Strategic Outsourcing in Business: Evaluating Supply Chain Outsourcing for DB Toys
Introduction
Outsourcing has been around for decades but has recently gained popularity because of its numerous benefits to businesses. Following an addition in the layers of management meant to support businesses expansion into economies of scale in the mid-20th century, companies found out that they could earn added profits by concentrating on business core activities. As a result, outsourcing increasingly became common in the business world. Outsourcing means contracting out of the firm's non-revenue producing and non-core activities to the experts of the domain. In business, however, outsourcing is not just contracting but rather it is used as a strategic management tool that helps an organisation to restructure its processes around its core competencies (Bányai, 2017). This assignment purposes to evaluate supply chain outsourcing for DB Toys to determine the benefits and risks of outsourcing their supply chain and the outsourcing options viable for them. For more insights, consider management dissertation help.
Types of outsourcing in supply chain management and the benefits and risks of sourcing
Types of outsourcing in supply chain management
Outsourcing has become a strategic necessity that allows a company to turn around resources very fast by focusing on core activities and as a result, helps improve the overall wellbeing of the economy (Carbonara and Pellegrino, 2018). Some of the outsourcing types in supply chain management include the following;

1. Business applications outsourcing; outsourcing in IT force processes that involve business applications. It includes service that is related to designing, testing and production of business applications. Businesses delegates these application works to avoid the risk of doing this work in-house. Lin, (2016) discusses an emerging business application outsourcing referred to the application service provider (ASP) available for businesses that allow them to attain information capabilities that give them a competitive advantage.
2. Business process outsourcing; involves the contraction of all non-core business activities such as accounting, customer care centre relations, human resources and payroll. Liu, Wang, and Huang (2017) looked at the control-performance relationship between the vendor and the client. They instead that using outcome control is highly effective in influencing the performance of an outsourced project under BPO.
3. Infrastructure outsourcing; helps a client to improve their IT spending management and therefore streamlines operations in IT service delivery.
Benefits and Risks of Outsourcing
As highlighted above, it is important to weigh both the benefits and risks of outsourcing. The stage of business growth is an important factor to consider when determining whether to outsource or not. For instance, when the business is at an infant stage, outsourcing the supply chain could be beneficial in that it would allow the business to accommodate growth and remain profitable. On the other hand, a more mature business that is at a stable growth state must assess its actual position to decide whether to continue outsourcing or to bring its supply chain back in. Using the key performance indicators (KPIs) provided in the service level agreement with the 3pl, a company should evaluate its readiness to bring back its supply chain from an outsourcer (Yao et al, 2018). Also, a company should determine the cost-effectiveness of outsourcing considering some of the advantages of insourcing such as increased quality control. In deciding to outsource, a company must define its motives and exact resources why it is outsourcing. These motives and reasons but be more elaborate than merely looking at some abstract reasons such as improved delivery or improved performance. Once in the outsourcing arrangement, the unfulfilled expectation by the customer or the outsourcer could be detrimental to both and this is a critical risk.
Getting into a service level agreement requires that both parties have clearly stated the desired outcomes, say for example, whether the outsourcing is strategic or tactical. Such clarity is important for the development of the implementation plan, setting a direction for service and process delivery and proper timing (Nagurney, Yu and Besik, 2017). For example, if the customer is outsourcing to achieve a 10% reduction in cost, this can be attained easily. When the goal is to reduce cost by 35%, it can only be achieved using very strategic approaches which also must be implemented properly.
Outsourcing involves introducing change to the management of the business. Any change comes with inherent risks and these also are dependent on the type and extent of change. There is an even higher risk if an anticipated risk is hidden as it becomes unexpected. Some of these risks include the following;
Differences in the corporate culture of the two parties; this may have a detrimental impact especially in risk-sharing and the success of the project. Corporate culture is subject to the company’s regional culture, the culture of the company and that of the employees.
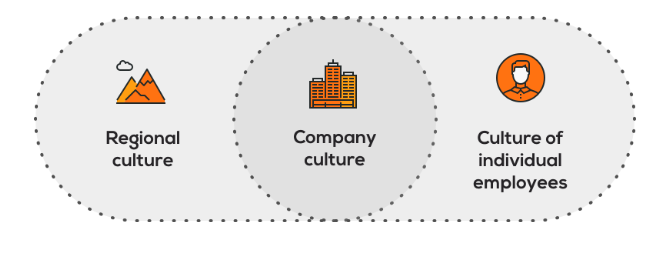
The corporate culture is significant in the operations of an organisation and it relates to the company’s mission, values and mission. It determines how decisions are made, influences communication and helps manage error (Cooper, 2017). Accordingly, cross-cultural in outsourcing partnership may result in friction when it is necessary for collaboration between the two companies. This risk is hidden because at first, the companies may not care to synchronise their cultures but its impact is critical on the business outcomes of the partnership (Chen et al., 2018). A profitable outsourcing partnership and only be achieved if the partners are working to win together.
