Health Outcomes in Elderly Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes
Introduction
Diabetes is a life-long critical health condition; there are 3.5 million people who diagnosed with diabetes in the UK, estimated 549,000 people (Diabetes UK, 2018). Diabetes refers to the condition that causes high levels of glucose or sugar in the blood. Insulin moves glucose from the bloodstream into the cells of the body for energy. If the body doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use the insulin it makes, glucose stays in the bloodstream and can’t move across into the cell to give the body energy to work properly. This paper aims at developing an intervention plan to improve health outcomes of the elderly people aged 65 and over living with Type 2 diabetes in London, Borough of Lambeth. It will also evaluate the health inequalities and social determinates of health in relation to the type 2 diabetes, leading to interventional planning and conclusion. Additionally, seeking healthcare dissertation help can support a thorough analysis of these issues, ensuring that the intervention plan is both effective and evidence-based.
There are two type of diabetes, type 1 is where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells that produce insulin. The type 2 is where the body doesn’t produce enough insulin, or the body’s cell doesn’t react to insulin (HMSTC, 2021). The type 2 happens when pancreas isn’t making enough insulin in the body, and it tends to develop gradually as people get older, usually after the age of 40. But more people every year are being diagnosed at a much younger age (BHF, 2021). According to Diabetes UK (2016), the type 2 diabetes affect the body in the following ways, after each meal, the body begin to digest foods and break carbohydrates down into glucose. Individual who don’t have diabetes, insulin is released automatically by the pancreas after eating. It acts as a signal for the cells around the body to absorb the glucose and use it for energy. However, in type 2 diabetes, the body fails to make enough insulin or cannot use the insulin that it makes, and the cells don’t absorb enough glucose, which causes high levels of glucose in the blood stream. According to (diabetes UK 2014), high levels of glucose in the blood mainly damages the walls of the arteries, and more likely to develop fatty deposits (atheroma). If atheroma builds up in the coronary arteries, (the arteries that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart), it can cause heart disease and leads to heart attack. If the atheroma happens in the arteries that carry blood to the brain, it causes stroke (BHF, 2021). The signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes are as follows: often individual are very thirsty, particularly at night, passing urine more than usual , often very tired, losing weight , unexpectedly, having blurred vision, itching of genital or regular episodes of thrush , noticing that cuts and wound are healing very slowly. It is important to be aware of the symptoms, and contact the health general Practitioners, for arrangement of a blood test to check the blood glucose level and also test the urine.

The World health Organisation (WHO, 2020) stated that, diabetes can be treated and its consequences can also be avoided through effective diet, medication, physical activity, and regular screening and treatment for complications. Diabetes has a lot of impact on people, for example gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy women with gestational diabetes that are at an increased risk of complications during pregnancy and at delivery (WHO, 2020). These women and possible their children are also at high risk of type diabetes in the future, so it is important to create for the people in Lambeth borough to go through prenatal screening, and find a solution of care rather than reporting symptoms. This intervention will mainly focus on the London borough of Lambeth. According to (diabetes UK 2018-19), there are 3.9 million people suffering with diabetes , round 90% have type 2 diabetes and around 8% of the people have type 1. Between Lambeth and Southwark, 16,000 people are living the diseases (John, 2018). Both type of 1 and 2 is diabetes are very serious conditions leading to divesting complications such as stroke, amputation, kidney disease , blindness , and heart disease , it people done received the right, screening training and treatment (Diabetes UK, 2018). According to London Borough of Lambeth (2018), obesity has one of a leading causes of type 2 diabetes, and Lambeth has one of the highest childhood obesity rate in the country, approximately 70% of obese children will become obese adults , statically almost half of the all adult are official classed as obese. There is a growing concern of type 2 diabetes in our community, (Millet & Dodhia 2006) suggested that, there should more determinants of screening taking place and interventions to tackle the disease.
Nevertheless, the burden of complications in diabetes is high, including stroke , neuropathy, heart disease , nephropathy and retinopathy. Roberts et al (2017), suggested that, type 2 diabetes develops as a result of genetic, environmental and behavioural factors, including sedentary lifestyle and energy-rich, nutrient-poor diet, both of which predispose to obesity. Diabetes takes a significant toll on health budgets around the world. Very controversial that they concluded in their research that lifestyle programmes and metformin appears to be cost effective in preventing diabetes among the high-risk individuals. However, community diabetes in south London 2013 suggested that, providing diabetes education and knowledge has proved to be very effective.
