Risk Management and Organisations
Introduction
Organisations have had a rough time in handling the current economic times that have been influenced by Coronavirus. With the current Covid-19, the only organisations that can manage to give attention to risk management and innovations can operate smoothly. As result, organisations have managed to look for ways that they can use to recognise and be able to mitigate the challenges that the organisation might face. This report is going to evaluate issues in business environment and how to manage innovation risk for the benefit of Adidas. The company aims to use the management of innovation risks to create a competitive advantage for the company, focusing on strategies that align with business dissertation help.
Identify and evaluate different business environments and the likely risks of those environments.
To identify and evaluate different business environments risks for Adidas we are going to use employ the use of PESTLE analysis to evaluate the likely risks of those external environments. The market is changing daily and so are the innovative techniques (Ravichandran,2018). The market changes due to positive and negative factors that are brought about by the external environment of a business. The PESTLE study reveals to the managers and strategic planners where their market is and where it is going to move in the future (Dendup et al., 2017). The PESTLE analysis is made up of elements that influence the business environment and every letter in the acronym refers to several aspects which affect each industry directly or indirectly.

Political Factors
This factor takes into account the political health of a country and the world as well. These are government decisions that affect how businesses operate. These factors are not limited to taxes and the levies from the government that affects business operations. These factors can impact and therefore halt Adidas business operations.
Economic factors
They are Factors such as, inflation rate, monetary policies, and interest rates foreign exchange rate that affects business operations in terms of imports and exports. These factors can influence the potential of the expansion of Adidas operations.
Social factors
Adidas can capitalise on culture, demographics, domestic structures and the social lifestyle to maximise its growth. This is because these are the major social factors that affect a business externally. If these factors are not taken into considerations, Adidas can come up with products that cannot be successfully sold in the market.
Technology
Technology changes every minute and Adidas must therefore remain connected and integrate as and when necessary. Technology is the primary factor behind the different innovations that we witness every day. Therefore, Adidas should try to understand the consumer’s behaviour to these trends as a way of mitigating innovation risks. The likelihood is just how likely the risk is to occur.
Legal Factors
Changing of legislative effects business environment, organisations are forced to follow strict legislative factors that affect business operations.
Environmental factor
The geographic location, the climate and the weather can affect the delivery of Adidas products to the market both nationally and internationally. These factors can affect Adidas trades and the way the consumer reacts to the products.
Examples of organisation's tolerance to risk-taking and an evaluation on how organisations can measure tolerance.
Risk tolerance is the loss an organisation is supposed to prepare to handle when they want to make an investment decision. Risk tolerance is but not limited to, high-risk investors, Low-risk investors, Megaprojects, Professional snowboarder and a high-risk start-up (Alwahaibi, 2019). An organisation uses likelihood as a way of measuring Risk tolerance. Data are frequently gathered from managers/employees' observations closest to the risk. The main input to this equation is their sense of reality (Harvey, 2018). However, organizations can look at historical figures which illustrate when and how risk has materialised, and also at how the risk may develop and evolve on the market for organizations from financial and operational viewpoints.
Looking for further insights on Organisation Change? Click here.
Produce a risk profile for an organisation.
The main aim of a risk profile is to ensure that levels of risks in an organisation are identified and then properly managed. Therefore, the purpose of this risk profile is to ensure that the levels of risks are identified and managed in a structured way. Risk management is an on-going process that never stops in any organisation (Chan et al. 2020). Estimation of all the risks linked with a plan, programme, project or activity is a synopsis of a risk profile. Risk profiles are documented and illustrated using various approaches but are usually based on the probability and effects estimations for a list of identified risks. The following is a risk profile of an organisation.
Safety
A documentation or diagram describes the risk of a task, a work or a sport (Ng & Clercq, 2021). This can be used to raise risk awareness or show areas that need to be reduced risk. A government could, for example, assess the risks posed by popular sports such as ice, football, snowboarding and water skiing to create security actions.
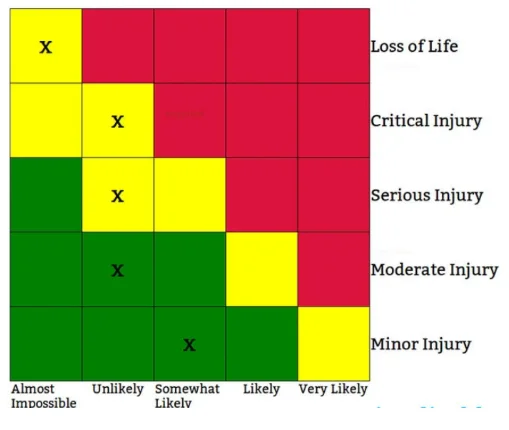
Investment
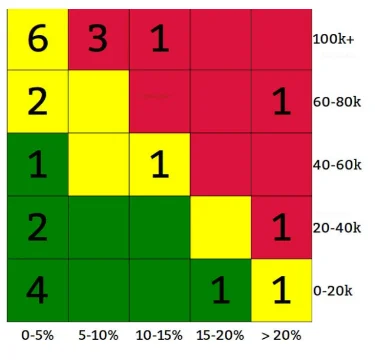
An individual investor might use the risk profile for losses in connection with several posts. Each number corresponds in the picture above to an active position in the risk class. The investor, for example, is in 6 positions, with a 0-5% risk of losses over $100,000. Such a risk analysis would be based on several assumptions including a time horizon.
