Strategic Planning for BME Luxury Care Homes
A strategic plan functions as a road map, clearly identifying the best path for your company to pursue in the next years. A strategic plan, whether it spans one, three, or five years in the future, can assist your business in meeting the difficulties that lie ahead (Catley, 2014).
The following document will elucidate on two of the strategic planning models which the BME Luxury Care Homes can adopt in their business model, and critically analyze them in order to understand which business model is the most superior one for the organisation. It will do so by listing out the pros and cons of each approach.
Flemming (2015), introduced the theory of evolution in an attempt to examine and analyse the development of various types of strategic constructions. They stated that evolutionary changes in strategic management have substantially impacted the paradigm in which a corporation functions, making it a crucial area for management dissertation help. They also claimed that slow environmental changes impacted organisational behaviour; hence, effective companies are those that created a strategic fit and adhered to environmental needs to the greatest extent possible (Wright et al., 1994). They also suggested that an economic environment has lengthy periods of stability interspersed with brief times of discontinuous and revolutionary upheaval (Scandura and Williams, 2000).
1. Issue Based Strategic Planning

The issue-based strategy paradigm is focused on the present while also looking ahead. Its goal is to identify the key obstacles your company is now facing—in other terms, you begin with the problems and work out the issues before expanding or changing your strategy. This is usually a short-term (6-12 months) procedure with an inward focus. For young or resource-constrained companies, issue-based planning is suitable. As a first stage, the management team or partners identify the primary challenges and goals. Following that, your company will develop action plans to solve the concerns, which will include money allocation. After that, you'll carry out your plan and keep track of your success. Your business could consider transitioning to a larger, more sophisticated strategic management model when an issues-based strategy has been executed and the key issues you identified have been handled (clearpointstrategy.com).
In terms of immediate goals, there is a pressing need which the company needs to address. The portfolio of the company suggests that there is a demand among the populace in England for the services of providing luxury care services for individuals who need them.
The UK population has been gradually ageing during the latter part of the twentieth century, and this trend is expected to continue in the future. In 2016, 11.8 million people aged 65 and above lived in the UK, accounting for 18% of the overall population — 25 years earlier, 9.1 million people aged 65 and up made up 15.8% of the population. Thinking forwards 25 years to 2041, the 1960s baby boomers (now in their 50s) will have reached retirement age, and by 2066, there will be an additional 8.6 million UK citizens aged 65 and more, bringing the overall number to 20.4 million and accounting for 26% of the total population. This rise in population is roughly comparable to the current population of London (ons.gov.uk). The group of people aged 85 and up will witness the greatest growth. In mid-2016, there were 1.6 million people aged 85 and up (2 percent of the total population); by mid-2041, this number is expected to double to 3.2 million (4 percent of the population), and by 2066, it is expected to triple, with 5.1 million people aged 85 and up accounting for 7% of the total population. In comparison, the population of those aged 16 to 64 is expected to grow by just 2% during the next 25 years, and by 5% by 2066 (assests.publishing.service.co.uk).
Hence, the growth in population has caught up with the care industry sufficiently enough to increase the demand for care homes. In a report published by The Financial Times, it was revealed that there is an increasing demand for luxury care homes in the UK, especially in the urban spaces in the posh areas of London. This recent trend is occurring because the though process of individuals is shifting from understanding care homes as a place where individuals go as a last resort. Rather, it is being seen as an alternative to living at home with no assistance and no company. The seniors who are availing these services are seeing it as an opportunity to socialize in the senior years and spending them productively. According to the report, the market for such services is projected to grow at a dramatic rate, whereby prices charged now are £300,000-£500,000 per bedroom. Five years ago, these prices were £200,000-£300,000 per bedroom. Hence, in five years, prices have increased dramatically (Plimmer, 2017).
Looking for further insights on Strategic Advertising Planning? Click here.
