Understanding the Challenges of Smoking Cessation
Introduction
Quitting smoking or Smoking cessation can be problematic because of psychological and physical dependence. Mainly habit and nicotine habit both are almost unbreakable. Various symptoms for example anxiety, insomnia, and agitation even depression can be observed for in taking tobacco. This smoke of cigarettes damages the lungs mainly which finally resulted in reducing inhaling capability of oxygen. Numerous chemicals caused by tobacco provokes the development of atherosclerosis which became the cause of heart attacks and strokes. Those seeking to explore the impact of smoking may consider seeking healthcare dissertation help to gain deeper insights. The worst effect of smoking is cancers (Alberg & Carpenter, 2012).
According to Ochsner , near about 70% smokers went to physician in a year and more than 70% of smokers’ wanted to quit smoking and they also took serious effort to quit it at least once (Milani & . Lavie, 1999). But the problem is when someone is taking effort to quit from it, the deficiency of nicotine in blood causes depressed mood, anxiety, restlessness, insomnia and irritability (Aveyard & Raw, 2011). Now a day’s different smoking cessation treatment has been practiced for helping all the smokers to quit smoking. Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches, e-cigarettes, and placebo e-cigarettes (no nicotine) are some popular treatments for quitting smoking. Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) is mainly substituting nicotine from end to end with a skin patch which helps to maintain a level of nicotine in blood. E-cigarettes (Electronic cigarettes) are planned for users such a way which permit to inhale nicotine but it prevents the destructive effects of smoking. This provide nicotine vaporising a solution which comprises with nicotine, flavourings and glycerine. There is no smoke in it as burning is not involved in it. That’s why it does not yield carbon monoxide and tar like normal cigarette. Placebo Electronic cigarettes is same as e-cigarettes but it does not contain nicotine. The present research is conducted in order to mainly determine the impact of various treatments on the smoking habits of the people and determine all those factors for causing smoking related disorders.

Research Question
Determine the statistically differences in different smoking cessation diagonosis
Determine the relation between occurrence of number of relapse related to tobacco use disorders and gender
Determine the relation between occurrence of number of relapse related to tobacco use disorders and nicotine level of the patient before treatment
Determine the statistically differences between the nicotine level of the patient before treatment, nicotine level of the patient immediate after treatment and the nicotine level of the patient post treatment
Determine the relation between nicotine levels of the patient immediately after finishing treatment and the nicotine level of the patient post treatment while controlling age
Method
Participants
As per the data, there were a total for 45 participants. 46.7 percent (21) of the participants were male while remaining 53.3 percent (34) of the participants were female. Maximum and minimum age of the participants 41 and 27 respectively and average age of the participants are 34.16.
16 participants are treated by nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches therapy. 15 participants are treated by e-cigarettes therapy and 14 participants are treated by placebo e-cigarettes (no nicotine) therapy.
Study Design
The study was quantitative in nature. This experiment used a between-subjects design. To interpret the effects of various treatment of smoking cessation process, the independent variables were different types of diagnosis as this is randomised in nature and dependent variable is nicotine level serum that is found three time before treatment (1 week before starting treatment), immediate after finishing treatment and post treatment (1week after finishing treatment). Three types of diagnosis method are there - nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches, e-cigarettes, and placebo e-cigarettes (no nicotine).
Information about the data set
Gender: This is categorical variable which depicted that the participants are male or female where 1 depicted male participants and 0 depicted as female participants.
Age: This is a continuous variable which is depicting the age of the participants. According to the result of Shapiro-Wilk test of normality, the p value or significant value is reported as .635 which is greater than 0.05 which means that the data is normally distributed (figure 1).
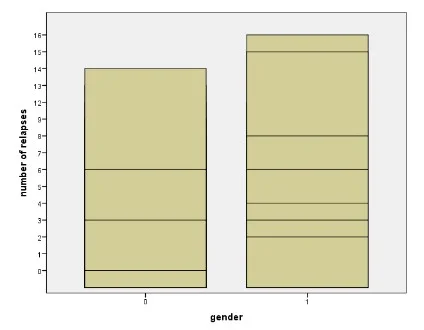
Number of relapse: This is a continuous variable which is depicting number of tobacco use disorder have been seen in the patients. According to the result of Shapiro-Wilk test of normality, the p value or significant value is reported as .004 which is lesser than 0.05 which means that the data is not normally distributed (figure 1).
Time 1, Time 2, Time 3: This is a continuous variable which is depicting the nicotine level of the patients where Time 1 is refereed as the nicotine level of the patient before treatment (1 week before starting treatment), Time 2 is refereed as the nicotine level of the patient immediate after finishing treatment and Time 3 is refereed as the nicotine level of the patient post treatment (1week after finishing treatment). According to the result of Shapiro-Wilk test of normality, the p value or significant value are reported as .142, .144 and .166 respectively which are greater than 0.05 which means that the data is normally distributed (figure 1).
Diagnosis: This is categorical variable which depicted various treatment of smoking cessation process where 1 depicted the nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches, 2 depicted the e-cigarettes treatment, and 3 depicted the placebo e-cigarettes (no nicotine). The selection the patients who will participate this programme is done randomly.
Result
To determine the statistically differences in different smoking cessation diagonosis
The first objective of this research is to identify any of the smoking cessation treatment is more effective than the others. For investigating the research question one way Anova ,a parametric, test has been chosen as the test is needed for determining if there are any statistically significant variances between the means of three or more independent variables. In this case independent variable is different diagnosis method of smoking cessation programme and the dependent variable is nicotine level of serum of the patient immediate after finishing the diagnosis (time 2). Other than that time2 variable is normally distributed.
Hypothesis of the test
Null hypothesis (H0): there is no statistically significant difference between the three types of treatments.
Alternative hypothesis (H1): there is statistically significant difference between the three types of drug treatments.
Result
The ANOVA table shows that the p-value or the significance value of the analysis comes out to be 0.707, which is grater r than 0.05 (figure 2). It means that obtainable null hypothesis is accepted. That is, there is no statistically significant difference between the three types of smoking cessation diagnosis as determined by one-way ANOVA (F (2, 42) = .349, p = .707).
To determine the relation between occurrence of number of tobacco use related relapse and gender
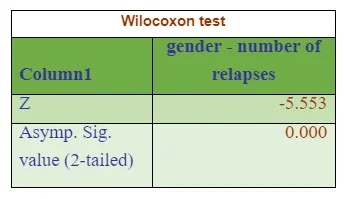
Second objective of the research is to understand the relation between gender (categorical variable) and number of relapse related to tobacco use disorders (continues variable). The research question is aimed to understand the effect of tobacco according to gender. For this Wilcoxon, a non-parametric test has been chosen, which relates the means between two unrelated groups in the context of same continuous, dependent variable. Here number of relapse variable is not normally distributed that’s why non parametric test has been chosen. Independent variable is gender and dependent variable is number of relapses.
Hypothesis of the test
Null hypothesis: Mean of relapses of male patient is same as mean of relapses of female patient
Alternative hypothesis: Means are not equal
Result
According to the result of Wilcoxon test statistics, the associated p-value 000 which is less than significance level 0.05 (figure 3). So null hypothesis is rejected and it depicted that Mean of relapses of male patient is not same as mean of relapses of female patient.
To determine the statistically differences between the nicotine level of the patient before treatment, nicotine level of the patient immediate after treatment and the nicotine level of the patient post treatment
Fourth objective of the research is to understand differences between the nicotine level of the patient before treatment, nicotine level of the patient immediate after treatment and the nicotine level of the patient post treatment. This research question was aimed to investigate the effects of different diagnosis. For measuring this difference Anova test is selected as the variables are normally distributed.
Hypothesis of the test
Null hypothesis (H0): there is no statistically significant difference in nicotine level of blood between three times.
Alternative hypothesis (H1): there is statistically significant difference in nicotine level of blood between three times.
Result
The ANOVA table shows that the p-value or the significance value of the analysis comes out to be 0.241, which is grater r than 0.05 (figure 5). It means that obtainable null hypothesis is accepted. That is, there is no statistically significant difference difference in nicotine level of blood between three times as determined by one-way ANOVA (F (2, 132) = 1.438, p = .241).
To determine the relation between nicotine levels of the patient immediately after finishing treatment and the nicotine level of the patient post treatment while controlling age
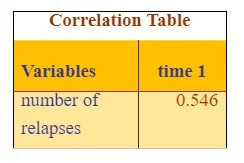
Fourth objective of the research is to association between nicotine levels of the patient immediately after finishing treatment and the nicotine level of the patient post treatment while controlling age. For this partial correlation method is chosen as it also helps to measure association of two continuous variables while controlling other continuous variable. This research question is investigated to understand the effect of the different diagnosis method of smoking cessation treatment while controlling the effect of age factor as different aged patients respond to the diagnosis differently. For understanding the impact of the treatment, age variable is controlled.
Result
According to the result, correlation coefficient value is reported as .546 which is greater than 0.5 (figure 6). The results indicated that there was high positive correlation between these variables which was statistically significant when controlling for age R (42) =0.918, p=0.000].

