Business Operation And Process Management
Introduction
Business operations are the activities being performed daily in the execution of business for the key purpose to generate profit. The process management is part of business operation involves developing methods for discovering, modelling and analysing, optimising as well as automating the business process with the key focus to improve corporate performance. In this assignment, the way business operation and process management are maintained in properly optimising supply chain operation is discussed. Further, way lean management helped during my tenure at the Accenture Solution Private Limited to resolve business problem for developing effective business operation and process management is also discussed. Lastly, reflection regarding my learning is the module is mentioned. For students seeking insights into business dissertation help, understanding these concepts can significantly enhance their understanding of operational efficiencies.
Task 1: Supply Chain Management Optimisation

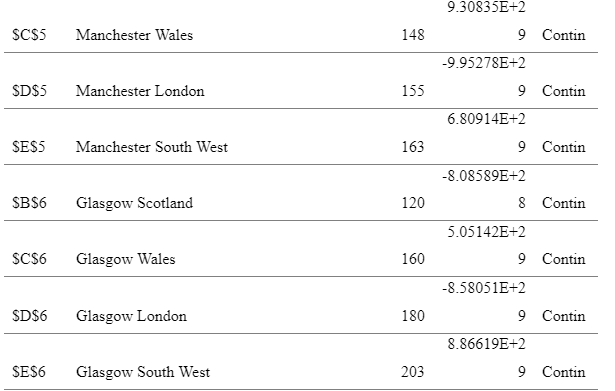
Table 1: The Excel Solver Spreadsheet
(Source: Author)
Most appropriate places to establish other plants
So as to minimise on costs, plants should be established in Scotland in the city of Glasgow and in South West in Swindon. These are the two locations where from the analysis the costs of production and transportation when added to the total fixed costs would be lowest. The demand forecasts for the four regions are 180,000 units for Scotland, 95,000 units for Wales, 175,000 units for London and 130,000 units for South West. According to the available business plans, the capacities for each plant could be 180,000 or 250,000 units annually. For Wales and South West, the plant with a capacity of 180,000 units would be most appropriate. On the other hand, the 250,000 unit plant would be most appropriate for Scotland and London. Given that the demand forecasts of these two areas are at par with the space of the 180,000 units plant, a plant with a higher capacity would be more appropriate.

Costs
The annual fixed cost for an 180,000 units plant in Swindon is 4,000,000 £, while the annual fixed cost for a 250,000 units plant is 4,400,000£. In Birmingham, the annual fixed cost for an 180,000 units plant in Birmingham is 3,500,000£, while the annual fixed costs for a 250,000 units plant are 3,850,000. The annual fixed costs for an 180,000 unit’s plant in Manchester are 3,900,000, while the annual fixed costs for a 250,000 unit’s plant are 4,290,000£. The annual fixed costs for an 180,000 unit’s plant in Glasgow are 3,100,000, while the annual fixed costs for a 250,000 unit’s plant are 3,410,000£.
Sensitivity analysis and other requirements
In this case, the production and transportation costs are the variable costs. At any location, an increase of any of these costs would see a general increase in the operational costs, while a decrease would see the costs of operation go down. Other factors that need to be taken into consideration include competition from other manufacturers, set up costs and financing options. Whenever researching about a market, there is really a lot that always needs to be done. There exists a high possibility that other manufacturers already offer what you intend to offer. As such it is always important to do an analysis of the competitors, their market share and the percentage of the market that will be available to you (Axin, Baffo and Xia, 2014). Additionally, starting a manufacturing firm is quite different from starting any other type of a firm. A lot of money may be required for the initial setup. It is also necessary to purchase specialised equipment and machinery. It will also be necessary to hire highly skilled specialists in the field you venture into. An analysis of the available financing options will also be necessary. So as to meet a business’s financial costs, it is important to have access to extensive amounts of capital. If there is only minimal capital available, then it will be necessary to rethink the plans in place. They could be halted until more money is available.
Task 2: Lean Management
Describing Jones’s statement regarding the chosen business problem
According to my experience, while working at Accenture, the business problem faced is experiencing issues with providing satisfactory and timely answers to resolve queries regarding HR and Payroll raised by the employees at North American centre of the same organisation. This is because in many instances I was unable to determine the way and which information is to be provided to effectively resolve the queries. Jones mentions that lean management involves the use of scientific methods for solving business problems with the purpose to create value (Biazzo et al. 2016). The statement is effectively applicable in relation to application of lean management theory to solve problems faced in relation to answering the HR and payroll queries for the employees at North America by me while working at the Accenture Solutions Private Limited.
