Structuring a Successful E-commerce Platform
Audit Report Brief
In this audit report, we look, in details, at the structure required to start and run a successful E-commerce business platform where goods and services trade at a fair value. For purposes of this particular report, ‘E-mall’ is the hypothetical name of our online business.
PESTEL Analysis for E-mall
Political Factors
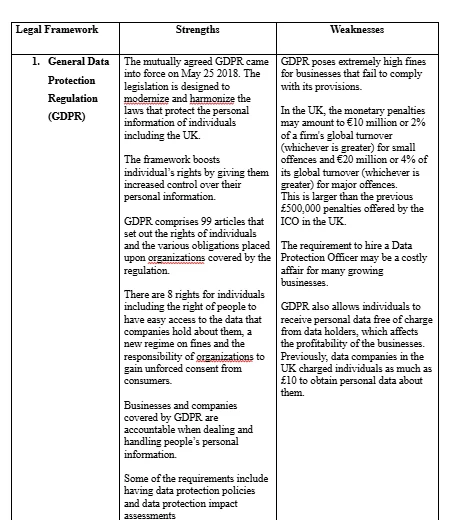
The 2000 e-commerce Directive (Carter, 2000) is the primary legislation – including other legislative instruments – that regulates the e-commerce industry. In the UK specifically, the Electronic Commerce (EC Directive) Regulations 2002 is the main legislation (York, 1999), which also incorporates the EU's Electronic Commerce Directive 2000 into UK law. The legislation was adopted to clarify, regulate and harmonize online business rules with the aim of boosting consumer confidence. Some of the issues addressed by the directive include consumer rights, data protection, intellectual property rights and tax obligation provisions (Kryczka, 2004).
E-mall needs to conform to the rules and legislations to operate successfully in the UK. The platform will put up measures that ensure data protection of its users e.g. hiring IT experts to design data protection systems and build hi-tech data storage sites in safe location across the UK. E-mall will design contracts that conform to the UK Consumer Rights Directive, 2011 e.g. fair pricing of products displayed on the platform and the protection of consumers from investors as well as possible online scammers (Giliker, 2015). To safeguards public interests and security, E-mall will require members to provide minimum information like name, location, e-mail address and VAT number to enhance transparency in the transactions.
Dig deeper into Quality Home Care Solutions with our selection of articles.
Economic Factors
E-commerce involves the transaction of business via automated technology systems and applications. Like any physical business, online business is also affected by economic factors like inflation, interest rates and government monetary policies that determine the availability and affordability of goods and services (Crespo, 2010). The cost of inputs such as electricity, online advertising, internet, and computer maintenance lead to high operational costs and decline in the demand for e-commerce products (Mohapatra, 2013). Interest rates, on the other hand, determine the circulation of money and consumers ‘disposable income. Low interest rates encourage borrowing, which culminates in high consumer purchase power, which is good for e-commerce business (Terzi, 2011).
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to E-commerce Venture in the UAE Travel Accessories Market.
E-mall ought to put in place mechanisms that ensure the affordability and availability of the products and services regardless of the state of economic affairs in the UK. One way of ensuring profitability during hard financial times is offering the lowest possible prices for the products and services displayed on the site.
Social Factors
The dynamic socio-cultural environment in the UK is a major factor of consideration for the e-commerce industry. Growing trends change the way consumers shop and consume products and services sourced from the online platforms. In the UK, for example, consumers are attracted to products that do not infringe human rights and which are sourced from credible producers and manufacturers (Sakarya, 2014). Consumers also prefer e-commerce businesses that benefit the communities within which they operate e.g. companies that uphold corporate social responsibilities (Martinuzzi, 2011). To remain socially significant, E-mall will put in place measures that enable the local UK community to prefer it to other industry players. The products and services offered on the platform will undergo quality checks to ensure that they are sourced and offered by credible producers and manufacturers. Products sourced from producers that infringe in human rights e.g. mistreatment of workers, child labour etc., for example, will not be displayed on the site. Moreover, the business will undertake numerous corporate social responsibility tasks like taking part in infrastructure improvement projects and other community projects beneficial to communities in the UK.
