Vaccination Of Children In The Uk
Introduction
The topic regarding consideration of compulsory vaccination of children in the UK from parent’s perspective is chosen because in the current state it is found that a small yet steady decline of vaccination rate among the children in the UK is observed. This is evident as in 2017-18, the vaccination rate of children at 24 months is found to be 91.2% whereas in 2018-19 it dropped to 90.3% with a steady decline since the last 5 years (Wise, 2018). The parents are mainly responsible for supporting vaccination of the children at an early stage as they are the key caregivers and decision-makers on the behalf of the children (Boseley, 2019). Thus, evaluation of the parent’s perspective regarding childhood vaccination to be mandatory is important to understand if they are willing to support the process or indirectly responsible for the current decline of the childhood vaccination rate in the UK. This is because the low vaccination rate in children in the UK is causing the rise of various marked diseases such as diphtheria, measles, mumps and others which are previously mentioned to be entirely eradicated from the population (Wise, 2018). Seeking healthcare dissertation help can further assist in analysing these dynamics comprehensively.
In the medical and nursing field, critiquing of the research articles is important because it helps to evaluate the strength and weakness of the evidence in the articles, books and others. This in turn helps to validate and determine reality of the evidence to be used in performing evidence-based practice and quality care delivery (Carlsson et al., 2017). In this assignment, a quantitative article by Pebody et al. (2019) and a qualitative article by Jackson et al. (2017) are to be critiqued by using Holland and Rees (2010) critiquing framework and CASP Tool Framework respectively for each study. Holland and Rees (2010) critiquing framework is to be used for analysing the quantitative article because it is the best tool available online for critiquing quantitative studies which use set of different questions to gather valuable quantitative data from the studies to be used in framing evidence-based practice (Randle and Dalby, 2021). The Critical Appraisal Skill Programme (CASP) tool is to be used by analysing the qualitative article because it is the generic tool used for analysing the strength and weakness of any qualitative research methodology. Moreover, the presence of varied systematic set of questions in the tools leads the researchers to appropriately determine the meaning and usefulness of the qualitative evidence in the study (Long et al., 2020).

Literature Search Question:
The PICO framework use in framing study questions helps to improve the conceptual clarity and specificity of the clinical problems leading the researcher to frame a well-developed question that allows effective concept gathering in resolving the problem (Morgan et al., 2018). The PICO Stands for population, intervention, comparison and outcome. In this study, the population include the children and their parents, intervention is childhood vaccination, there are not variable for comparison and outcome is enhanced health of the children. The study questions are:
Should vaccination be compulsory for children in the UK?
What are the parents’ perspectives regarding compulsory vaccination of children?
Literature Search
The electronic literature search is executed to identify the two articles for the study. This is because electronic searching of articles is cost-effective and less time consuming along with avoid physical and geographical barriers to be created which eases the way of gathering potential articles for the study (Grewal et al., 2016). The electronic databases used for the search are CINHAL and PubMed. This is because CINHAL contains to medical and nursing literature from around the world that support exploring various health-related topic and resolving associated issues identified with them in common population (ebsco, 2021). PubMed is to be used because it is a free source that provided supporting retrieval of biomedical and life science-related data aimed at improving healthcare personally and globally (pubmed, 2021). The search terms to be used are: “Childhood vaccination”, “parents’ perspective”, “effectiveness of vaccination”, “parent’s attitude” and others.
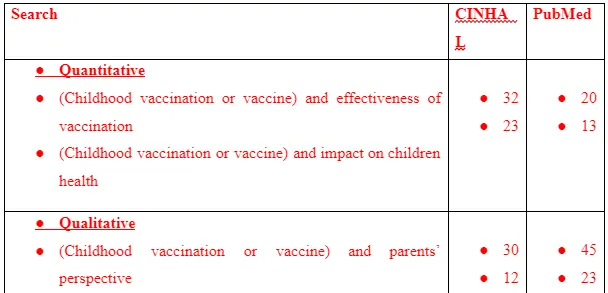

After the search, total of 30 studies (11 quantitative and 19 qualitative studies) are combined for the final result.

