Leadership Theory and Practice
- 28 Pages
- Published On: 04-12-2023
Abstract
The aim of this assignment is to discuss different concepts in leadership theory and practice. There are different leadership theories used in the past and which are still being used to achieve great organisational success. Examples of such leadership theories include the trait theory of leadership which focus on the specific leadership abilities and traits that leaders possess, behavioural leadership theories which concentrate on the behavioural aspects of top-notch or effective leaders and transformational leadership theory which focuses on leaders doing the right thing and putting sufficient effort to achieve the desired performance goals in the company. With this in mind, this paper critically examined a handful of leaders in today’s contemporary organisations, their leadership traits and how they made use of these leadership theories to be successful. Lastly, this paper found that an individual can develop their leadership capabilities in different ways such as emulating top leaders, taking control of projects and attending seminars and workshops which can allow them to learn how to communicate effectively and sharpen their leadership skills like conflict resolution. For students seeking business dissertation help, understanding these theories and applying them in practical contexts can significantly enhance their academic and professional growth.
Introduction
First of all, this paper will outline a critical literature review of the key theories of the nature and exercise of leadership in companies. Theories like trait leadership theory, behavioural theories and transformational leadership will be discussed critically. A critical evaluation of some selected leaders encountered during the course of my career, relative to the leadership theories will be done. The behaviour of the selected leaders relative to their success will also be analysed. Lastly, different strategies on how different leadership capabilities can be developed will also be discussed.

Literature review of key leadership theories in organisations
The Trait Theory of Leadership
Chow, Salleh and Ismail (2017) note that this theory began with the early 1940s leadership studies which attempted to find the characteristics or leadership traits. The development of this theory was because of a systematic effort of researchers and psychologists to try and understand the concept of leadership. These groups came to the conclusion that leaders have certain common inborn traits or personalities. In this context, the earliest theory was in fact that ‘the great man’ concept that dates back to the era of the ancient Romans and Greeks. Based on this concept, leaders are not made and are instead born. A lot of effort has been made by researchers to try and identify the personality, mental and physical traits of leaders. However, the great man concept lost its importance with the growth of the psychology behaviourist school (Chow, Salleh and Ismail (2017).
The work of Salihu (2019) add on the claims of Chow, Salleh and Ismail (2017) by stating that with time, studies on leadership theories have linked certain traits to the abilities or capabilities of leaders. These researchers have associated five physical traits including height, energy, and appearance to leadership qualities. Additionally, four ability and intelligence traits, and sixteen personality traits like self-confidence, aggressiveness, enthusiasm and adaptability are considered critical leadership traits. Salihu (2019) claims that there are also six task-related traits, including persistence, initiative, drive and achievement which are linked to good leaders. These claims are supported by Uslu (2019) who suggest that psychologists and researchers have found nine social characteristics like administrative ability, cooperativeness and interpersonal skills as key traits which good leaders should have.
Most recently, evidence by Buchanan and Huczynski (2019) have supported these claims by determining that important leadership traits include leadership motivation or the desire to be a leader and not being power thirsty. Furthermore, these researchers opine that good leaders are now considered to be the individuals with drive including tenacity, initiative, ambition, energy and achievement. They are also people who show integrity, honesty and self-confidence or emotional stability. Today, good leaders are those with cognitive ability and the capacity to understand business and its operations. Overall, research on leadership traits claim that not all these traits are owned by leaders. Research also agree that there are certain desirable traits or behaviour patterns which leaders must or should have (Buchanan and Huczynski, 2019).
Continue your exploration of Warren Buffet Leadership Style with our related content.
Behavioural Theories
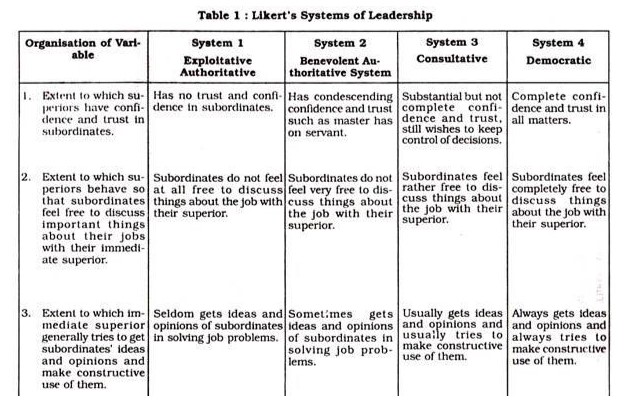
This behavioural theory came about because of researchers attempted to examine the behavioural aspect of good leadership (Gifford et al., 2017). Rather than looking into what makes effective leaders, they determined what is done by effective leaders, that is, how these individuals delegate duties, their communication approaches and the way they motivate and encourage their employees or followers. Researchers also looked to determine how leaders conduct or complete their responsibilities. To understand important leadership behaviours, Amzat et al. (2020) note that it is imperative to review Likert’s four management system. See appendix 2 on Likert’s management system.