For this intervention, the type 2 diabetes 65 + and over are the targeted group according to Winkley et al (2018), and also the other groups was benefiting on the education up take but the 65 years + and the over some of them are having difficulties in communication, and interaction of education management plans. There is poor attendance, including follow-up sessions and support for 65 years and over with pre-existing psychological issues and poor levels of health literacy and English is not their first langue (BJD, 2015). Lambeth only offers an education courses for the people with type 2 diabetes and their families in Portuguese.
Aim
The Aim of this intervention is to improve the Self-management of blood glucose diabetes among the people (65+) with type 2 diabetes
Method
Information and Advice through educational program and interventions planning
Identified need: Demographic and epidemiological data
The Joint Strategic Need Assessment was introduced by department of health in April 2008 with the purpose of strengthening joint working between the NHS (National Health Service) and the local authority. Under the health and social care Act 2012 (Lambeth Council, 2013) local authorities are responsible to improve the health of their populations. Lambeth set out key priorities which are child oral health, childhood obesity, long-team conditions, children in care and care leavers, safeguarding , sexual health and mental health , Alcohol misuse, Alcohol misuse is a common problem in England and Lambeth has high rates of alcohol misuse and abuse according to Lambeth council (2013). It is important to know that local health and CCGs have equal responsibilities to prepare JSNA through local authorities to improve the health wellbeing of their population (CCG. 2015).
Health Inequalities and social Determinants of health
Influencing social determinants are such as housing, income and employment, education that have been shown to have a wider impact on health (public health report Lambeth, 2018). The majority of the children in Lambeth have access to good quality education where the Lambeth’s school have made significant progress in performances, to guide the children (Lambeth council, 2018)., There is a strong evidence that, both deprivation a lack of money, resources and access to life opportunities is associated with poorer health increasing deprivation and inequality. According to JSNA Lambeth council (2018), large numbers of residents are affected by significant deprivation, nearly one third of the Borough’s population lives in areas which are among the most deprived fifth of areas in the country. Poverty and income insecurity as previously stated is worst determinant of health inequalities, because the individuals lack opportunities, which leads to stress and eventual contribute to unhealthy behaviours.
BAME residents are likely to have mental health issues, unemployed and low-paid work. They are also likely to be victims of crime and disproportionately represented in the criminal system. The health behaviours and lifestyles are the second most important driver of health, which includes alcohol consumption, smoking, diet and exercise. Lambeth also believe that, the health issue affecting the Borough have to be addressed, which also covered : multiple long-term health conditions like type 2 diabetes , childhood obesity, sexual health, mental health, and smoking. This inequalities are likely driven by inequalities social, economic, psychological, cultural, and physical environments of Lambeth residents, so Lambeth public health Team (2018) carried out extensive intervention programme of engagement in the communities by involving the adult, children , and other stakeholders working in healthy weight, wellbeing and food issues. Lambeth too wider approach to address childhood obesity, which includes a range of prevention and treatment interventions in the community and at Borough level implementing universal targeted approaches to deal with the existing problems. The Universal initiatives including supporting breastfeeding, through UNICEF BABY friending and National initiatives, for example Healthy Public Capital Funds, change 4 Life.
Espelt (2012) suggested that, presence of Socioeconomic inequalities in the incidence and prevalence (SEP)-related inequalities in type 2 are mediated by the unequal distribution of risk factors , the author indicated that obesity, physical inactivity, and unhealthy diet are most prevalence among those with the lowest SEP. NICE (2006) recommended that, started metformin treatment in a person who is overweight or obese . Metformin accounts for the great number of items prescribed for diabetes in England. The NICE guidance also underpinned that identification, assessment, management and prevention, of obesity in adults, in collectively recommendation on supporting the behavioural changes, for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through cultural appropriateness, effective weight-loss programmes and physical activity .
