Impact of TGFU on Student Learning
Using Teaching Games for Understanding
The teaching games for understanding was a research that was created and developed by United Kingdom researchers from Loughborough University known as Bunker, Werner, and Thorpe in the year 1982, their initial idea of this project was to apply physical education through games to improve the techniques and transfer the given practices to be a competition like situation through the help of their teachers. The group of intellectuals proposed that decision making, skills, and problem-solving are essential tactics that place a student in a given gaming environment whereby they have to learn to be tactical more than they are technical. The students are taught when playing a given game they have to ask themselves the question of what to do in a given game before the question of how to do it has been considered. The approach given by these scholars suggests that the traditional gaming practices that only focuses on the skills of the gamer are irrelevant if they do not focus on the tactics of the game inclusive of wise decision making. (Werner, Thorpe, & Bunker, pg 28,1996).
Ever since the approach of teaching games was proposed there has been several sections that were amended to improve its relevance. For instance in the year 2002 Butler, Kirk, Claxton & Light did a research that was in proposition to that the teacher who is applying teaching games for understanding has to have an approach in which the facilitator offering the learning from the director while making changes in reference to the role played in the learning process can make the idea of TGFU challenging to be established, early career teaching and also the preserving of it. This study has enabled teachers to offer the services in focusing on both the personal and the social nature of the player (student) towards their development. (Werner, Thorpe, & Bunker,pg 30, 1996).

Recently, this study has enabled teachers to develop and articulate the students understanding on pedagogy and its now it is recognized universally and constructed for the betterment of the students learning ability. Isolated skill development is applied when the individual concerned with the study acknowledges its importance. There are various studies conducted in reference to teaching games for understanding whereby the relevant games are being modified so as to suit the learners choice of interest. When applying the use of teaching games for understanding, there is a particular model that was developed by Bunker, Werner and Thorpe for a better understand and they include:
Games
The model has indicated that learning is based on games whereby the learner has some of the defence so as to use the opposition for education purposes. In this stage the student has to have the knowledge of the game this will help the student to outline the problem at hand and how it can be solved through tentative decision making.
Appreciating the game
Once the student has identified the game, they should be given enough time for a better understanding of the game. This ensures that the learner has developed a knowledge whereby they have a better understanding of the general rules that make the game unique, for instance, the height of the net in invasion games tends to affect the pace in which the game is played, increasing or reducing the number of fielders will make it easy or hard to score runs.
Tactics
Problem-solving tends to be a critical approach in regards to using teaching games for understanding. Amateurs usually are introduced to the relevant tactics and principle movements whereby they are based on simple ideas of both space and time. The researchers would argue that just like skills for instance throwing tends to transfer across the given game, so will the given tactical knowledge.
Decision making
Once the students have learned to appreciate the game through understanding the technical part of it which are the rules and has applied the tactical knowledge they will know what to when to do and how to do it. The learner will tend to appreciate more when they get to understand how to control the ball for instance how to pass, how to dribble and how to shoot. Once these factors have been appreciated, they will influence the decisions made about the skills execution.
Performance and execution of skills
Take a deeper dive into Mechanical Principles of the Standing Broad Jump with our additional resources.
The students have to identify the need for a particular skill so as to actualized their performance in the game, this requires an individual assessment. Technical instructions are provided once the learner has provided the skills needed within the context of the game. For instance, a student who is playing basketball when they are guarded intimately they will understand when its appropriate for applying different techniques of bounce and chest passes in conjunction to foot and head fakes.
Comparison between Sport Education and TGFU against the Old Fashion of PE
Models based practices in teaching has been suggested as a valid way of moving from the limitations that are within the traditional models of physical education. The traditional method of physical education has been characterised as a model which is dependent on multi-activities and the focus of the program is the content whereby students are able to experience various forms of physical education. The traditional method has been considered to lack competence since there is no sufficient time given to any of the given activities and students tend to leave school without even learning any positive attributes.
Traditional based program offers a given limited coherence and the achievement of the outcomes is limited since there is no accountability. The advantage of traditional models is that the physical educators within the various learning institution have applied the method to achieve diverse and at given times offer educational benefits that are competing for students. Model based activity offers a solution to the limitations that are within the traditional model whereby the students are able to learn appropriate strategies to the individual pedagogical model. The traditional model approach offers the students’ technique development while model based approach focuses on the tactical approach and the skills for solving problems and making wise decisions.
Advantages of Teaching Games for Understanding
Teaching games for understanding consists of games that are designed with the intended purpose of improving and motivating the quality of the lesson that is being offered.
The motivation of the students is considered to be relatively high since the players practice their sessions in gaming context.
Teaching games for understanding offers opportunities to the players to solve more complex problems and also in making tentative conclusions.
Teaching games for understanding provides the opportunity for students to learn various skills in the way they occur in the game, this is a major concern since the players learn various technical skills and they apply the given skills to improve their game.
Teaching games for understanding is a tool applied that benefits the students in understanding the importance and value of each player in the game and they are able to utilize any given opportunity within the game.
While applying teaching games for understanding students are able to think strategically about various game concepts and in the process their technical skills continue to develop within the realistic nature of the game.