Likert’s Four System used in management is the brainchild of Professor Rensis Likert and colleagues of the University of Michigan (Amzat et al., 2020). According to Amzat et al. (2020), this group of researchers examined leadership styles and patterns which have been used by managers in the past decades. Because of their research, they came up with certain approaches and ideas which can help comprehend leadership behaviour. Based on this management system, the researcher argue that an efficient or effective manager is one that is robustly oriented towards the subordinates and who uses communication as a vital means of keeping all individuals and departments in alignment or unison (Amzat et al., 2020).
Within the four management systems, the first system is also known as the exploitive-authoritative leadership style or dictatorial leadership style and behaviour. In the first system, managers make all decisions with little or no employee participation. System one is a highly autocratic form of leadership where junior employees or subordinates are hardly trusted. In organisations where this approach of leadership is used, negative tactics of motivation such as punishment and fear are also used. Top leaders also work to ensure that the power to make decisions remain or stay with them (Dorsch, 2020).
Within the second management system, benevolent-authoritative leadership style and behaviours are adopted by leaders in organisations (Likert and Bowers, 2013). These authors claim that in organisations where this form of leadership is used, managers and leaders are patronizing even though they trust and are confident in their subordinates. Managers also allow upward communication to some degree and request for junior employee participation. Additionally, both punishment and rewards are used to encourage or motivate junior employees to work hard and complete their duties. Subordinates also take part in the process of decision-making to some level even though top leaders maintain close or tight policy control (Likert and Bowers, 2013).
In the third system of management, also known as consultative style of leadership, managers lack complete trust and confidence in their subordinates. Nonetheless, they request for advice from them while still maintaining the right and ability to make the last or final decision. In consultative leadership style, occasional punishment and rewards are used. General decisions and broad policy making are done at the top leadership level with some decision-making left for junior employees or lower level subordinates. These organisations also use both downward and upward communication with managers acting or behaving as consultants working to resolve different problems (Dorsch, 2020).
Research by Ju and Jim (2019) clearly discusses the last management system proposed by Likert and his colleagues. The research talks about participative leadership, an approach where managers trust and have confidence in subordinates’ abilities. As a result, managers seek their advice and opinions in critical decision-making processes. Advice which are used constructively. Managers and top leadership also encourage the participation of their juniors in all stages of decision-making either through downward and upward communication. In this system, managers and subordinates work as a team. The participation of everyone alike helps during objective setting and completion or fulfilment of gaols. Rewards such as financial stipend are also often used in this style of leadership. According to Likert’s management system, leaders who uses the forth management system realizes the biggest success compared to those using the other styles. These leaders have an advantage over the other styles in terms of goal setting and the realization of these goals through increased productivity (Ju and Jim, 2019).
The theory of transformational leadership
In recent studies, it has been shown that while there are some leader managers, other managers are not leaders. According to Ding, Li, Zhang, Sheng and Wang (2017), managers seek to do the right things while leaders innovate and similarly do things right. Besides inspiring others to follow them, leaders also create major changes. Their followers are usually inspired to put in a lot of effort to reach successful levels together. Max Weber introduced charisma as an important aspect of leadership as noted by the peer reviewed work of (MacNeill, Silcox and Boyd, 2018). These authors highlight that according to this German sociologist, charisma refers to individual adaptation of divine grace with charismatic leaders showing the ability to influence their followers greatly. These followers are greatly attracted to their leader’s oratory skills, exceptional ability and magnetic personality (MacNeill, Silcox and Boyd, 2018). These arguments are supported by Rowland Jr (2018) who also looked into the work of James MacGregor Burns who started the idea of a ‘hero’ in leadership. According to (Rowland Jr, 2018), heroic leadership is the one displayed by leaders who transform and inspire followers (Rowland Jr, 2018).