Critical Analysis of Quantitative Article
The Holland and Rees (2010) framework mentions that for critical analysis of quantitative study the concern of the topic is to be identified and ensure the variables in the title could be measured (Holland and Rees, 2010). The study by Pebody et al. (2019) has mentioned the concern to be focused in the article is the effectiveness of influenza vaccination in children and adults living in the UK. The variables mentioned in the study could also be measured which acts as strength because the success of the study in representing the main interest can be evaluated. The Holland and Rees (2010) framework mentions that the worthiness of the topic and extent of problem from the background are required to be examined (Holland and Rees, 2010). The background in the study by Pebody et al. (2019) mentions the topic to be worthy as it informs various concerns are raised regarding influenza vaccine on children as well as adults in the UK for which good evidence is to be gathered to determine the potentiality of the use of the vaccine for children and others.
The Holland and Rees (2010) framework also mentioned well-structured aim is required to be present in the study. This is because it mentions the key intention of the researchers in formulating the study (Holland and Rees, 2010). Pebody et al. (2019) has mentioned its aim to estimate the effectiveness of end-of-season influenza vaccination in the UK on children and adults. The well-developed aim acts as strength for the study as it helps to mention the key context of focus of the article. The Holland and Rees (2010) framework mentions determining the nature of the qualitative approach used in the study and its suitability in framing the research (Holland and Rees, 2010). Pebody et al. (2019) has used case-control design as quantitative approach in framing the study. The advantage of using case-control design is that it helps determine the association of an exposure to the outcome i.e disease or condition of interest of the study (Solerte et al., 2020). In the study by Pebody et al. (2019), the case-control study did assist in determining the exposure of influenza vaccination in UK children and adults to control the disease. However, the weakness of the case-control design is that it leads to cause selection or observational bias (Kahi et al., 2018).
In the study by Pebody et al. (2019), no selection bias is mentioned due to which the impact of weakness of the design on formulation of the study could not be determined. It leads the reader fail to understand if inaccurate estimations are made in the results. According to Holland and Rees (2010) framework, the data collection tool used in framing the study is to be analysed and its validity, as well as reliability of use, is to be determined (Holland and Rees, 2010). The study by Pebody et al. (2019) used the population-based seroprevalence survey method as data collection method. The advantage of using population-based survey method is that it helps in gathering increased response, allows clarification of data and ensures cost-effectiveness way of gathering data (Franco et al., 2017). However, the disadvantage of population-based survey is that it does not inform the views which led to the response rate and causes self-selection of participants leading to raise bias (Keränen et al., 2017). In the study by Pebody et al. (2019), the use of survey method of data collection does created limitation of failing to inform the views behind acceptance and non-acceptance of the influenza vaccine. Moreover, selection bias may be raised as in including the patients, the data of vaccination for few individuals was imputed according to self-analysis of the researcher since the dates are not available.
The study by Pebody et al. (2019) does not related if the mentioned data collection tool is used in previous studies due to which accurate and reliability of the data collection process could not be ensured. It led the researcher fails to effectively justify the validity of the data collection tool used in gathering potential facts for the study. Holland and Rees (2010) framework mention determining and explain the validity of the data analysis process used in executing the study (Holland and Rees, 2010). In the study by Pebody et al. (2019), multivariate logistic regression is used as data analysis method along with statistical analysis and sensitivity analysis. The advantage of using multi-variate analysis is that it helps to correlate between dependent as well as independent variables to determine the relationship of variables across a dataset (Umut et al., 2021). Thus, the use of the method helps in determining the correlation of influenza vaccination with avoiding presence of influenza among the patients. In addition, the use of statistical analysis helped in gathering percentage data about the efficiency and impact of different influenza vaccines in children and adults.
Holland and Rees (2010) framework inform for critical analysis of quantitative article, the sampling strategy is to be analysed to determine if it supported the execution of the study (Holland and Rees, 2010). In this context, it is seen that Pebody et al. (2019) has included 3080 children and adults out of which 453 were children and rest were adults above the age of 18 years. The limitation raised with the small number of children as population is that it created hardship in widely determining the range of effectiveness of influenza vaccination on them compared to the adults. In selecting the sample, the individuals who provided consent to participate in the study are included and the individuals who have received the influenza vaccination before the analysis. Thus, it creates limitation to gain results regarding the effectiveness of the vaccine in avoiding influenza in vaccinate children compared to non-vaccinated children. The Holland and Rees (2010) framework mention to determine ethical consideration in the study. This is important as ethically approved ensures research obligation are followed and informed consent from participants are taken that void forceful inclusion of sample in the study which may cause bias (Robertson, 2021). Pebody et al. (2019) have gained ethical support from the PHE SEU archive and used informed consent for including participants that avoided forceful participant inclusion in the study and ethical consideration been effectively followed.
