Redefining Healthcare Dynamics
Abstract
The rising healthcare costs, evolving patient expectations, changing patient demographics, employment dynamics, effect of Brexit, and rapid change and increasingly complex health-technology ecosystem are major challenges currently faced by the healthcare industry. The hospitals including its management and staff need to institute widespread changes that include adopting transformative leadership structures, value-based care, implementing team-based working culture, advanced technologies, and alternative employment models in order to address issues and challenges faced. For those researching these challenges, healthcare dissertation help can provide valuable insights. Following the death of a woman in childbirth and report of widespread negligence in maternity section, the CQC inspection found Basildon University Hospital to have ‘dysfunctional’ working environment and culture where staff failed to engage, coordinate, communicate, and encourage each other. The solution to the issue and challenges faced include implementing effective communication structures, emphasising on engagement and working together, interaction between the senior and junior members, training employees, and adoption of advanced equipment.
1. Introduction
1.1 Sector Background
The UK healthcare system in made up of the National Health System (NHS), which is a state funded and provide health care service such as maternity industry, emergency care, ambulance services, nursing, and social care for all the UK citizens. The private health care systems, for profit and non-profit, also exist where individuals who would like a private medical and health care service pay ‘out of their pocket’ or through private insurance coverage. The industry, although either privately of publicly owned, it is structured as hospital trusts with three hierarchical levels: regional (inter-regional), district, and community hospitals. Different professions each have bodies overseeing ethics, professionalism, and adherence to regulations. For example, midwifery who oversees maternity and infant care is under Nursing & Midwifery Council (NMC). The council regulates the nursing and midwifery in the UK by setting standards, register qualified personnel in the field, ensure quality education, and investigate complaints within the area. The General Practitioners administer primary care that include general practice, community pharmacy, dental, and optometry services. Across the UK, the sector has employed approximately 1.4 employees in 2009 increasing to 1.54 in 2019 (Statista, 2021).

Approximately 90% of the hospitals in the country are NHS-funded. The sector has been criticised for long waiting time and overcrowded hospitals. The growth of individuals seeking private treatment has been attributed to frustration, overcrowding, and low efficiency in public sector. According to IBISWorld (2021), the biggest private companies in the industry include BMI Healthcare Ltd, Spire Healthcare Ltd, and Nuffield Health. In addition to pressure overcrowding challenges particularly due novel COVID-19 virus, the sector faces challenges that include an aging population, growing population, medical advancements including rapid technology changes, increasing reliance on privatised services, centralisation drive, and evolving healthcare needs (The Medic Portal, 2021).
In term of expenditure, the industry has seen a gradual increase. In 1997, the expenditure stood at £54.9 billion increasing to £214 billion in 2018 (Statista, 2020). A survey conducted by Robertson et al. (2019) found that 76% of the respondents perceive the NHS as a world class health service, 72% saying it provide a ‘comprehensive and accessible high quality care’, 61% being satisfied with it, while 60% saying in addition to high quality GP service, it is easy and convenient to access.
1.2 Company Background
Basildon University Hospital, is one of the major three hospitals under management of the Mid and South Essex NHS Foundation Trust. The trust established on 1st April 2020, following the merger of the three hospitals: Southend University Hospital HNS Foundation Trust, Mid Essex Hospital Services NHS Trust, and Basildon and Thurrock University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. In 2019, the hospital faced a widespread criticism on their maternity services. This came particularly after a woman bled to death in childbirth. In 2020, the Basildon and Thurrock University Hospitals had a budget of more than £288 million. According to the NHS Digital (2021), in 2020, the hospital had approximately 103,000 patients in accident and emergency, and provided around 300,000 outpatient appointments and treated 77,500 inpatients and day.
1.2.1 Issues
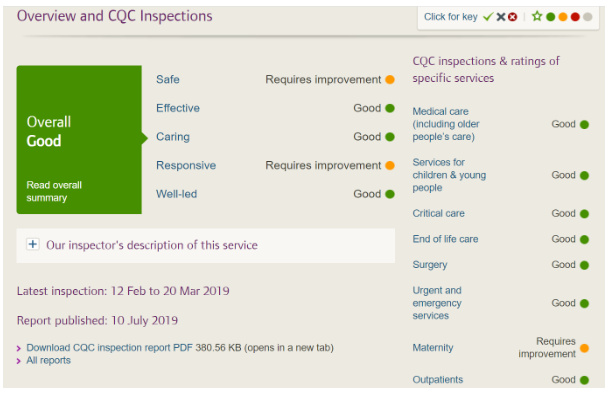
On its routine inspection in 2019, the CareQuality Commission (CQC) rated service offered by the hospital as ‘Good’ with such parameters as ‘effective, caring and well-led’ being good. It further found staff treated the patients with dignity and respect with interactions across staff, patients, and loved one being compassionate (CareQuality Commission, 2019). The commission stating that such areas as ‘safety’, ‘responsive’, and ‘productive uses of resources’ require improvement.