Supply chain management involves the crossing of the organisation and this can result in conflict due to the organisational silos. Poor interaction between the parties involved in a business process because they are from different "silo" it is impossible to work together (Kurniawan et al., 2017). Additionally, organisational silos do not work well with change and will often prevent the smooth flow of information. Without communication, collaboration is not possible as each business will only work to pursue its interest. For instance, the outsourcing company when protecting its interests may fail to communicate to their customers about the market’s reaction to packaging or any other critical information.
Unreasonable expectations: a test for reasonableness is important for identifying the risk for all the parties involved in the outsourcing partnership. Expectations must be tangible and the timing of all the activities must reflect the transition. Therefore, unreasonable anticipation is likely to negatively impact the relationship between the parties and as a result, increase the risk.
Outsourcing, on the other hand, can add value and present numerous opportunities for a company when done correctly. Some of the benefits of outsourcing include the following;
Increases the company’s supply chain capabilities: this benefit is particularly important for an organisation whose resources are limited. Outsourcing provides a company with supply chain expertise, capabilities and solutions beyond their scope of operations (Nakasumi, 2017).
Increased security in supply: outsourcing helps a business to improve in supply chain control, security and visibility in important aspects such as in inventory levels, compliance with supply chain regulations and by reducing the lead time. Additionally, working with supply chain partners helps a company in mitigating risk in many ways.
Improves in meeting the customers’ demand: customer satisfaction is paramount for business growth and as such, meeting demand is important and is only achievable through consistency in production (Ding, Huang, Tang, 2018). Meeting production schedules even when there are fluctuations in demand requires proper planning that can be achieved through consultation with the outsourcing partners. An organisation is, therefore, able to mitigate many risks including the risk of shutting down business processes.
Supply chain outsourcing as a viable option for DB Toys
Outsourcing as a viable option for DB Toys
Before deciding to outsource, a company such as DB Toys must evaluate the suitability of that options especially having seen that outsourcing the supply chain may be risky or beneficial to a business. In a competitive business environment, only businesses fittest to survive to stand a chance. As such, it is important to shed all the non-core businesses, it is one of the most efficient ways to cut cost and improve performance (Yap, 2018). To beat the competition, an organisation cannot do everything in the house as this would be handicapping. Other than the goal of cutting the operating cost, there are other many reasons for considering outsourcing. One major reason is that consumers and markets are unpredictable because they will make demands of things they want any time they want it and in particulars of how they want it (Carbone and Gouvernal, 2017). Failure to meet such demands will harm the company's reputation and will lose them. The need to meet these demands puts pressure in the supply chain and with time a company may lose to tough time and competition.
Based on this background of the reasons for outsourcing the supply chain, and the state of function of DB Toys, it is my position that outsourcing is a viable option for this company. The following are the particular reason for this observation;
First, as stated by the CEO, DB Toys is incurring much of its IT budget in supply chain functions. Intending to cut down this cost, as well as other resources such as labour and infrastructure, (operating costs are at 50% of the revenue) outsourcing is an option that would be very efficient. This is in addition to the fact that Inflection is highly experienced with IT and supply chain and DB would highly benefit from this expertise.
Secondly, it was observed that the supply chain at DB Toys was performing badly. Particularly, the company was struggling with meeting a day’s inventory schedule and lead time; DT Toys; inventory lead time is 120 days and met only 75% on-time delivery. Also, the with customer services lagging behind that of the industry average. All these problems have a detrimental impact on a company's performance and productivity and as such, outsourcing to a company such as Inflection would be viable to revert these issues.
Thirdly, according to the breakdown of the supply chain expenses for DB Toy's, this function is badly being managed and is not strategic to a company's goal of profit-making. This is because when compared to the industry's average where the largest portion of the expense is used in the development of supply chain, DT Toys is only able to commit 10% compared to the industry average of 40%. The largest portion of expenses for DB Toy’s is used for support as compared to the industry average which is 25%. Accordingly, outsourcing would help them deal with this challenge.
Outsourcing Option
The business application outsourcing is when a business outsources the management of applications such as in the maintenance and development of the software and IT applications of a certain function (Scott, Lundgren and Thompson, 2018). The main advantage of application outsourcing is the enhancement of quality for the particular function because the outsourcer takes over the operation, development and maintenance and the company is left to focus on the performance of that application concerning the business goals (Namdar, et al., 2018). Effective application outsourcing helps with the implementation of new solutions as the outsourcer ensures that the applications are market-driven, customer-centric and ready for business.