Rosari (2019) researched a later time researcher known as Bernard M. Bass who developed the heroic leadership concept further when he argued that transformational leadership is one that motivates followers to work beyond what is excepted of them, inspiring them to concentrate on the goal of transcending their immediate self-interests and focus on higher-level objectives or goals like self-actualisation and achievement, instead of extrinsic lower objectives such as security and safety. According to Rosari (2019), Bernard M. Bass’ transformational leaders make their followers feel confident in themselves and their abilities to complete challenging missions which their leaders have articulated (Rosari, 2019).
Rosari (2019) also discussed Bernard M. Bass in their recent work and argue that the theorist believes that transformational leaders show attributes like individualised consideration and intellectual stimulation where they offer fresh and new ideas which encourage and stimulate followers to find different possible solutions to a single problem. These kind of leaders foster creative problem solving, particularly to the challenges that appear insurmountable (Rosari, 2019). Based on these insights, leaders are individuals who can use the needs, beliefs and values which their followers have, and transform, as well as stimulate them to complete certain tasks excellently. Transformational leaders do this in crisis-laden and changing situations. Other leadership techniques used by what is referred to as transactional leaders include situational or behavioural approaches, used intellectually in a charismatic manner to stimulate their followers to complete tasks. One significant differences between transformational and transactional leaders is that the latter motivates followers or subordinates to complete tasks as expected or at articulated levels while transformational leadership inspires followers to go beyond what is expected of them (Keskes, Sallan, Simo and Fernandez, 2018).
Most importantly, the researchers such as Breevaart and Bakker (2018) note that transformational leadership is not a replacement of transactional leadership. Instead, it supplements transactional leadership by adding the effect of subordinates performing beyond the articulated expectations. Nonetheless, even highly successful transformational managers and leaders need transactional abilities and skills to manage daily events effectively. Evidence shows that a critical analysis and interpretation of transformational leadership shows some similarities to the trait theory of leadership. This is because examining what makes up the ability to influence, attraction and divine grace is similar to assessing the traits of physical attributes, self-confidence and the trait of intelligence to find out what makes successful leaders (Breevaart and Bakker (2018).
The behaviour of leaders I have encountered in the course of my career in relation to the leadership theories
Trait Leadership in Practice
I attended a leadership workshop in 2019 in the United Kingdom where the theme was trait leadership and how this can lead to successful leadership in companies. During the workshop, one leader and his leadership traits caught my attention. During the workshop, I got the opportunities to learn different leadership characteristics of individuals who have revolutionized their specific industries, achieving immense success. The first leader we were introduced to passed on in 2011. This was a great industrial designer, media proprietor and founder of a giant computer company in the United States. He had made significant changes in this sector through his state-of-the art computer gadget designs and inventions which are loved worldwide even today. One characteristic that made this leader to stand out is his charisma. He had the ability to articulate his visions passionately. This made other employees want to be his followers. This inventor also stood out as an intelligent, determined, self-confident leader was maintained the highest level of integrity.
He showed a great understanding, mastery and use of trait leadership, an approach which embodies the concept of exceptional individual leaders that possess numerous valuable traits. As a result, he was perceived as an individual who was set art from other people and was a born leader. To those who interacted with him who also attended the workshop, they mentioned that as an individual who showed trait leadership, he could not be ignored even when one disagreed with him as a rebel, a troublemaker or a person who sees things from a different perspective because he had the ability to change things. Those who spoke about him noted that this leader had the ability to push our human race ahead. One of his famous quotes was ‘Think Different’.
One of the characteristics of this leader, based on the trait theory, which came out strongly is his ability to not only hire but also develop individual’s talent. Those who spoke about him in the workshop said that this leader believed that great people are those who are self-managing. The noted that the leader believed that great employees do not necessarily have to be controlled or managed. As a result, the leader hired, as well as developed a talented team which only requires one idea to operate well, not waiting to be told how to do their work. He always endeavoured to recruit smart people and developed their talent further so as not to always follow them around to tell them what they should do to complete their assignment.
Additionally, as an individual who demonstrated trait leadership, he had a clear mission and vision. It was noted that he did not seek to replicate other people’s efforts but had a unique mind-set. What inspired people to follow him is his ability to know what was needed by customers even before this was mentioned or asked for. It was noted that this individual knew how his products and inventions would change the world even before he built them. I heard one individual who has interacted with him call him a ‘magical storyteller’ with the ability to talk and tell people about how he envisioned his products changing the world in the near future. He had the ability to paint a vivid picture about how people would benefit from his inventions, especially how computers would be used to not only educate children but also entertain people. As a result, people could not help it but buy-in his vision.