According to Jones’s Lean Management, value is able to be created when the needs and demands of the customers or others are effectively understood and strategies are developed to meet them (Plenert, 2016). In relation to this, the application of lean management helped me to develop knowledge that problems regarding satisfactorily answering queries of HR and payroll of the employees at North America can be resolved if the needs and demands of information to be mentioned for the queries are effectively understood by me. This is because by delivering answers according to the needed information for the queries of the employees it would make them feel valued that no details are hidden from them. As commented by Zhou (2016), value creation is important as it makes the employees become trusted and loyal to the organisation out of satisfaction. Thus, creating value by answering as per the need and demand for information in the asked queries by the employees would also lead me to lower turnover of employees in Accenture along with satisfactorily resolving their queries. This is because the employee out of trust created through valuing them would make them remain working for the organisation.
Take a deeper dive into NCFE Business skills with our additional resources.
The Jones’s scientific method in lean management involves mapping the value stream in which the key goal is to identify all the activities that offer value to the employees or customers (Kadarova and Demecko, 2016). The activities which do not offer value to them are considered as waste and the waste in this aspect are of two types that are non-value added yet necessary and the other is non-value added and necessary. The later is referred to be pure waste which is to be eliminated whereas the former is required to be reduced as much as possible to reduce cost (Bhasin, 2015). This information led me to understand that unnecessary steps in answering the queries of the employees at the North American centre are to be reduced so that wastage of resources in the process is limited. It is going to make me be able to answer queries of the employees regarding HR and payroll at the appropriate time, in turn, avoiding them to feel that their queries are being ignored as they are not timely replied. Thus, lean management leads me to create value in the end as the employees are provided answers regarding their queries in an appropriate manner within reduced time.
The scientific methods of lean management informs that to create flow of actions in the changed way effective monitoring is to be done to ensure the changed actions are running smoothly that are created after removal of wastes from the value stream (Urban, 2015). This principle informed me that the changed actions for answering made according to the value stream of the employees while resolving queries related to HR and payroll are to be assured that they are running smoothly. It is essential as inability to ensure the changed action in answering the queries to be running smoothly would lead to face the same problems that are being previously experienced. Thus, this principle was able to create value in the end by ensuring consistency of actions to resolve previous problems being faced while answering the queries of HR and payroll made by the employees in North American centre of Accenture. As stated by Kumar et al. (2015), scientific method of lean management informs to establish pull which means that no changes in actions are to be made until the customers or employees orders it to be done. This principle informed that no extra changes in actions for answering the questions regarding the HR and payroll to the employees are to be done until they order it. Thus, it allows providing answers to the queries to the employee just in time and not before they place it.
The other scientific method of lean management informs that perfection is to be perused which can be established by systematically as well as continuously removing the root causes of the poor quality activities in the organisation. It requires collaborative effort from the employees for its success (Bortolini et al. 2016; Seth et al. 2017). According to this method, it is understood that the changes in actions made by me in the HR and Payroll department of the Bangalore centre of Accenture for resolving the queries of employees of North American centre of Accenture are to be adopted by all other employees in the centre working at the HR and Payroll department. This is required so that the root causes of facing problems in providing satisfactory and timely answers to the queries of employees of the North American centre can be resolved in the Bangalore Accenture. Thus, applying the lean management theory was effective as it lead to develop proper value in an efficient way to resolve problems in solving the queries regarding HR and payroll made by North American employees of Accenture.
Explaining and Discussing benefits and challenges related to broader Lean Management regarding the chosen organisation
The implication of broader lean management methodologies in the Accenture is going to help them receive various benefits. As mentioned by Yang et al. (2015), organisations by implementing lean management methodologies at work are able to create increased efficiency of employees in accomplishing tasks. This is because by its implication the organisation is able to eliminate actions that are not at all required in accomplishing the goals of the department and avoid movement pattern of employees that do not create any value. Thus, by its implication, Accenture is able to reduce defects in the work strategies ensuring increased efficiency of the employees to work appropriately. As argued by van Assen (2018), defects in the work strategies often lead to expensive inspection and increased rework that takes increased time is meeting targets reducing the efficiency of employees at work. Accenture by adopting broader lean management methodologies would be able to reduce rework by avoiding defects ensuring timely meeting of the deadline of the tasks, in turn, ensuring better efficiency of the employees.