The business process outsourcing (BPO) is when a business outsources an outsourcer to perform business processes such as the supply chain for a manufacturing company. The outsourced process is however unrelated to the core activities involved with the production. There are many reasons why an organisation will use BPO as the outsourcing options and some of these include expanded coverage by the business in terms of hours of operations and geographical reach in the case of a market, and, financial gain because the outsourced company may be operating in large scale and therefore can perform the process at a lower cost.
Having looked at the two option in terms of what DB Toys will be benefiting from, it is important to look at the particulars of each option as explained by Inflection CEO. Hiring the business application outsourcing will mean that the supply chain management IT infrastructure will be managed by Inflection but all the supply chain business processes will be managed internally. With this option, the supply chain IT spending will be reduced by 20% which means that instead of spending $30 million, DB Toys will spend $24 million but with an extra $6 million upfront fee in the first year. On the business process outsourcing option, Inflection will take over the operations in the supply chain and to effectively run the function, there was proposed a change in the supply chain system that will cost $28 million and will only be usable after 9 months, this is in addition to $6 million upfront fee. The annual cost to run the new system is $25 million and there are other anticipated implications on the running of the organisation even though there are no prospects in revenue growth. The advantages, however, is that Inflections anticipates that it will achieve better forecasting that would result in a reduction in the operating cost.
In this report, the most profitable and effective outsourcing option is the business process outsourcing because while it may be expensive, it is more promising in the long terms. DB Toys first has the problem of overspending on the IT but additionally, the spending breakdown in this section shows that there is the problem of poor management. To deal with the two issues and also enjoy other benefits from the economies of scale exhibited by Inflections, the BPO option is the best.
Pricing Alternatives
The appropriateness of a pricing model in outsourcing is determined by the two factors and these are the metrics used to measure the success of a project and the pricing variability available (Tate and Bals, 2017). In outsourcing, pricing plays a predominant and vital role in any outsourcing decision considering that in most cases, outsourcing engagements are for cost-saving. The three pricing models suggested by Inflection to DB Toys are the fixed price model, cost plus and transaction-based. The fixed price model is referred to as the lump-sum model and is mainly preferred for outsourcing projects with a particulate set of requirements, scope and management methodologies. It applies when the outsourced service provider has extensive details about the project and the two can agree on the deliverables in particular millstones. Any changes result in extra costs or a reduction in profits (Sindi and Roe, 2017). The success of such an agreement is dependent on rigorous monitoring, quality control and quality assurance. The service provider assumes all the risks and therefore will charge extra cost to the contract price to cover the risk. In a cost-plus model contract, the service provider charges back all the costs of the project to the outsourcing organisation. Therefore, while the fee is fixed, the costs vary which means that there is zero motivation for the service provider to control the cost. The transaction-based pricing contract requires that the service provider is paid a minimum fee in addition to a unit price per a business transaction volume unit. Risks and rewards of the project are shared by the client and the service provider and are also profitable to the client is because the fee is paid with usage.
Accordingly, the most appropriate pricing option for DB Toy’s is the transaction-based contract. The reasons for this conclusion is that besides the advantages of this contract as mentioned above, there is a predetermined growth in the number of a purchase order for 10 years for both outsourcing options. It means that DB Toys can easily plan their cost into the foreseeable future considering that using this pricing contract, the cost per perchance order is also fixed.
Expected return on investment from the two outsourcing options
The expected return on investment
The return on investment (ROI) is used to determine the return gained from an investment. It calculated as a ratio of investment gain to cost. it is used to evaluate potential return from an investment (Kristjansdottir et al, 2018). It is therefore used to evaluate the attractiveness of an investment alternative and rank than in the case of many different alternatives. This section shows the expected returns for DB Toys for business application outsourcing and business process outsourcing.
Dig deeper into Strategic Management Report with our selection of articles.
ROI for business application outsourcing
Upfront cost = $ 6 000 000
Reduction in IT spending= by 20% = (20% of $ 30,000,000)= $ 6,000,000
New IT spending expected to be $ 24,000,000
The NPV of the project is $ 27,800,000 and an internal rate of return of 111% (from the excel file). Other benefits include a 20% reduction in IT supply chain spending, outsourcing the supply chain applications and the implementation period of just 4 weeks
ROI for Business process outsourcing
Upfront cost- 3 months = $ 6,000,000
Build phase lasting for 9 months costing $ 28 million
Annual run cost at $ 25,000,000 which would increase by 12% for 9 years
The NPV of the project is $180,050,000 with an internal rate of return of 71% (from the excel file). Other benefits include installation of a new IT supply chain process (design-build-run outsourced), reduced annual first-year IT spending, improved customer service, reduced operating cost and inventory saving.