Projects
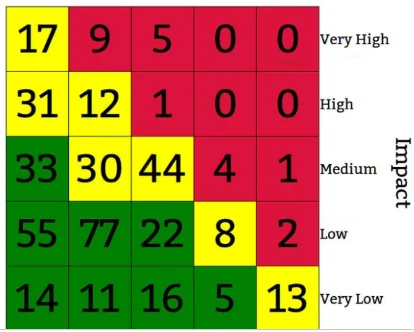
The non-financial risk effects, such as high, medium and low, are frequently estimated in projects. The following project risk profile lists the number of risks assessed by probability and impact for a project. Each box is the number of detected hazards in the risk category in the diagram above. For example, with a chance of 20-40 per cent, the project has 77 low impact hazards.
Review and comment on risk profiles of organisations in different industries
Coca-colas Risk profile
Coca colas main goal that have contributed to its success is employee safety. They believe that every individual's fundamental right and a necessity in business is a safe and healthy workplace. To limit the risk of accidents, injuries and exposure to health hazards for all of their staff and contractors, it is the workplace rights policy that they accept responsibility for ensuring productive employment across all of our companies. An investment risk score of 9.00 is presented in the Coca-Cola Company (Chorazy, 2020). 0 is a very large risk, and 10 is a very little risk." The Coca-Cola Company's investment risk score is substantially greater than its peer group (Ahaibwe et al., 2021). The Coca-Cola Company is therefore considerably less risky in terms of investments than its peer group. Nevertheless, before Coca-Cola invests in a project, they would first analyse the project to evaluate its potential returns and risks.
McDonalds Risk profile
Even though McDonald's strives so hard to ensure the safety of all the employees. There are complaints from form employees of about work safety and working conditions (Kmiecik, 2020). In addition they are striving had to make sure that the food that is served from the store is healthy and safe for human consumption. However there are several risk factors in investing in McDonald's such as Market risks, the economy has government restrictions to help in covid-19 mitigation that has impacted the sector. Currently, McDonald's cannot engage in new projects because of the current state of the economy.
Discuss the enterprise-wide risk and the benefits and drawbacks of such an approach.
With the increasing business risks, businesses feel that some formal system of risk management needs to be implemented. An efficient ERM program can help firms manage their risks and optimize opportunities (Verbrugge et al., 2020). Organizations in various kinds of industries, commercial and public, have seen a range of advantages by improving their risk management programmes. Organizations that have implemented the ERM have pointed out that increased risk attention at the senior levels leads to more risk conversation at all levels. The consequent cultural transformation makes it possible to take risks more freely into consideration and brings silos on how to manage risk (Saeidi et al., 2019). ERM promotes improved structure, reporting and risk analysis. Standardized reporting on corporate risk tracking can help managers and managers focus on data that enable better risk mitigation decisions to be made. The diversity of information (status of key risk indicators, mitigation measures, new and emerging hazards, etc.) enables management to comprehend the most relevant fields of risk.
Take a deeper dive into Risk Management with our additional resources.
On the other hand, the expenses of taking the time for ERM are associated. However, ERM employers are well aware that the cost is worth preserving your most important assets (like reputations) and placing the business in the right direction for its strategic goals (Rafiei & Ricardez-Sandoval, 2020). As ERM is often extremely appreciated by senior management, it has a great influence on the strategic strategy of ERM. If the risks and opportunities are not effectively grasped, it may lead to the implementation of wrong plans (Alijoyo & Norimarna, 2021,).
Analyse the possible risks of innovation in an organisation
Innovation can impact other areas in an organization, Including such as manufacturing standards, workplace culture, and staff training, if not properly handled. Not every innovation succeeds. Some do not accomplish the advantages for which they were intended, while others succeed in ways that nobody imagined (Eling & Lehmann, 2018). In addition, an innovation gives a competitive advantage only if competitors cannot copy it in their own companies. While patents offer legal protection, many new items and techniques are difficult to protect. The risk is one of making an initial investment and risking for an original research-driven company - it only competes with numerous me-too competitors riding on innovation's tack (Bienhaus & Haddud, 2018). Nevertheless, numerous research projects are speculative and future earnings and profits are not guaranteed. The longer the development period, the greater the possibility of competition overcoming research. There is no assumption then that innovation always works best; it might sometimes lead to failure and disappointment. How do you determine if you take too huge a risk with some success tales mingled with numerous failures? When it comes to innovation, Adidas should be conscious of its limits and not take more risks than it can afford for a higher level of success (Greenhalgh et al., 2020). Lean Management helps to reduce expenses and reduce risk if this happens. To gain precise feedback as to whether the success or failure will result before investing too many resources and time in them, Adidas should create a system to assess the advantages and risks of innovation when carrying out new initiatives or change its business model (Coccia, 2017). Innovations can be a game for many entrepreneurs, but they may also be the key to success.

