A Comprehensive Literature Search and Critical Appraisal
Introduction:
A literature search is associated with conducting the relevant search methodology and retrieve the highly appropriate research papers thereby analysing as well as comparing the content the selected research papers to answer the research question (Ekkekakis et al. 2018). This research study is going to conduct a literature search for finding relevant research articles on the selected topic “is exercise an effective intervention for depression in UK”. First this research study will present suitable definition of evidence based practice in relation to the selected topic. Then this research study will demonstrate the search methods, which are used by the researcher to select 5 relevant research articles on the selected research topic. In this search method, researcher will discuss key terms, inclusion and exclusion criteria and the search strategies that are used to select the 5 research papers. Then a discussion on the 5 research papers will be presented in which the critical appraisal of the all the selected research papers will be presented. In this section, the content on the selected research articles will be analysed and compared by using the other relevant research papers. For those seeking healthcare dissertation help, understanding this process is crucial. Finally this research study will present a conclusion in which it will infer the main aspect of the entire discussion. This this literature search will present a discussion the implications of this research study on the learning and knowledge development of the researcher.
Evidence based practice can be defined as the process in which the best available evidences are used for improving the quality of care to patients by improving the decision making and way of care delivery (Negaresh et al. 2019). In case of using exercise as an effective intervention for treating depression in patients, EBP is crucial which enables the healthcare professional to bring together the best available evidence and the professional expertise to improve usefulness of the intervention. In modern healthcare context, exercise is considered as effective intervention in treating depression by improving the self-confidence, self-motivation and self-management skill in patients. However, there are many contradictory arguments regarding this aspect which state that, exercise can only be effective in treating depression, when used in line with proper medication and systematic lifestyle .this literature search will conduct a critical appraise in which it will critically compare and discuss the contents of selected research papers to answer the research question:

Is exercise the effective intervention for treating depression in the UK?
Search method:
Search strategy:
As mentioned by Largan and Morris (2019), CINAHL is one of the widely used and most trustworthy as well as convenient online academic database system that assists modern healthcare professionals to search for the best available research articles on any particular research topic and conduct an effects EBP to improve the clinical decision making and optimise the quality of care delivery to patents. In this literature search, researcher used the CINAHL online database system to find out and retrieve relevant research articles researcher to meet the research question and objectives and answer the research question. as opined by Rothwell et al. (2019), there are also some limitations of using online database system, , such as researchers may face difficulties in choosing the relevant research papers on the topic is broad because the search can generate huge search result. In this context short topic is highly appropriate in searching for the highly appropriate research papers in limited time. Here researcher have used the flowing key words to search for the relevant research papers:
Key terms:

Inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria:

First search:
First literature search was conducted by going to the EBSCOhost website and then clicking to CINAHL database option (Largan and Morris, 2019). In this CINAHL webpage articles are searched by using key terms related to the topic “exercise as an effective clinical intervention for treating depression. In this first search the research papers are search based on their publication years. Here research has used the time scale of 5 years (2016-2021). The research papers that are published in the last 5 years (not before 2016) are select for conducting this research study. Boolean operators AND, NOT and OR are used here to narrow or extend the literature search. After using the times scale on the CINAHL search option, to total of 468 research papers were obtained. The search terms that are used in this foist literature search are, depression AND clinical intervention AND mental disorder OR depressive symptoms OR exercise AND physical workout NOT medicine management
Second research:
After conducting the first research, it was seen that there were many duplicates of selected research papers. Therefore a second literature research had been conducted for removing the duplicated. In this context, the search term so the first literature search was analyse the the duplicate research paper is deleted from the list to narrow the literature research. After removing the duplicates a total of 240 research papers were obtained.
Third search:
For narrowing the literature research of 2nd search, a third search was conducted in which language of research paper was considered. First it was checked that whether here are any research papers that are not published in English, and the research papers were exclude from the lists. As mentioned by Harrison et al. (2019), while conducting literature search, researcher must use such inclusion and exclusion criteria that are highly appropriate to find out the relevant research papers that can assist the researcher to meet the research objectives and answer the research question. In this way a total of 70 research papers were selected that are published in UK English.
