Tesco Plc: An E-Commerce Pioneer
Part 1A
Organization identification and Initial audit document
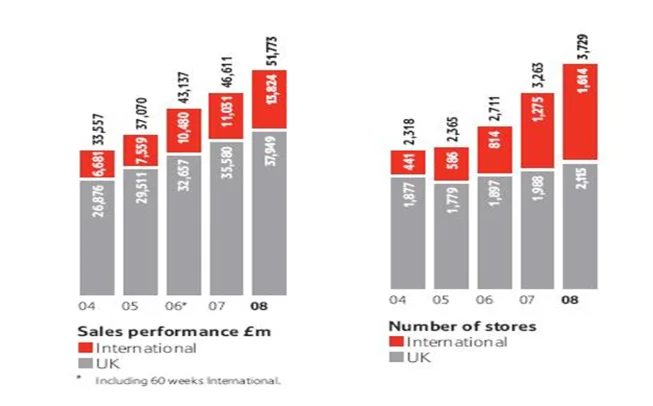
The task demanded that an organization should be selected bearing an online presence thereby attracting an interview that provide a lead to details associated to the company. Based on the research conducted on companies in the United Kingdom, it could be established that Tesco Plc. is better placed as both a company and an online brand that has been benefitting from e-commerce. Tesco is essentially regarded as a British multinational groceries as well as general merchandise retailer with its headquarters in the Welwyn Garden City, United Kingdom. Tesco is also ranked the third largest retailer across the world on the basis of the gross revenues. The choice of Tesco was accompanied by a number of reasons. First, the company has 6234 stores across 13 countries, which attracted sales amounting to 72 billion pounds. This implies a vast presence of the company thereby tapping into a larger market. Secondly, Tesco is ranked third in terms of Internet Retailer across the Top 400 Europe. The initiative was put into place in the year 1984 when goods could be sold electronically. Finally, Tesco has shown a significant investment in e-commerce while using the site and the mobile apps. With more than 70 stores in the United Kingdom, most of the customers are given room to order most of the goods through online. Interacting with Tesco provided me a chance to meet the sales and marketing manager in one of the outlets in London. However, consultations on when and how the interview was to be conducted could only be achieved through one of the junior officers. The phone interview was conducted on 26/10/2019 with key areas touching on how e-commerce has influenced the performance of the company, the growth of Tesla in the digital era, challenges and the future of Tesco in the digital landscape.
Through the engagement I would have with different parties of the organization, I intend to extent consultative services to Tesco Plc. This shall be accompanied by appreciation of the area of strength and taking note of the areas that need improvement. However, it is worth noting that Tesco is such a big company and handling or assessing all the operations is likely to be tedious in the end. I also stand a chance to challenge the organization on the need of continuous assessment and evaluation through internally triggered auditing process arranged by the relevant departments. A number of methods are considered for the audit. First, the process will consider examination of the process of inspecting evidence. This tool is more effective when it comes to determining whether the manual controls have been performed or ignored. More attention is given to backups and the review of the written documentation. The second tool that would be utilized is inquiry in which the auditor is given room to ask the relevant staff and management about the controls and other significant information. For instance, the auditor can make inquiries into online traffic linked to Tesco.

Part 1B – The Audit report
a. Market Analysis
A market analysis is regarded as a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the market. The tool digs deep into the volume, value and size of the market while narrowing down to customer segments, competition, economic environment and the buying patterns. For this context, the market analysis looks into the demographics and segmentation, target market, competition, market need, barriers to entry and regulations.