Furthermore from what I heard about this leader in the workshop, it is clear that he had focus. He was focused on making great products. He also had the ability to concentrate on fewer products which could successfully propel their brand to the future. He had the ability to turn things around and focus on what he believed was good. His vision was to not only identify customer needs but also command people’s energy into creating few high quality products based on customers’ needs. According to him, focusing was all about rejecting the unnecessary even when this can make some people angry.
He also delivered results, because of these leadership traits, he made his company the second largest firm globally with a revenue surpassing 260 billion USD. His success strategy was very simple which included, to simplify everything, to unleash creativity, to do one’s passion, to create unforgettable customer experience and to be a great storyteller of one’s own vision. From these characteristics, it is apparent that this leader demonstrated certain trait theory features which made him stand out as a great leader. He had task-related traits like persistence, initiative, drive and the desire to reach great heights and make achievements. He also had administrative abilities, was cooperative and had vital interpersonal skills mentioned by (Alvesson and Sveningsson, 2015). He not only had leadership motivation, but also had ambition, energy and self-confidence discussed by Salihu (2019). These trait theories not only made him a great leader but an inspiration to his team which worked together to achieve great success.
Behavioural Theory Leadership in Practice
In my own personal research about great leadership examples in global companies, I read about how one global beverage mogul with its headquarters in the United Kingdom has experienced behavioural theory leadership to a great success. This company, whose drinks are loved all over the world, by people of all ages, especially the youth, have been led by individuals who have shown the significance of behavioural theory leadership style in companies. As evidence suggests, behavioural leaders are not judged by what makes them to be effective but rather what they do to be effective leaders (Denison, Hooijberg, Lane and Lief, 2012). In this regard, one aspect that emerged from the company’s leadership is that leaders are task-oriented. These individuals show effective leadership by remaining both people-oriented and task-oriented. The task oriented leaders demonstrated a special focus on their organizational structure and system, ensuring that the team remained focused on the task at hand. Leaders in this company meticulously ensured that the procedures of standard operation were meticulously adhered to and that the communication lines, team and organizational structure were streamlined, operational and perfectly functioning. Additionally in this company, leaders paid special attention to their subordinates and worked to motivate them. The leaders demonstrated behaviours such as information gathering, clarifying, organizing and initiating
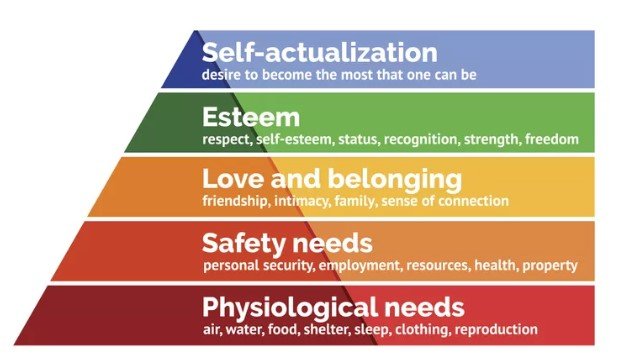
The company’s executive demonstrated people-oriented leadership. From my research on the company, leaders are both task and people-oriented. They equally put significant effort in ensuring that the needs of their staff members are met and that they are motivated sufficiently to complete their duties. They put a lot of effort and focus on the behaviour of their subordinates as people with needs and wants. What caught my eye in this company is their special understanding and use of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and how they employ these to satisfy different needs of their employees based on their order of priorities to ensure that everyone behaved as articulated in the company’s codes of behaviour policy to fulfil the firm’s objectives. According to Cui et al. (2021), human needs vary based on their order of priority and people work in an attempt to satisfy them according to what they consider should be satisfied first. While focusing on the tasks, leaders behave strangely as they go straight to their employees when there is a problem to find a way both leaders and the employees could work together to help one another to solve the problem. Some of the behaviours which leaders in this company demonstrated include mentoring and coaching, listening, observing and encouraging their subordinated to perform better. See appendix 1 for Maslow’s hierarchy of needs pyramid
I also noticed that leaders in this beverage company embraced and used democratic leadership, a behaviour that has been associated with numerous successful leaders and companies globally. In line with Likert’s management system and a leader’s behaviour and characteristics, I realised that leaders in the company also had effective leadership behaviours. As noted by Likert in his series of management system, I noted that leaders in this firm follow participative leadership as opposed to dictatorship or autocracy. Top leaders consult with subordinates both in system development and in working to achieve common organizational objectives. In this company, all leaders and heads of different departments ensure that a collaborative atmosphere prevails in the company. The whole team is allowed to own their duties and procedures used in completing different tasks. As a result, employees in the company are always motivated to complete their duties accurately and consistently as required because, after all, it deals with the production of consumable products which errors can be tragic and fatal. By involving all staff members in critical processes of decision-making, the entire team is made to understand their responsibilities clearly and are motivated to take the right action at the right time
