Understanding Male Impotence and ED
Introduction:
According to the Oxford Dictionary, the origin of impotence words derived from the old French from Latin word impotent, which means weaker deficient of power. Impotence, also usually known as Erectile Dysfunction (ED) can be defined as the persistent failure to reach and keep a firm and strong erection satisfactory for sexual intercourse(NIH Consensus 1993). In this article, we will explain the physiology, the pathophysiology and the drug therapy of male sexual function with a particular focus on the guidelines, also we will highlight some of the new trends in impotence therapeutics.
Prevalence:
The Massachusetts Male Aging Study (MMAS), a large observationalcommunity-oriented, randomisedmulticentre survey, found that among men aged 40 to 70 years, the total prevalence of impotencewas 52%. (Feldman et al.,1994).
The Cologne study which was published in August 2000 was investigating the prevalence of ED in German men. The study reported that the prevalence of EDwas 19.2%, with a sharprise from 2.3% to 53.4 % as the age increases(Braun et al., 2000).

From the results mentioned above, it is clear that ED prevalence among men increases with age and it affects more than 50% of men at old ages. Some experts believe that the percentages of ED may be higher than those found in the previous studies due to poor reporting of such embarrassing issue.

Physiology of erection:
In the penis, the erectile tissue comprises two large chambers which are known anatomically as (corpora cavernosa) as shown in Figure 2. In the flaccid or nonerect penis, they are moderately filled with blood,but they become expanded and filled with blood when arterial blood flow into them under pressure whereas the venous outflow is partly collapsed. Penile erection occurs after emotional or physical sexual excitation. Erection is due to parasympathetic signals that originate from the sacral part of the spinal cord till reach the male penile tissue via the pelvic nerves. These parasympathetic nerve endings, unlike most other parasympathetic endings, release nitric oxide (NO) and other vasoactive peptides.
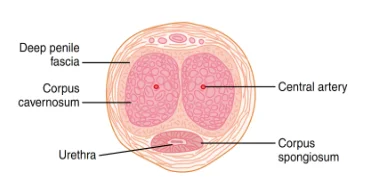
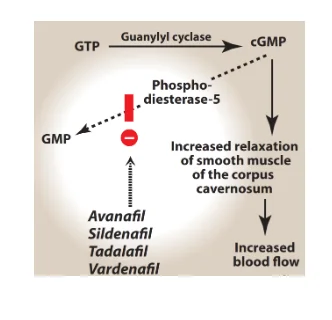
Nitric oxide could be understood to be reponsible to play one of the most critical roles regarding the erection of the penis through the activation of the guanylyl cyclase, which has been an enzyme for the catalysis of the cyclization of the Guanosine Triphosphate (GTP) and leads to the formulation of the Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate (cGMP). The effecto of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) is the formulation of the arterial vasodilation within the tissue residing inside the corpora cavernosa as well as inside corpus spongiosum which have been demonstrated in the following Figure 3.
Dig deeper into Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Disease with our selection of articles.

Pathophysiology of impotence:
Erectile dysfunction has many aetiologies, it may be vascular, neurogenic, anatomical, endocrine, drug-induced, psychological or due to a mix of the previous causes.(Gratzke et al., 2010). In the majority of cases, multiple pathophysiological pathways can coexist and compromise the erectile function. ED usually is caused by a mix of psychological and physical factors (Hatzimouratidis et al., 2010 and Shamloul et al., 2013). In the following section, we will highlight the causes that can precipitate erectile dysfunction (Gratzke et al., 2010):
Vascular causes:
Lifestyle (e.g., cigarette smoking) Sedentary lifestyle. Being overweight or obese. Cardiovascular risk factors. Diabetes mellitus DM Type 1 and Type 2;dyslipidemia; metabolic syndrome, etc. Major pelvic surgery.
Neural causes can be divided into central and peripheral causes:
Centralcauses such as
Neurodegenerative diseases e.g., parkinsonian disease. Cerebral stroke. Spinal cord injuries. CNS malignancies.