The implication of broader lean management methodologies in the Accenture would lead them to achieve better quality products and services to be developed for delivering them to the customers. This is because the methodologies help the organisation to get rid of flaws and faults at work. As commented by Wang et al. (2015), lean management methodologies lead the project team of the organisation being able to identify the root cause of the faults at work. This leads the team in the organisation to improve their actions and processes at work from the root level creating long-term benefits. Therefore, Accenture by adopting lean management methodologies is beneficial to create long-term solutions for reducing defects at work and improving the quality of services through improvement of their actions. As commented by Netland et al. (2015), lean management methodologies lead the organisation to eliminate overproduction of services by adjusting production according to the customer demand in the market along with simplifying the services for eliminating extra processing. It helps the organisation to meet the demands in the market of their target customers with the use of fewer employees without laying them off. This is because lean management makes it mandatory for the organisation that the extra employees are to be trained for reassigning them to more effectively use their talents in other fields for improving the business of the organisation (Leyer et al. 2015). Thus, lean management methodologies are beneficial for Accenture as it allows them to use their employees in a better way without turning them off. This result Accenture to assure the employees of their job security, in turn, helping employees to feel valued and provide more work effort.
The lean management methodologies assist the organisations to eliminate overproduction of services. This results the organisation to have increased time and space for more services to be produced as producing services which are no more than the demand of the customer makes the organisation deliver the services more quickly than expected (Chugani et al. 2017). Thus, the lean management methodologies benefit Accenture to be able to effectively optimise time to put it in a more productive way for deriving better profits from their business operation. As asserted by Olesen et al. (2015), in lean management the organisation is able to provide opportunity to the employees to improve their skills as well as abilities. Thus, adopting broader lean management methodologies is going to benefit Accenture to let their employees develop their talent which in turn is going to make them happier to work with greater effort.
In order to implement broader lean management methodology, the organisation requires acquiring right resources. The cost for arranging the resources are to be covered by the company before they are able to see the benefits due to its implication in the business process (Nogueira et al. 2018). Thus, the limitation of applying lean management methodologies in Accenture is that the company require waiting before their investment in the lean payoff. Therefore, it is challenging for Accenture to determine whether to take the step as it is not always sure that the changes in actions made through lean would offer them early benefits. As stated by Agarwal and Sharma (2016), making changes through lean management methodologies leads the organisation to face increased labour cost as new and innovative skills are to be taught to the employees through training. Thus, adopting theses methodologies poses challenge for Accenture to increase their labour cost to make the employee being suitable for the change. However, after the changes are implemented through the lean methodologies the labour cost is going to lower down allowing Accenture to be able to manage the challenge.
The weakness faced as a result of implication of broader lean management methodologies is that employees in the organisation feel fear of adopting new innovation through the process even though it is about to bring improvement. This is because the employee experiences hardship to set aside their previous processes and practices to work in a new way (Powell and Netland, 2016). Thus, Accenture by adopting broader lean management methodologies would face opposition from employees who are not willing to innovate and stick to the previous ways of working due to fear that they cannot work in the same effective way as of present with adoption of the new innovative action strategies.
Illustrating the way relationship between Quality and Performance measurement is able to be enhanced by the Lean Management intervention
An effective lean management intervention informs that people who are involved at the work are able to more effectively understand the problem faced at work and they are to be involved in creating solution for making the changes to be sustained (Jayaram and Xu, 2016). This is because the employees involved at work have practical knowledge and perception regarding the areas to be searched for to identify the cause of the problem and nature of changes to be made in activities for properly resolving the problem. This intervention of the lean approach enhances relationship between quality and performance measurement at Accenture as the defects or faults at work are effectively resolved by the staffs to deliver quality services in turn showing better performance measurement at work by delivering upgraded services. As asserted by Bevilacqua et al. (2015), lean management intervention informs that all nature of waste is to be eliminated including the steps in the service production process that do not create any value for the organisation. This is because it is going to improve quality and performance at work by the strategic use of resources in an efficient way to reach the demanded nature of services. Thus, it is able to improve the relationship between quality and performance measure at Accenture as the employees are seen to perform with efficiency without wasting any resources resulting to deliver quality services.
