A2 Revision questions
Gene’s business has the following balances at 30 November:
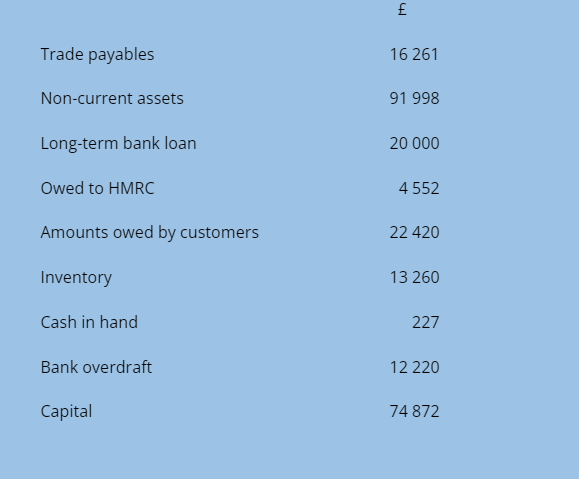
Gene’s business has an overdraft limit of £14 000. Half of the amount payable to HMRC has been owed for almost two months.
Prepare a statement of financial position for Gene’s business at 30 November
Comment on the cash position of the business
-
Deirdre’s business has non-current assets of £30 000, current assets of £17 500 and current liabilities of £3 600. There are no long-term liabilities. Deirdre’s capital is?
- £51 100
- £16 100
- £43 900
- £8 900
-
The following figures has been provided by Jennifer for her catering business. Sales £8,200, Opening inventory £1,300, closing inventory £900, Purchases £6,400, Carriage inwards £200. Calculate Jennifer’s cost of goods sold
- £6,800
- £1,200
- £7,000
- £6,200
-
TB Wallis started trading on I January 2019, he has the following figures for the first year of trading: Carriage inwards£3,470, Returns outwards£1,390, Return inwards£7,470, Sales £249,000, Purchases £168,300 and Inventory as at 31December 2019£25,630.
Calculate his gross profit for the first year of trading:
- £104,250
- £100,250
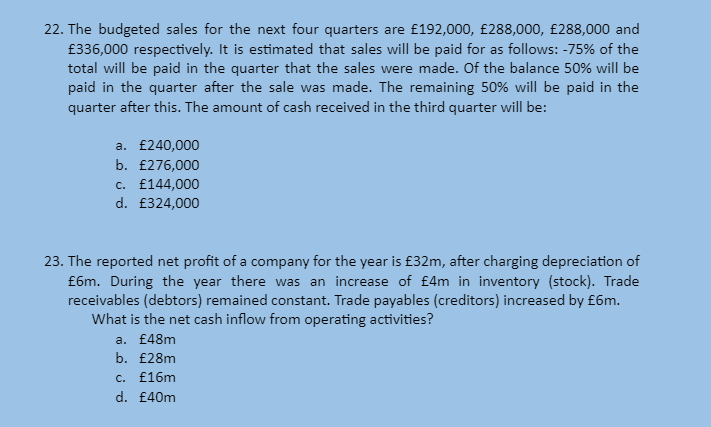
- £96,780
- £116,380
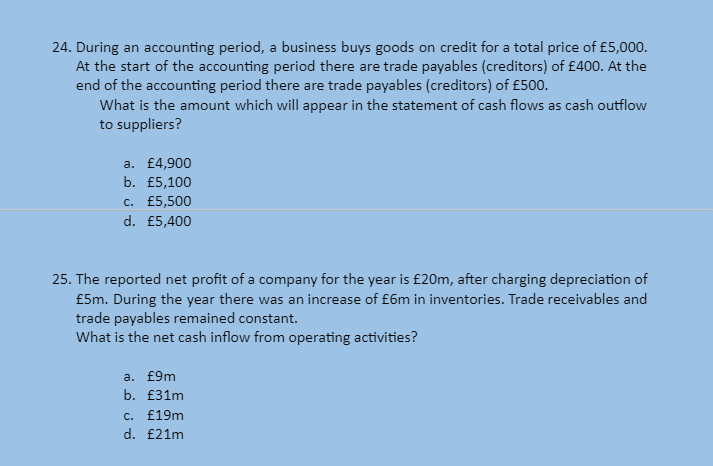
-
A motor vehicle which cost £30,000 is depreciated at 20% per annum using the reducing balance method. The depreciation charge for the second year would be:
- £13,800
- £8,000
- £4,800
- £7,200
-
If a business’ rent for the year is £38,000 but it had only paid £32,000, this means:
- The total rent incurred during the year should be £32,000
- There is an accrual of £32,000 for the year
- The total rent incurred during the year should be £38,000
- There is a rent accrual of £6,000 for the year to bemade in the accounts