Outsourcing option based on the pricing alternatives
With the introduction of the shareholders’ value incentive clause, there is a positive net present value for all the options in all pricing alternatives. Similar to the outcome based on the benefits of each of the outsourcing option which concludes that the business process option is the most profitable (option 2), a comparison of the pricing alternatives shows that option 2 is most appropriate. The fixed price alternative is most preferred according to the calculations, however, with the introduction of shareholders value incentives, the transaction-based alternative is most preferred especially because of its ability change a negative return on investment into positive with an increased in EPS.
A brief summary about the strategic context of outsourcing and its impact on supply chain metrics.
In business strategy planning and implementation, focus on strategies that leverage company competencies, resources and capabilities are important (Grant, Trautrims and Wong, 2017). Accordingly, businesses reduce the resources and time invested in non-core activities and processes to free up management resources for core functions to achieve competitive advantage (Brindley et al, 2017). The business processes that are not strategic needs are sourced externally. The value of outsourcing is thus measurable by the overall benefits for a project in terms of effectiveness and efficiency benefits from the outsourced process.
The rationale for a strategic business decision is based on an assumption that with all other factors held constant, companies that concentrate on investing on core processes perform better than those that are trapped into focusing on activities that do not require special capabilities and skills (Yao, Minner, 2017). By developing specific resources in particular competences, a firm is, therefore, able to build a competitive advantage. Business functions and processes that contribute to the competitive advantage of a firm needs substantial and on-going management and investment and thus the strategic need for outsourcing.
The effectiveness and efficiency of outsourcing and pricing models vary considerably. Using the BPO services, for example, the client must understand that that the service provider will perform better if there is value in performing the in-house activity that best suits the client. Most importantly is that the service provider in outsourcing is most successful if they have economies of scale in the service they are providing (Giri and Sarker, 2017). Additionally, the economies of scale are vital when the activities being outsourced are asset-intensive. This is particularly important for the case of DB Toys because of the IT supply chain management services they need. The supply chain management system requires the implementation of a new IT infrastructure or the expert management of the existing one (Luo, Zhang and Wang, 2018). The advantage of outsourcing with a company that with economies of scale-like Inflection in a business function of IT supply chain management is that the client is not likely to suffer from the unpredictable riser in the cost as the service provider have the capacity to spread operating costs that are fixed over a large number of organisations (Bendul, Rosca and Pivovarova, 2017). Accordingly, therefore, DB Toys will benefit the most if they purchase a BPO outsourcing model.
Another important factor to consider when purchasing outsourcing services for the client like DB Toys is the pricing model. In its strategic context, outsourcing is only beneficial if the purchasing cost is appropriate for the client. An unexpected rise in cost in the middle of a project could have a negative impact on the profit gain of an outsourcing project and the overall profitability if an organisation. The pricing model selected should allow the predictability of the costs involved and should have a direct relationship with the expansion of the function. In the case of DB Toys a customer who wants to outsource the supply chain should be such that the costs of outsourcing should be directly proportionate to the purchase order so that as demand in the market increases, the pricing model should ensure that any increase in cost is also reflected in the profits gained (Mota et al., 2018). Among the three considered pricing models, the most appropriate for use is the transaction-based model because there is a minimal up-front fee required and the rest of the expenses are charged based on the purchase order. Therefore, DB Toys will only incur an additional cost if the purchase order increase as the pricing model allows the expansion of expenses based on the expansion of unit orders. Increase in purchase orders means that the outsourcing partnership is successful in the improvement of supplies management and this it's evidence in the revenue, it is only fair that the organisation incurs extra to support the expanded growth.

Using business process outsourcing model and the transition based pricing model will have a positive impact on the supply chain metrics including the customer service, inventory, revenue and the operating cost among others. The discussion above has shown that from a strategic context, the outsourcing decision is made to cut down the operating cost, improve in inventory level, improve the customer services and resultantly generate more revenue. The models selected are effective and efficient for DB Toys in achieving these goals.
Conclusion
The purpose of this assignment was to explore the concept of supply chain management outsourcing through an evaluation of a case study of DB Toys supply chain issues. The report has four sections discussing different aspects of DB Toys viability for supply chain management outsourcing. Having established that supply chain management outsourcing has both some benefits and risk, it was concluded that DB Toys would greatly benefit from a business process outsourcing. While this option was found to be relatively expensive, the long term impact on the company's profitability would be significantly positive. It was also established that the most appropriate pricing option for DB Toys is the transactional-based contract as it allows DB Toys to easily plan their cost in the foreseeable future.