Demographics and Segmentation
E-commerce and the online retail market have realized a significant growth over the years with increased performance noted by such key players like Tesco and Amazon among others. In the year 2014, the United Kingdom’s Centre for Retail Research noted that e-commerce and online retail business accrued a total of £38.8 billion from the sales. In the year 2013, the market shares linked to e-commerce sales were reported to have stood at 13.5% (Clarke et al. 2015). The trend was remarkable with research pointing at the need to extract the socio-demographic information. The information noted that the market that contributed towards the increase in online and e-commerce sales comprised of the internet users described as browsers as well as buyers. However, this is not enough to describe the consumer dynamics and relationships. The socio-demographic analysis noticed a number of significant segments. The first one could be described through age and gender. Over 98% of the internet users are young people aged between 16-24 years. 23% of the internet use can be assigned to the aging people. However, e-purchasing patterns keep varying across the gender (Clarke et al. 2015). Another segment is based in income. High income earning households have a high tendency of using better broadband and internet services compared to low income earning households. Other factors include area of residence, social groups and mobile technologies available.
Target Market
Based on the demographic analysis, it could be noted that young people tend to be more internet users when compared to the aging population. It can still be established that most of the outlets linked to Tesco are established in urban settings more than it is for the rural settings. Therefore, there are high chances that online purchasing behavior can be more persistent in young people who are urban dwellers. The choice of this target market is based on the fact that there has been low penetration of e-commerce services in rural settings (Berman 2012). Urban dwellers have an almost immediate access to mobile technologies and internet connectivity, which are paramount in accessing online platforms thereby making significant purchasing decisions.
Market need
There is observable increase of the UK population that is moving online each day. Internet or online shopping is currently more popular in United Kingdom. Consumers are said to have spent £233 billion through online in the year 2018. E-commerce currently accounts for a quarter of the retail market, which sends implication of growing online platforms. Therefore, internet services are becoming more paramount to people each day.
Continue your exploration of Tesco's External Factors and Strategy with our related content.
Competition
Like any other industry, e-commerce and online retail market is equally faced with competitive forces. First, e-commerce has been challenged by other platforms that are even doing better. Some of the platforms include M-commerce and B2C websites realized with the companies (Loonam et al. 2018). Secondly, the industry has seen a domination of the key industrial players that purely deal with online sales. Notable brands include Amazon, Boots, Argos, Mark and Spenser and Tesco among others. The industrial players are known for changing tact and conforming to the dynamics.
Barriers to entry
E-commerce and online retail may call for experience and expertise, which is likely to be missing for most of the investors. If such scenarios are realized, then investors would be reluctant to invest in e-commerce as a result of the complexities. In addition, e-commerce may lack regulations that guide the users and protect consumers and retailers. Most of the entrepreneurs may shy off the projects linked to e-commerce and online services (Clarke et al. 2015). Finally, areas with poor ICT infrastructure may impede the process of implementing the e-commerce services and applications.
b. Infrastructure – including risk management
While looking at the performance of Tesco as an online store, it is important that the same attention should be channel to its infrastructural capacity in supporting its online presence. Tesco Plc is known for operating tesco.com, which is responsible for generating e-commerce sales across the United Kingdom. Notably, tesco.com has the capacity of standing out as an all-round store with products serving different categories such as electronics and media, food and personal care and hobby and toys. According to Dave Lewis, the CEO at Tesco, the growth noted with the company is based on the channels and store formats. The context further analyzed how the company is running its retail technology and maintaining the IT infrastructure, which forms the backbone of all operations. The company managed to highlight efficiency in its current performance and the possible future (Berman 2012). This made the company to shut down the Tesco Direct Business while opening the cashless store that incorporated the “Scan and Go” proposition. The ongoing innovations and the use of the underlying IT infrastructure led to the realization of automated online shopping. Tesco is believed to have manifested in a simplistic way, which paved way for automated online grocery shopping. The company also offers infrastructural l support towards mobile payments.