Fourth search:
After selecting the research papers that published in English, a fourth search was conducted, a screening test was performed for the research papers. In this screening test, the validity of each research elements of each research article were checked. As mentioned by Largan and Morris, (2019), research elements are the major aspects of a research paper that enables researcher to meet research outcomes such as research design, research strategy data collection, and research philosophy and data analysis. In this fourth search, it was checked that whether all the research element of each research paper are valid and authentic that can assist this research study to answer the research question. After this screening process a total of 12 research papers were selected.
Fifth search:
After conducting the fourth literature search it was seen that there were many research papers that contain some vague and irritant research database that cannot fort the the research topic. Therefore a fifth search was conducted in which the test validity and relevance of research content was checked. Additionally, it was also checked that whether selected research articles could be downloaded in full texted format. After conducting this research a total of 5 research papers was selected.
Discussion:
Throughout the above-mentioned searches 468, 240, 70, 12 and 5 research papers are retrieved by using the CINAHL online database system. As mentioned by Largan and Morris, (2019), while conducting any literature search , researcher need to check whether the research papers that are selected contain the best available statistical and theoretical database on the selected research topic. some research papers although seemed to have the relevant contents, cannot present the roper interfere to the particular topic. on the other hand, many research papers although having valid research elements can nt present the justified and high authentic database on the research topic. therefore a proper screening and search strategy are important for conducting an effective literature search that can enables researcher to find out the relevant research papers on selected topic. In this research papers, first a total of 468 research articles were obtained. However majority of these research papers discuss the broad spectrum of mental disorders rather than discussion the depression and its treatment by using exercise as effective clinical intervention. Therefore the net search was generated. The second search yielded 240 research articles. The analysing and screening of these research papers had shown that among these research article, there are many research papers that discussed other clinical intervention such as pharmacological intervention and CBT (cognitive behavioural theory) rather then focusing on usefulness of exercise in treating depression. Therefore the next search had been generated which yield a total of 70 research articles. However, out of these research articles there were many research which had irrelevant information in line with discussing the impacts of using exercise as a clinical intervention to treat depression. Therefore a next search had been conducted which retrieved 12 articles. Among these 12 articles all research articles were not downloaded in full texted format. Therefore a next and final; search was generated to select only articles that were easily accessed through online in full texted format. Therefore a total of 5 research papers are select which contain highly relevant and authentic content on effectiveness of exercise as the useful intervention for treating depression”.
Appraisal of search paperrs:
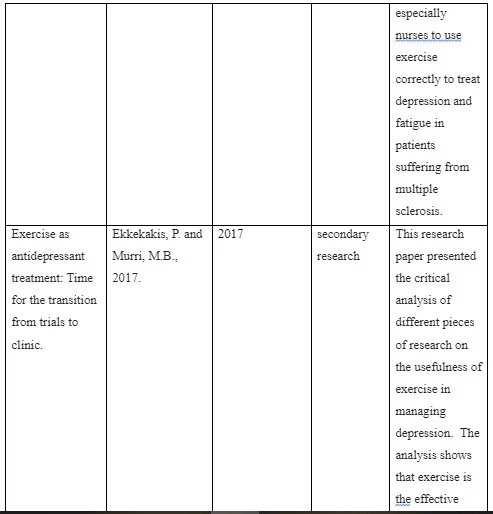
Negaresh et al. (2019) conducted a randomised control trial that had shown that exercise is the effective therapeutic intervention for treating depressive symptoms. In this study, research had conducted a randomised control trial on 66 older patients who joined a weight management raining and exercise program. After the end of the exercise program it was seen that, the depressive symptoms are reduced and their mental state had shown significant improvement. This research paper is proved to be highly useful in assisting modern healthcare professionals, especially nurses to use exercise correctly to treat depression and fatigue in patients suffering from multiple sclerosis. As argued by Ekkekakis et al. (2018), exercise although is proved to be effective in managing depressive symptoms, the lack of skill of physiotherapist and nurses can interfere with outcomes of exercise in managing depression. Evidence suggest that, in modern healthcare filed, patients who suffer depression can haver complex physical health condition. Therefore, healthcare professionals must be highly trained and skilled in advising patient to do the right exercise that does not go wrong to physical health of the patients. However, although the research paper by Negaresh et al. (2019) is able to discuss the usefulness of the exercise in reducing the depressive symptoms. It is failed to discuss the limitations that healthcare professionals and nurse can face if the exercise are not performed correctly.