One of the biggest benefits which this company has reaped from using behavioural theory of leadership is allowing it to make use of all its employees’ strengths. Everyone’s voice in the team is heard. This has encouraged engagement and creativity in the company. It has also created an avenue for incoming leaders to showcase their skills and abilities to the company and to take advantage of everyone’s strengths and to improve each other’s weaknesses. Through participative leadership, the company has created an atmosphere of free communication and extensive collaboration, leading to a blossoming or thriving organizational culture. The only challenge which this leadership style and behaviour has resulted in is the lengthy time it takes to make critical decisions. Speaking to all members of a team has meant that the company often experiences greater delay to take action. Nonetheless, leaders in the company stood out as individuals who are encouraging, open to comments and feedback, collaborative and people who embrace free communication to enhance teamwork and organizational success.
Moreover, leaders in this company demonstrated sound leadership. In my analysis of this company, leaders were more result focused, achieved through ensuring that there is team sustainability and happiness. The leaders in this company took the spotlight because of their motivational abilities because of their actions and words. Leaders in the beverage company came out as highly ambitious individuals who often set high yet achievable goals. Most often, the leaders thrived in the organisation’s and team’s cultures and were open to working problems together through open discussions. This approach has helped ensure that all parties or stakeholders in the company are satisfied with the decisions made and actions taken.
The company’s leaders’ sound leadership approach reminds me of the management theory created by Douglas McGregor cited in (Brdulak, Senkus and Senkus, 2017), which states that sound leaders believe that employees are often proud of their work and efforts and are more willing to take on challenges. These leaders also benefit from the ownership and autonomy of their employees’ work. Indeed leaders in this company have worked to ensure that they have a positive relationship with their employees which has motivated staff members to reach the goals and objectives of the company. Through sound leadership, managers in the beverage company have worked to tutor, train and mentor those who lack certain critical skills to expand their abilities and repertoire or tool-set needed to perform specific tasks. These leaders also often conduct and chair regular meetings and assessment or appraisal of employee performance, encouraging low performers to improve instead of pointing out or picking their faults to shame them.
Through collaboration and communication, the cornerstones of sound leadership, leaders in this company have created appropriate connections with junior employees and the entire team. This has allowed all employees to take their responsibilities and workloads with the seriousness required propelling the company to great success. In a nutshell, leaders in this company exhibited great listening skills, encouragement, and constant communication with subordinates. They have always ensured that there is employee ownership of their work and autonomy and have provided them with the necessary resources to build their skills and complete their tasks efficiently. As noted in behavioural leadership theories, good leaders focus on their subordinates and maintain constant communication with everyone and all departments to ensure that all teams work in alignment (Cameron and Quinn, 2011). Rather than being benevolent-authoritative leaders, others can follow the consultative and participative leadership as has been done in this company, bringing everyone on-board to work as a team towards achieving or reaching the same goal (Wilson, 2001).
To my surprise, I also noticed that leaders in this company demonstrated a great ability to use the opportunistic leadership style. These leaders demonstrated the ability to adjust their techniques based on what can help the company to reach its objectives. Leaders here adopt different leadership styles according to the prevailing situations to ensure that success is achieved, however, not at the expense of their employees or customers’ needs and preferences. They also portrayed themselves as masters of the paternalistic leadership approach where leaders set goals for their employees and themselves and rewarded good performance. This was also shown by how much the leaders cared for and valued members of their team, always improving their skills and offering them the resources and opportunities to top their performance expectations. Leaders in this company occasionally demonstrated that they be stern, parent and fair and quite intolerant to constant failure. As behavioural theory-based leaders, they have shown that even though they can support their employees by enhancing their skill level through training and offering opportunities, working with them and listening to them, they can also be tough to ensure that the right success path is taken by all team members, a clear demonstration of behavioural theory in operation.

