.
- Edgar, R. C. and Batzoglou, S. (2006) ‘Multiple sequence alignment’, Curr Opin Struct Biol. 16:368–73.
- Fitch, W. M. (2000) ‘Homology a personal view on some of the problems’, Trends Genet., 16:227–231.
- Koonin, E. V. (2011) ‘Walter Fitch and the orthology paradigm’, Brief Bioinform, 12:377–378.
- Thompson, J. D., Linard, B., Lecompte, O., et al. (2011) ‘A comprehensive benchmark study of multiple sequence alignment methods: current challenges and future perspectives’, PLoS One, 6:e18093.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