Ekkekakis and Murri (2017) conducted the secondary research which presented the fact that, exercise can be used as the antidepressant therapy that can not only improve the mental hath of patients but also can improve their decision making and self-management skill. This research paper presented the critical analysis of different pieces of research on the usefulness of exercise in managing depression. The analysis shows that exercise is the effective non-pharmacological process which enables patients with depression ad other mental health condition to maintain a healthy relationship between their body and mind. In this context Sukhato et al. (2017) argued that, sometimes exercise that are not performed as per the guidance of trainer or physicians can cause severe breakage of fatty tissues and cells which cause excessive weight reduction. Clinical intervention suggest that, exercise although have many criticism, are considered to be the most effective way of improving own control on personal decision making, emotion and cognition which assist people to get rid of the depressive thoughts. As mentioned by Glowacki et al. (2017) regular exercise enables patients with depression to improve the blood circulation into brain which generate innovative and positive thoughts. Ekkekakis and Murri (2017) is useful in discussing the ways in which exercise acts as antidepressant and how it assist modern health professionals to optimise the usefulness of mental health treatment by using right exercise. However, the only limitation of this research article by Ekkekakis and Murri (2017) is it fails to discuss the factors that health professionals need to consider while treating depressive symptoms in patients by using exercise as an effective therapeutic intervention. These factors that needs to be considers are patients’ age, presence any physical health condition, additional mental health disorders in patients and the choices of patients for doing exercise (Zanetidou et al. 2017).
Gujral et al. (2017) conducted a systematic review to show how exercise effect on depression. This study mentioned that exercise is proved to be highly effective in managing symptoms that are related to depression such as mood swing, lack of pleasure and sadness. Gujral et al. (2017) mentioned that, depression is the global mental health issue that can be managed by performing right exercise regularly. According to Elkington et al. (2017), while using exercise as an effective therapeutic intervention in managing depression, health professionals must emphasize on other two factors that are healthy lifestyle and social support. However, Gujral et al. (2017) fails to discuss how these social, psychological, economic and pharmacological factors affect the usefulness of exercise in treating depression. Modern healthcare intervention of depression shows that, exercise if performed correctly can pose positive impacts on the cognitive skills of patients thereby improving their ability to take thte right decision in critical time (Roberts et al. 2018). on the contrary (0 argued that, although exercise improves the depressives symptoms in patients, it is obscure whether it is associated with providing the critical thinking skill in people.
Li et al (2020) carried out a systematic research which shows that, exercise is proved to be highly effective in reducing depression and anxiety in patients with COPD. This research study mentioned that, in case of managing depression and anxiety in COPD patients, aerobic exercise is highly useful which improves the breathing condition of patients thereby reducing depression and negative thoughts in them. As mentioned by Prior and Suskin (2018), exercise improves the mental health condition of patients with depression by promoting their physical psychological and emotional wellbeing.
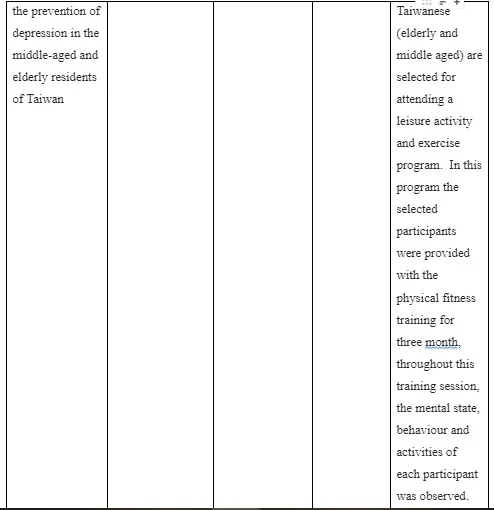
Lee et al. (2018) conducted a randomise controlling trial in which 3727 Taiwanese (elderly and middle aged) are selected for attending a leisure activity and exercise program. In this program the selected participants were provided with the physical fitness training for three month, throughout this training session, the mental state, behaviour and activities of each participant was observed. The result showed the depressive symptoms of these participants had been reduced after the three month of this exercise program. As argued by Carter et al. (2019), although exercise is effective intervention in managing depression in patients, it is not clear that how exercise impacts on thoughts, intelligence and behaviour of patients. Many researchers mentioned that exercise improves the physical health of people which reduces the tension and worries of people regarding the health and wellbeing thereby reducing their risk to depression (Saravanan et al. 2019).