Lambeth has a large population of ethnically minority groups, 8 % are older adults, age 65 plus, 31 % of the population live in the areas of high deprivation and 44th most deprived local authority in England, the 9th most deprived local authority in London (Lambeth Demography 2017). Type 2 diabetes prevalence is strongly associated with ethnicity, and according to Health Survey for England (HSE, 2005), the data found that, all minority ethnic groups have higher risk of diabetes as compared to the general population. The factors that’s were observed are as follows, with the numerous evidence of type 2 diabetes that can be prevented or delayed by lifestyle interventions or by various classes of medication, screening, educational programmes .
The other factor that could influence the type 2 diabetes is Lambeth has the one of highest migration rates. According to ONS internal migration statistics 2012, Lambeth is the 5th highest local authority in the field of internal migration, and in the country Black and Asian and Minority ethnic (BAME) community accounts for around 43% of the total population (Public health Report for Lambeth ) statistical bulletin 2013-14 . 17.4% of the resident do not have English as the first language, specially the 65 years and over with type 2 diabetes are at risk of not adhering to the education, screening and attending programme due to language barriers . As a matter of fact, Lambeth ( DESMOND) continuing to provide range of initiatives to improve the lives of the people, including structuring diabetes education and virtual clinics. The team offers an education courses for people with type 2 diabetes and their families in Portuguese’s and also access the on-line “ Help” It has stated that the outcome of the this services has been successful because there been reduction in referrals to hospital diabetes clinics and reduction in local admissions due to diabetes (Lambeth Clinical Commissioning Group in Lambeth have sustained improvement in outcomes, the community diabetes in south London (2015) . This education intervention helps to reduce the health inequalities, making it more easier every on in the Borough specially the elderly 65+ to be treated equally, regardless of the social determinants of health and existing health inequalities already known.
Evidence based local policies and services provisions
Health care public health advice group’s services to clinical commissioning groups (CCGs, 2012) stated that, good population outcomes including reducing health inequalities, health protection and health improvement. The shift of local leadership on the Local authorities ensure that CCGS benefit from public health advices and also make maximum impart population health (CCGs, 2016). So, Lambeth makes an improvement with the regarding 65 years and over suffering with type 2 diabetes , in Lambeth joint health and well-being Strategy (JHWS, 2013-14) developed “transitional strategy on behave of Lambeth people it has been recognised that there is room to improve the health of 65 years + living with type 2 diabetes. The JHWS (2020) rolled out programme of support for self-management for the people, suffering with diabetes.
There are also polices and services provision like programme that are in place to promote the health of the community, by tackling the childhood obesity , because Lambeth beliefs that obesity, can develop due to fast food which is tend to be high in fat and salt which are one of risk factors for obesity, cardiovascular and others. Lambeth Public Heath team ( Oki et al., 2013), due to obesity associated to diabetes, the Borough develops their service provision more, such as the national obesity observatory in the borough to monitor the community health wellbeing, especially for the venerable people and the programme has strong focus management and prevent of disease. According to NHS diabetes prevention programme (2016-21), in their findings regarding diabetes programmes, the evidence reviewed that there are averages weight loss during the uptake of the programme such as physical activities, healthy eating, blood glucose monitoring and others.
The challenges for 2015 up programme suggested that, it is important to prevent type 2 diabetes by reducing avoidable complications, improving the diabetes care, and their conduction for supporting the people with diabetes to manage their health condition effectively. The programmed targeted type 2 diabetes suffering, because type can be prevented or it onset can be delayed; they why the programme belief that it can be identified those high risk, and implement effective risk reduction intervention. The strategies in all this programme like (NHS Health Check, 2013) is to encourage care professionals , local authorities, the CCGS, media and others to raise awareness of this dangerous and chronic illness. It is also one of the General practitioner (GP) obligation to identify those elderly people 65 years and over suffering from type 2 diabetes at are high risk, by regularly searching their databases and offering services and following update of the their health ( Public health England, 2013).