Disadvantages of Teaching Games for Understanding
For the class to be interesting and also to increase the participation of the students it requires a vast motivating coach, if the session is being led by a poorly motivated coach the participation of the students will also diminish.
Students who had being exposed to technical approach and later learned the tactictal approach through teaching games for understanding, some of the students find it uncomfortable when they were asked questions also when the focus is being shifted from the coach to the student.
Questions which are constructed poorly tend to be taken as rhetorical questions hence the students do not rely on their conscious thinking.
The observation skills of the facilitator will either improve or hinder the application of teaching games for understanding, in addition when the observation skill is limited there tend to be negative implications on the questions asked and the effective game progression.
Teaching games for understanding is more appropriate compared to the traditional model of teaching since there is effectiveness in the tactical approach of a game compared to the technical approach. The is a wide range of focus on the players of a given game since teaching games for understanding employs questions, keen observation and also modified games that are relatable.
There has been a decreased involvement of students who participate in physical education and majority of them just participate because it is part of the curriculum or the application of traditional model of teaching, but TGfU has generally aimed in encouraging the students to be more tactical and making relevant decisions as the game progresses. The conceptual and contextual approach of teaching games for understanding also enables the students to think strategically in relation to the concept of the game while in the process they develop skills they will apply in a realistic idea of life. Ever since the introduction of TGfU to the curriculum, in my study I have applied the theories of several scholars in context to the TGfU. These theories include promoting the development of knowledge tactic (Turner, 1966), ways that are designed to assess the performance of the game(Oslin, Mitchell and Griffin, 1998) and developing the technical skills(Lawton, 1989).
Plan Resources for a Sport Education Unit
For my research I used soccer as a preferred game whereby 16 participants were selected and they formed a football affiliated squad. The large group was further divided into a smaller group of six defenders whereas the rest of the players were members assigned as the attacking group. The defenders were majorly used for the assessment whereby they were the tool for observation. The lesson was schedule to take place at the university football pitch, and was to last for 12 weeks with one session per week, each session concentrated on a given particular concept that makes up the overall theme. The formation of the game was concentrating on the defenders ensuring they are three in each side but the formation of the attackers could be altered as in 3-5-2, 3-3-4 or 3-4-3.
Football match schedule
The session table for the 12 weeks of training is used to create the playoffs that will see through the development of the player from one game to the other. The games are set for week 1, week 6 and week 11, for the case of week twelve whereby they will play as a full soccer team the game will be assessed but not recorded in the schedule.

The game schedule was created so as to introduce smaller game concepts that make up the entire theme of the lesson. As the coach ensures that there are sufficient balls for the game and the players are playing within the rules that are administered to them. In each session players are provided with new sets of challenges as they are asked questions, the format of the session followed the basic outline below:
Warming up
Play off
Challenges introduced and question and answers session
Play off
Further challenges in cooperated
Further questions
Game progression
Repeating the cycle
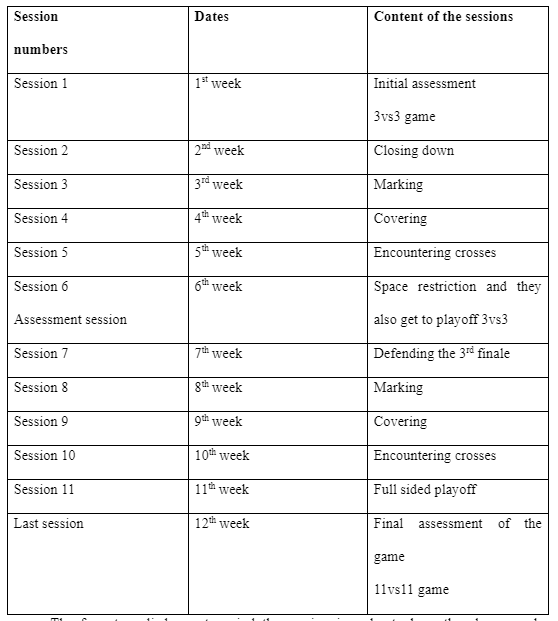
The format applied was to spiral the session in order to keep the players under pressure as more challenges were introduced. The sessions that were considered to be spiralled are marking, covering and encountering crosses, as seen in the football match schedule these sessions were repeated on week 8, 9 and also week 10. On the week of the sessions a full game was played this was to examine the understanding of the player of what it means as on the concept of defending as a whole unit.
The game would later be developed to make it suitable for the game play assessment index, this was important since it provided the measurements of the involvement of the game and also the performance of the players. Since the concentration was based on the defenders, the game started off by three attackers and three defenders whereby they played on half of the football pitch and up to a given width of the 18yard box. The game components of adjustment, decision making, cover and skill execution were applied in assessing the players, also it was a clear way of showing out what the unit of defenders was striving to achieve.
Scoring

Scoring key:
10 = the performance is always very effective 8 = effective performance (usual)
6 = moderate effective performance 4 = the performance is weak (rarely)
2 = the performance is very weak
Rules of Play
Players are to use their feet while moving or passing the ball.
