Payback Period and Internal Rate of Return
Section A
Question A3
a)
In the context of investment planning and resource management, companies consider different techniques of investment appraisal to evaluate the profitability and reliability for attainment of different objectives. In this regards, the payback period is being termed as the most popular and easy approach to evaluate investment proposal. The payback period is being termed as the time duration in which an investment options could recover the whole initial investment through future cash flows. By comparing the payback periods of different investment proposals, an organisation or investor would be able to select the most appropriate investment options that are having minimum payback periods. The shorter payback period provides higher earning opportunities (Jiambalvo, 2019). The computation of payback period has found very simple approach. Moreover, it provides a great support to investors for assessing the risk of the investments. On the other hand, the internal rate of return determines the present value of future cash flows that are aligned with the particular investment proposals. Moreover, the internal rate of return is highly dependent inflow and outflow in relation to investment. In addition to that, it has found that internal rate of return assists investors for determining whether an investment proposal increase’s the firm’s value or not. This tool considers all future cash flows that are aligned with certain investment proposal. On the contrary, the payback period method considers the cash flow only for particular period in which the whole initial investment could be recovered in an efficient manner (Warren, Reeve and Duchac, 2016). This method is crucial in the field of finance dissertation help, where students explore various investment appraisal techniques to understand their applications in real-world scenarios.

Moreover, the internal rate of return is also considered the time value of money or cost of capital but the payback period method is failed to consider the time value of money in the investment planning and resource management. Moreover, the internal rate of return has been found very effective to consider the all kind of future cash flows for checking the project viability. However, the computation of the cost of capital has been found a very difficult task to management because it requires a systematic assessment of the cost of capital for making appropriate decisions. In addition to that, the internal rate of return does not provide appropriate support for managing the value-maximisation decisions in the investment planning and resource management (Davis and Davis, 2019). Therefore, it would not find an appropriate tool in the capital rationing decisions. Moreover, this model cannot be used in situations in which the sign of the cash flow of a project has been changed. In similar way, the payback period ignores the time value of money along with risk factor in future cash flow. Furthermore, the payback period ignores the cashflow beyond the payback period. Apart from that the payback period approach has found a quick and easy approach to execute in the investment planning and project selection. In addition to that, it also provides a crude measure of liquidity for carrying investment appraisal. Therefore, the payback period is being termed as the better method as compared internal rate of return.
b)
In the context of contemporary business environment, outsourcing of different projects or tasks is being termed as the most critical tool that is used by different companies for managing the business expenditures. In this regard, the application of full costing would support the companies in consideration of all business expenditures associated with outsourcing operations in assessing the final product cost. The outsourcing operations-based on full costing approach provides a great support for carrying the marginal analysis through an organisation would be able to deal with qualitative costs and other benefits (Islam and Hu, 2012). In this regards, the cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis has been found very effective for the identification of the implication of the change in fixed and variable costs over the business profitability. In this context, the application of full costing approach in the outsourcing operations would support companies or managers for carrying out an optimum assessment of cost of final goods and services in an efficient manner. Moreover, the CVP analysis has been found very effective in determining average number of units that should be sold by an organisation for attainment of the breakeven point along with attainment of minimum profit margin values (Appelbaum, Vasarhelyi and Yan, 2017). For performing a systematic assessment of the pricing of different products and services that are aligned with the outsourcing practice, the CVP analysis would be emerged as a great tool for carrying out profit planning with consideration of all fixed and variable expenditures that are also linked with the full costing system. It would offer accurate information about the cost per unit so as an organisation could be able to determine an appropriate sales price with appropriate profit margin. For the application of full costing, the CVP analysis makes several assumptions related to sales price, and fixed and variable cost per unit should constant in which an organisation would be able to estimate a particular sales volume that would be found essential to cover-up all business costs (Ibarrondo-Dávila and Gámez, 2015). The consideration of CVP in the outsourcing operations has been found very effective tool in cutting the business expenditures because an organisation could ensure about the optimum utilisation of resources in an efficient manner and could identify new areas where an organisation could achieve the cost control related goals. It supports the business entity in attainment of quality control related objectives in an efficient manner without increasing the business expenditures.
Question A4
In the context of contemporary business environment, the usage of budgeting practices has been enhanced on significant manner for optimum allocation of different resources or funds in different activities for attainment of different business objectives. For supporting a variety of business operations, the budgeting is being termed as a systematic process of designing, implementation and development of different kinds of operating budget (Butler and Ghosh, 2015). It is considered as an important managerial process that covers different variables such as budgeting planning, preparation, and budgetary control. It applies the highest level of accounting for supporting a variety of business operations to manage availability and allocation of funds to meet distinct business requirements. Moreover, it could be considered in managing the forecasting operations for assessing the future state of world but the efficiency of budgeting practices is highly dependent on the validity and reliability of data collection process along with its appropriateness to meet different aspects of corporate financial planning and resource management.
The budgeting process is used by an organisation to attain the different projects objectives. Therefore, the primary purpose of the budgeting is to manage an appropriate planning for different phases and activities of business operations and managing the coordinated business operation to maximise the efficiency of different department with consideration different of the effective organisational control (Mihăilă, 2014). In the context of contemporary business environment, the concept of budgeting assists companies and managers to manage optimum business planning in which management is focused to evaluate the firm’s future sales value, production cost and other business expenditure for attainment of desired goals. Moreover, it is also considered by manager to ensure an appropriate composition of capital with reference to availability of funds and cost of capital. The budgeting seems a great tool to support the coordinated efforts in the strategic planning and financial management.
In the context of budgeting process, companies are mainly considered two types of budgeting process i.e. top-down and bottom-up approach. In the top-down approach, the budgeting process involves the preparing the budget by the company’s senior management or top managers with reference to company’s objectives (Matherly and Burney, 2013). The departmental managers are assigned different roles and responsibilities for its successful implementation. Every department can opt to create its own budget based on the company’s broader budget allocation and goals. It seems as quick approach of financial planning and resource management. In this context of research process, companies are following either top-down approach or bottom-up approach. The top down process involves the preparing the budget by top managers with reference to business objectives and departmental managers are aligned different roles and responsibilities for the successful implementation of budget. This process of budgeting has been perceived as the time effective solution for the business entity (Hrabal, 2016). On the other hand, the bottom-up budgeting process starts at the departmental level and transposes to higher levels In this context, different departments prepare different types of budgets so as top management combines the all types of budgets for creating all-inclusive budget. Therefore, the bottom-up budget has been addressed as the lengthy and time consuming process.
Section B
Question B1
a) Calculating the relevant annual cash flows associated with buying the machine