Mobile payment capabilities can be noted with launch of pay+, which represented the earlier version of PayQwiq solution. Further attention is given to a cashless store, which allows users to make their payments with the help of a card. The technology affirmed clear efficiency and is accompanied with cost benefits as noted by the CEO. Other areas of interests include the automated response on the Facebook platform. Shoppers with frequently asked questions are likely to receive feedback or response that is generated automatically. SpoonGuru is another tool that attracts in-depth product knowledge. The tool helped in reclassifying the product range before introducing the 180 proprietary tags. Another feature is that of upsides of the robust Wi-Fi. The latter is regarded as a hygiene factor which provides a number of benefits including running the in-store systems. Apart from the infrastructural support Tesco has given the system, the company is also involved in risk management. Tesco is more concerned with a number of core risks, which can be noted while purchasing products from the suppliers, sending goods to the distribution centre, moving goods to the stores, banking the receipts and taking cash. Based on the core risks, Tesco entrusts risk management practices encountered at group level and the one encountered at the sub group level (Loonam et al. 2018). At the group level risk register is essentially maintained via the internal audit, which is updated regularly while identifying responses. The annual board meeting is commonly charged with the responsibility of reviewing the strategic risks and the audit committee is involved in reviewing internal control system. At the sub group level, the CEO and the local boards are engaged in holding on the risk register. The national based boards are given room to also manage the core operational risks associated to trading or IT.
c. Micro and Macro environment
The report narrows down to PESTEL analysis and SWOT analysis of Tesco
PESTEL analysis
This is a strategic analytical tool applied in evaluating the external environment linked to the business. PESTEL analysis linked to Tesco narrowed down to the evaluation of political, economic, social, legal, technological and environmental factors linked to the retail chain. Political factors: Tesco operates across the world, which implies that its performance can be affected by global political factors. Some of these factors include the legislative acts, tax rates and the stability of the hosting country. Government actions are significant in determining the performance of the company. For instance, tangible impacts of Brexit are likely to be felt on the food prices, limited food imports and devaluation of the pound (Harvey 2016). Established firms such as Tesco are likely to be compelled in looking for UK suppliers who might end up being expensive, as preferred against the EU suppliers for the same core grocery items. In addition, a Tesco Tax proposed by UK local council was rejected by the government. Same initiatives can affect the company in a detrimental way. Economic factors: Factors in this context influence the prices, leverage cots, profit and affect demand. Tesco is supposed to be aware of the changes in policies and changes in taxation. Despite having a global presence, Tesco heavily relies on the UK market in which h it controls 30% of the market shares. On the other hand, Brexit carried with it economic consequences, which led a decline in terms of consumer spending as a result of slow wage growth during the post-Brexit period and the imminent inflation (Panigrahi et al. 2016). The outcome of these two forces is the consumer price inflation with wages failing to keep the race. The hard economic times have attracted the merger between Asda and Sainsbury. If the merger occurs, then it means that Tesco will encounter squeezed margins as well as experience loss of the market shares.

Social factors: Consumer shopping trends are consistently changing with time. Tesco largely depends on the UK consumers before providing goods or even services. Dynamics which are affecting consumption of Tesco products include the dietary and health trends. Under these trends, it could be established that the macro social environment may constitute significant changes across the lifestyles of people, demographic trends, the labor composition and even fashion among other elements which may serve as a source of an opportunity or a threat. Currently, consumer focus on safe and healthy foods and beverages serves as a turning point to the United Kingdom and other major markets that are consistently faced with dynamics (Dwivedi et al. 2017). Most of the UK adults are more concerned with non-alcoholic drinks and sugar foods with some of them showing efforts in reducing the sugars across their diets. If the trend persists, it would adversely affect the supermarkets with the likes of Tesco left to count losses. On the other, the growth of weekly top-up shopping has changed the face of grocery shopping habits. As a result of the changing demographics, home ownership in the United Kingdom continues to fall as a result of rising prices for houses. Private renters are currently controlling the dynamics. The demographic segments settles in urban areas with almost lack of space. As result, the shopping habits shift towards online (Adom et al. 2016). Another area under observation is growing plus size fashion. This comes in the face of rising obesity levels thereby presenting a gap market chance for such retailers like Tesco. Technological factors: In the world of e-commerce, technology takes a significant space. The first area of focus is the growth of the device apps, which are commanding the way consumers shop and alter their habits towards food. Notably, the trend has already discovered the use of voice controlled shopping with the help of voice recognition apps like Siri. Secondly, it is common to touch on the superfast delivery in the face of an ever changing technology. Most of the food retailers are commonly locked in competitive bids believed to provide consumers with the fast delivery. Mark & Spencer, Tesco and Sainsbury have all launched the one-hour grocery delivery, which is a trend that can speed home delivery. Lastly, the industry is increasingly being influenced through automation and automated delivery. Automated home delivery is already changing the trading landscape in the retail market. Environmental factors: UK has recently realized the growing numbers of environmentally and ethically conscious consumers that call for firms to embrace practices that will reduce pollution. The trend is also extended to the retail industry where supermarkets are called upon to embrace zero waste supermarkets.