Peripheral causes
DMType 1 and Type 2. Chronic nephropathy Chronic hepatitis. Surgical interventions or radiation therapy of pelvis Surgical interventions of the urethra
Structural disorders in the penis anatomy:
Micropenis (abnormally small penis). Hypospadias (congenital abnormaility in which the urethral opening is on the underneath of the penis instead of at the tip). Penile cancer (tumours of the external genital system).
Endocrine or hormonal causes:
Diabetes Mellitus; Metabolic Syndrome Thyroid disorders Hypogonadism(testosterone deficiency). Cushing’s disease. Hyperprolactinemia. Panhypopituitarism.
Mixed pathophysiological causes:
Chronic diseases (e.g., DM, hypertension, chronic kidney failure, chronic liver disorders, etc.) Psoriasis – Gout (hyperuricemia)
Drug-induced causes:
Antihypertensives especially beta-antagonists and diuretics Antidepressant drugs (e.g. SSRIs, fluoxetine and sertraline) Antipsychotic drugse.g phenothiazines and haloperidol. Antiandrogens Abused substances (e.g., alcohol, opioids, methadone, cocaine, heroin, cannabis, marijuana, anabolic steroids, etc.)
Psychological causes:
Generalised type (e.g., sexual intimacy disorders and lack of excitability and) Certain situations (e.g., relationship issues, performance-related problems or due to stress)
Traumatic causes:
Penile trauma Pelvic fractures
Fortunately, the majority of these causes are curable, so carefullytaking a medical history is very important, A completephysical examination should be performed together withappropriate laboratoryinvestigations to determine if any of them are existing.
Treatment of impotence:
General approach
- Identify the aetiology. - Promote lifestyle changes to reduce risk factors. - Initiate medical therapy.
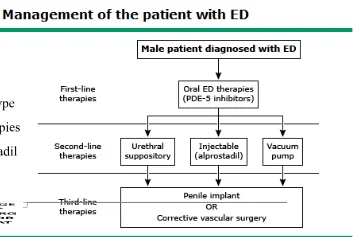
First line therapy:
Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors (PDE5Is):
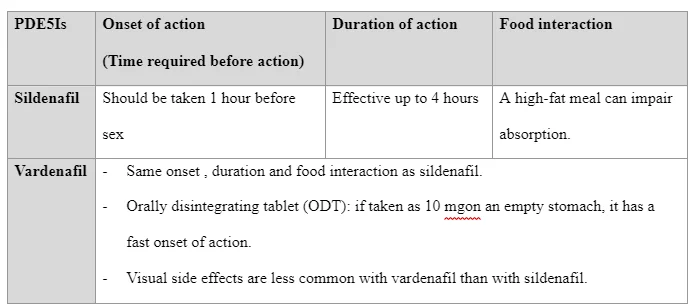
As a primary therapy, the PDE5 inhibitors are recommended because they are effective, easy to use, and well tolerated (Tsertsvadze et al. 2009). All PDE5 inhibitors have the same mechanism of action, indications, side effects and drug-drug interactions. They are equally effective when used at equipotent doses. However, these drugs can vary in the duration of effect and the impact of food on drug bioavailability. The following table summarises the main similarities between the four commercially available PDE5 inhibitors.


Intable2,we will summarise the major differences among the four commercially available PDE5 inhibitors(WHALEN et al., 2015).

Which one is the PDE5 enzyme inhibitor of choice?
So far, no data are existing from large multicentre studies exploring the effectiveness and patient preference for the four commercially available PDE5Is mentioned above. The pharmacological properties of PDE5Is regarding efficacy,tolerability,contraindications and drug-drug interactions are comparable.The choice of the best PDE5I will dependon each patient personalexperience, the degree of satisfaction about the sexual relation and the number of successful intercourses per week. In 2015,a recent meta-analysis reported that impotence patients who pay more attention towards high effectiveness and better performance should use sildenafil (Viagra) 50 mg. However, those who prioritise safety and prefer to experience less side effects, should firstly use tadalafil (Cialis) 10 mg (Chen et al., 2105).