There are various interventions in place to promote type 2 diabetes for elderly people 65 and over , the members of the diabetes prevention programme group are listed (Knowler et al., 2002) the elderly needs education and support helping with telephone reminders, posting leaflets, to explain the important of checking their glucose level, diet and involving in the programme. There also educational video designed by NHS to increase awareness of typed 2 diabetes videos (southern health NHS foundation trust diabetes 2016) individual can access YouTube video subtitles in English, polish, Arabic and others. All this intervention, health check are designed to increase awareness of the type 2 uptake , management and prevention, individual need to book appointment measurement of height and weight will be taken by including blood pressures and blood test. The intervention has improve evidence of efficacy because many people suffering from type 2 have benefited from the NH’s health check and diabetes programme which include physical activity , According to Diabetes UK (2016), it estimated that, 4,000 people in a year was prevented from diabetes and is an essential part of type 2 diabetes prevention.
Effective intervention
Interventions to increase the uptake of type 2 diabetes for 65 years plus can be further emphasised as public health problem (Sazlina et al., 2013) stated that older people with T2DM will benefit from physical activity for the better disease control and delaying complication. The authors suggested that, in their randomised controlled trials, the quasi-experimental designs comparing that the strategies to increase physical activity level in person aged 65 years plus with Type 2 DM was included . The researcher’s pointed out that personalising coaching, good setting peer groups support programme and use of technology, follow-up support were successful strategies. In addition, the exercise interventions promote the well-being of 65+ living with the disease.
The other effective intervention include community health care workers, homes visiting and monitoring the glucose level of the target group, For working in partnership to develop physical activity, cost -effective practice, dietary and weight management intervention, the professionals should take into account the religious beliefs, cultural practices , age and gender, language and literacy of black , minority ethnic and lower socio-economic groups. Use of websites like Health Matters (2018) and others is another recommended intervention to increase individual knowledge and understanding of the diseases. Harvery (2015) suggested that, electronic addressing for example advertising campaigning using a well-known celebrity, increases awareness . Above all the health professionals, family, friend and individual can be advocate for 65 years living with diabetics. American diabetes Association (ADA, 2012) said, that if you have diabetes or know someone with diabetes , you are already an advocate.
Intervention planning to support the diabetic patients
The objective of this intervention is to increase awareness of the self –management practice of blood glucose by using the information and advice methods. Type 2 diabetes refers to a lifelong metabolic disease, characterised by hyperglycaemia that gradually leads to the development and progression of the vascular complications.(Blaslov et al., 2018). The self -management of this disease continues to be a major problem globally , the best present strategy that could contribute the most to the reduction of morbidity and mortality should be focused on primary prevention. IT is important to keep good record of blood glucose monitoring at all time , which will enable the individual to understand the level of hyperglycaemia and hypoglycaemia. According to WHO (2016), there are multiple changes in the care of people with type 2 diabetes over the recent years, to prevent, reverse or treat the diabetes thus avoiding its major complications. It is important to educate and train the people on how to manage their diseases. This emphasises the importance of this intervention which targets elderly people age (65 years plus living with type 2 diabetes) in Lambeth Borough.
Information and advice methods of health promotion were chosen as it is best method to increase the-self management of blood glucose. There is no cure for type 2 diabetes , but some people are able to put their diabetes into remission. This means that the blood sugar levels are healthy and individual don’t need to take diabetes medication any more. According to (diabetes UK, 2018), remission can be life changing, but it is not possible for every specially the elderly. Elderly people with type 2 DM, should be supported in the management of their condition, due to high sugar levels in the body blood that can seriously damage the parts of the body including heart, eyes, and feet.
The information will be provided in a form of a leaflet, through telephone, leaflets and letters. The leaflets will be handed out by the diabetes Advisory Team in the community and will consist the general management of diabetic. Education of the 65 years and over with diabetes should include the following content based on their assessed needs for example treatment, disease process, knowledge of acute and chronic complications, psychosocial issues, individual strategies to promote their health and knowledge of diabetes medicines prescribed blood glucose monitoring ( Ebenezer et al., 2011). It is important to equipped the 65 + with accurate and evidence-based data to aid them through the ethical decision-making process. Sometimes one to one visit is also offer
to address the concerns more visual. According to Asif (2014 ) stated that, IT is important to acknowledge the existing limitations of every intervention, although this intervention focuses on improving the self-care management among the people (65+) with type 2 DM by changing their behaviour , there will be some 65 + whose attitudes will remain the same even after reading the evidence based information. According to Asif (2014), education and support for the self-management are fundamental for caring the people with a chronic diseases like diabetes. Ekaterini et al. (2019) concluded that, the health professional should provide their patient self-care support based on the degree of personal responsibility where the patient would be willing to assume the diabetes self -care management.