Legal factors: Tesco has been facing the 2014 accounting scandal in which the company is accused of overstating the profits. This damaged the reputation of the company. Tesco is expected to comply with sugar tax that has the fundamental aim of reducing content of sugar in drinks by almost 20%.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a business analytical tool that checks on the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. The following is the SWOT analysis of Tesco Strengths: Tesco is the biggest grocery retailer across United Kingdom characterized by higher sales and revenue. It also has the leading market share commanding 27% of it. The company is geographically diversified with at least 6800 stores across the 14 countries. It also has diversified stores with diversified divisions such as Tesco superstores, Tesco express, Tesco homeplus, Tesco Extra and Tesco metro. Tesco has superior technology usage and efficient supply chain characterized by reduced costs, simplified business model and effective waste management policies.
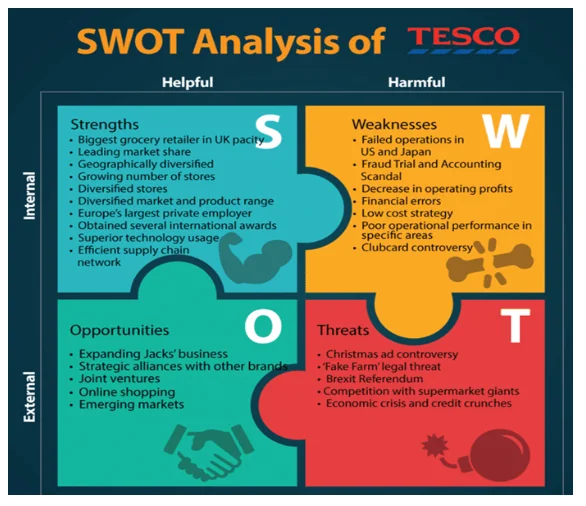
Weakness: Tesco has encountered a decrease in operating profits with share prices going down with more 9%. The company has also faced poor operational performance in some of the markets. Fraud Trial as well as the Accounting Scandal cost the company its reputation after a misrepresentation of profits. Opportunities: Tesco has an opportunity of expanding the Jack’s business, which is a new discount store that has indicated signs of growth. The company can still strike strategic alliances and joint ventures, which would help the company to explore new markets and boost its reputation via strategic partnerships. Online shopping is a growing platform that can bolster the efforts of the company in attaining the home delivery services. Threats: The Brexit referendum posits a looming danger to the company as far as trade deals as well as cost matters are put into consideration. Credit crunches and the economic crisis can bungle legal and tax issues, impede operational efficiency and hamper the performance of the stores. Giant supermarkets such as Walmart, Aldi and Carrefour have threated the competitive position of Tesco.