Shockwave therapy:
Using shockwave therapy for ED is one of the new and less invasive therapies to treat this common sexual condition. Also commonly known as penile extracorporeal low-intensity shockwave therapy (LI-SWT), this technique involves the use of lower intensity acoustic waves that focus on and break up micro plaques in the penis, which causes an improvement in blood flow. Acoustic waves activate biological responses leading to release of angiogenesis growth factors (these are responsible for promotion of the constitution and development of blood vessels which could be newly formed) as well as the factors responsible for the proliferation of endothelial cells as well as the proliferation fo the antigen of the nucleous of the cells. The formulation of the new blood cells are consistently contributed to by all of such meidators and the blood supply gets enhanced to the erectile tissues of the penis and this results in the more effective and more sustanable erection. Generally, manystudiesshowed promising results, irrespective of the difference in LI-SWT set-up parameters or therapeutic regimens (Clavijo et al., 2017). Information and data from nine different and previously observed trails had been undertkaen through a systeatic review which had been performed recently, involveing 637 patients. As per this study, there had been a marked improvement in the LI-SWT concerning the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) and the Erection Hardness Score (EHS). Furthermore, each treatment could last as a minimumof three months (Man et al., 2018). In aprevious clinicaltrial, the authors reported that shockwave therapy was useful in men who responded to phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors (e.g., Viagra or Cialis) and could also convert the poor responder to PDE5Is to become responders (Tasi et al., 2017). Another studyexamined the use of shockwave therapy in men who were unable to respond to PDE5Is. The 52 men received 3,000 shockwaves as one session everyweek for three months while also continuing administration of PDE5Is. At the end of the duration of one month regarding the commencement of treatment 35 of the 52 men (67%) had achieved the ability to sustain the erection which could be adquate for the performance of the sexual intercourse. When the period of three months had lapsed, the extent of 33 of the 35 (94.3%) of the patients had been able to sustain the capability of satisfactory and firm erection (Abu-Ghanem et al., 2014).
Second line therapy:
Vacuum erection devices VEDs:
VEDs could be understood to be the instrument which could offer the proposition for the corpora cavernosa to expand mechanically, through the utilisation of a ring which could be positioned at the foundation of the penis for the purpose of the prevention of any venous reverse flow and this could then be effective in retention of the blood flow within the corpora cavernosa. The findings from the data which had been published previously could be understood to be palpable in the format of effectiveness being 90% of the cases which had been put under consideration. These outcomes could be judged irrespective of the causality of impotence and indicated the measure of the adequacy of erection concerning the achievement of successful intercourse. In this respect, the success rate of the satisfaction could be identified to be 27% to 94% (Yuan.et al. 2010). Most men who stopped using VEDs did so within the first three months of treatment. However, the continuous use of VEDs decreases dramatically after two years (Cookson et al., 1993). The most frequently encountered side effects are pain, failure to ejaculate, hematomas, bruising, and tingling sensation, which occur in < 30% of patients (Yuan.et al. 2010). The patients should be guided to remove the ring within half an hour after finishing the sexual intercourse in order to avoid the severe side effects. VEDs are contraindicated in patients who are suffering from bleeding tendencies or those on antiplatelet or anticoagulant drugs. VEDs can be the therapy of choice in geriatric males with infrequent intercourse and comorbid diseases necessitating non-invasive, nonpharmacotherapeutic management of ED.