Looking for further insights on Demographics and Patient Professional Dynamics? Click here.
In safe category, the commission found that women who were identified as ‘high risk’ not always received appropriate care or access to staff and equipment. Similarly, the hospital did not apply consistently infection and prevention control mechanism particularly in maternity areas. According to CQC inspection report, the hospital ‘long-standing poor staff culture had created an ineffective team’ particularly at the maternity unit. The report goes further to state the maternity services were ‘inadequate’ with ‘several serious concerns’ in different areas. First, according to the report, the staff has a ‘dysfunctional’ working culture and do not support each other to advance care given (CQC, 2020). Dyer (2020) pointed out that senior medical staff failure to coordinate and work with junior staff brew the dysfunctional working environment. Secondly, the inspection findings indicated staff lacking appropriate technological skills and experience especially in regard to dealing with high risk pregnant women. This connected to the hospital failure to modern and aligning to advances in medical field. Thirdly, the UK leaving European Union (Brexit) presents a significant challenge on NHS’s medical staffing and supply chains (Fahy et al., 2019). NHS employs more than 60,000 EU nationals including 20,000 nurses and 10,000 doctors.
1.2.2 Challenges
The issue identified by CQC in their inspection report regarding to poor staff engagement and coordination can be liked to lack of engagement structures as well as staff working as a team. As pointed by the inspection report, the death of the pregnant woman was avoidable if the employees had communicated and coordinated more effectively (CQC, 2020). Therefore, for the company, in attempt to prevented another such deaths and negligence, the biggest challenge is developing and building a team that can work together.
The second challenge faced by the organisation is related to technology experience held by employees. Technological advancement in not only medication field by also immediate surrounding has been significantly rapid that organisations and employees need to restructure and learn constantly in order to catch up (Fazal et al., 2020). Moreover, the organisational efficiency is largely grounded on adoption and improves record keeping, delivery service, management of staffing, availability, and suitability of resuscitation equipment, and, importantly, trained and skilled employees. Lastly, the uncertainty caused by the Brexit on EU workers caused the per EU nationals registering particularly as nurses in the county to drop significant, by up to 90%. Similarly, the cross border regulations have put access to medical supplies to a serious risk.
1.2.3 Solutions
In addition to building and ensuring teams are functional, the company need to implement a robust communication system within team and across all employees as a new organisational culture. Concerning, technology, the company need to content with having suitable equipment as well as trained employees. It needs to update its equipment and systems to improve efficiency and reducing avoidable errors. The hospital should use new beds for high-risk pregnant women in maternity rooms. Improvement process should encompass service delivery process supported by available and suitable resources. Although modernising of the hospitals, which follows confronting deficient new equipment and systems as well as training staff with proper skills to use is quite costly both financially and resources (Deery, and Fisher, 2017). In addition to training, the company should increase the number of nurses and midwives. Thirdly, although this is beyond the company’s control, the challenges brought by Brexit is upon the UK to institute proper policies, regulatory framework, and trade agreement governing its healthcare systems and working with other regional and international partners such as European Union, European Medicines Agency, and Food & Drug Administration (FDA) in the US.
1.3 Research Method
1.3.1 Research Methods- Qualitative & Qualitative Approaches
The research search methods grounded on either developing a deeper understanding of the research problem from participant perspective, experiences, and opinion or discovering facts measured statistically. In qualitative approach, reality is perceived to be dynamic and take from individual respondent concepts, experience, and views. Whereas, quantitative research deals with viewing a problem from a statistical point of view rather than having insight of such parameters as causing factors, effects, and underlying reasons (Brannen, 2017; Park, J. and Park, M., 2016). For this research, a mixed approach incorporating both qualitative and quantitative methods was used. The enabled visualising statistically the problem variables while at the same time delving into underlying factors in answering such questions as why the variables exist the way there are as captured by respondents experiences and held beliefs.
In data collection process, the secondary data will be used. According to Johnston (2017), secondary data sources are a collection of previously data by any other party other than the researcher. The data sources can include but not limited to administrative data, census from government, existing articles, geodata from specialised sources, and institution reports (Dunn et al., 2015; Alvarez et al., 2012). This research study focused specifically on two sources, peer-reviewed journals and reports (from the government institutions). The sources were located by online search of several databases that include the university library, Google scholar. Sage Journals, ProQuest, EBSCO, British Medical Journal (BMJ), and JSTOR as well as NHS databases.