The value creation through lean management intervention is able to enhance the relationship between quality and performance measurement in the organisation. This is because during value creation the needs and demands of the customers are kept in mind by the employees and they accordingly make changes to assure quality of the services. It also leads to their better performance as the employees understand the aspects to be focussed on at work to deliver the demanded quality of service (Thurston and Ulmer, 2016). As mentioned by Sony (2018), lean management intervention leads the employees to create sustainable change in delivering services by moving their attitude from being compliant to commitment towards work. This means that lean management intervention makes the employees do their work with the development of believe that their proper effort is going to create value for the service they are presently providing. It leads to enhance relationship between quality and performance management at Accenture because employees working with commitment in the company provides every effort to show their best performance to deliver quality services to the customers to make them effectively satisfied while receiving the services.
The lean management intervention has the principle that all staffs in the organisations are to be equally involved at work and they are to be encouraged and fostered as well as all their opinions are to be heard while resolving a problem at work (Hussain and Malik, 2016). This is because it is going to result the employee feel valued which would lead them to show better performance by delivering greater effort at work due to satisfactory working environment. It also leads to improved delivery of quality services as due to greater value at work the employee works more minutely to ensure less or minimum faults are experienced to deliver at the end best quality services. As commented by Antony et al. (2016), use of visual cues to communicate information at work is one of the basic principles of lean management intervention. This is because visual cues develop clear mental imagery in the minds of the employees regarding the things they are to achieve through their services to the customers. It leads to enhance the quality and performance measurement for the organisation as the clear mental image leads them to perform in a better way without any confusion regarding what they have to achieve in turn making them deliver quality services.
Task 3: Reflection
Critically reflecting on personal learning from the module
In this module, I initially learned sensitivity analysis model is also known as “what-if” analysis which informs the way of predicting the outcome of any decision based on certain number of variables. The knowledge regarding this model helped me to develop understanding as leader in my organisation regarding the way investment is to be made so that total cost of any project is minimised. Moreover, this model also helped me to make decision by considering actions that may assist me in strengthening the weaker spots in the project. However, I was unable to develop knowledge regarding the use of the sensitivity analysis model in identifying and exposing inappropriate forecasts. Thus, I am still unable to concentrate on relevant variables as a leader to act efficiently in minimising the total cost of any projects. This module led me to understand the way excel Solver is to be used in executing sensitivity analysis to make decision regarding financial management.
In the next part of the module, I learned about lean management that it is process to run an organisation which supports the concept related to continuous professional improvement. This nature of improvement is a long-term approach at work which systematically seeks towards achieving small and incremental changes in the business process to improve quality and efficiency. The idea about lean management developed from the module lead me as the leader in the Accenture to take effective decision that creates minimum waste during production of services to be delivered to the customers. Moreover, the idea regarding this concept helped me as leader to identify the changes to be made in the working process in the Accenture so that fewer problems are encountered by the employees. This led me to ensure less interruption is encountered at work creating smoother workflow for the employees at Accenture.
The idea regarding lean management principles informed me as a leader at Accenture to develop ways in which the sustainability of the business can be increased. Further, I learned that to implement broader lean management methodologies in Accenture I as a leader require to arrange right amount of resources before I can actually see the benefits of it for the organisation. This is because the change to be executed through the implementation of these resources in lean management requires time for showing they are payoff. As leader in the Accenture, I understood that I may face opposition from the employees in making changes through lean management as they may fear towards accepting the change. However, I would be able to resolve this resistance if the fear of the employees can be lowered through training them in making them proficient to accept the change. I also learned regarding the way certain lean management interventions such as employee commitment, value creation by understanding customer orientation, waste reduction and others are able to create enhanced quality and performance measurement for the organisation.
At the end of this module, I personally feel that I require taking action to involve into lean management training so that I can effectively implement the concept at work in more detail for assuring better business sustainability of Accenture. I also require developing more information through research and training about identifying inappropriate forecasts that would guide me to concentrate more on effectively identifying relevant variables responsible for proper minimisation of total cost of projects.

Dig deeper into Change Management at EMPRESS Hotel Group with our selection of articles.
Conclusion
The discussion informs the plants are to be established in Scotland in the city of Glasgow and in South West in Swindon to let the organisation have minimum expenditure. The Jones’s statement regarding lean management was true as by using the scientific methods mentioned in the approach it was seen that the problem faced in not being able to timely provide satisfactory answer to employees of North American Accenture was resolved and value was able to be created among them. Further, it is seen that the benefits of using lean management by Accenture are minimum wastage of resources, happier employees, better business sustainability and others. However, the challenges to be faced with its implementation are opposition from employees, prior arrangement of resource investment, increased labour charges and others. Lastly, it is seen that lean management intervention of value creation, employee commitment and others are able to enhance quality and performance measurement in the organisation.