Technological Factors
E-commerce survives and operates on technology. Advanced technology systems that offer better consumer experiences when shopping online enhance the business, which translates to increased profits (Klopping, 2004). To remain significant in the UK market, E-mall will invest in technology that is advanced compared to its competitors. Shopping on the platform ought to be fast and convenient to boost consumer experience and confidence in our platform. E-mall will also ensure that the time spent between shopping and delivery of a purchased product is minimal to boost consumer experience and boost loyalty (Anderson, 2003).
Environmental Factors
In the wake of global warming, changing weather patterns and extreme weather conditions, the most successful businesses – whether physical or online, are those concerned about the environment (Popescu, 2015). UK consumers, for example, prefer products produced and manufactured using renewable energy sources and those that uphold environmental sustainability standards (Christie, 2014). As part of its environmental sustainability goals, E-mall will invest in renewable energy to gain freedom from non-renewable energy resources. One way of doing this is through sustainable packaging e.g. delivering products in sustainable packages to ensure waste reduction. The platform will also give priority to products manufactured using renewable energy.

Legal Factors
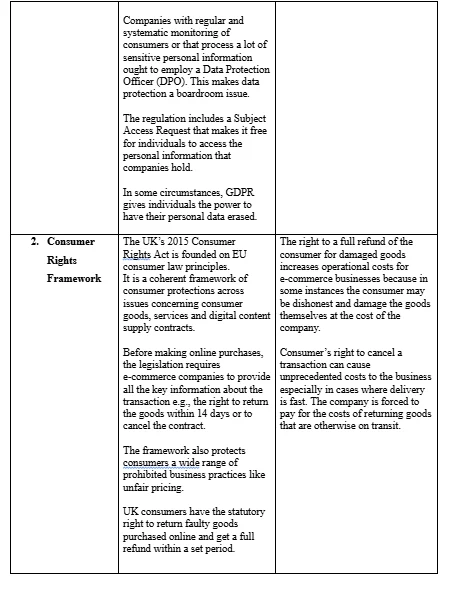
Legal compliance is as crucial for online businesses as it is for physical businesses. A tussle with the law can be costly and result in financial losses as well as image and reputation loss (Gillies, 2016). Labour laws, sustainability laws and other human rights laws should be considered and complied with for an online business to remain profitable and significant (Corkery, 2013). E-mall will comply with the various laws and legal rules that govern how the business operates. The business will comply with the labor, consumer, sustainability and human rights laws in the UK e.g. GDPR framework (Goddard, 2017), Consumer Right Framework (Stazi, 2012) etc. In the event of grievances, the company will offer amicable solutions of dealing with the grievances that are less costly and more effective e.g. alternative dispute resolutions instead of litigation (Cortés, 2010).
Sourcing Funds for the establishment of E-mall
Like many businesses, an e-commerce business requires considerable amounts of capital to start and run effectively. Some of the common sources of funding for many e-commerce businesses include venture capitalists, bank loans, personal savings and crowdfunding (Gerber, 2013). E-mall will source most of its funds from personal savings, crowdfunding, loans from family friends and in extreme financial requirements cases, venture capitalists. In order to flourish, the company needs to source funds from sources that would not jeopardize future operations. Bank loans, for example, are repulsive sources due to the high interest rates (Cressy, 1995). The company will also consider sources that do not require it to lose or sell its stakes to the sources through the purchase of stakes in the company.
Sectors in the UK that E-mall will operate
The UK is a major economy with a high demand for online service and delivery. E mall intends to establish a niche in major sectors of the UK market. As an online operating business, Email intends to invest in key areas such as the hospitality, finance and service delivery industries.
Finance Sector
The UK has a vibrant economy supported by strong economic features, the country’s economy runs on four major sectors, which include hospitality and tourism, production, manufacturing and agriculture (Mort, 2019). Finance is a key contributor to the country’s economy; the Bank of England is a powerful financial organization within Europe and has successfully implemented monetary and fiscal policies that have been instrumental in ensuring the country remains economical strong after centuries of industrialization (Singh, 1977). This makes the financial sector viable for E-mall to invest in the form of e-loans for customers shopping online. Customers who are short on cash can obtain payday loans and overdrafts to shop on our platform (Mbiti, 2015).