Implication to practice:
This research study is expected to provide a good support to the modern healthcare professionals, especially nursing professionals to improve the mental health treatment by motivating patient to perform the right exercise. This research study also presents the evidence based research which improve the professional knowledge and understanding of healthcare professionals regarding the limitations and factors that are associated with exercise that are need to be considered while treating depression.
Reflection and learning:
This literature search is highly informative to me which improve my skillets in conducting any literature review. Through working on this literature search, I have gathered a good knowledge on the correct way of conducting a secondary research. I have gained clear knowledge on how to use the online database system by using the Boolean operators and key words to select the relevant literature. This literature search also provides me with the opportunity in grabbing in-depth knowledge in the usefulness of exercise in managing depression and barriers or limitations that are associated with exercise that health professional need to consider.

During working on this literature search is faced difficulties in understanding the topic. Then I discussed this issue with my professors and lecturers who helped me a lot to have good conceptualisation on this topic. I also faced issues in searching literature on the selected topic as I did not know the right way to search for literature on CONAHL. However my team leaders and team members helped me to carry out the literate search in system way to accomplish the literature search. This literature search improves my teamwork skill and resilience which will assist me in near future to perform synergistic work
Conclusion:
From the above-mentioned discussion it can be stated that, exercise is the effective therapeutic intervention in treating depression in UK. Exercise can improve the connection between body and mind thereby promoting a good mental health by improving physical health and wellbeing. However, there are some factors that can interfere with the usefulness of exercise such as the skills of physiotherapist ad nurses in guiding patients for performing right exercise, patient’s additional health issues, age and physical health of patients. Therefore, while using exercise for treating depression, health professionals in the UK must consider these factors to avoid any kind of health risk
Reference list:
Asher, G.N., Gartlehner, G., Gaynes, B.N., Amick, H.R., Forneris, C., Morgan, L.C., Coker-Schwimmer, E., Boland, E., Lux, L.J., Gaylord, S. and Bann, C., 2017. Comparative benefits and harms of complementary and alternative medicine therapies for initial treatment of major depressive disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 23(12), pp.907-919.
Bang, Y.Y., 2019. Convergence analysis of depression managing program for menopausal women in Korea. Journal of the Korea Convergence Society, 10(4), pp.257-264.
Carter, T., Bastounis, A., Guo, B. and Morrell, C.J., 2019. The effectiveness of exercise-based interventions for preventing or treating postpartum depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of women's mental health, 22(1), pp.37-53.
Ekkekakis, P. and Murri, M.B., 2017. Exercise as antidepressant treatment: Time for the transition from trials to clinic. Gen Hosp Psychiatry, 49, pp.A1-5.
Ekkekakis, P., Hartman, M.E. and Ladwig, M.A., 2018. Mass media representations of the evidence as a possible deterrent to recommending exercise for the treatment of depression: Lessons five years after the extraordinary case of TREAD-UK. Journal of sports sciences, 36(16), pp.1860-1871.
Elkington, T.J., Cassar, S., Nelson, A.R. and Levinger, I., 2017. Psychological responses to acute aerobic, resistance, or combined exercise in healthy and overweight individuals: a systematic review. Clinical Medicine Insights: Cardiology, 11, p.1179546817701725.
Glowacki, K., Duncan, M.J., Gainforth, H. and Faulkner, G., 2017. Barriers and facilitators to physical activity and exercise among adults with depression: A scoping review. Mental Health and Physical Activity, 13, pp.108-119.
Gujral, S., Aizenstein, H., Reynolds III, C.F., Butters, M.A. and Erickson, K.I., 2017. Exercise effects on depression: possible neural mechanisms. General hospital psychiatry, 49, pp.2-10.
Harrison, C.N., Garcia, J.S., Mesa, R.A., Somervaille, T.C., Komrokji, R.S., Pemmaraju, N., Jamieson, C., Papadantonakis, N., Foran, J.M., O'Connell, C.L. and Holes, L., 2019. Results from a phase 2 study of navitoclax in combination with ruxolitinib in patients with primary or secondary myelofibrosis.