The Holland and Rees (2010) framework mentions to determine if the main findings are linked with the aim of the study (Holland and Rees, 2010). This is because lack of link of main findings with the aim would indicate failure of the research in resolving the focussed problem in the article. The main findings of Pebody et al. (2019) revealed that in 2-17 years old children the LAIV4 aVE was 26.9% effective in controlling all range of influenza and 60.8% against controlling influenza B in children. The results further revealed that compared to trivalent inactivated vaccine (TIV), live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV4) was effective in avoiding development of influenza indicating its link with the aim where the key focus was to determine effectiveness opf influenza vaccine. This informs that vaccination in children was effective in avoiding influenza development. The overall strength of the study is that the use of triangulated data of vaccination effectiveness and seroprevalence data provided greater insight regarding varied seasonal observation seen among individuals. However, the limitation of the study is misclassification of the influenza vaccination in patients that created bias in presentation of results.
Critical Analysis of Qualitative Article
The CASP tool qualitative study analysis mention initially to determine if a clear state of the aim in the study is provided or not (CASP, 2018). This is because presence of clarified aims helps to understand if the study is valid to be explored in resolving the raised question in the study. In study by Jackson et al., (2017), clarified aim is mentioned which is exploring the existing knolwdege of the parents and their attitude as well as views regarding the use of serogroup B meningococcal (MenB) vaccine for young children. The CASP tool mention to determine if the qualitative approach used is appropriate in framing the study (CASP, 2018). This is important as inappropriate use of qualitative methodology would lead to hindered collection of data that are not able to resolve the raised questions in the study (Allan, 2020). The use of qualitative methodology is appropriate in the study by Jackson et al., (2017) because qualitative methodology helps in gathering feelings, thoughts and views of the participants regarding any particular problem focused in the study. Since Jackson et al., (2017) focused on gathering attitude, views and knowledge levels of the parents regarding children vaccination process of serogroup B meningococcal (MenB) vaccine, the qualitative method is appropriate for the study.
The CASP tool informs to determine the appropriateness of research design in addressing the study aim (CASP, 2018). This is because justified use of research design helps in indicate the researcher has progressed in the right direction to execute the study (Rivera-Hernandez et al., 2020). The cross-sectional qualitative research design is used by Jackson et al., (2017). The advantage of using the cross-sectional design is that it helps in determining the prevalence of the disease along with the prevalent attitude and knolwdege regarding the issues among the patients and others person (Mills et al., 2017). Since Jackson et al., (2017) aimed to determine parents’ perspective regarding vaccination process, the use of the cross-sectional design is appropriate. However, limitation of using cross-sectional research is failure to analyse any behaviour overtime (Tillmann et al., 2018). Thus, the use of the design creates limitation to determine parents’ perspective of MenB vaccine for children over a period to determine way or if it changes with time. The CASP Tool informs to ensure the recruitment strategy is appropriate regarding the aim of the research (CASP, 2018). This is because inappropriate recruitment strategy le to selection of wrong participants that are invalid in executing the study leading to create error.
The parents recruited for the study from London and Yorkshire. The participants from London are recruited from five Children’s Centres (CC) with sociodemographic mix and in Yorkshire, the participants are selected from mother and toddler group through midwife-led Facebook group. Thus, the recruitment strategy is appropriate as the key participants which are parents of the children are selected. However, the limitation raised is that perspective of mother as carer for children regarding vaccination is included in the study while father’s perspectives were avoided. It led to partial determination of the knowledge and views of parents regarding vaccinating their children for MenB vaccine. The CASP tool mentions to determine if the way of data collection is effective to address the issue raised in research (CASP, 2018). In the study by Jackson et al., (2017), the data collection is made through group and personal interview process which is appropriate for addressing the raised issue in the study. This is because it helped to determine the way parents have personal views, knowledge and attitude regarding vaccinating their children with MenB vaccine and the way their views remain stable or change in group.