1.3.2 Sampling process
Keywords were keyed into the search boxes of the databases in search of any documentation, data, and articles relating to issues, challenges, and solutions faced by Basildon University Hospital. The keywords included but not limited to ‘Basildon University Hospital’, ‘Basildon University Hospital Challenges’, ‘Basildon University Hospital+ maternity + issue’, ‘NHS Basildon University Hospital Maternity issues’, ‘NHS Mid & South Essex NHS Foundation Trust’, ‘NHS + Brexit + Healthcare’, ‘Healthcare + Maternity + UK + NHS’, and ‘Midwives + Midwifery + nursing + Basildon University Hospital + NHS’. The returned findings were sampled using inclusion and exclusion criteria. The inclusion criteria included any article English written, UK-based hospitals, peer-reviewed articles, and reports from specialised body (NHS and CQC) were included.
1.4 Research questions
This research revolved was informed by the questions;
What are the challenges facing Basildon University Hospital?
What is the extent of the challenges faced by Basildon University Hospital?
What are some possible solutions that can be followed to solve the problem faced by the hospital?
2. Main Body
In preventing risk of death in the future, the secondary data on ‘lack of team working, coordination, and communication’ among medical staffs was derived from 3 journals and CQC reports. The inspection by CQC the working relation among midwives, consultants, and other doctors as a source of several safety problems, including death of a mother (CQC, 2020). The report further stated the staff did not support, supervise, or mentor others particularly junior staff members effectively. The findings indicate staffers held that lack of “an open culture” was a leading factor that led them not to approach other staff members (Dyer, 2020). Moreover, leaders lacked skills and abilities to lead effectively and failed to have effective governance processes. The concept of employee engagement and coordination not only function to institute effective communication but also motivate towards improving job performance, attitude, feedback, and learning (Deery, and Fisher, 2017). Secondly, according to CQC (2020) and Dryer (2020), staff lacked right skills and experience to deliver necessary service and care such as resuscitation as well as lacking of proper equipment.
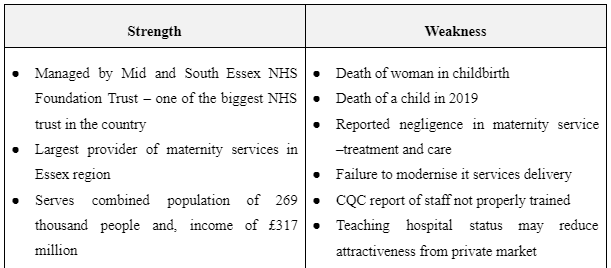
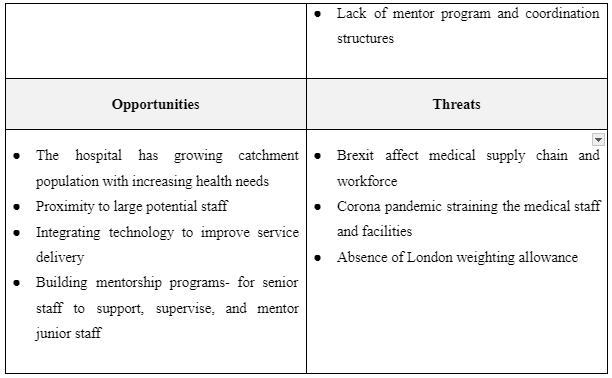
SWOT Analysis
PEST Analysis
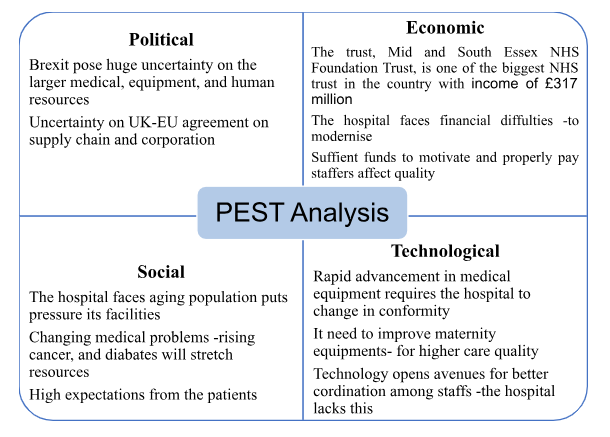
PEST is an acronym of Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors influencing an organisation operation particularly towards is competitiveness in a market.