2. Goals Based Planning
From the future to the present, goals-based (or vision-based) management is used. Planners choose a future date and then recommend particular targets to be accomplished by that date. Goals are sometimes stated in terms of particular milestones. Ideally, planners would link each goal to an action plan. In order to attain the goal, action plans specify who will do what and when. Explaining the mission statement and scanning the external and internal surroundings to determine priorities to handle in the plan are all possible parts of the planning process. Goals-based planning is often focused on a long-term strategy, spanning at least 3-5 years (McNamara, 2010).
In the case of BME Luxury Care Homes, the objective that lies central to their initiative is to establish long-term business in the luxury care home market, as they want to establish a body of institutions which will provide luxury care to seniors in not juts medical sense, but also provide them with a community and social environment they would like to be a part of. Hence, long term planning is a definitive part of this process.
Majorly, there are four steps involved in the goal based strategic planning method. First, the company can include the SWOT analysis as a method to initially understand their advantages and disadvantages. Understanding your Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats can assist you in identifying your primary concerns and pointing you in the proper path for making adjustments. A SWOT analysis is important as it allows the business managers to understand which areas need more attention before the actual planning has begun (mindtools.com).
The second step of the process is for the company to describe their main objectives. At this stage, the company must propose solutions to the problems that are preventing you from achieving your objectives.
The third step is to make a strategy of action. It should be founded on the answers we devised during the previous stage. The purpose and vision statements should be updated. The mission statement needs to be considered at the core of the plan and should properly reflect the ideas of the company in general (keepsolid.com).
3. Final Recommendations
Given the strengths and limitations of the organisation, strategic planning aids in defining who we are and where we want to go so that ecological risks and opportunities may be utilised. It is a comprehensive self-examination on the goals and ways of achieving them so that the company is given both purpose and cohesion. Strategic planning is a methodical, officially recorded process for determining what are the handful of crucial decisions that an organisation, as a whole, must do correctly in order to prosper in the next years (economicsdiscussion.net).
Based on the company that BME Luxury Care Homes is at present and based on their aspirations in the future, it would be advisable for them to adopt the issue based strategic planning. This is because the company has clear and specific short term goals at present which it wants to address and issue based strategic planning focuses more on establishing the short term goals rather than delving into the long term goals. However, BME Luxury Care Homes can afford to avoid doing research on their own as it has been made by studies like the study revealed by The Financial Times, cited in the paper earlier, about how the need for luxury care homes in growing fruitfully in the UK. Hence, they can rely on research being conducive to the kind of business they want to do. Additionally, if they want to gain a competitive edge over their competitors, they should start the initiatives as soon as possible.
Task 2
2a
The DuPoint Analysis provides a great support to shareholders in the financial decision making process. It presents the strengths and area of opportunities so as investors would be able to decide where to make adjustments to increase an organisation’s return on equity (Sheela and Karthikeyan, 2012). It supports shareholders to compare the business performance of an organisation with reference to industry average.