The target population for the intervention will be defined by geography as they live in London borough of Lambeth, According the development of innovation, the diabetes care management is very important in order to improve healthy lifestyle, provide continuity of care, and reduce the patient risk factors and comorbidities. In addition to these effects , tele-monitoring offers continuous care at a distance and improve care, including the smartphone technological solution for telemedicine, exercises and social interaction. An important sense of support is hereby necessary, coming from connection or even technical support and sharing experience. Vaala et al (2015), stated that, social media can also use for self-management in chronic conditions including diabetes.
The information will be in a form of a leaflet which will includes Self-management education, self-care includes adherence behaviours like exercise, dietary change, self-monitoring of blood glucose, regular self-mention (Harvey, Reissland and Mason 2015). The information will be in a form of a leaflet because the provision of written information in conjunction with verbal communication increases acceptance , written information is viewed as more trust worthy by the elderly people. Although the aim of the intervention is to improve the self-management practice among the people (65+ ) with type 2 diabetes and it is important to respect the rights of the people to decide whether to make changes in their self-management. This intervention will adopt a behavioural change approach to increase awareness, which will improve the self-management in people (65+) to change the attitudes and behaviour so that they will adopt a healthy thinking. This intervention will be based on Transtheoretical models/stages of change. It is one of the behavioural change models which state that changing a behaviour is not a coincidence but instead is a process and different people are in different stages of change and readiness (Hashemzadeh, 2019). The authors stated that, Transtheoretical Model includes the process of change, decisional balance and self-effective nature and it has used in prevention interventions for chronic condition such as diabetes and various forms of cancers. Information and advices and education will be used to communicate with the target group. Transtheoretical models addressing individual, that is 65+ with type 2 DM on the important of self-management for example taking the advice from diabetes advisory team on testing for (HBac) very six month or yearly, the test is beneficial because it monitor the disease progress and treatment follow-up., monitoring their daily glucose level , and education on healthy eating and exercises. Change in attitude may facilitate behavioural change, which is the major objective of this intervention (Harvey, Reissland and Mason, 2015).
There are Five settings for health promotion, according to Whitelaw, Baxendale and Bryce (2001), the setting for this intervention is active since it lies with the behavioural change of the individuals and the intervention is going to use some resources of the setting. The intervention will be cost -effective in terms of utilising the resources ready provided by diabetes advisory team, in the GP surgery or clinics (diabetes specialist nurse and venue). The setting was also selected to enable flexibility, and it is convenient for elderly people with 65 years and over because is within the community and they are familiarise with the environment.
The participants will be recruited from the diabetes advisory clinics in Lambeth to identify the population size that they cover, where they are located to get better understanding of which centre are located in the most deprived areas and the least deprived. The information is hereby crucial to make sure the intervention covers elderly people from diverse background and ethnicity. 6 clinics will be chosen from those that responded to the invitation ensuring that. the chosen clinics are from different parts of the Borough. This process should take around five weeks (12/2/21- 19/3/21), where some of the clinics might not responds in time. It is vital to send the invitations again to the participates , follow it by phone calls or email. The design of the questionnaire for the data collection and the leaflet will use this time to be design while waiting for the responds of the people involve. The diabetes advisory clinic is part of the GP surgeries , where the intervention is taking place , it is important to invite the GP surgeries to participate, those they are part of the clinics. The data time frame for this is still same (12/2/21- 19/3/21. Data will be gatherd before the intervention commence, and there will be a baseline recording to measure the level of improvement after the intervention planning. If this intervention is successful, that means 65 years + has improved in self -management of their condition with an increase in numbers. This will provide quantitative data, but qualitative data is also required to understand better the reasons behind the numbers. Hammersley (2018) stated that, qualitative research is an effective tool to improve the research designs that a qualitative dimension is presented in quantitative work as well.