Only the goalkeeper is allowed to use their hand in touching the ball but only when the ball is at the goal side.
The teams are not allowed to interfere with each other.
Each player on the team must at least touch the ball more than once
The defender is not allowed to play as goalie the entire time but he is required to attack the opponent to slow down their progress.
The game will last for 20min per half time with a 5 min half time.
The players are required to play fairly and avoiding to injure the opponent.
Looking for further insights on Olympic Games Environment Overview? Click here.
The diagram below is a representation that of the modification applied using the games performance assessment index for data analysis, these helps the players to understand what it means to play with three defenders all acting as a unit.
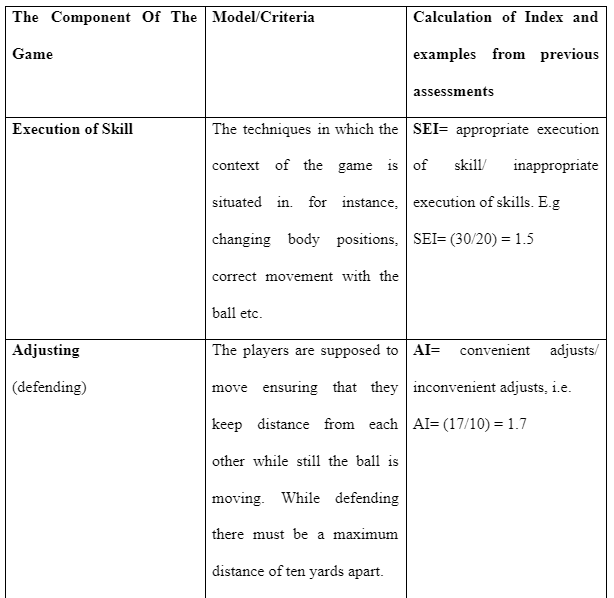
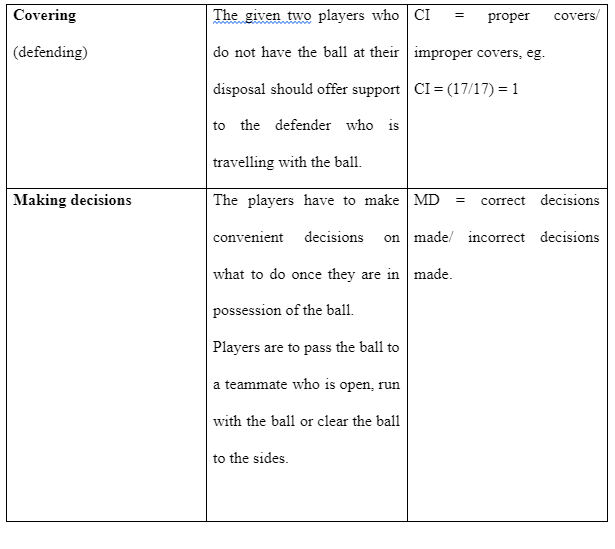
At the end of the 12 sessions it was evident in approach of applying teaching games for understanding the players are set to improve their game involvement, and this is important since once the game involvement has improved it is evident that the game performance will also improve. Professional players rather than the typical physical education students can elevate their execution of skills, making decisions, covering and adjustments while set more complex challenges that will strengthen their game performance in the context of TGfU.

Conclusion
The study of teaching games for understanding and applying it towards teaching players and even students in physical education has proven to be convenient theoretical framework towards enhancing both the players’ involvement in the game and skill execution. The initial theory of teaching games for understanding depends heavily on the ability of the teacher to identify the given problems of the players as the game progresses. Once the teacher has clearly identified the problem, it is possible to assist the player on where their weakness or strength lies on. The use of teaching games for understanding requires knowledge since knowledge is considered to form the basis of observation; if the facilitator is not observing the players enough they tend to work slow and inappropriate.
REFERENCES
Allison, S., & Thorpe, R. (1997). A comparison of the effectiveness of two approaches to teaching games within physical education. A skills approach versus a games for understanding approach. British Journal of Physical Education, 28(3), 9-13.
Butler, J. I. (1996). Teacher responses to teaching games for understanding. Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance, 67(9), 17-20.
Griffin, L. L., & Butler, J. (2005). Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice. Human Kinetics.
Hopper, T. (2002). Teaching games for understanding: The importance of student emphasis over content emphasis. Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance, 73(7), 44-48.
Kirk, D., & MacPhail, A. (2002). Teaching games for understanding and situated learning: Rethinking the Bunker-Thorpe model. Journal of teaching in Physical Education, 21(2), 177-192.
Griffin, L. L., Brooker, R., & Patton, K. (2005). Working towards legitimacy: two decades of teaching games for understanding. Physical Education and Sport Pedagogy, 10(3), 213-223.
Werner, P., Thorpe, R., & Bunker, D. (1996). Teaching games for understanding: Evolution of a model. Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance, 67(1), 28-33.
Turner, A. P., & Martinek, T. J. (1999). An investigation into teaching games for understanding: Effects on skill, knowledge, and game play. Research quarterly for exercise and sport, 70(3), 286-296.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



