Comparative Analysis of Physical Activity Interventions on Mental Well-being in Older Adults
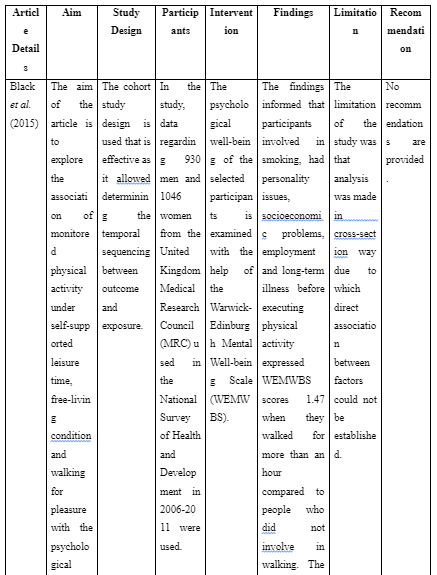
Article 1: Black, S.V., Cooper, R., Martin, K.R., Brage, S., Kuh, D. and Stafford, M., 2015. Physical activity and mental well-being in a cohort aged 60–64 years. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 49(2), pp.172-180.
The aim of the article is to explore the association of monitored physical activity under self-supported leisure time, free-living condition and walking for pleasure with the psychological well-being of people 60-64 years of age.
The cohort study design is used that is effective as it allowed determining the temporal sequencing between outcome and exposure.

In the study, data regarding 930 men and 1046 women from the United Kingdom Medical Research Council (MRC) used in the National Survey of Health and Development in 2006-2011 were used.
The psychological well-being of the selected participants is examined with the help of the Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (WEMWBS).
The findings informed that participants involved in smoking, had personality issues, socioeconomic problems, employment and long-term illness before executing physical activity expressed WEMWBS scores 1.47 when they walked for more than an hour compared to people who did not involve in walking. The people involved in walking at least five times in a month expressed WEMWBS scores 1.25 which is higher than those were sedentary. This suggests that incorporating regular physical activity may benefit individuals facing various challenges, highlighting the importance of health promotion in broader contexts, which is crucial for research requiring healthcare dissertation help.
The limitation of the study was that analysis was made in cross-section way due to which direct association between factors could not be established.
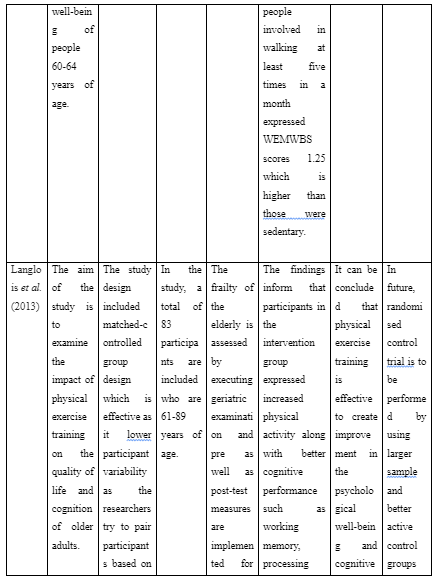
Article 2: Langlois, F., Vu, T.T.M., Chassé, K., Dupuis, G., Kergoat, M.J. and Bherer, L., 2013. Benefits of physical exercise training on cognition and quality of life in frail older adults. The Journals of Gerontology: Series B, 68(3), pp.400-404.
The aim of the study is to examine the impact of physical exercise training on the quality of life and cognition of older adults.
The study design included matched-controlled group design which is effective as it lower participant variability as the researchers try to pair participants based on similar characteristics and ability.
In the study, a total of 83 participants are included who are 61-89 years of age.
The frailty of the elderly is assessed by executing geriatric examination and pre as well as post-test measures are implemented for examining the cognitive performance, physical activity and quality of life of the participants.
The findings inform that participants in the intervention group expressed increased physical activity along with better cognitive performance such as working memory, processing speed and others compared to the control group.
It can be concluded that physical exercise training is effective to create improvement in the psychological well-being and cognitive function of frail older adults.
In future, randomised control trial is to be performed by using larger sample and better active control groups for supporting the current findings. Moreover, it is recommended that future studies are examine training-induced cognitive improvement for generalising information in real-life condition.
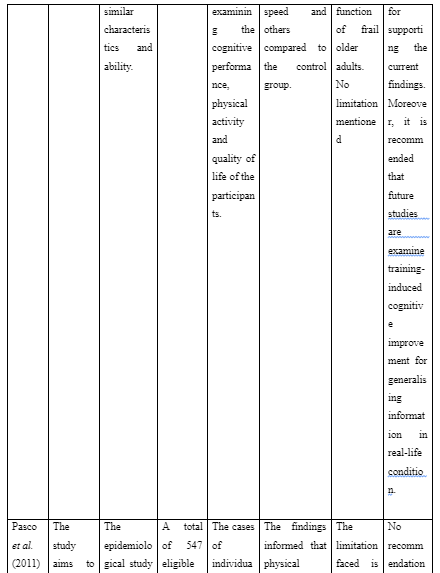
Article 3: Pasco, J.A., Williams, L.J., Jacka, F.N., Henry, M.J., Coulson, C.E., Brennan, S.L., Leslie, E., Nicholson, G.C., Kotowicz, M.A. and Berk, M., 2011. Habitual physical activity and the risk for depressive and anxiety disorders among older men and women. International psychogeriatrics, 23(2), pp.292-298.
The study aims to explore the impact of habitual physical activity on the risk factors of anxiety and depression of older men and women.