Transformational leadership in practice
I am a follower and enthusiast of media moguls and one media personality particularly caught my eye as a transformational leader as I constantly follow her programs. Often called ‘the Queen of All Media,’ and host of one of the world’s most popular show since 1986 through 2011, her program has been top-rated historically as global talk show. She even became one of the richest or wealthiest African American of this century (21st century). Additionally, she became the first North America’s black multi-billionaire, names one of the most popular and influential people since 2004 through 2009. Some of the features which made her stand out is her transformational leadership skills such as excellent communication skills, her ability to work and connect with other people from different and diverse backgrounds, as well as her inspiring personality. Her charismatic nature and leadership has often made her worth emulating and is a role mode to millions of girls and young people worldwide, especially those from ethnic minority groups. It is evident that she inspired her staff to complete their tasks and reach her vision, otherwise this level of success would not have been possible. To deconstruct her style of leadership, three branches emerges including her values, her vision and the ability to work efficiently in a team. It is because of these leadership qualities that her wealth has also been spread through her philanthropic ventures and foundations. She is admired by many people globally as a leader role model.
The learning from this task and how I will develop as a leader
The lesson I have taken from this assignment is that being a leader is an immense opportunity to change the lives of followers and to ensure that the goals of a company one is working for are achieved. It takes thorough understanding of different leadership theories and styles, and developing certain leadership attributes to have the ability to steer a team towards a certain desired direction to reach the glass ceiling. As a leader, one must learn and master the skills of optimizing efficiency suing various leadership concepts based on the prevailing situations to reach success. Evidently, great leaders are those who have learned to communicate, consult, innovate, transform, behave like leaders and be in control. Success does not require hard headedness and leaving everyone else out of critical decision-making processes. Rather, successful leaders are those who seek help from their colleagues, including from juniors and subordinates, to receive the best advice on how to tackle various challenges effectively.
Besides being able to adopt the right leadership style and theory depending on the situation, soft-skills play a critical role and are inevitably applicable to social and work environments. Evidently, from these theories and leadership concepts, communication takes the centre-stage as a characteristics which leaders must not only have but hone. Good leaders are those who can speak up concerning their visions or the course of action which they believe is right. It is this ability to communicate and share one’s vision that can attract and inspire others to listen to and follow the leader. As a potential great future leader in prospective companies which I will work in, I have a great need and desire to develop my leadership skills in preparation for the future leadership roles, including tackling some challenging situations and conflicts. I have the desire for growth and understand that there is no limit to my personal development.
As noted above, leaders with great achievements are those with great mind-sets and who have worked to overcome different challenges using their unique leadership styles and concepts, always striving to reach greater heights. There are various areas, personal leadership areas and skills that I would like to develop. One of these is time management. My observation from my interaction and research concerning great leaders is that they are usually time conscious. They are individuals who can take different responsibilities and understand how to prioritize specific duties to complete them with specified timeframes. I want to be able to plan ahead and be able to tackle unanticipated interruptions. Another area which I would like to improve on is goal-setting. It is obvious from before mentioned content that great leaders have goals and visions which guide their decisions and actions. They see challenges as a means to make milestones and create lasting solutions. I want to be able to evaluate my progress according to the set goals as a leader and seek innovative and creative ways of reaching them. In this regard, it will be useful if I learned how to set timely, reasonable, actionable, specific and measurable goals.
The above leadership concepts and theories have shown that great leaders share their goals with colleagues and networks and remain receptive and open to feedback to move forward as a team. It has also been mentioned that communication is key towards achieving this kind of leadership. Therefore, developing my communication and interpersonal skills will not only allow me to reach my followers and make them understand me but also make them inspired to walk and work with me towards achieving my goals and those of my company. Leaders must also be good decision-makers, decisions which affect different stakeholders in the company. My goals is also to develop and master this invaluable leadership skill, to be able to make decisions which count and which can lead to the fulfilment of my companies visions.
Admired leaders are those who can defend a chosen path, direction of course of action (House et al., 2004). I want to learn how to make claims based on evidence and stand with the facts to inspire my followers to support me after believing that it is the right path to take. Lastly, I would like to grow my network by developing networking skills. I would like to learn how to build a team of people who support me and campaign or advocate for my vision. There can be no leader without followers or supporters. This will enable me to turn my personal success mission and progress into a team or joint mission. I would like to understand and master how to develop social connections which can work as a tool to navigate through challenging circumstances. Working in a team is important because through this, I will be able to achieve best practice and solve problems by getting the best advice from a pool of ideas. Therefore, I want to learn how build a team-spirit and collaborative efforts, how to manage a team of diverse people to work together as a unit.