Prior to the intervention commencement a questionnaire will be designed to gather information on whether the 65 years and over want to make change how to manage their type 2 diabetes or not . What information, advice and education that they require for decision making and how much access they have in reliable and evidence based practice. For example regularly checking of blood glucose level, healthy eating, and exercises will help in self -management of type the disease. The questionnaire will also be useful as it will assure primary stakeholders engagement for gathering valid information that is important to implement intervention and design of the leaflet. Once the clinics and GPs accept the invite, the data collection will be the first task to complete; and in this context, five weeks will also be allocated to data collection and analysis (30/03/21- 19/04/21).
3 weeks (20/04/21 - 26/4/21) will be allocated to develop the leaflet by using the data collected. In this context, short training will also be provided to all the diabetes advisory team explaining the vision of the intervention, how the intervention is going to run, as well as what is expected from them and also the guidance on where to find further information about type 2 diabetes to get ready beforehand. The intervention will commence on 30/4/21 on the 6 clinics that have been chosen and it will run for five weeks. Close contact will be maintained with the diabetes clinic in order to ensure that, there is always enough supply of the leaflets for rising awareness. The questionnaire will be distributed again and data will be collected from the GP’s database for the second data collection, four weeks from 11/05/21 –24/ 21) that will be allocated to the second data collection and analysis. This intervention will be evaluated by using this gathered data to determine the usefulness of the intervention and it’s worthy to be continue and applied nationwide.
Ethical practice:
Throughout the intervention planning and implementation, however, it is possible to achieve the aim in a systematic process by maintaining the ethical practice. So, ethical consideration is line with the Nuffield Council on Bioethics (2007) will be applied throughout this intervention. Factors will include translating those leaflets in many different languages to enable other non- English speaking 65 years from different ethnicity to read before making decision to how to manage their diabetes. Department of health (2005) also suggested that, it is a ideals too. This is important that, the design and delivery of this intervention are completed and cultural sensitivity is considered and acceptable in different communities. Lambeth Council acknowledges that it should be taken into consideration for health promotion and service planning in designing awareness programmes to help the individuals to beat type 2 diabetes in Lambeth (2016). To accommodate this need, a translator will be need to offer one to section to those elderly people who needs it. Advising someday to make changes is sensitive issue and need to be dealt very carefully in order to respect individual autonomy. Considering the different public health approaches, this intervention will be taking the nudge theory into consideration , nudge theory stated that , nudge is about improving decisions about health, wealth and happiness , which Thaler and Sunstein (2008) the authors contend that, there exists a “choice architecture” because it preserves freedom of choice but gives authorisation to steer people to the directions that promote health. How much can the heath professional intervene with individual behaviour while still respecting choice and autonomy. This interventions level of intrusiveness is low, and the objective is to change the individual behaviour towards the self-management of the disease through providing adequate information (Local Government association, 2013).

Designing health promotion interventions, it is vital that acknowledges the importance of working with different stakeholders, who have different roles, power, knowledge and alliances to carry out effective implementation of the intervention, I will use the following table that has been adapted from the WHO Stake holder Analysis Guidelines’, which will show the information on the stakeholder involvement in the intervention.