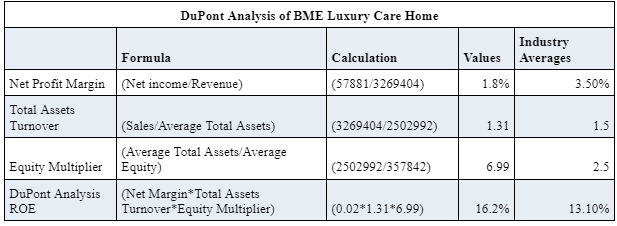
In the context of DuPont analysis, the calculation of net profit margin is carried out that determines the percentage of net earnings of an organisation with reference to total revenue. It is termed as the first section of DuPont analysis. In the context of present case of BME Luxury Care Home, net profit margin is 1.8%. The second stage is to calculate the total assets turnover ratio that determines the efficiency of business operation or sales generation capabilities of a firm with reference to total assets employed by an organisation. The value of total assets turnover of BME Luxury Care Home is 1.31. In the next stage of DuPont Analysis, the calculation of Equity Multiplier has been carried out that is used to determine the proportion of total assets in relation to total equity for examining the efficiency of business operations (Turner and Lee, 2015). As per the financial data of BME Luxury Care Home, the Equity Multiplier is extracted near to 6.99. At the end, the calculation of DuPont return on equity has been conducted by multiplying the net profit margin with total assets turnover and equity multiplier. The application of DuPont ROE formula in the case of BME Luxury Care Home has disclosed that DuPont ROE of the selected company is 16.2%. The comparison of DuPont of BME Luxury Care Home with industry average Return on Equity has disclosed that the selected brand is offering the higher returns to shareholders. The comparison of different ratios of BME Luxury Care Home with industry average has determined that the company has recorded the low net profit margin of 1.8% as compared to 3.5%. In addition to that, the total assets turnover ratio of BME Luxury Care Home is also lower than the industry average. However, the high value of equity multiplier of selected firm is 6.99 that is higher than industry average of 2.5 that determines the higher earning capabilities of the selected firm.
2b
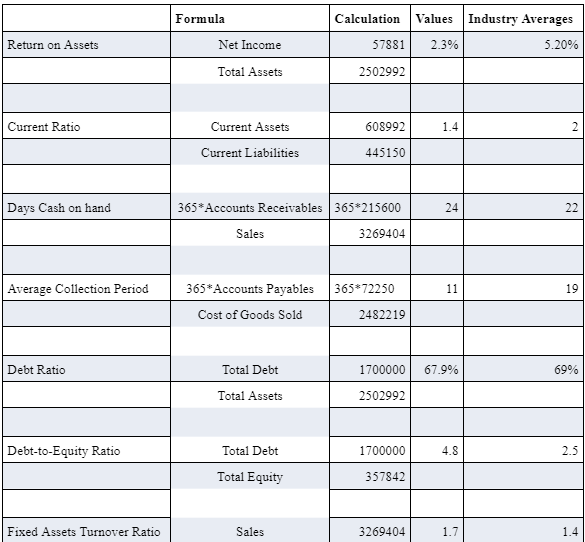

The first ratio is the Return on Assets that is used to evaluate the profitability of n organisation’s investment in the total assets. It is calculated by assessing the percentage of net income with reference to total assets. In the case of BME Luxury Care Home, the return on assets of the company is 2.3% that is lower than the industry average of 5.2%.
The above table contains the current ratio that assists companies and stakeholders in evaluating the liquidity position of business entity (Faello, 2015). It is mainly calculated by taking the proportion of current assets to current liabilities In case of BME Luxury Care Home, the current ratio of company is 1.4 that is lower than industry average of 2 so as it can be stated that the selected company is facing some liquidity issues.
The ratio is called Day cash on hand that determines the average time duration in which an organisation receives the funds from debtors. It is calculated with reference to total value of accounts receivables, days in year, and total sales. The above table determines that the BME Luxury Care Home is facing delay while receiving dues from the debtors as compared to industry average of 22 days. Day Cash on hand of BME Luxury Care Home is 24 days.
The average collection period ratio shows the time duration in which an organisation gets time duration from the creditors (Delen, Kuzey and Uyar, 2013). It is mainly calculated with reference to accounts payable values and cost of services. In the case of BME Luxury Care Home, company has got the average collection period of 19 days that is higher than the industry average of 11 days. Therefore, the management of BME Luxury Care Home should have to provide the extra time to creditors for managing the payment of all accounts payables.
The debt ratio determines the percentage of debt capital with reference to total assets. In the case of BME Luxury Care Home, the debt ratio is 67.9% that is lower than industry average of 69% that shows that the management of BME Luxury Care Home has maintained a low proportion of debt capital with reference to total value of company’s assets.