d. Digital Business Strategy
Tesco has shown the most promising performance over the years. However, it took the company an entire process to rediscover the digital journey, which made it to realize the profitable online platform. In this journey, the company began by tapping into the most relevant humor. In this case, Tesco was previously seen to be stable, recognizable and with a robust corporate marketing strategy. However, in the wake of the accounting scandals which plagued the reputation of Tesco in 2013-2014, it could be realized that changes were necessary. The company began pursuing a new form of marketing across the Christmas commercial campaigns. This would create a familiar spirit behind the humor concept. Secondly, Tesco went ahead developing new product lines. This was characterized by rebranding the products while appealing to cost-conscious consumers who never valued Tesco’s offerings before. The brand noted the need to compete in terms of the process with a reduction in prices leading to an increase in fish sales (Kirby-Hawkins et al. 2019). Third, the company started making strides towards digital marketing. This was part of the strategic moves by the supermarket which saw it spending 30% of the marketing revenue in a move to embrace digital marketing. The strategy helped in reaching out the targeted individuals that could be found in social media platforms. Fourth, the company overhauled product packaging. New packaging designs as well as branding campaigns were organized in an effort to rebrand the business. Tesco desired to elicit the imagery connected to home-grown atmospheres. Fifth, alongside the growing online presence, Tesco started competing with the smaller chains in an effort to stabilize its market shares (Xie 2019). This comes at the time when such chains like Aldi went ahead competing on social media. Lastly, Tesco went customizing media while boosting individual experience. The marketing team was given an opportunity to float ideas regarding the customization process.
e. Customer relationship management
Customer Relationship Management denotes the efforts by the business to retain customers and win their loyalty. Tesco has equally expressed interest in CRM with a number objectives tagged along. Tesco intends to build continuous relationships with customers. Tesco also intended to individually recognize customers while trying hard to address customer satisfaction. Based on the objectives, a number of strategies can be floated to address the objectives. With the help of the digital approach, the company is taking advantage of the multichannel client management, which takes advantage of the design, deployment, coordination and assessment of the channels for the purposes of enhancing the value of consumers through gaining, development and maintenance (Sivalingam 2018). The multichannel client management is regarded as marketing function that can allow customers to interrelate. Call centers, internet and even kiosks can be used as commonplaces for consumers to buy the Tesco products.
In an effort to assess the needs and values of the customers, Tesco strategically sends club card account to its 10 million consumers in every quarter. Tesco dishes out extra coupons and vouchers that intent to reward and provide enticements for the shopping behavior. On the other hand, market segmentation has been key for Tesco to identify individual customers (Fatricia 2017). In doing so, Tesco could analyze the market by grouping the customers in terms of the behavior, promotional responsiveness, lifestyles, regency and redemption of coupons. The company could visibly take note of the consumer value accompanied with knowledge accumulated via the club account scheme. Besides, analysis of the customer data has paved way for strategic decision making. Finally, a vast online platform supported through e-commerce, the company website and the social media platforms has helped in managing trends and customer data, which is paramount in identifying gaps. However, online presence is still vulnerable to attacks especially where precautions are not considered.
f. Digital business service
Tesco has progressively invested in technology while creating the omnichannel customer experience in the face of a digitized grocery landscape. Digital business service can be felt in three technological advancements. First, the digital service can be felt in terms of the movement from bricks and motor to the version of bricks and clicks with the help of Tesco Direct. The latter has the click and collects functionality. In the year 2006, Tesco had already enjoyed the use of online grocery channel with online sales growing exponentially. With attempts of maintaining the performance profile, Tesco went ahead in offering the omnichannel click and collect, in which customers are allowed to place orders through online platform and later collect the bagged groceries through collection points. However, the shift was accompanied with heavy investments in the online platform, grocery dotcom centers and supply chain ordering. Secondly, the digital service could further be felt through implementing the digitalized in-store experience. For the purposes of enhancing the efficiency and operability of the operating model adopted by Tesco, the company went ahead investing in the digital in-store initiatives. The initiatives included the scan as you stop; check out stations and self-check-out stations. From this perspective, Tesco is scene fighting thievery by improvising the digital receipt technology as well as specialized cameras. The in-store video cameras like broccoli cam could detect the time when the fruit or vegetable trays are depleted thereby triggering instant messages to employees for replenishment. Finally, the digital service is felt through development of the Tesco Clubcard. Notably, the loyalty scheme tags have a unique customer ID thereby leading to amalgamation of numerous purchasing data points. The company also leverages on algorithms and data analytics, which helps it to adapt the purchasing trends and the supply chain while predicting the purchasing habits.