The CASP Tool mentions determining if the relationship between the participants and researchers are adequately considered. This is important to determine the way researcher responded to the participants in the study and implication made for better data collection for the study (CASP, 2018). However, Jackson et al., (2017) did not mentioned the aspect due to which the role of the researcher in relation to the participants to gather data remained unclear. The CASP Tool mentions ethical issues in the study are to be considered so that legal obligations and safety of the participants are ensured (CASP, 2018). In the study of Jackson et al., (2017), ethics approval has been accessed from Research Ethics Committee in University of London and written consent of the participants are taken for inclusion in the study that approves effective ethical consideration are followed. The CASP tool mentions to determine if the data analysis is sufficient and done in-depth (CASP, 2018). Jackson et al., (2017) used audio recording for transcribing the verbatim of the participants and analysed them in developing themes for systematic presentation of data without duplication.
The CASP tool mentions to determine if clarified findings regarding the study is provided (CASP, 2018). In the study by Jackson et al., (2017), the findings clearly mentioned parents consider vaccinating their children with MenB vaccine to develop preventive measures from all concerns to be created by meningitis. Moreover, they mentioned severity of the health issue and its recognition would create better successful vaccination. Thee strength of the study is that it is first study to determine the parent’s views for the implementation of MenB vaccine for children in the UK. However, the limitation of the study is that parents with university degree are over-represented in the research which may have led to cause bias in collection of data.
Personal Discussion
The critiquing of both the studies informs that qualitative, as well as quantitative approach, are both suitable in regard to the area of the research. This is because quantitative approach informs about the effectiveness of introducing compulsory vaccination for children and qualitative approach informs about the parents’ perspective that are acting as support or in some cases barrier to vaccination. It indicated the actions to be taken to create more positive approach of children vaccination process among parents. The use of only quantitative paradigm acts as limitation because it fails to explain the reason which led to the gathered results and what thoughts or attitudes of the participants led to such interpretation to be gathered (Krainovich-Miller, 2017). Thus, both approaches that is qualitative and quantitative approach is best to be used in framing studies regarding the topic.
The studies are seen to explain to great extent the answer regarding the research question raised. It is evident as the studies mentioned to what extent vaccination is important for the children as well as provided data which ensures parents’ perspective regarding vaccination process for the children which was found to be mainly positive. Thus, it indicates further research is to be executed to determine the other reason that may be responsible in hindered compulsory vaccination process of the children as the parents who are the primary caregivers of the children are found to be react positively to the suggestion. The findings from the study can contribute to the current nursing practice in the UK to understand that parents’ attitude is not hindered vaccination of children and they need to execute further research to determine what other are raising the problem. The evidence gathered can be implemented in nursing practice to understand the reason behind the parents considering the regular vaccination for the children to be useful which they can deploy to promote better childhood vaccination.

Conclusion
The above discussion informs that Pebody et al., (2017) used quantitative research design and Jackson et al., (2017) used qualitative research design in framing the studies. In both the studies, aim, background and focus of the study are mentioned in detail. Moreover, both the studies are found to follow ethical consideration indicating they were done by following all legal obligation in research. In both the study, the information regarding the sampling strategy effectively mentions that the way data analysis is made is clearly focussed. The evidence from the studies can be applied in nursing practice to promote enhanced vaccination among children in the UK.
Looking for further insights on Utilizing Rolfe's Model of Self-Reflection? Click here.
References
Allan, G., 2020. Qualitative research. In Handbook for research students in the social sciences (pp. 177-189). Routledge.
Boseley, S., 2019, Drop in vaccination rates in England alarming, experts warn, Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/society/2019/sep/26/drop-in-vaccination-rates-in-england-alarming-experts-warn [Accessed on: 19 October 2021]
Carlsson, I.M., Blomqvist, M. and Jormfeldt, H., 2017. Ethical and methodological issues in qualitative studies involving people with severe and persistent mental illness such as schizophrenia and other psychotic conditions: a critical review. International journal of qualitative studies on health and well-being, 12(sup2), p.1368323.
CASP 2021, CASP, Available at: https://casp-uk.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/CASP-Qualitative-Checklist-2018_fillable_form.pdf [Accessed on: 19 October 2021]
EBSCO 2021, CINHAL, Available at: https://www.ebsco.com/products/research-databases/cinahl-database [Accessed on: 19 October 2021]
Franco, A., Malhotra, N., Simonovits, G. and Zigerell, L.J., 2017. Developing standards for post-hoc weighting in population-based survey experiments. Journal of Experimental Political Science, 4(2), pp.161-172.
