Innovation for Managing the Increase in Cases of Obesity and Diabetes in the Hospital
Introduction
The innovation will aim to improve obesity management. Obesity has over the years been termed as a risk factor of diabetes. According to the National Health Service (NHS), obesity accounts for an approximation of 80-85% of the risk of developing diabetes (Walshe, 2010). Relative to the general population, individuals rare 80 times more at risk of developing diabetes as they have a higher BMI compared to the general population with a BMI of less than 22 (Dobbs & Manyika, 2015). In Europe, the UK has been ranked as the country with the highest levels of obesity as the have a statistical data of 28.1% adults that are obese while 63.4 % of the adults are overweight (Dietz et al., 2015). Following the risk of developing diabetes as a result of obesity and the complications that are caused by the same, the issue is an area of great concern that needs to be addressed (Flint & Lavallee., 2016). Consequently, this paper aims to explore the increase in obesity and diabetes that has seen a dramatic upsurge not only in the UK hospitals but also the world as a whole (Dobbs & Manyika, 2015). The gap that exists and needs to be filled is the lack of innovations to be used in the management of obesity and diabetes that has increased in hospitals. As a result, this paper discusses the innovation that involves the incorporation of exercise classes. Besides, the paper discusses the proposed evaluation strategy for the success of the implementation innovation. In the context of healthcare dissertation help, addressing these gaps with innovative solutions is crucial for advancing effective management strategies.
Context and Background

The National Health Service is currently faced by various healthcare challenges such obesity and diabetes that have seen the great deterioration in patient outcomes. The report by Francis (2003), notes that many patients in the UK suffer due to the failure of the Trust Board to listen sufficiently to the patients and staff in ensuring the correction of various deficiencies within the healthcare settings. Besides, Francis report goes on to state that the Trust Board failed to tackle an insidious negative culture involving a tolerance of poor standards in leadership responsibilities with in the settings (2013). The report boldly points out the areas of failure by the NHS as well as the UK government regarding the health sector. The report was critically to the drivers for change thus the formulation of this innovation for change. The concerns of patients besides their families should be adequately addressed in the quest of ensuring patient safety (Francis, 2013). According to Dietz et al (2015), government policies such as initiation of exercise activities have been suggested that would ensure curbing of obesity challenge in the UK. Reports such as the Francis report have noted that the NHS through the government has pledged to reduce the child obesity rates in the UK by half besides putting down policies and measures to reduce the gap in obesity. The report by Berwick (2020), notes that the NHS has the need to continually and reduces patient harm through a wholehearted embracement of ethical learning across the nation. Besides, the reports goes on to mention that all the leaders that are concerned with healthcare need to prioritize patient safety through management of the health challenges that face the UK (Erickson et al., 2003). The Keogh report notes that the NHS of the UK is the only healthcare system in the world with a definition of quality enshrined in legislation (2013). The UK thus has the ability to effectively prevent and manage diabetes so as to improve the safety of patients.
Studies such as Smith (2020) and Jones (2021) have noted that the cost to the National Health Service in the UK of obesity and other health related complication such as diabetes has drained the resources of the NHS. Treating the conditions is very expensive as the same has derailed the finances in the UK (Flint & Lavallee, 2016). Despite the various measures that the UK government has put in place to manage the conditions, there still exists a gap in nursing that sees the increase in diabetes and obesity. Possibly, healthcare providers have failed to effectively address the condition despite its significance to the patient safety and outcomes. The paper thus aims to introduce an innovation that would involve exercise within the community that would engage both male and female adults that are either diabetic or at risks of developing diabetes.