The debt-equity ratio is mainly used to determine the proportion of debt capital in relation to total equity capital for assessing the assessing the solvency risk that would support companies in financing decisions (Tian and Yu, 2017). The debt-equity ratio of BME Luxury Care Home is 4.8 that is higher than the industry average of 2.5. It determines that the business entity has maintained the high proportion of debt capital that would enhance the overall solvency risk in different decisions related to capital structure.
In the above table, the last ratio is fixed assets turnover ratio that examines the revenue generation capabilities of fixed assets by assessing the relationship between the revenue and fixed assets an organisation (Tian and Yu, 2017). In the case of BME Luxury Care Home, the selectd company is generating the higher revenue from the total value of fixed assets invested by the business entity that is 1.7 time as compared to industry average of 1.4.
Task 3
A business model is a blueprint for how a firm intends to earn money in a given market with its goods and client base. A business model describes four things at its core: What will a company's product or service be? How it plans to promote that product or service, what expenditures it expects to incur, and how it plans to make a profit.
Because there are so many different sorts of organisations, business models are always evolving. While we'll go through some of the more popular types below, there is no one-size-fits-all strategy that can be implemented to every company (Kriss, 2020).
In order for firms to be profitable in a sustained fashion, they need to take into account non-financial aspects of a business model as well. Non-financial measures are quantifiable that aren't denominated in monetary terms. Profits, profit margin, volume of sales, and return on assets are all common financial indicators. Non-financial measures include customer happiness, market share, category leadership, and the pace at which new products are adopted (visiondesignmarketing.com). It is imperative that companies look at the non-financial aspects of their performance as well. Many businesses' boards of directors and management are interested in non-financial performance metrics, according to studies conducted by Deloitte Touché Tohmatsu Limited and others, despite their inability to monitor these aspects. Because financial performance indicators like earnings and return on assets are regarded lagging indicators. These measurements do not sufficiently represent a company's strengths and problems on their own (deloitte.com).
Another important aspect of performance management is the multidimensional model of performance management. The development of techniques that seek to balance the conventional focus on financial success with other characteristics of performance that are generally deemed "non-financial" has been a significant advancement in performance management. Among examples are the French Tableau de Bord and Lynch and Cross's (1991) Performance Pyramid. The Balanced Scorecard by Kaplan and Norton (1992) is by far the most well-known (BSC). Customers, internal business processes, learning, and growth are three more elements of performance that the BSC seeks to relate. Despite several theoretical and practical criticisms of the BSC, research shows that it is now widely used twenty-five years later. It isn't always referred to as a balanced scorecard, and it doesn't always fully utilise the intended cause and effect linkages or linkages between performance metrics and incentives. Kaplan (2009) addresses this in depth in his book Conceptual Foundations of the Balanced Scorecard.
One of the most important aspects of measuring performance management is the performance pyramid method. The Performance Pyramid is a technique for finding performance improvement initiatives and a conceptual framework for assessing performance problems. The pyramid has grown from three contributing components and one outcome factor, or major accomplishments, when it was first introduced in 1998 to a more sophisticated framework, a limited collection of diagnostic tools, and a high-level implementation methodology (Wedman, 2010). The Performance Pyramid was created to give a simple yet thorough approach to assessing performance issues and enhancing individual, group, and organisational performance. The pyramid is based on Gilbert's and other researchers' work, as well as the experiences of a variety of performance transformation practitioners and consumers. It has developed over the previous ten years and will continue to do so while adhering to the concept of "clear, yet extensive.” (Ibid).