Grewal, A., Kataria, H. and Dhawan, I., 2016. Literature search for research planning and identification of research problem. Indian journal of anaesthesia, 60(9), p.635.
Holland, K. and Rees, C., 2010. Nursing evidence-based practice skills. Oxford University Press.
Jackson, C., Yarwood, J., Saliba, V. and Bedford, H., 2017. UK parents’ attitudes towards meningococcal group B (MenB) vaccination: a qualitative analysis. BMJ open, 7(4), p.e012851.
Kahi, C.J., Pohl, H., Myers, L.J., Mobarek, D., Robertson, D.J. and Imperiale, T.F., 2018. Colonoscopy and colorectal Cancer mortality in the veterans affairs health care system: a case–control study. Annals of internal medicine, 168(7), pp.481-488.
Keränen, N.S., Kangas, M., Immonen, M., Similä, H., Enwald, H., Korpelainen, R. and Jämsä, T., 2017. Use of information and communication technologies among older people with and without frailty: a population-based survey. Journal of medical Internet research, 19(2), p.e5507.
Krainovich-Miller, B., 2017. Gathering and appraising the literature. Nursing research: methods and critical appraisal for evidence-based practice, 9th edn. Elsevier, Mosby, St. Louis, MO, pp.45-65.
Long, H.A., French, D.P. and Brooks, J.M., 2020. Optimising the value of the critical appraisal skills programme (CASP) tool for quality appraisal in qualitative evidence synthesis. Research Methods in Medicine & Health Sciences, 1(1), pp.31-42.
Mills, S., Brown, H., Wrieden, W., White, M. and Adams, J., 2017. Frequency of eating home cooked meals and potential benefits for diet and health: cross-sectional analysis of a population-based cohort study. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 14(1), pp.1-11.
Morgan, R.L., Whaley, P., Thayer, K.A. and Schünemann, H.J., 2018. Identifying the PECO: a framework for formulating good questions to explore the association of environmental and other exposures with health outcomes. Environment international, 121(Pt 1), p.1027.
Pebody, R., Djennad, A., Ellis, J., Andrews, N., Marques, D.F., Cottrell, S., Reynolds, A.J., Gunson, R., Galiano, M., Hoschler, K. and Lackenby, A., 2019. End of season influenza vaccine effectiveness in adults and children in the United Kingdom in 2017/18. Eurosurveillance, 24(31), p.1800488.
pubmed 2021, PubMed, Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ [Accessed on: 19 October 2021]
Randle, M. and Dalby, D.C., 2021. Exploring the effects of having an autistic sibling on typically developing young people. Learning Disability Practice, 24(4).pp.45-67.
Rivera-Hernandez, M., Blackwood, K.L., Moody, K.A. and Trivedi, A.N., 2020. Plan switching and stickiness in medicare advantage: a qualitative interview with medicare advantage beneficiaries. Medical Care Research and Review, p.1077558720944284.
Robertson, C., 2021. The Ethics of Research That May Disadvantage Others. Ethics & human research, 43(1), pp.2-16.
Solerte, S.B., D’Addio, F., Trevisan, R., Lovati, E., Rossi, A., Pastore, I., Dell’Acqua, M., Ippolito, E., Scaranna, C., Bellante, R. and Galliani, S., 2020. Sitagliptin treatment at the time of hospitalization was associated with reduced mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: a multicenter, case-control, retrospective, observational study. Diabetes care, 43(12), pp.2999-3006.
Tillmann, S., Tobin, D., Avison, W. and Gilliland, J., 2018. Mental health benefits of interactions with nature in children and teenagers: A systematic review. J Epidemiol Community Health, 72(10), pp.958-966.
Umut, K.A.Y.A., Yaprak, G., Yilmaz, A. and Alaattin, Ö.Z.E.N., 2021. Is There Any Advantage of Machine Learning to Multivariate Regression Analysis for Predicting Disease-Related Deaths in Patients with Gastric Cancer? Reevaluation of Retrospective Data. Turkish Journal of Oncology, 1(1).pp.56-78.
Wise, J., 2018. Child vaccination rates drop in England as MMR uptake falls for fourth year. BMJ (2018). p.362
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