References
BÁNYAI, T. (2017). Supply Chain Optimization of Outsourced Blending Technologies. Journal of Applied Economic Sciences, 12(4).
Bendul, J. C., Rosca, E., & Pivovarova, D. (2017). Sustainable supply chain models for the base of the pyramid. Journal of Cleaner Production, 162, S107-S120.
Brindley, C. (2017). Supply chain risk. Routledge.
Carbonara, N., & Pellegrino, R. (2018). Real options approach to evaluate postponement as supply chain disruptions mitigation strategy. International Journal of Production Research, 56(15), 5249-5271.
Carbone, V., & Gouvernal, E. (2017). Supply chain and supply chain management: appropriate concepts for maritime studies. In Ports, cities, and global supply chains (pp. 27-42). Routledge.
Chen, H., Yan, Y., Ma, N., & Yang, L. (2018). Coopetition strategy and pricing timing in an outsourcing supply chain with uncertain operation risks. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 27(5), 979-993.
Cooper, R. (2017). Supply chain development for the lean enterprise: inter-organizational cost management. Routledge.
Ding, H., Huang, H., & Tang, O. (2018). Sustainable supply chain collaboration with outsourcing pollutant-reduction service in the power industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 186, 215-228.
Grant, D. B., Trautrims, A., & Wong, C. Y. (2017). Sustainable logistics and supply chain management: principles and practices for sustainable operations and management. Kogan Page Publishers.
Giri, B. C., & Sarker, B. R. (2017). Improving performance by coordinating a supply chain with third-party logistics outsourcing under production disruption. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 103, 168-177.
Kristjansdottir, K., Shafiee, S., Hvam, L., Bonev, M., & Myrodia, A. (2018). Return on investment from the use of product configuration systems–A case study. Computers in Industry, 100, 57-69.
Kurniawan, R., Zailani, S. H., Iranmanesh, M., & Rajagopal, P. (2017). The effects of vulnerability mitigation strategies on supply chain effectiveness: risk culture as moderator. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal.
Lin, S. W. (2016). The critical success factors for a travel application service provider evaluation and selection by travel intermediaries. Tourism Management, 56, 126-141.
Liu, S., Wang, L., & Huang, W. W. (2017). Effects of process and outcome controls on business process outsourcing performance: Moderating roles of vendor and client capability risks. European Journal of Operational Research, 260(3), 1115-1128.
Luo, J., Zhang, X., & Wang, C. (2018). Using put option contracts in supply chains to manage demand and supply uncertainty. Industrial Management & Data Systems.
Mota, B., Gomes, M. I., Carvalho, A., & Barbosa-Povoa, A. P. (2018). Sustainable supply chains: An integrated modelling approach under uncertainty. Omega, 77, 32-57.
Nagurney, A., Yu, M., & Besik, D. (2017). Supply chain network capacity competition with outsourcing: a variational equilibrium framework. Journal of Global Optimization, 69(1), 231-254.
Namdar, J., Li, X., Sawhney, R., & Pradhan, N. (2018). Supply chain resilience for single and multiple sourcing in the presence of disruption risks. International Journal of Production Research, 56(6), 2339-2360.
Nakasumi, M. (2017, July). Information sharing for supply chain management based on blockchain technology. In 2017 IEEE 19th Conference on Business Informatics (CBI) (Vol. 1, pp. 140-149). IEEE.
Sindi, S., & Roe, M. (2017). The evolution of supply chains and logistics. Strategic supply chain management (pp. 7-25). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.
Scott, C., Lundgren, H., & Thompson, P. (2018). Guide to Outsourcing in Supply Chain Management. In Guide to Supply Chain Management (pp. 189-202). Springer, Cham.
Tate, W. L., & Bals, L. (2017). Outsourcing/offshoring insights: going beyond reshoring to right shoring. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management.
Yao, X., Huang, R., Song, M., & Mishra, N. (2018). Pre-positioning inventory and service outsourcing of relief material supply chain. International Journal of Production Research, 56(21), 6859-6871.
Yao, M., & Minner, S. (2017). Review of multi-supplier inventory models in supply chain management: An update. Available at SSRN 2995134.
Zamfir, M., Manea, M. D., & Ionescu, L. (2016). Return on Investment–Indicator for Measuring the Profitability of Invested Capital. Valahian Journal of Economic Studies, 7(2), 79-86.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