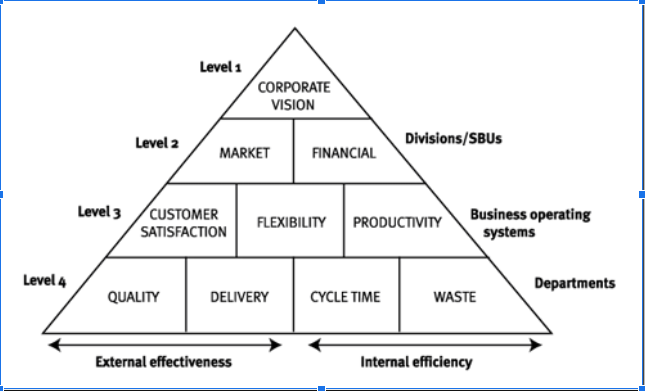
Performance Pyramid and Care Homes
A central aspect of providing care in care homes is the provision of health care services. The BME Luxury Homes wants to focus on the provision of both medical and non-medical care of elderly people who’d like to pay for luxury services. CTIS elucidated a comprehensive plan of incorporating the performance pyramid in a health care and care setting.

There are three indications that can assist the corporation accomplish its corporate objectives at the commercial business system or unit level.
Customer satisfaction is the first. In order to guarantee that the company accomplishes its corporate objectives connected to the market aim, client satisfaction at the corporate level
At the corporate level, the second component in the Performance Pyramid is flexibility, which essentially refers to how adaptable the company's product or service, as well as its operations and finance, are to market changes. The strategic plan and operating system should be carefully examined to see if they are capable of responding. For example, if technology changes, will the company operating system be able to react or not. The managing of resources such as labour, equipment, skill, time, and others is referred to as productivity.The firm should have adequate labour, material, and other resources to adapt to market changes, consumer demand, and market demand (accaglobal.com).
This component, according to the performance pyramid, might assist the business in achieving its corporate goals.According to the pyramid which is elucidated below, as pictured in this figure, is a top down approach of improving health care. The four sides depict the institution (whether public or private, in the case of BME Luxury Care Homes, private) side of the industry's organisation structure and management; the necessary framework for constructing universal healthcare and disease management; performance mechanisms for delivering high Return on Investment (ROI) and best patient care; and information technology solution components that achieve the outcome (icaew.com).
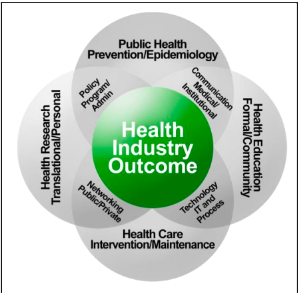
Health-care organisations are complex and adaptable systems with a wide range of organisational structures, many vertical and horizontal linkages, and a high level of centralized rules combined with a high degree of personal professional autonomy and authority. Indeed, health-care organisations rely heavily on their physicians to provide high-quality treatment, promote population health, and ensure the long-term viability of the industry (Berwick et al, 2008; Kaissi, 2014). This is the reason approaching performance management through the performance pyramid, is because it is a good non-financial indicator of performance in health care sector, where indicators like quality of care provided is an important indicator.
The base of pyramid indicates the major aspects of the health care service that the institution that it is trying to provide. In the case of BME Luxury Care, the most important points that need to be taken care of are health research, technology and health care. Health research indicates the institutions endeavors to innovate to a greater degree in the health care field and the services which is being provided (Yoon and Koo, 2009). Additionally, innovation in health care is also important for health care principles in general as senior citizens are more likely to demand higher intensities of health care.Older people's health promotion differs substantially from that aimed at younger generations. This is due in part to the fact that the health of elderly individuals is typically poor. Seniors are more prone to have chronic illnesses and multimorbidities, and their functional ability is often reduced. This means that health promotion initiatives for the elderly must take into consideration these limits in health and everyday activities, requiring more professional health promoter participation and more personalised methods. Certain lifestyle problems are also more prevalent among the elderly (Sowa et al., 2014; Golinowska et al., 2016).
However, the model needs to be adapted keeping in mind certain things which it cannot deliver. Models, frameworks, and taxonomies, on the other hand, are insufficient for making difficult judgments on what to do to increase human and organisational performance. There are no formulae for deciding which initiatives will help your company accomplish its goals. The Performance Pyramid is no different; it does not specify which actions should be used to improve performance. It also doesn't specify which combinations of treatments are most effective in your organisation. It does, however, give a road map for assessing where your organization's performance systems may be failing, deciding what choices are open to business, and guaranteeing that all components of your improvement process are contributing to achieving substantial outcomes (Pershing, 2006).