Agricultural sector
The agricultural sector is responsible for ensuring adequate food supply for the population, currently; the sector depends on imports, a factor that has made the United Kingdom a major player in the global agricultural affairs in the global economy (Godfray, 2010). The UK has a strong manufacturing sector, with a reputation for producing quality equipment and machinery (Huxtable, 2016). The financial sector in the UK is quite strong with London officially the financial hub of Europe with many businesses accepting credit cards as a payment system (Deku, 2016), making it easier to shop within the country. As part of E-mall’s fresh produce department, the company intends to contract farmers to grow fresh produce for the company. The agricultural produce will be sold via the platform and delivered fresh or used the company’s hospitality department.
Hospitality Industry
The UK also has numerous tourist attraction spots supported by multiple hospitality agencies, the contribution of the UK's hospitality sector to the country’s GDP (Jones, 2005). Online-based companies continue to flourish in the city as the country has made strong technology advancements to support existing economic pillars. E mall will invest in fresh produce to help cater for the food deficit within the hospitality sector to supply to individuals, hotels, restaurants and grocery stores. Produce will be available online with orders made prior to delivery. This will improve consumer experience within the sector, the product will be available on wholesale and retail with the prices set to ensure a more cost friendly environment within the sector E mall expects to enhance (B2B, B2C and B2E transactions) (Eid, 2006) with the aim of improving service delivery as well as ensuring quality management within the sector.
Marketing sector
The marketing sector in the UK has witnessed a radical shift from a traditional approach to a more modern and technology backed method. Consumer data reports a decline in older advertising forms such as direct and main media advertising to easier internet-based marketing. Established digital companies have increased ads and run several sales promotions to ensure customer loyalty as well as target new markets. The last two years have seen exponential growth in the digital marketing sector, with improvements in voice search, mainstream acceptance of AI and the increase online spending of major economies within Europe (Chaffey, 2019). E mall intends to create online marketing and advertising platform that runs alongside its major platform, a contribution to the country’s key economic sector. The company will run effective marketing campaigns within its platform, which will help in sales improvement as well as promoting new and quality products at a consumer-friendly price. The company expects to generate revenue from successful advertisements as well as improve the consumer's access to the information on products.

Technology sector
Technology is a major contributor to the United Kingdom’s economic sustainability given that it accounts for 19% of the country’s GDP. Growth in the technological sector has brought improvements in the running and coordination of the country’s economy and has brought about better service delivery to consumers. UK businesses continue to adopt and implement new improvements in technology to cater to customer interests. The sector continues to face challenges especially relating to cybercrime and user privacy. Most consumers complain of privacy infringements by online companies, where some require highly sensitive information such as passwords and access to personal accounts. In this respect, a business census conducted in 2018 highlights online fraud rising to 37% (Economics, 2008). E mall will invest to secure customer confidentiality especially when engaging with consumers in the online platform. Improved cybersecurity apparatus, voice-generated passwords, and incorporation of AI will set precedence to the firm’s online operating policy. The firm will create jobs in the sector by employing IT experts and business management professionals whose main task will be to improve the overall consumer experience. E mall will create a friendly platform in compliance with the UK’s policies on online businesses.