Discussion
Obesity as a common disorder has complex causes. Obese individuals have an excess body fat with BMI that is greater than 30. The chronic medical condition leads to diabetes amongst other chronic illnesses (Dobbs & Manyika, 2015). A modest weight loss of approximately five to ten percent contributes to significant health benefits such as lowering the risks of diabetes. Nutritional approaches have proven fruitful in the treatment of obesity. Dieting helps in stopping weight gain besides establishing realistic weight loss goals for the obese or diabetic individuals (Dobbs & Manyika, 2015). Eating fewer calories is an effective way of losing weight that has been proven fruitful by researchers. Introducing a dietary intake that creates an energy deficit is essential. Thus, the innovation would consider the same as nurses and other practitioners would need to consider a targeted risk factor modification manipulation of the nutrient profile of the weight reducing diet that would be adopted. The strategy would provide a significant weight loss and improvements in Cardiometabolic risk factors (Bray et al., 2016). The efforts to reduce fat content in the body contribute significantly to the management of obesity and other related conditions such as diabetes. A fat-reduced diet reduces most of if not all of the risk factors for diabetes (Bray et al., 2016). More effectively, if a reduction of dietary fat and energy is combined with other strategies that burn calories from the body, has been proven to reduce the incidences of diabetes by approximately 58% (Bray et al., 2016). Reducing dietary fat and increasing fiber intake instead contributes to weight loss and consequently offers diabetic-protective effects. Research has shown that a low glycemic index as well as high protein diet provides significant benefits to weight control (Bray et al., 2016). Also, low carbohydrate intake can also be an option in the efforts to induce weight control for diabetic or obese individuals.
Continue your exploration of Diabetes is Considered as an Autoimmune Health Condition with our related content.
Obesity management is crucial not only to the management but also the prevention of diabetic cases in hospitals. In fact, it has been noted that obesity management delays the progression of prediabetes and other related conditions. First, the innovation aims to adopt a modest weight loss program to improve the glycemic control in efforts to reduce the need for glucose lowering medications (Dobbs & Manyika, 2015). The weight loss programs to curb the cases of obesity will include diet classes and diet change. The interventions will be of significance and focused on diet to achieve approximately kcal/day energy deficit of 500-750 which is ideal for a healthy individual (Bray et al., 2016).
The Innovation: Diet
The innovation will target male and female adults that are either diabetic, obese or at the risk of developing either of the conditions. Concerning the dietary strategy, meals that have a similar caloric restriction will be considered as effective though they may differ in carbohydrate, protein, and fats contents. Long term comprehensive weight maintenance programs will be prescribed for patients who achieve the short term weight loss goals (Petridou et al., 2019). The programs will offer at least a monthly contact besides encouraging a continuous monitoring of body weight of the patients. This will either be on a weekly basis or even on a more frequent basis.
The innovation will ensure a safe and effective long-term weight reduction as well as maintenance diet to contain not only a balanced but also nutritious foods but avoiding vitamin deficiencies and other diseases of malnutrition. Also, the participants will be required to eat more nutritious foods that have low energy density with relatively few calories per unit weight of the meals (Dobbs & Manyika, 2015). This will be monitored closely by the practitioners that will be taking part in the implementation of the innovation. Examples of these foods will be inclusive of vegetables, fruits, lean meat as well as grains and other cereals such as beans (Scarborough et al., 2011). Besides, the participants will be required to eat less of energy dense foods that are high in fats and simple sugars. Such foods that would be avoided will include red meat, red yolks, fried foods, sweets, pastries, butter, and high fat salads. The participants will be required to eat more complex carbohydrates such as whole-grain breads, fruits, vegetables and brown rice (Hall & Kahan, 2018).
The proposed innovation for the management of the conditions will require a limited calorie diet (Scarborough et al., 2011). Trained nurses will prescribe very low calorie diets besides total meal replacements for the chosen patients from the community and the hospitals (Hall & Kahan, 2018). The program will incorporate a long-term and comprehensive weight maintenance counselling in the quest to maintain weight loss for the obese or diabetic patients. The program will also consider diet changes for overweight or obese patients with diabetes and with less glycemic, blood and lipid control besides other medical conditions that are related to obesity (Dobbs & Manyika, 2015). The diet changes are believed to will result not only in modest but also sustained weight loss that will further lead to clinically meaningful reductions on the levels
The innovation aims to incorporate observation of diets of the obese or overweight patients as well as the other community members that may be at the risk of potentially developing the conditions. These diets will to some extent be different in the aspects of the types of foods that will be restricted to the patients that may include foods that are high in fat or those that are high in carbohydrates (Hall & Kahan, 2018). However, the restricted foods will be of utmost significant as they will ensure achievement of the need energy deficits for weight loss. The diet choice for the patients will be based on their individual and particular statuses of health as well as their personal preferences. The innovation that is designed for the program will be offered by trained nurses in their care delivery times for six months as studies have found out that nurses spend most of the time with patients (Petridou et al., 2019). After the six months of 20 or more sessions, patients that will have lost weight will be enrolled in long term comprehensive weight loss, maintenance programs that will offer a monthly contact trained nurse and will put emphasis on the continuous monitoring of body weight as regular as a weekly basis (Morgan et al., 2014). During this period, the trained contact nurses will ensure a continued intake of reduced calorie diet (Hilton et al., 2017). Through the designed short term and long term programs offered by trained practitioners such as nurses who offer close monitoring and high intensity diet interventions with low calorie diets and total meal replacement is believed that will attain great weight loss for the obese or overweight patients at the risk of developing diabetes (Scarborough et al., 2011).