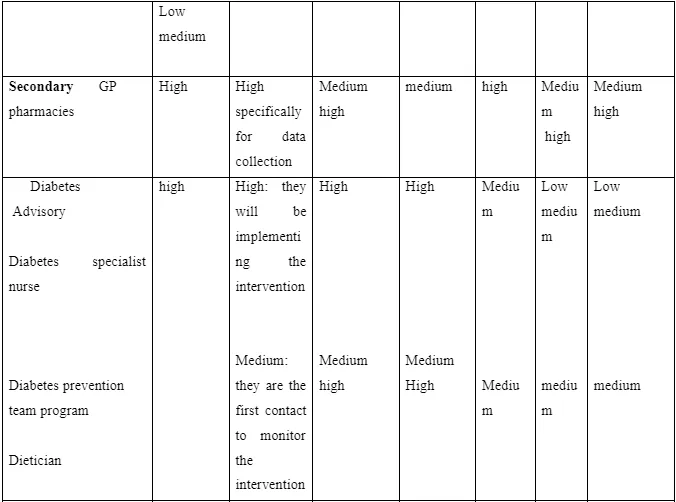
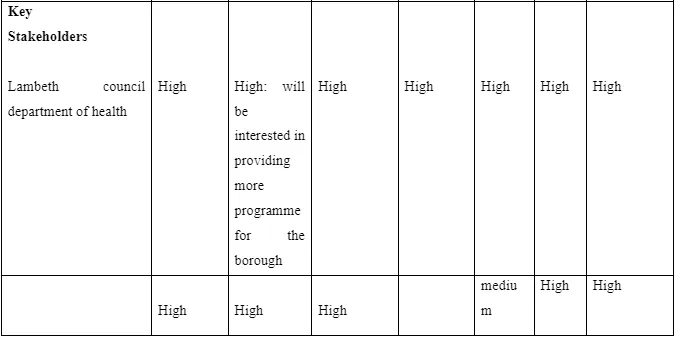
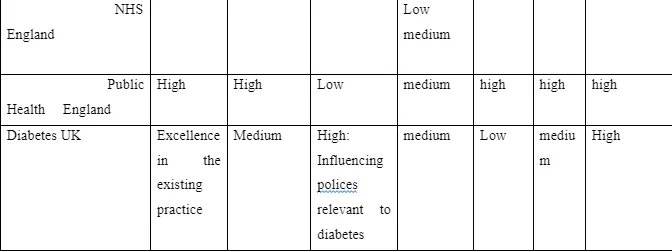
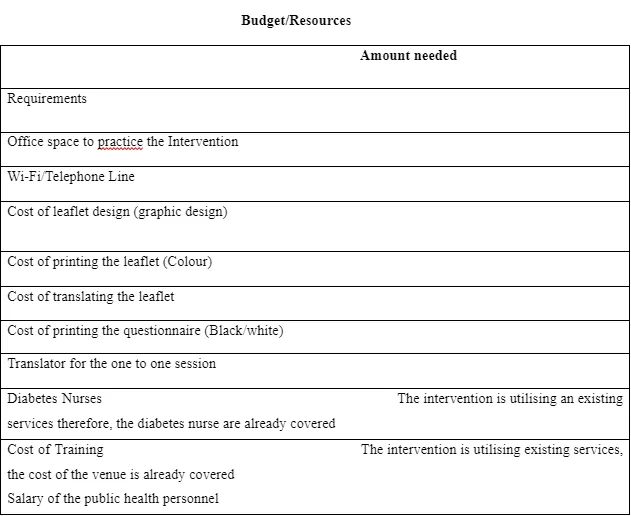
Conclusion
Lambeth has adverse population and health varied ways as compared to the England average, the social determinates include deprivation, inequality, poverty , crime , education ethnic minorities and migration. There are diabetes programme for further enforcement of the plans in every local authority. The expected outcome, empowerment, education, nutritional counselling, the progress and improvement on how 65 + has improved on their self-management of their type 2 DM disease. This is to ensure that, they have access to information on safety monitor and control of blood glucose. Advised on yearly GP review, HbA1c to be checked every 6 months to yearly, advised on hyperglycaemic symptoms polydipsia fatigue, advised to speck to GP if unplanned weight loss noticed changes to vision or tingling/numbness/changes in colour /circulation to feet. Throughout the planning and implementation of the intervention, ethical consideration including choice and individual autonomy respected confidentiality, and valued are followed efficiently.
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Health Interventions.
References
Nyenwe, A. E., Terri W Jerkins, T. W., & Kitabchi, A. E. (2011).Management of type 2 diabetes: Evolving strategies for the treatment of patients.
https://www.ncbi nlm. Nih. gov>pmc
Hashemzadeh (2019). Transtheoretical model of Health behaviour change: A systematic review. Retrieved from:
https://www.ncbi nlm. Nih.gov >.pmc
Diabetes Atlas (2017). International Diabetes federation: Diabetes atlas. Retrieved from: https://www. diabetesatlas.org
NHS Lambeth clinical commissioning group, Lambeth (2017). What we do. Retrieved from: https://www.lambeth.nhs.uk.