Discussion
The present research is conducted in order to mainly determine the impact of various treatments on the smoking habits of the people and this process affects the smokers. To determine the statistically differences in different smoking cessation diagnosis, Anova test has been done. According to the result there is no statistically significant difference between the three types of smoking cessation diagnosis which means that three treatment is giving same result. For understanding the gender wise effect of number of tobacco related relapses Wilcoxon test has performed and according to the result it depicted that number of relapses is varied according to gender. For understanding the effect of nicotine level on number of tobacco related relapses correlation test was performed. A strong significant positive association is reported which proved that nicotine level in blood is an effective reason behind the occurrence of tobacco related relapses. For understanding the differences between the nicotine level of the patient before treatment, nicotine level of the patient immediate after treatment and the nicotine level of the patient post treatment, Anova set was performed. There is no statistical difference is found in before, post and immediate after treatment. There can be various reason for it like most of the patient could not quit smoking after the treatment or the time gap is less as the test was happened just after 1 week of the treatment. Further research can be run on searching the appropriate cause. For clarifying the importance of age factor more clearly, partial correlation test was also performed between the relation between nicotine levels of the patient immediately after finishing treatment and the nicotine level of the patient post treatment while controlling age. According to the result there is not such difference occurred for controlling age which clearly proved that age is a significant factor for the occurrence of tobacco related relapses. In precisely, it can be depicted that all smoking cessation diagnosis method do not have same impact on the patients and nicotine level in blood is significant factor for occurrence of tobacco related relapses. Other than that age in not a factor for having this type of relapses. Intake of nicotine is the one of the main reason for occurring tobacco related disorders and the effect of this disorders also varied gender wise.
References
Alberg, A. J., & Carpenter, M. J. (2012). Enhancing the Effectiveness of Smoking Cessation Interventions: A Cancer Prevention Imperative. Oxford journal, 260-262.
Aveyard, P., & Raw, M. (2011). Improving smoking cessation approaches at the individual level . BMJ journqal .
Milani, R. V., & . Lavie, C. J. (1999). Smoking Cessation: The Importance of Medical Intervention. Ochsner Journal , 141-144.
Appendix


ANOVA Table




Continue your exploration of From Linguistic Roots to Contemporary Perspectives with our related content.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