Research has documented that variety of macronutrient and food based dietary patterns effectively contribute to weight loss. The basis of this particular intervention is the reduction of energy density for the body (Dyson et al., 2011). Besides, it has been proven that the reduction of energy density has been effective for weight loss as well as weight loss maintenance (Baboota et al., 2013). Basically, dietary interventions during the proposed innovation will call for reduction of energy density, provision of portion control, and improvement of diet quality.
Macronutrient Patterns in the Innovation
The nurses will need to alter the proportion of the macronutrients that the participants will be consuming as this will be the foundation for weight loss by the patients. The nurses will need to highlight fats, carbohydrates, and proteins at different times of the programs as an essential step for curbing obesity among the patients (Bray et al., 2016). During the six months of short term intervention, reduction of energy density and increase in fiber intake by the patient will be greatly focused on as the key predictors of weight loss (Dyson et al., 2011). Consequently, various strategies to lower the energy density will be put in place. These will include increasing the vegetable and fruits consumption by the patients besides reducing the consumption of high calorie foods.
Food based Patterns in the Innovation
Whole diets and patterns of consumption instead of reductionist approach will also be considered in different sectors of implementation of the improvement innovation. These will focus on single foods or nutrients. The patients will have to adopt a healthy eating pattern as advised by the Dietary Advisory Committee. For the innovation, the Diet, and the Health Mediterranean style Eating Pattern (DASH), will be adopted. According to this eating pattern, intake of less health fats will be reduced. Besides, fat intake will be reduced to an approximation of 25% or less of the total energy of the diet (Baboota et al., 2013). DASH will ensure an increase in the intake of low energy dense foods such as the vegetables and fruits alongside other low-fat dietary products. (Arathuzik & Goebel, 2011). Following the DASH diet, a lower-energy dense pattern of eating will be adopted by the patients and enforced by the nurses to ensure that the patients consume less energy without typically lowering the weight of food that they take. The DASH pattern will also ensure an intake of low energy dense fruits, vegetables, legumes, seafood, besides dairy foods. The pattern will however recommend high levels of fat from olive oil as this is considered as healthy fat for the body (Dyson et al., 2011).
Proteins and Fiber in the Innovation
When the two are taken, they will provide satiety, that is, the feelings of fullness by the patients. Higher protein intakes will manage hunger effectively while increasing satiety. (Arathuzik & Goebel, 2011). As the most satiating macronutrient, its incorporation would possible decrease daily energy intake by the patients at greater levels. The patients will thus be encouraged to incorporate various sources of proteins such as legumes and low fat dairy products that will create low energy but dense meals (Baboota et al., 2013). On dietary fibers, research has noted that they promote the feelings of fullness via the upsurge in mastication times which promotes stomach expansion and reduce the efficiency of absorption. Consequently, the innovation will involve increasing fibers in the meals of the patients to decrease the energy intake by increasing the ratings of fullness. (Arathuzik & Goebel, 2011). The fibers will be found in foods of low energy such as the vegetables, the fruits, and particular dairy products.
Information Leaflet
Information leaflets will be used to inform the people about obesity and diabetes. The information leaflet will be presented in a way that it will effectively educate the patients on the various ways of managing obesity and diabetes as well as the clinical complications that the two conditions cause. The leaflet will contain brand color for diabetes which is a blue circle as well as the logo. Besides, it will be made different and unique to meet the preset objective pf education and creating awareness among the patients in various hospitals in the UK. Also, enough details will be included in the leaflet to ensure the patients are exhaustively informed on obesity and diabetes.