Mastering these skills is key to become a great resilient leader. Evidence suggests that great leaders are those who can align these skills into one coherent framework (Richard, 2006). They focus on one direction, with an open-mind to change direction if things are not working for them. Additionally, they are individuals who can cultivate the team or collaborative cultures by building trust using clear expectations and communications. They concentrate on team effort rather than self. Leaders are those who have a plan and who advocate for accountability. They have a network of supporters and seek sustainable results (Morgan, 2011).
In an attempt to try and attain these skills, I begin to take part in governance roles in clubs within my learning institution. This will give me the chance to learn from other leaders, especially how to behave as a leader. This role will also give me an opportunity to learn how to communicate as a leader, as well as how to overcome difficult situations and solve problems. I will also find and join volunteering programs where I can interact with different people and work in a team. In the volunteer groups, I will learn how to appreciate people’s cultures and remain sensitive of other people’s believes and values. To further learn how to create networks and take on serious responsibilities as a leader, I will take on internship opportunities where I will be able to apply the leadership concepts as an employee or leader depending on the roles I will be given. I will also seek to complete a research project during this period, where I will not only be in charge of my team but will be able to make use of different leadership styles and adopt various leadership characteristics and traits to ensure that the project is successful. During my internship and completion of my project, I will create a vision and determine my motivations. I will look for opportunities to be connected with other people, to expand my network or supporters who can make my aspirations a reality. As noted by Smith (2016), great leaders are those who ask themselves what they want or need and come up with attainable goals which can make their visions successful. In this regard, I will be able to set a purpose and inspire people, a team, to work towards positive and desirable outcomes.
Conclusion
This work has shown the role of trait theory of leadership which linked certain traits to the abilities or capabilities of leaders like leadership motivation, the desire to be a leader, tenacity, initiative, ambition, energy and achievement. It has also discussed behavioural theory which, rather than looking into what makes effective leaders, it deals with what is done by effective leaders, that is, how these individuals delegate duties, their communication approaches and the way they motivate and encourage their employees or followers. In this regard, it has delved into the work of Likert’s four management system which exploits exploitive-authoritative leadership style or dictatorial leadership, benevolent-authoritative leadership, consultative style of leadership and participative leadership which is mostly associated with successful and great leaders. This paper has also assessed the theory of transformational leadership in which leaders seek to do the right things while leaders innovate and similarly do things right. Besides inspiring others to follow them, leaders also create major changes. Their followers are usually inspired to put in a lot of effort to reach successful levels together because of their oratory skills, exceptional ability and magnetic.
Further, the work has examined the behaviour of leaders I have encountered in the course of my career in relation to the leadership theories. It has shown how trait Leadership has been used by an inventor to inspire his followers to work independently without being managed or controlled to do their work. Learning trait leadership through the workshop I attended demonstrated just how some traits possessed by leaders can inspire a team and help revolutionise the specific sector one is in. Additionally, the work examined behavioural theory leadership used by leaders in one of the biggest beverage producing company in the world. It has shown how leaders using the behavioural approach are both task-oriented and people-oriented, enforcing specific behaviours at the workplace to ensure certain success activities are taken to reach tremendous success. Lastly to show transformational leadership at work, I have noted that watching a media mogul, a lady who origin and background did not limit her from achieving her gaols has used her charisma and great interpersonal skills to transform herself and the media industry by amassing global viewership and becoming an idol to many. Evidently, communication has come out as a key feature in almost all leadership aspects, be it building a team, setting goals, creating a vision and communicating it to amass followers and ensuring that the whole team is working as a unit to achieve success. To acquire these leadership skills, I plan to attend volunteer activities, take on projects and go through internship opportunities to learn from other leaders and be able to practice the learned leadership concepts and theories.
Dig deeper into Leadership theories and styles with our selection of articles.
References
Alvesson, M. and Sveningsson, S., 2015. Changing organizational culture: Cultural change work in progress. Routledge.
Amzat, I.H., Taslikhan, M., Walters, L.M. and Walters, T., 2020. Likert's 4-Management System Instrument Psychometric Properties-University Management-Malaysia. Pertanika Journal of Social Sciences & Humanities, 28(3).