References
- Agarwal, A. and Sharma, M.K., (2016). Lean management–a step towards sustainable green supply chain. Competitiveness Review, 26(3), pp.311-331.
- Antony, J., Setijono, D. and Dahlgaard, J.J., (2016). Lean Six Sigma and Innovation–an exploratory study among UK organisations. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 27(1-2), pp.124-140.
- Askin, R.G, Baffo, I and Xia, M., (2014). Multi-commodity warehouse location and distributionplanning with inventory consideration.International journal of Production Research. 52 (7), pp.1897-1910.
- Bevilacqua, M., Ciarapica, F.E. and Paciarotti, C., (2015). Implementing lean information management: the case study of an automotive company. Production Planning & Control, 26(10), pp.753-768.
- Bhasin, S., (2015). Lean management beyond manufacturing. New York, NY: Springer.
- Biazzo, S., Panizzolo, R. and de Crescenzo, A.M., (2016). Lean management and product innovation: a critical review. In Understanding the Lean Enterprise (pp. 237-260). Springer, Cham.
- Bortolini, M., Ferrari, E., Galizia, F.G. and Mora, C., (2016). A reference framework integrating lean and green principles within supply chain management. International Journal of Social, Behavioral, Educational, Economic, Business and Industrial Engineering, 10(3), pp.859-864.
- Chugani, N., Kumar, V., Garza-Reyes, J.A., Rocha-Lona, L. and Upadhyay, A., (2017). Investigating the green impact of Lean, Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma, 8(1), pp.7-32.
- Hussain, M. and Malik, M., (2016). Prioritizing lean management practices in public and private hospitals. Journal of health organization and management, 30(3), pp.457-474.
- Jayaram, J. and Xu, K., (2016). Determinants of quality and efficiency performance in service operations. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 36(3), pp.265-285.
- Kadarova, J. and Demecko, M., (2016). New approaches in lean management. Procedia Economics and Finance, 39, pp.11-16.
- Kumar BR, R., Sharma, M.K. and Agarwal, A., (2015). An experimental investigation of lean management in aviation: Avoiding unforced errors for better supply chain. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 26(2), pp.231-260.
- Leyer, M., Vogel, L. and Moormann, J., (2015). Twenty years research on lean management in services: results from a meta-review. International Journal of Services and Operations Management, 21(4), pp.389-419.
- Netland, T.H., Schloetzer, J.D. and Ferdows, K., (2015). Implementing corporate lean programs: The effect of management control practices. Journal of Operations Management, 36, pp.90-102.
- Nogueira, D.M.D.C., Sousa, P.S. and Moreira, M.R., (2018). The relationship between leadership style and the success of Lean management implementation. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 39(6), pp.807-824.
- Olesen, P., Powell, D., Hvolby, H.H. and Fraser, K., (2015). Using lean principles to drive operational improvements in intermodal container facilities: A conceptual framework. Journal of Facilities Management, 13(3), pp.266-281.
- framework. Journal of Facilities Management, 13(3), pp.266-281. Plenert, G.J., (2016). Lean management principles for information technology. US: CRC Press.
- Powell, D.J. and Netland, T., (2016). The Routledge Companion to Lean Management. London: Routledge.
- Seth, D., Seth, N. and Dhariwal, P., (2017). Application of value stream mapping (VSM) for lean and cycle time reduction in complex production environments: a case study. Production Planning & Control, 28(5), pp.398-419.
- Sony, M., (2018). Industry 4.0 and lean management: a proposed integration model and research propositions. Production & Manufacturing Research, 6(1), pp.416-432.
- Thurston, J. and Ulmer, J.M., (2016). The Principles of Lean Manufacturing. Franklin Business & Law Journal, 2016(2).pp.89-122.
- Urban, W., (2015). The lean management maturity self-assessment tool based on organizational culture diagnosis. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 213, pp.728-733.
- van Assen, M.F., (2018). Exploring the impact of higher management’s leadership styles on lean management. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 29(11-12), pp.1312-1341.
- Wang, T.K., Yang, T., Yang, C.Y. and Chan, F.T., (2015). Lean principles and simulation optimization for emergency department layout design. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 115(4), pp.678-699.
- Yang, T., Kuo, Y., Su, C.T. and Hou, C.L., (2015). Lean production system design for fishing net manufacturing using lean principles and simulation optimization. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 34, pp.66-73.
- Zhou, B., (2016). Lean principles, practices, and impacts: a study on small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Annals of Operations Research, 241(1-2), pp.457-474.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