Evaluating Success of the Innovation
Information on the progress of the proposed innovation is crucial to the evaluation of the success of the innovation. A framework for evaluation of the improvement innovation will be adopted. First, the inputs, that is, the resources and activities will be discovered and described before being quantified through the assessment phase of the evaluation innovation. Thereafter, the need of the stakeholders who will work at various levels for the success of the innovation such as nurses amongst other healthcare practioners will be considered to determine what to measure and use the information from the evaluation. The objectives of the study will thus be assessed whether they had been met. For instance, it will be assessed whether the patients will have changed their diets and lost weight as that will be the main objective of the improvement innovation besides ensuring a reduction in the increase in obesity and diabetes cases in hospitals.

Conclusion
Diabetes and obesity are significant health concerns in a global context. These paper has effectively appraised the current healthcare challenges that are faced not only in England, but the UK as a whole. Besides, the paper clarified a gap in service in the field of nursing that needed address. In identifying the gap, this essay noted that the management of obesity as a risk factor for diabetes has greatly failed in most healthcare settings across the UK. Consequently, the paper was thus based on deriving the possible improvement innovations to fill the gap in service. In doing so, the essay has discussed the NHS besides other external reports regarding the same. The paper has discussed the noted proposed improvement in service by the reports before critically discussing an improvement innovation that would help manage obesity and reduce the risk of obesity thus improving patient safety. The paper has demonstrated a critical awareness of the current issues in healthcare practice and leadership and evaluated the role of nurses in leading and managing and changing practice through innovation to improve patient outcomes. Undoubtedly, this paper is significant to the improvement of patient outcomes. However, more research needs to be conducted on the management and prevention of obesity as a risk factor of diabetes to ensure the problem is a thing of the past.
Take a deeper dive into Innovation to improve and maintain with our additional resources.
References
Abdali, D., Samson, S. E., & Grover, A. K. (2015). How effective are antioxidant supplements in obesity and diabetes?. Medical Principles and Practice, 24(3), 201-215.
Abuyassin, .,B & Laher, I. (2015). Obesity-linked diabetes in the Arab world: a review. East Mediterr Health J, 21(6), 420-39.
Acosta, A., Dayyeh, B. K. A., Port, J. D., & Camilleri, M. (2014). Recent advances in clinical practice challenges and opportunities in the management of obesity. Gut, 63(4), 687-695.
Arathuzik, G. G., & Goebel-Fabbri, A. E. (2011). Nutrition therapy and the management of obesity and diabetes: an update. Current Diabetes Reports, 11(2), 106-110
Baboota, R. K., Bishnoi, M., Ambalam, P., Kondepudi, K. K., Sarma, S. M., Boparai, R. K., & Podili, K. (2013). Functional food ingredients for the management of obesity and associated co-morbidities–A review. Journal of Functional Foods, 5(3), 997-1012.
Bray, G. A., Frühbeck, G., Ryan, D. H., & Wilding, J. P. (2016). Management of obesity. The Lancet, 387(10031), 1947-1956.
Craig, S. L., Gault, V. A., & Irwin, N. (2018). Emerging therapeutic potential for xenin and related peptides in obesity and diabetes. Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews, 34(6), e3006.
Dameri, R. P. (2017). Smart city definition, goals and performance. In Smart City Implementation (pp. 1-22). Springer, Cham.
Dietz, W. H., Baur, L. A., Hall, K., Puhl, R. M., Taveras, E. M., Uauy, R., & Kopelman, P. (2015). Management of obesity: improvement of health-care training and systems for prevention and care. The Lancet, 385(9986), 2521-2533.
Dobbs, R., & Manyika, J. (2015). The obesity crisis. The Cairo Review of Global Affairs, 5.
Dyson, P. A., Kelly, T., Deakin, T., Duncan, A., Frost, G., Harrison, Z., ... & Diabetes UK Nutrition Working Group. (2011). Diabetes UK evidence‐based nutrition guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes. Diabetic Medicine, 28(11), 1282-1288.
Erickson, S. M., Wolcott, J., Corrigan, J. M., & Aspden, P. (Eds.). (2003). Patient safety: achieving a new standard for care. National Academies Press.
Flint, S. W., Hudson, J., & Lavallee, D. (2016). The portrayal of obesity in UK national newspapers. Stigma and Health, 1(1), 16.
Flynn, M., & Citarella, V. (2013). Winterbourne View Hospital: a glimpse of the legacy. The Journal of Adult Protection, 15(4), 173.