HR Policies adopted by E-mall in the UK
Human resource management continues to be a challenge on major online operating business in the UK (Guest, 2003). Factors like the rights and responsibilities of both employers and employees are entrenched in numerous UK legislations, which companies are expected to abide by (Prassl, 2013). E mall will operate within the legal framework as directed by the law to create and implement a suitable human resource policy for its employees. For the purpose of this study, we look into two HR policies that influence employer-employee interaction within the firm Data protection in the UK is a matter of concern among many consumers and the government has put in place stringent policies to safeguard the privacy of its citizens (Carey, 2018). Victims of data mining and online fraud confess to having shared valuable information within online platforms. Hacking groups are frequently posting and updating data mining programs with the intent of financial sabotage to unsuspecting users. E mall will operate a data protection policy on all consumer accounts; the firm expects to prevent cyber threats within its operating framework. As a legal requirement, the company will obtain consent to use and retain information provided, sensitive data such as race, origin, religious or political affiliation will not be stored or recorded. In the event that such data may be required the company promises to use the data for the intended purpose and not to share with any undisclosed third parties. E mall will collect minimal data to support its business activities where such data will be limited to authorized access only. Stored data will be stored in offshore servers to enhance location security; E mall has put in additional safeguards to prevent loss of data, theft, and tampering of data. The company and platform will consider HR policies related to gender and rights of different genders (Derbyshire, 2012). The platform will not discriminate any consumer regardless of their gender and gender-based views. dictate employer-employee relationships, they determine the level of professionalism required as well as the responsibilities of the employer to the employee, topics like employee benefits and responsibilities are discussed within the human resource policies identified by the company (MacLeavy, 2011). E mall will implement an ethical interactions policy to improve customer experience. E mall requires all of its employees to be courteous, professional and with integrity. This will relate to all interactions with all of its customers. E mall expects confidentiality of sensitive customer information as well as efficiency in delivering commodities. This includes allowing third parties to access customer information such as passwords or sensitive account details. E mall expects its employees to desist from any forms of unethical behaviour and corruption, which is a legal offense punishable by law. The company will not tolerate any form of unethical practice, as each set of employees will receive guidelines relating to their field of expertise.
References
Anderson, R. E. &. S. S. S., 2003. E‐satisfaction and e‐loyalty: A contingency framework. Psychology & marketing, 2(20), pp. 123-138.
Carey, P., 2018. Data protection: a practical guide to UK and EU law. London: Oxford University Press, Inc.
Carter, S., 2000. E-Commerce: The UK. IEEE Software, (2), pp. 90-91.
Christie, I. &. H. M., 2014. 6 Towards the sustainable e-region. Digital Futures: Living in a Networked World, p. 140.
Corkery, J. F. J. S. D. &. M. E., 2013. Taxes, the internet and the digital economy. Revenue Law Journal, 23(1), p. 6742.
Cressy, R., 1995. Business borrowing and control: A theory of entrepreneurial types. Small business economics, 7(4), pp. 291-300.
Derbyshire, H., 2012. Gender mainstreaming: recognising and building on progress. Views from the UK Gender and Development Network. Gender & Development, 20(3), pp. 405-422.
Eid, R. &. E. I., 2006. The influence of the internet on B-to-B international marketing activities: An empirical study of the UK companies.. Journal of Euromarketing, 15(2), pp. 51-73.
Gillies, L. E., 2016. Electronic commerce and international private law: A study of electronic consumer contracts. Abingdon, United Kingdom: Routledge.
Huxtable, J. &. S. D., 2016. On Servitization of the Manufacturing Industry in the UK. Procedia CIRP, 52, pp. 46-51.
Klopping, I. M. &. M. E., 2004. Extending the technology acceptance model and the task-technology fit model to consumer e-commerce. Information Technology, Learning & Performance Journal, 22(1).
MacLeavy, J., 2011. A ‘new politics’ of austerity, workfare and gender? The UK coalition government's welfare reform proposals. Cambridge journal of regions, economy and society, 4(3), pp. 355-367.
Mbiti, I. &. W. D. N., 2015. Mobile banking: The impact of M-Pesa in Kenya. In African Successes, Volume III: Modernization and Development. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Nugroho, R. P. Z. A. J. M. &. d. J. M., 2013. A comparison of national open data policies: lessons learned. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy, 9(3), pp. 286-308.
Prassl, J., 2013. Freedom of Contract as a General Principle of EU Law? Transfers of Undertakings and the Protection of Employer Rights in EU Labour Law: Case C-426/11 Alemo-Herron and others v Parkwood Leisure Ltd.. Industrial Law Journal, 42(4), pp. 434-446.
Stazi, A., 2012. Digital copyright and consumer/user protection: moving toward a new framework. Queen Mary J. Intell. Prop , 2(1), p. 158.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