The findings further indicated that the company failed to implement a system to check and ensure staffs had trained and proper skills – competent for their roles. CQC (2020) found that in addition to failure to by the staff to engagement and communication effectively, the hospital lacked of enough staff to provide adequate care and treatment staff engagement and team building. The problem with grading incidence incorrectly where high risk women were giving birth in a low risk area is attributable to not having suitably technology to monitor patients and properly diagnose and identify problems faced. In addition to disruptions of the medical supply chain from the EU nations, the indication of stringent movement of goods and services (human resource) indicate long-term increased cost of healthcare, reduced competitiveness, difficulty in accessing care, medications, and medical devices. Free movement of labour force across EU and now limited entry into the UK will ultimately have a lasting impact on the healthcare labour market. However, this growing uncertainty requires proper mitigation plan by the government but should be more transparency to stakeholders and representatives from the industry.

3. Conclusion
The findings found dysfunctional working environment led to fail to employees to engage, coordinate, and motivate each other coupled with inadequate skills and experience by staff. It further indicated failure by leadership to lead and govern effectively. Moreover, in addition to not have to modernise by adopting advanced technology in the maternity areas, the employees lacked suitable skills and experiences. The solutions to these issues range from emphasising on building team culture that include team collaboration, team work, team engagement, and structured team communication; secondly, restructuring leadership models to one focusing on patient and staff welfare as well as visionary enough to conform with changing health care needs and environment.
References
Alvarez, J., Canduela, J. and Raeside, R., 2012. Knowledge creation and the use of secondary data. Journal of clinical nursing, 21(19pt20), pp.2699-2710.
BBC News, 2020. Baby died after failed forceps delivery at Essex hospital. [online] BBC News. Available
at:
BBC News, 2020. Basildon maternity unit handed 'urgent' safety deadline. [online] BBC News. Available at:
Brannen, J. ed., 2017. Mixing methods: Qualitative and quantitative research. Routledge.
Care Quality Commission. 2021. CQC takes action to drive improvements in maternity services at Mid and South Essex NHS Foundation Trust | Care Quality Commission. [online] Available at: https://www.cqc.org.uk/news/releases/cqc-takes-action-drive-improvements-maternity-services-mid-south-essex-nhs-foundatio-0 [Accessed 10 March 2021].
Crowe, C. and Manley, K., 2019. Person-centred, safe and effective care in maternity services: the need for greater change towards best practice. International Practice Development Journal, 9(1).
Deery, R. and Fisher, P., 2017. Professionalism and person-centredness: developing a practice-based approach to leadership within NHS maternity services in the UK. Health Sociology Review, 26(2), pp.143-159.
Dunn, S.L., Arslanian-Engoren, C., DeKoekkoek, T., Jadack, R. and Scott, L.D., 2015. Secondary data analysis as an efficient and effective approach to nursing research. Western journal of nursing research, 37(10), pp.1295-1307.
Dyer, C., 2020. Basildon hospital:“Dysfunctional” working between staff in maternity care led to safety risks. BMJ: British Medical Journal (Online), 370.
Fahy, N., Hervey, T., Greer, S., Jarman, H., Stuckler, D., Galsworthy, M. and McKee, M., 2019. How will Brexit affect health services in the UK? An updated evaluation. The Lancet, 393(10174), pp.949-958.
Fazal, N., Webb, A., Bangoura, J. and El Nasharty, M., 2020. Telehealth: improving maternity services by modern technology. BMJ open quality, 9(4), p.e000895.
IBISWorld, 2021. Hospitals in the UK - Market Research Report. [online] Ibisworld.com. Available at:
Johnston, M.P., 2017. Secondary data analysis: A method of which the time has come. Qualitative and quantitative methods in libraries, 3(3), pp.619-626.
Knight, M., Nair, M., Tuffnell, D., Kenyon, S., Shakespeare, J., Brocklehurst, P. and Kurinczuk, J.J., 2016. Saving Lives, Improving Mothers' Care: Surveillance of maternal deaths in the UK 2012-14 and lessons learned to inform maternity care from the UK and Ireland Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths and Morbidity 2009-14. Oxuniprint.
NHS Digital. 2021. Supplementary information archive - NHS Digital. [online] Available at: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/find-data-and-publications/supplementary-information [Accessed 1 March 2021].
Park, J. and Park, M., 2016. Qualitative versus quantitative research methods: Discovery or justification?. Journal of Marketing Thought, 3(1), pp.1-8.
Robertson, R., Appleby, J., Evans, H. and Hemmings, N., 2019. Public satisfaction with the NHS and social care in 2018: Results from the British Social Attitudes survey. King's Fund, March, 7.
The Medic Portal, 2020. Challenges Facing The NHS - The Medic Portal. [online] The Medic Portal.
Available at:
Take a deeper dive into Rapid Sequence Induction (RSI) in Emergency Care with our additional resources.
Appendix

- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