The epidemiological study uses case-control study design which is effective as it helps to assessment the association of exposure with indented outcomes regarding any illness or disease.
A total of 547 eligible participants are recruited for the study who are equal or over the age of 60 years.
The cases of individuals who expressed depressive and anxiety disorder were diagnosed with the help of Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR. A questionnaire is used for habitual physical activity and the others were documented at baseline.
The findings informed that physical activity ensures effective protection of individuals against the occurrence of anxiety and depression. This is evident as each increase in standard deviation in the transformed physical activity was related to reducing by half the likelihood of anxiety and depression.
It is concluded that physical activity protects subsequent risk related to the development of de novo anxiety and depression in older adults.
The limitation faced is inconsistency in physical activity pattern, exclusion of individuals with poor movement and others.
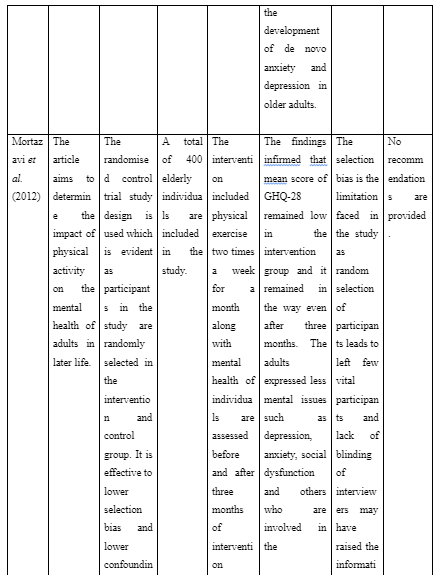
Article 4: Mortazavi, S.S., Mohammad, K., Ardebili, H.E., Beni, R.D., Mahmoodi, M. and Keshteli, A.H., 2012. Mental disorder prevention and physical activity in Iranian elderly. International Journal of Preventive Medicine, 3(Suppl1), p.S64.
The article aims to determine the impact of physical activity on the mental health of adults in later life.
The randomised control trial study design is used which is evident as participants in the study are randomly selected in the intervention and control group. It is effective to lower selection bias and lower confounding variable influence out of unequal distribution of the population.
The intervention included physical exercise two times a week for a month along with mental health of individuals are assessed before and after three months of intervention through 28-item General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-28).
The findings infirmed that mean score of GHQ-28 remained low in the intervention group and it remained in the way even after three months. The adults expressed less mental issues such as depression, anxiety, social dysfunction and others who are involved in the intervention group.
The selection bias is the limitation faced in the study as random selection of participants leads to left few vital participants and lack of blinding of interviewers may have raised the information bias to also face as limitation.
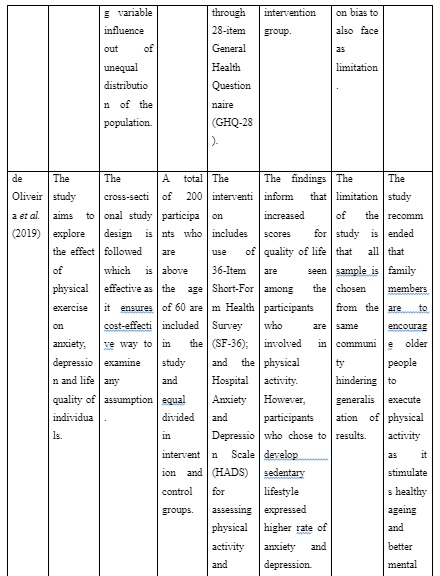
Article 5: de Oliveira, L.D.S.S., Branco, C., Souza, E.C., Rodrigues, R.A.S., Fett, C.A. and Piva, A.B., 2019. The effects of physical activity on anxiety, depression, and quality of life in elderly people living in the community. Trends in psychiatry and psychotherapy, 41(1). pp.36-42.
The study aims to explore the effect of physical exercise on anxiety, depression and life quality of individuals.
The cross-sectional study design is followed which is effective as it ensures cost-effective way to examine any assumption.

A total of 200 participants who are above the age of 60 are included in the study and equal divided in intervention and control groups.
The intervention includes use of 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36); and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) for assessing physical activity and mental health along with quality of life of individuals.
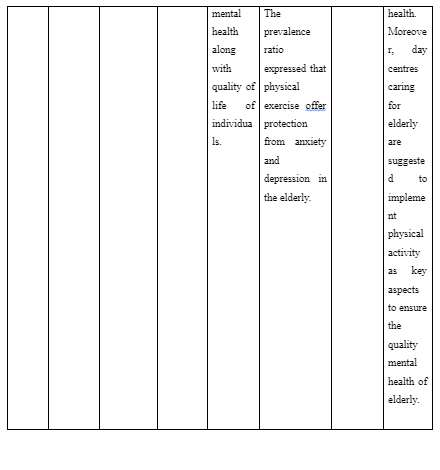
The findings inform that increased scores for quality of life are seen among the participants who are involved in physical activity. However, participants who chose to develop sedentary lifestyle expressed higher rate of anxiety and depression. The prevalence ratio expressed that physical exercise offer protection from anxiety and depression in the elderly.
The limitation of the study is that all sample is chosen from the same community hindering generalisation of results.
The study recommended that family members are to encourage older people to execute physical activity as it stimulates healthy ageing and better mental health. Moreover, day centres caring for elderly are suggested to implement physical activity as key aspects to ensure the quality mental health of elderly.
Looking for further insights on Comparative Analysis of Developmental Therapeutics Programs? Click here.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