Intraurethral Alprostadil:
Alprostadil is a prostaglandin analogue with vasodilator properties; it is marketed under the brand name MUSE® for the treatment of ED. The urethral suppository is a tiny rice sized suppository that goes down the urethra through the hole at the tip of the penis. It comes in the form of the small applicator; this applicator has the drug already pre-loaded inside of it after the patient urinated so the urethra is wet. The patient will stick the applicator down the tip of the penis then push the button to drop the drug inside the wet urethra The patient should roll the penis between his hands for about ten to thirty minutes to make sure it is dissolved in there once that pellet dissolves it will travel across the urethra and dilate the blood vessels and the penis will become engorged with blood resulting in a steady erection.(Padma-Nathan et al 1997). Erections adequate for the necessary measure of intercourse could be determined to have been achieved in 30-65.9% of patients. Furthermore, the suggestion could be identified regarding the initiation of the alprostadil at the primary dose of 500 μg, this could be suggested for the specific purpose that this is of greater effectiveness in comparison with that of the 250 μg dose and the differences regarding the side effects are mostly minimal (Mulhall et al., 2001). The occurrences of pain in the penis and ligh-headedness with hypotension could be considered to be the adverse effects which are also the commonality in this regard. In spite of this, the occurrence of fibrosis at the penis as well as priapism could be considered to be rare in terms of sequence of occurrences (Shabsigh et al., 2000).
Intracavernosal injection of vasoactive drugs:
If no response to the oral drugs the patients are candidates forintracavernosal injections. The success rate is high (85%) (Coombs et al., 2012). Intracavernosalinjectionof vasoactive agentswas the first medical therapy for ED presented more than twenty years ago. Alprostadil (CaverjectTM)was the first and only agent approved for intra cavernosaltherapy of ED (Eardley et al., 2010). Intra-cavernosal alprostadil is most effective when used alone as a single vasoactive agent at a dose of 5-40 μg. The erection is achieved after 5 to 15 minutes, and the duration of erection depends on the dose of the injected alprostadil. Complications of intra-cavernosal alprostadil include local pain - prolonged erections - fibrosisand priapism(Eardley et al., 2010). Pain is usually diminished after prolonged use. Addition of local anaesthesia or sodium bicarbonatecan alleviate the pain(Moriel et al.,1993)
Combined vasoactive drug therapy
Combined vasoactive drug therapy increase the efficacy bymaking use of the multiple mechanisms of action of the drugs being used, and reduce the side-effects by lowering the doses of each vasoactive drug. Papaverine, an opium alkaloid with vasodilator effect was used as a combined vasoactive drug therapy but nowadays, papaverineis not approved for the therapy of impotence. Phentolamine, an old alpha-blocker with vasodilator properties,was used amongthe combined vasoactive drug therapy to enhance the efficacy. As monotherapy, it results in an inadequate erection.

Third-line therapy (penile prostheses):
In impotence patients who showed inadequate response towards medical therapy or who favour a life-timecure to their problem, surgical implantation of a prosthesismaybe a good option(Antonini et al., 2016).There are two main currently existing types of penile prosthesis or implants: inflatable devices and the non-inflatable semi rigid devices. Inflatable type of devices consists of 2 or 3 pieces namely cylinders inserted into the erectile chambers, a reservoir containing fluid and a pump in the scrotum. The non-inflatable, semi rigid type of devices(malleable, mechanical, soft flexible) comprise rods surgically implanted into the penile erectile tissue and can be set into position as required for sexual intercourse (Casabé et al., 2016).
New trends in the treatment of impotence:
Stem cell therapy for ED:
Recent research suggested that stem cell therapy can be a useful therapeutic option for ED. The stem cell therapy includes injecting the patients' own stem cells into the penile tissue (Lin et al., 2018). The authors reported that within six months of the intervention, 8 of the 21 men treated were able to perform anatural and spontaneous sexual intercourse and this outcome remained evident at 12 months after treatment. Overall, the study had favourable findings, but there were some disappointing results. It appears that the injected stem cells escaped the penile tissue, and homed into the bone marrow.
Topical Nitric Oxide (NO) Nanoparticles for ED :
Nanoemulsions with NO that could encourage penile erection when applied locally or transdermally on the penis skin (Nam et al., 2018).The water-in-oil nanoemulsions have been tried experimentally and can be an attractive non-surgical therapy for ED patients within sufficient response to PDE5 inhibitors such as elderly patients.