-
A business buys equipment costing £28,000 and depreciates it using the reducing balance method at 20% per annum. Three years later it was sold for £15,000. The profit or loss on the transaction was:
- Neither a profit or a loss
- A profit of £8,784
- A profit of £664
- A loss of £664
-
A motor vehicle which cost £30,000 is depreciated at 20% per annum using Straight line method. The depreciation charge for the second year would be:
- £12,000
- £6,000
- £3,000
- £4,800
-
Which of the following three statements about marginal costing are correct?
- Marginal costing:
- is an approach to costing that excludes fixed costs?
- provides a sounder basis for decision making than absorption costing
- is only useful in respect of businesses that incur variable costs
-
Which of the following three statements about marginal costing are correct?
- Marginal costing:
- is an approach to costing that excludes fixed costs?
- provides a sounder basis for decision making than absorption costing
- is only useful in respect of businesses that incur variable costs
-
A business makes 2,000 units of a particular product. It spent £24,000 on material and it paid its operatives £40,000. Other costs of running the factory were £50,000. The sales force was also paid £18,000 and the head office costs were £100,000. In order to break even the selling price per unit will have to be:
- £84
- £116
- £32
- £66
-
A company currently sells 10,000 units of a product at £9.00 per unit and makes £20,000 profit. Variable costs currently stand at £6.00 per unit. By how much would variable costs have to increase before the company makes neither a profit nor a loss?
- £2.00
- £3.00
- £4.00
- £1.00
-
Prate’s business makes an operating profit of £29 975 in the year ended 31 December 2018, after deducting £7668 for depreciation. At 31 December 2018 her statement of financial position showed inventory of £33 250, receivables and prepayments of £26 772 and payables of £35 556. On 31 December 2019 the corresponding figures were: inventory £34 490, receivables and prepayments £22 894 and payables £29 493. What is the net cash inflow from operating activities to be included in Prate’s statement of cash flows for the year ended 31 December 2019?
- £33 400
- £34 218
- £38 588
- £41 068
-
he breakeven point in units is represented by the equation:
- (Sales revenue - Fixed costs)/ Contribution per unit
- Fixed costs / selling price per unit
- Fixed costs / Contribution per unit
- Fixed costs / Variable costs
-
Bakersfield Limited purchases some of its goods on credit and some for cash. On average, in any given month, the company would expect 20% of its purchases of goods to be paid for in cash. 60% of the purchases on credit would be paid for in the next following month, and 40% in the month after that.
- September £126 000
- October £135 000
- November £128 500
- December £121 500
-
Bertrand sells goods entirely on credit. In respect of sales in any given month, he expects 50% to be paid for in the next following month, 40% in the month after that, and 10% in the month after that. (So, for example, 50% of sales made on credit in January would be received in February, 40% in March and 10% in April).
- May 352 000
- June £53 500
- July £57 800
- August £56 000
-
Grimsby Ltd is specialist in bath products. They are about to introduce a new product into the market. The estimated selling price is £1,452, the variable cost is £353 unit and the fixed cost is £94,325. The directors will like to know many baths they have to sell to achieve a profit of £50,000.
- £124
- £144
- £131
- £136

-
Which of the following transactions increases or decreases the net cash flow from operating activities?
- Sale of a non-current asset
- Purchase of inventory for resale
- Payment of interest on a loan
- Drawings
-
A business has trade payables at its year end of £206,460. Purchases for the year are £1, 952,278 of which 90% were made on credit. What is the trade payable turnover?
- 42.9 days
- 38.6 days
- 34.7 days
- 11.7days
-


Continue your exploration of A Visual Exploration of Recent Protests and Research Findings with our related content.
What Makes Us Unique
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts
Dissertation Samples
Assignment/Essay Samples
Research Proposal Samples