Produce examples of how to manage innovation risk so that innovation can be used to create advantage.
If an organization wants to survive and thrive in a fast-paced business environment, innovation must be part of a company its DNA (Bustinza et al., 2019). However, the moon shoots are prepared and tested and risk management takes a solid dose as you go about it. Five examples to create a proper risk-reward balance in the context of innovation should be taken by companies:
Put the culture of risk at the top. Leaders should inform the innovation process of the necessity of risk management.
Include risk management in a complete cycle of innovation. Adapters have learned to integrate the second line of defense — risk and compliance — with innovation strategy. According to the Institute of Internal Auditors, the first line in a three-line defense concept is operational management, followed by risk and compliance and internal audit.
Adjust the risk appetite. This does not imply that a corporation takes more risk than it can bear, but that it regularly updates how it sees innovation-related hazards. The drafting of a risk appetite statement is viewed by non-adopters as a unique task.
Develop new skills. New talents should be wide-ranging, not just an innovation team. To verify these innovations efficiently, an enterprise that uses RPA will need internal auditors, for example.
Conclusion
This report was to evaluate the business environment and how to manage innovation risk for Adidas. The successes of an organization are determined by the level of how it can play around with the risks of innovations to maximize its profits. Organisations can only make it if they learn how to survive in the current world full of new inventions and consciously changing technology.
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Reward Management System.
Reference
Ahaibwe, G., Abdool Karim, S., Thow, A. M., Erzse, A., & Hofman, K. (2021). Barriers to, and facilitators of, the adoption of a sugar sweetened beverage tax to prevent non-communicable diseases in Uganda: a policy landscape analysis. Global Health Action, 14(1), 1892307.
Alijoyo, A., & Norimarna, S. (2021, March). The Role of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Using ISO 31000 for the Competitiveness of a Company That Adopts the Value Chain (VC) Model and Life Cycle Cost (LCC) Approach. In 3rd International Conference on Business, Management and Finance. Oxford, United Kingdom (pp. 11-14).
Alwahaibi, S. S. O. (2019). Is demographic information influence risk tolerance/aversion in investment decision? Evidences from literature review. International Journal of academic research in accounting, finance and management sciences, 9(1), 111-122.
Bienhaus, F., & Haddud, A. (2018). Procurement 4.0: factors influencing the digitisation of procurement and supply chains. Business Process Management Journal.
Bustinza, O. F., Gomes, E., Vendrell‐Herrero, F., & Baines, T. (2019). Product–service innovation and performance: the role of collaborative partnerships and R&D intensity. R&D Management, 49(1), 33-45.
Chan, H. F., Skali, A., Savage, D. A., Stadelmann, D., & Torgler, B. (2020). Risk attitudes and human mobility during the COVID-19 pandemic. Scientific reports, 10(1), 1-13.
Chorazy, E. (2020). Coke and health. In Decoding Coca-Cola (pp. 207-225). Routledge.
Coccia, M. (2017). Varieties of capitalism's theory of innovation and a conceptual integration with leadership-oriented executives: the relation between typologies of executive, technological and socioeconomic performances. International Journal of Public Sector Performance Management, 3(2), 148-168.
Dendup, T., Feng, X., Clingan, S., & Astell-Burt, T. (2018). Environmental risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. International journal of environmental research and public health, 15(1), 78.
Eling, M., & Lehmann, M. (2018). The impact of digitalization on the insurance value chain and the insurability of risks. The Geneva papers on risk and insurance-issues and practice, 43(3), 359-396.
Greenhalgh, T., Wherton, J., Papoutsi, C., Lynch, J., Hughes, G., Hinder, S., ... & Shaw, S. (2018). Analysing the role of complexity in explaining the fortunes of technology programmes: empirical application of the NASSS framework. BMC medicine, 16(1), 1-15.
Harvey, E. J., Waterson, P., & Dainty, A. R. (2018). Beyond ConCA: rethinking causality and construction accidents. Applied ergonomics, 73, 108-121.
Kmiecik, J. (2020). Wpływ kultury na budowanie wizerunku marki. Analiza firm Reserved i McDonalds.
Ng, P. Y., & Clercq, D. D. (2021). Explaining the entrepreneurial intentions of employees: The roles of societal norms, work-related creativity and personal resources. International Small Business Journal, 0266242621996614.
Rafiei, M., & Ricardez-Sandoval, L. A. (2020). New frontiers, challenges, and opportunities in integration of design and control for enterprise-wide sustainability. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 132, 106610.
Ravichandran, T. (2018). Exploring the relationships between IT competence, innovation capacity and organizational agility. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 27(1), 22-42.
Saeidi, P., Saeidi, S. P., Sofian, S., Saeidi, S. P., Nilashi, M., & Mardani, A. (2019). The impact of enterprise risk management on competitive advantage by moderating role of information technology. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 63, 67-82.
Verbrugge, J., Niehaus, G., Coleman, W., Lawder, K., Smith, C., Briscoe, C., ... & Chew, D. (2020). UNIVERSITY OF GEORGIA ROUNDTABLE ON: Enterprise‐Wide Risk Management. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 32(1), 14-35.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