Apart from that, generally speaking, there are some things which one needs to be mindful of when trying to measure non-financial methods of performance. One of them is the standardization that implementing a mechanism like the performance pyramid in increasing performance. Performance measurements may lead to a lack of creativity since they foster relatively inflexible behavioural results. Employees get focused on changing their work habits in order to match with certain methods and processes that yield a rewarded result. Employees may be discouraged from trying with creative ideas that might yield a better result as a result of this. Additionally, non-financial performance measures sometimes run the risk of becoming too unpredictable, whereby they cannot really predict if the quality of the service or customer satisfaction will remain the way it is showing at present. Hence, businesses should use tools of performance measurement should be used carefully and personalized to the business in which they are being implemented (Akers, 2019).
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Strategic Pathways to Project Completion.
References
Deloitte Croatia. 2021. Non-financial reporting - Compliance analysis. [online] Available at:
NerdWallet. 2021. What Is a Business Model? - NerdWallet. [online] Available at:
VisionEdge Marketing. 2021. Six Non-Financial Metrics Every Marketer Should Measure. [online] Available at:
Kaplan, R.S. and Norton, D.P., 1996. The Balanced Scorecard: Translating strategy into action, Harvard Business School Press, Boston. Massachusetts.
Kaplan, R.S., 2009. Conceptual foundations of the balanced scorecard. Handbooks of management accounting research, 3, pp.1253-1269.
Yoon, H.S. and Koo, B.M., 2009. The Mediating Effects of Social Support on Health Status and Ddepression of the Elderly. Korean Journal of Social Welfare, 61(2), pp.303-324.
Berwick, D.M., Nolan, T.W. and Whittington, J., 2008. The triple aim: care, health, and cost. Health affairs, 27(3), pp.759-769.
Kaissi, A. (2014). Enhancing physician engagement: An international perspective. International Journal of Health Services: Planning, Administration, Evaluation
Icaew.com. 2021. [online] Available at:
Sowa, A., Topór-Mądry, R., Tobiasz-Adamczyk, B. and Golinowska, S., 2015. Health status of older people: evidence from Europe. Zeszyty Naukowe Ochrony Zdrowia, Zdrowie Publiczne i Zarządzanie, 13(4).
Golinowska, S., Groot, W., Baji, P. and Pavlova, M., 2016. Health promotion targeting older people.
https://www.accaglobal.com, A., 2021. The pyramids and pitfalls of performance measurement | ACCA Qualification | Students | ACCA Global. [online] Accaglobal.com. Available at:
Pershing, J.A., 2006. Human performance technology fundamentals. Handbook of human performance technology, pp.5-34.
Bizfluent. 2021. What Are the Disadvantages and Advantages of Performance Measures?. [online] Available at:
Assets.publishing.service.gov.uk. 2021. [online] Available at:
Strategic Planning. 2021. Should I Use Goals-Based or Issues-Based Planning? - Strategic Planning. [online] Available at:
Flemming, P.L., 2015. A review of strategic planning models developed over the past 50 years, and their effectiveness in public sector organizations. In International Conference of Leadership, Management and Stratetic Development. Doi: https://doi. org/10.13140/2.1 (Vol. 4314).
Scandura, T.A. and Williams, E.A., 2000. Research methodology in management: Current practices, trends, and implications for future research. Academy of Management journal, 43(6), pp.1248-1264.
KeepSolid Blog. 2021. The Whats and the Hows of Strategic Planning Models — KeepSolid Blog. [online] Available at:
Economics Discussion. 2021. Strategic Planning: Meaning, Features, Importance and Limitations. [online] Available at:
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