d) Recommendation
As per the case, “Stay on beat” is looking to undertake a new project, building and selling high-end electronic traditional pianos so as the business entity has focused to acquire the multi-purpose machine that has initial cost of £550,000. In this context, the assessment of proposed investment project has disclosed the management should not consider the multi-purpose machine for maximising the efficiency of the business operations. This is because this investment option would not provide appropriate returns to investors due to negative net present value at the discount rate of 15%. Therefore, it can be stated that this project would not facilitate the expected rate of return of 24%. In addition to that, the payback period of the proposed investment project is very long that is near to 4.84 years. Overall, the proposed investment of Stay on beat in new machine would not find appropriate due to low returns.
Question B3




As per the above calculation, it has addressed that the Teddys Ltd would find the reduction in its operating profit when the company would remove the Big Bears as a customer that would be reached to £11,500 as compared to existing operating profit of £15,000.
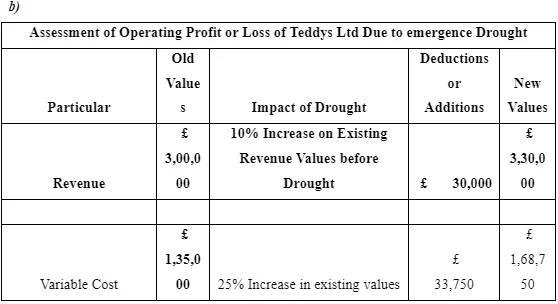

The above calculation the presents the comparison of operating profit of Teddys Ltd before and after emergence of the situation of drought. In this regard, the business entity has recorded the huge downfall in its operating earnings. Therefore, the emergence of drought makes the situation more worse.


The above calculation has tried to evaluate the implications of the new production plan of Teddys Ltd over its profitability in which company is looking to generate the additional revenue of £80000 with the help of new job plan that would also increase the variables cost by £54000. In this regard, the above calculation shows a significant in the company’s profitability with consideration of new production plan.
d)
In the context of production planning, the management of Teddys Ltd has to consider different elements before expanding the production volume or selecting the new projects with existing production capabilities that would generate the additional revenue of £80000. For taking the production expansion related decision, the management should have to consider different variable to enhance the effectiveness of the production planning and decision making process such as fixed overheads that are aligned with production capabilities, requirements of materials, cost of materials, market demand and quality standards that are having a significant impact implications over the production planning and resource management (Baiman, 2014). In addition to that, the management has to consider variable cost and other expenditures that are having significant implications on the final cost and business profitability.

e)
The break-even analysis has been found very effective to determine the relationship between the cost volume and profit at different levels of productions. It is considered as an important point or production volume in which an organisation receives neither profit nor loss. However, this model has different disadvantages such as higher dependence on the similar prices at the different level of production output (Hrabal, 2016). Moreover, it has found as the time consuming tool. The break-even model is mainly applied to evaluate the production quantity of a single product but it cannot implement in an efficient manner for consideration of break-even point when an organisation is producing the multiple products and services. However, it could increase the chances of inaccuracy in different business conditions. Moreover, it influences the application rigid decision making that would not find appropriate in implement quick changes in allocation of different resources. Apart from that, it has been termed as a very time consuming process that could limit its usefulness in various business operations (Matherly and Burney, 2013). Moreover, this tool does not qualitative factors in decision making process.
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Passwords and Authentication in the Digital Landscape.
Reference
Appelbaum, D., Kogan, A., Vasarhelyi, M., and Yan, Z. (2017). Impact of business analytics and enterprise systems on managerial accounting. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 25, 29-44.
Baiman, S. (2014). Some ideas for further research in managerial accounting. Journal of Management Accounting Research, 26(2), 119-121.
Butler, S. A., and Ghosh, D. (2015). Individual differences in managerial accounting judgments and decision making. The British Accounting Review, 47(1), 33-45.
Hrabal, M. (2016). Process-Oriented Managerial Accounting. International advances in economic research, 22(2), 225-227.
Ibarrondo-Dávila, M. P., López-Alonso, M., and Rubio-Gámez, M. C. (2015). Managerial accounting for safety management. The case of a Spanish construction company. Safety science, 79, 116-125.
Islam, J., and Hu, H. (2012). A review of literature on contingency theory in managerial accounting. African journal of business management, 6(15), 5159-5164.
Jiambalvo, J. (2019). Managerial accounting. John Wiley and Sons.
Matherly, M., and Burney, L. L. (2013). Active learning activities to revitalize managerial accounting principles. Issues in Accounting Education, 28(3), 653-680.
Mihăilă, M. (2014). Managerial accounting and decision making, in energy industry. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 109, 1199-1202.
Warren, C. S., Reeve, J. M., and Duchac, J. (2016). Financial and managerial accounting. Cengage Learning.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