Largan, C. and Morris, T., 2019. Qualitative secondary research: A step-by-step guide. Sage.
Lederman, O., Ward, P.B., Firth, J., Maloney, C., Carney, R., Vancampfort, D., Stubbs, B., Kalucy, M. and Rosenbaum, S., 2019. Does exercise improve sleep quality in individuals with mental illness? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of psychiatric research, 109, pp.96-106.
Lee, H.Y., Yu, C.P., Wu, C.D. and Pan, W.C., 2018. The effect of leisure activity diversity and exercise time on the prevention of depression in the middle-aged and elderly residents of Taiwan. International journal of environmental research and public health, 15(4), p.654.
Li, Z., Liu, S., Wang, L. and Smith, L., 2020. Mind–body exercise for anxiety and depression in COPD patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(1), p.22.
Mikkelsen, K., Stojanovska, L., Polenakovic, M., Bosevski, M. and Apostolopoulos, V., 2017. Exercise and mental health. Maturitas, 106, pp.48-56.
Negaresh, R., Motl, R., Mokhtarzade, M., Ranjbar, R., Majdinasab, N., Khodadoost, M., Zimmer, P., Baker, J.S. and Patel, D., 2019. Effect of short-term interval exercise training on fatigue, depression, and fitness in normal weight vs. overweight person with multiple sclerosis. Explore, 15(2), pp.134-141.
Prior, P.L. and Suskin, N., 2018. Exercise for stroke prevention. Stroke and vascular neurology, 3(2).
Roberts, M., Parkhill, A.L., Skalla, D. and Miller, K., 2018. Assessment of the Use of Non-Pharmacological Methods for Managing Depression in Patients with Myotonic Dystrophy (DM) and Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy (FSHD).
Rothwell, E., Johnson, E., Riches, N. and Botkin, J.R., 2019. Secondary research uses of residual newborn screening dried bloodspots: a scoping review. Genetics in Medicine, 21(7), pp.1469-1475.
Saravanan, C., Mohamad, M. and Alias, A., 2019. Coping strategies used by international students who recovered from homesickness and depression in Malaysia. International journal of intercultural relations, 68, pp.77-87.
Smith, J., Newby, J.M., Burston, N., Murphy, M.J., Michael, S., Mackenzie, A., Kiln, F., Loughnan, S.A., O'Moore, K.A., Allard, B.J. and Williams, A.D., 2017. Help from home for depression: A randomised controlled trial comparing internet-delivered cognitive behaviour therapy with bibliotherapy for depression. Internet interventions, 9, pp.25-37.
Son, H.G. and Choi, E.O., 2018. The effects of mindfulness meditation-based complex exercise program on motor and nonmotor symptoms and quality of life in patients with Parkinson's disease. Asian nursing research, 12(2), pp.145-153.
Sukhato, K., Lotrakul, M., Dellow, A., Ittasakul, P., Thakkinstian, A. and Anothaisintawee, T., 2017. Efficacy of home-based non-pharmacological interventions for treating depression: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ open, 7(7), p.e014499.
Way, K.L. and Reed, J.L., 2019. Meeting the needs of women in cardiac rehabilitation: is high-intensity interval training the answer?. Circulation, 139(10), pp.1247-1248.
Wellsandt, E. and Golightly, Y., 2018. Exercise in the management of knee and hip osteoarthritis. Current opinion in rheumatology, 30(2), pp.151-159.
Zanetidou, S., Belvederi Murri, M., Menchetti, M., Toni, G., Asioli, F., Bagnoli, L., Zocchi, D., Siena, M., Assirelli, B., Luciano, C. and Masotti, M., 2017. Physical exercise for late‐life depression: customizing an intervention for primary care. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 65(2), pp.348-355.
Zhang, J., Qin, S., Zhou, Y., Meng, L., Su, H. and Zhao, S., 2018. A randomized controlled trial of mindfulness-based Tai Chi Chuan for subthreshold depression adolescents. Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment, 14, p.2313.
Appendix 1: PRISMA tool

Appendix 2:



Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to A Comprehensive Literature Review on Fall Prevention in Adult In-Patients.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