Buchanan, D.A. and Huczynski, A.A., 2019. Organizational behaviour. Pearson UK.
Breevaart, K. and Bakker, A.B., 2018. Daily job demands and employee work engagement: The role of daily transformational leadership behaviour. Journal of occupational health psychology, 23(3), p.338.
Cameron, K.S. and Quinn, R.E., 2011. Diagnosing and changing organizational culture: Based on the competing values framework, [E-reader Jossey-Bass].
Chow, T.W., Salleh, L.M. and Ismail, I.A., 2017. Lessons from the major leadership theories in comparison to the competency theory for leadership practice. Journal of Business and Social Review in Emerging Economies, 3(2), pp.147-156.
Cui, L., Wang, Y., Chen, W., Wen, W. and Han, M.S., 2021. Predicting determinants of consumers' purchase motivation for electric vehicles: An application of Maslow's hierarchy of needs model. Energy Policy, 151, p.112167.
Dorsch, T.G., 2020. Development of an Effective Organizational Performance Instrument to Facilitate Post-Secondary Institutional Change: A Variation on Likert's Management Systems 1-5 (Doctoral dissertation).
Denison, D., Hooijberg, R., Lane, N. and Lief, C., 2012. Leading culture change in global organizations: Aligning culture and strategy (Vol. 394). John Wiley & Sons.
Ding, X., Li, Q., Zhang, H., Sheng, Z. and Wang, Z., 2017. Linking transformational leadership and work outcomes in temporary organizations: A social identity approach. International Journal of Project Management, 35(4), pp.543-556.
Gifford, W., Graham, I.D., Ehrhart, M.G., Davies, B.L. and Aarons, G.A., 2017. Ottawa model of implementation leadership and implementation leadership scale: mapping concepts for developing and evaluating theory-based leadership interventions. Journal of Healthcare Leadership, 9, p.15.
House, R.J., Hanges, P.J., Javidan, M., Dorfman, P.W. and Gupta, V. eds., 2004. Culture, leadership, and organizations: The GLOBE study of 62 societies. Sage publications.
Ju, M.Y. and Jim, L.J., 2019, September. UX Design Management: Type of Management Systems and Communication Strategies in Technology Industry. In 2019 3rd International Seminar on Education, Management and Social Sciences (ISEMSS 2019) (pp. 659-663). Atlantis Press.
Keskes, I., Sallan, J.M., Simo, P. and Fernandez, V., 2018. Transformational leadership and organizational commitment: Mediating role of leader-member exchange. Journal of Management Development.
Likert, R. and Bowers, D.G., 2013. Management Systems'. Attitudes, Conflict, and Social Change, p.101.
Morgan, G., 2011. Reflections on images of organization and its implications for organization and environment. Organization & Environment, 24(4), pp.459-478.
MacNeill, N., Silcox, S. and Boyd, R., 2018. Transformational and Transactional Leadership: a false dichotomy of leadership in schools. Education today, 11.
Richard, D.L., 2006. When cultures collide: leading across cultures. Nicholas Brealey International.–2006.-342 p.
Rowland Jr, C.R., 2018. Book Review: Politics, Ethics, and Change: The Legacy of James MacGregor Burns by George R. Goethals & Douglas Bradburn, Eds.
Rosari, R., 2019. LEADERSHIP DEFINITIONS APPLICATIONS FOR LECTURERS’LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT. Journal of Leadership in Organizations, 1(1).
Salihu, M.J., 2019. A Conceptual analysis of the leadership theories and proposed leadership framework in higher education. Asian Journal of Education and Social Studies, pp.1-6.
Smith, N.K., 2016. Authentic Leadership can be measured within Organizations Through the use of Leadership Assessment Centres: A Factor Analytic Study of the Authentic Leadership Construct (Doctoral dissertation, Kent State University).
Uslu, O., 2019. A general overview to leadership theories from a critical perspective. Маркетинг і менеджмент інновацій, (1), pp.161-172.
Wilson, F., 2001. The International Handbook of Organizational Culture and Climate, CL Cooper, S. Cartwright and PC Early (Eds). Wiley, Chichester. 2000. European Management Journal, 19(6), pp.683-684.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Likert’s four system of management (Amzat et al., 2020)
Appendix 2: Maslow’s hierarchy of needs (Cui et al., 2021)
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