g. Usability of web site
While talking about digital presence, it is also recommended that the report should check on the website usability by Tesco. Perhaps, closer observations were made on the tesco.com where one is first exposed to sensible and guessable categories. The categories found in the second level navigation are easy to guess and one is likely to pick on the right. Secondly, the website has the mega menus which are easier to read (Weenk 2019). One can scan vast amounts of data with a human eye. After this, one is allowed to perform a multisearch where an entire shopping list can be entered. Then, there is a basket view by the category before sorting the search results. The latter is a useful feature especially where there is cost per unit. After this, one is also allowed to remove the items from the search results to avoid chances of buying an item that were never planned for before. The shopping basket can be shown with the feature appearing on the front of the screen. At this point, the website attracts one to one-hour delivery slots. The usability of the website depends on how well customers can place their order, make payment, select delivery and identify the pickup points. However, it could be noted that user experiences can be different depending on how well one can understand and operate the portal.

Conclusion
The report provides research and interview-based findings on Tesco’s online presence. The report has provided an overview of Tesco in terms of location and the nature of business the supermarket handles. The audit report further shares the market analysis in which most of the internet users were identified as young people aged between 16 and 24 years. The market is also competitive with more established brands scooping a bigger market share. The report also shared insights on the infrastructure and the micro and macro environmental factors that influence the performance of Tesco. Further details include the usability of the website, digital business services and the online tools to be adopted.
Recommendation
Tesco is required to adopt a holistic approach across its multichannel approach while tracking how consumes interact through digital, in-store and online points of contact. The management needs to understand that the future of Tesco lies behind the successful integration of online and offline points of contact. In addition, importance and relevance of the digital transformation at Tesco should be accompanied by a committee or a managerial team assigned the digital marketing task.
References
Loonam, J., Eaves, S., Kumar, V. and Parry, G., 2018. Towards digital transformation: Lessons learned from traditional organizations. Strategic Change, 27(2), pp.101-109.
Berman, S.J., 2012. Digital transformation: opportunities to create new business models. Strategy & Leadership, 40(2), pp.16-24.
Harvey, D., 2016. Digital transformation in banks: The trials, opportunities and a guide to what is important. Journal of Digital Banking, 1(2), pp.136-145.
Kirby-Hawkins, E., Birkin, M. and Clarke, G., 2019. An investigation into the geography of corporate e-commerce sales in the UK grocery market. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 46(6), pp.1148-1164.
Panigrahi, D., Upadhyaya, R. and Raichurkar, P.P., 2016. E-Commerce Services in India: Prospects and Problems. International Journal on Textile Engineering and Processes, 2(1).
Dwivedi, Y.K., Rana, N.P. and Alryalat, M.A.A., 2017. Affiliate marketing: An overview and analysis of emerging literature. The Marketing Review, 17(1), pp.33-50.
Sivalingam, R., 2018. Strategic Management. Industry Analysis, Strategic Drift and Re-Strategizing. GRIN Verlag.
Adom, A., Nyarko, I. and Som, G.N., 2016. Competitor Analysis in Strategic Management: Is it a Worthwhile Managerial Practice in Contemporary Times?. Journal of Resources Development and Management, 24.
Fatricia, R.S., 2017. Strategic Analysis of Tesco Supermarket. Jurnal Manajemen Terapan dan Keuangan, 6(02), pp.69-86.
Xie, Y., 2019, February. The Research on Value Evaluation of B2C Online Shopping Platform in Jiangxi Province with EVA Model. In International Conference on Application of Intelligent Systems in Multi-modal Information Analytics (pp. 1443-1448). Springer, Cham.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