https://www.hertsmstherapy.org.uk/conditions/diabetes/?gehd=ealalqobchimhszw.diabetes
https://www.bht.org.uk/information support/conditions/stroke
Diabetes UK, UK diabetes (2004). diabetesonthenet.com
NHS Diabetes prevention Programme E.barron, R Clark, R Hewings, J.smith (Diabetic 2008)
C.Thomas. S. Sadler, P. Breeze, H. squires, M gillet,(bmj open 2017)
NHS diabetes prevention programmes an observational study of services delivery and paient experience re:Hawkes, E Cameron, BMC health 2020
NHS Diabetes Prevention programmes intervention delivered as planned? An observational study of Fidelity of Intervention delivery
Pp French, RE haukes, P, Bower, Annals of behavioural 2021 (ds pace. Stir.ac.uk)
The Healthier you NHS diabetes prevention programe, digital model B. mc Ooush, E murray, L Brownlee, E barron Diabetic zoiq ncb,nlm. Nln.gov
A.J. Sinclair, A.H Abdelhafiz A. forbes, M. munshi. Evidenece- based diabetes care for older people with type 2 diabetes.
https://doi org/10.1111/dme.13859/08 November 2018
Southeast London prescribing commiitte: A partnership between NHS organizations in south East London: Bexly/Bronley/Greenwich/Lambeth/Lewisham & southwark clinical commission groups(CGS)GST FFT/KCH/SLAM/Oxleans and NHS foundation Trust and Lewish & Greenwich NHS Trust
LAM CCG. Medicine optimization @nhs.net
World Health Organization Diabetes 2020. https://www.who.net/newsroom/fact-sheet/detail/diabetes.
John Kethryn(2018) dose adjustment for normal eating (DNFNE)
Annual Public Health Report Lambeth 2018, People, Place and opportunities, reducing Health Inequalities in Lambeth
Diabetes retinopathy screening audit of equity in participation and selectal outcome in south east London, C.millet, H. Dodhia, 2006. Journal of medical screening, 2006. Journals. Sagepub.com
Preventing type 2 diabetes: systematic review of studies of cost- effectiveness of lifestyle programmes & metformin with and without screening for prediabetes
Samatha Robertis Eleanor barry down criag, mara airold, Gwyn Bevan, Trisha Greenhalgh 2017
British Journal of Diabetes BR J. Diabetes Vasc dis 2015; 15: 78-81
https://dx.dol.org/10.15277/bjdvd.2015.013.
Public Health England (2015a) Lambeth Health Profile: Available from……… (assessed 30/03/201)
National Life table-life expectancy in the UK office for national statistics http;//www,ons,go.uk(2020)
Lambeth council 2016/17 annual report of the direction of public Health JSNA Children and young people 2016/17
Population pyramid, Lambeth vs London and England
ONS mid-2017 Population estimates (MYE)
Espelt (2012) socioeconomic inequalities in the incidence & Prevalence of type 2 Diabetes
National Institute for Health and care excellence(2014) nice obesity pathway. https://pathways.nice.org.uk/pathways/obesity. Reproduced with permission
Healthcare of public health advice service to clinical community groups Guidance to support the provision of health care public health advice to (CCG’s) (2012)
Improving services for people with long term conditions(2020) www.selondonccg.nhs.hel scu.information.governance @nhs.net
Lambeth public Health team NHS lambeth Bimpe Oki, Vida Cunningham public health specialist
Elizabethwatch.diabetes.org.uk (2012-2013) www.diabeteswatch.diabetes.org.uk
National Diabetes adit 2012-13 Report calculated using the figures on page 29 for people with Abbi of 25 and over
Public Health England, UK screening portal (2013-14) quarter 3 KPI screening data reports
Knowler WC, Barrett- connor E, fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, walker EA,
Lifestyle Intervention or metformin (2002)
Sharih-Ghazali sazlina, Colettle Browniy Shajahan yasin (2013).
Interventions to promote physical activity in older people with type of diabetes mellitus
Type 2 diabetes prevention population and community-level interventions public health guideline (ph 35) 2011
Health matters: Preventing type 2 diabetes public health matters(2018)
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