References
Abu-Ghanem, Y., Kitrey, N.D., Gruenwald, I., Appel, B. and Vardi, Y., 2014. Penile low-intensity shock wave therapy: a promising novel modality for erectile dysfunction. Korean journal of urology, 55(5), pp.295-299.
Antonini, G., Busetto, G.M., De Berardinis, E., Giovannone, R., Vicini, P., Del Giudice, F., Conti, S.L., Gentile, V. and Perito, P.E., 2016. Minimally invasive infrapubic inflatable penile prosthesis implant for erectile dysfunction: evaluation of efficacy, satisfaction profile and complications. International journal of impotence research, 28(1), p.4.
Braun, M., Wassmer, G., Klotz, T., Reifenrath, B., Mathers, M. and Engelmann, U., 2000. Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction: results of the ‘Cologne Male Survey’. International journal of impotence research, 12(6), p.305.
Casabé, A.R., Sarotto, N., Gutierrez, C. and Bechara, A.J., 2016. Satisfaction assessment with malleable prosthetic implant of Spectra (AMS) and Genesis (Coloplast) models. International journal of impotence research, 28(6), p.228.
Chen, L., Staubli, S.E., Schneider, M.P., Kessels, A.G., Ivic, S., Bachmann, L.M. and Kessler, T.M., 2015. Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: a trade-off network meta-analysis. European Urology, 68(4), pp.674-680.
Clavijo, R.I., Kohn, T.P., Kohn, J.R. and Ramasamy, R., 2017. Effects of low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy on erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The journal of sexual medicine, 14(1), pp.27-35.
Eardley, I., Donatucci, C., Corbin, J., El-Meliegy, A., Hatzimouratidis, K., McVary, K., Munarriz, R. and Lee, S.W., 2010. Pharmacotherapy for erectile dysfunction. The journal of sexual medicine, 7(1), pp.524-540.
Feldman, H.A., Goldstein, I., Hatzichristou, D.G., Krane, R.J. and McKinlay, J.B., 1994. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. The Journal of Urology, 151(1), pp.54-61.
Hatzimouratidis, K., Amar, E., Eardley, I., Giuliano, F., Hatzichristou, D., Montorsi, F., Vardi, Y. and Wespes, E., 2010. Guidelines on male sexual dysfunction: erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation. European Urology, 57(5), pp.804-814.
Moriel, E.Z. and Raifer, J., 1993. Sodium bicarbonate alleviates penile pain induced by intracavernous injections for erectile dysfunction. The Journal of Urology, 149(5), pp.1299-1300.
Padma-Nathan, H., Hellstrom, W.J., Kaiser, F.E., Labasky, R.F., Lue, T.F., Nolten, W.E., Norwood, P.C., Peterson, C.A., Shabsigh, R., Tam, P.Y. and Place, V.A., 1997. Treatment of men with erectile dysfunction with transurethral alprostadil. New England Journal of Medicine, 336(1), pp.1-7.
Tsai, C.C., Wang, C.J., Lee, Y.C., Kuo, Y.T., Lin, H.H., Li, C.C., Wu, W.J. and Liu, C.C., 2017. Low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy can improve erectile function in patients who failed to respond to phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors. American journal of men's health, 11(6), pp.1781-1790.
Tsertsvadze, A., Fink, H.A., Yazdi, F., MacDonald, R., Bella, A.J., Ansari, M.T., Garritty, C., Soares-Weiser, K., Daniel, R., Sampson, M. and Fox, S., 2009. Oral phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors and hormonal treatments for erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of internal medicine, 151(9), pp.650-661.
Yuan, J., Hoang, A.N., Romero, C.A., Lin, H., Dai, Y. and Wang, R., 2010. Vacuum therapy in erectile dysfunction—science and clinical evidence. International journal of impotence research, 22(4), p.211.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