Fock, K. M., & Khoo, J. (2013). Diet and exercise in management of obesity and overweight. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology, 28, 59-63.
Francis, R. (2013). Report of the Mid Staffordshire NHS Foundation Trust public inquiry: executive summary (Vol. 947). The Stationery Office.
Hall, K. D., & Kahan, S. (2018). Maintenance of lost weight and long-term management of obesity. Medical Clinics, 102(1), 183-197.
Heymsfield, S. B., & Wadden, T. A. (2017). Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and management of obesity. New England Journal of Medicine, 376(3), 254-266.
Hilton, S., Patterson, C., & Teyhan, A. (2012). Escalating coverage of obesity in UK newspapers: the evolution and framing of the “obesity epidemic” from 1996 to 2010. Obesity, 20(8), 1688-1695.
Hruby, A., Manson, J. E., Qi, L., Malik, V. S., Rimm, E. B., Sun, Q., ... & Hu, F. B. (2016). Determinants and consequences of obesity. American journal of public health, 106(9), 1656-1662.
Keogh, B. (2013). Review into the quality of care and treatment provided by 14 hospital trusts in England: overview report. 2013.
Morgan, K. L., Rahman, M. A., Hill, R. A., Khanom, A., Lyons, R. A., & Brophy, S. T. (2015). Obesity in pregnancy: infant health service utilisation and costs on the NHS. BMJ open, 5(11).
Ntuk, U. E., Gill, J. M., Mackay, D. F., Sattar, N., & Pell, J. P. (2014). Ethnic-specific obesity cutoffs for diabetes risk: cross-sectional study of 490,288 UK biobank participants. Diabetes care, 37(9), 2500-2507.
Nudel, J., & Sanchez, V. M. (2019). Surgical management of obesity. Metabolism, 92, 206-216.
Petridou, A., Siopi, A., & Mougios, V. (2019). Exercise in the management of obesity. Metabolism, 92, 163-169.
Pollock, R. F., Muduma, G., & Valentine, W. J. (2013). Evaluating the cost‐effectiveness of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding versus standard medical management in obese patients with type 2 diabetes in the UK. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 15(2), 121-129.
Reeves, M., & Fuller, J. (2018). When SMART goals are not so smart. MIT Sloan Management Review, 59(4), 1-5.
Robertson, C., Archibald, D., Avenell, A., Douglas, F., Hoddinott, P., Van Teijlingen, E., ... & Fowler, C. (2014). Systematic reviews of and integrated report on the quantitative, qualitative and economic evidence base for the management of obesity in men. Health Technology Assessment (Winchester, England), 18(35).
Scarborough, P., Bhatnagar, P., Wickramasinghe, K. K., Allender, S., Foster, C., & Rayner, M. (2011). The economic burden of ill health due to diet, physical inactivity, smoking, alcohol and obesity in the UK: an update to 2006–07 NHS costs. Journal of public health, 33(4), 527-535.
Walshe, K. (2010). Reorganisation of the NHS in England.
Wang, Y. C., McPherson, K., Marsh, T., Gortmaker, S. L., & Brown, M. (2011). Health and economic burden of the projected obesity trends in the USA and the UK. The Lancet, 378(9793), 815-825.
Appendices
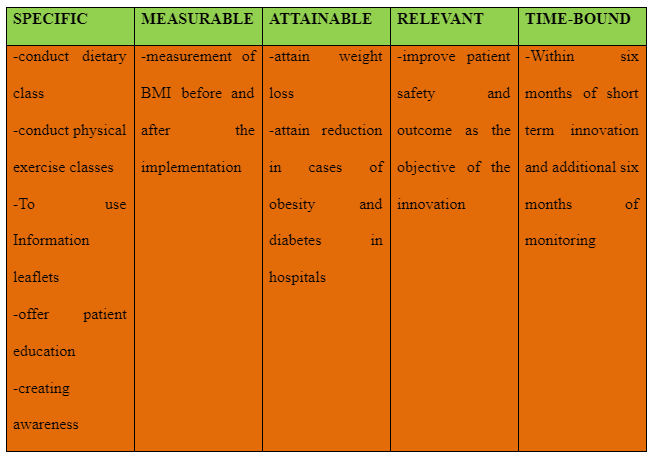
Appendix 1: SMART goals framework
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



