Mental Illness Challenges in Single Parents
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.0 Introduction
Mental Illness is referred to health condition that involves changes in thinking or behaviour, emotion and feelings due to distress and problems faced in the social condition, work or family activities. The presence of mental illness is common in single parents due to the hardship faced by them out of the need of managing parenthood duties single-handedly for supporting growth and development of children (Firth et al., 2019). It is evident as parenthood is mentioned to be key transition in life which especially demands increased skills and responsibility management by both the parents of the child. However, being a single parent lead the entire responsibility of care to be managed by a person without assistance from their partners which makes them stressed regarding the ability to perform their duties that eventually negatively affect their psychological health to make them develop mental illness as health challenge (Tarar et al., 2021). The presence of mental illness in single parents is a major health concern as such condition makes them incapable to effectively care for their children who out of lack of support face developmental and growth difficulties. Therefore, in this research, the mental illness challenges faced by single parents are to be identified and the way they are to be managed is to be determined. This is important as it would provide overview regarding the mental illness faced by single parents and the way they are to be supported to overcome the illness to execute their responsibilities of parenting towards their child or children in an enhanced manner. For single parents facing mental health challenges, seeking a psychology dissertation help as it supports them in navigating their parenting journey effectively along with managing their mental well-being.
1.1 Background of the Topic
Parenting is vital responsibility to be played by individuals as it supports the emotional, physical, intellectual and social development of the child from infancy to adulthood. As a single parent, the individuals require to struggle enhanced magnitude for managing care and supporting the child. The single parenting condition leads the single parent to face mental illness. This is evident as 20.6% of mothers who are single from childbirth are found to suffer from postpartum depression. Moreover, 11.5% mother whop cohabits at childbirth are seen to suffer depression (Agnafors et al., 2019). This indicates that single parents struggle with mental illness from the instance of childbirth which is required to be managed for their better health and well-being.

1.2 Rationale of the Topic
In life, becoming a parent at any age is a great transition that brings new challenges to be managed by the individuals. Globally, 20 million children were reported to be managed and living with single parents that is either the mother or father. Among them, 19 million children are living with their single mothers and 3 million of them are living with their fathers (healthofchildren, 2021). This informs that single parenting is mostly faced by female compared to male as there are less children found to be managed by single father compared to single mothers globally. Across Europe, 18.1% of the children are reported to belong from single-parent homes with the least present in Greece (5.3%) and most in the UK (28.1%) (OECD, 2016). In the UK, it is reported that 1.8 million single parents are present and among them a quarter of the families involve dependent children. Among them, 90% are single mothers and 10% are single fathers along with it has been determined that the average age of single parents in the UK is 39 years (gingerbread.org.uk, 2021). Over the decade in the UK, 25% of families are found to have single parents (gingerbread.org.uk, 2021). This indicates that the number of single parents are present in considerable numbers in the UK. In the study by Widan and Greeff (2019), it is mentioned that single parents are more likely to suffer from mental illness which challenges their ability to care for the child and manage person behaviour. This indicates that considerable high number of single parents in the UK and global areas make mental illness be common challenge been faced by most parents.
The mental illness in single parents is considered as an issue because they are solely responsible for managing the family. The interference of their mental illness makes hindered family structure to be formed that negatively affects the growth and development along with social life of the children as the parents show incapability to perform the basic duties of parenting with effectiveness for the children and the family (Richter and Lemola, 2017). According to Damaske et al. (2017), the children of single parents with mental illness show increased likeliness to develop hindered psychological health. This is because the negative behaviour and emotions of the single parents due to their mental illness creates challenges for the children to be appropriately cared and managed. It causes hindered effect on the mental development of the children making them show mental illness in the later stages of life. It is also evident from the reports by ONS which mention that children with families that have mental illness are likely to struggle with their mental ill-health compared to those who belong from healthy functioning families (ONS, 2019). It is also evident from the study of Daliana and Antoniou (2018) which mentions that single parents with mental illness challenges lead the children to drop out of school so that they can care for the parent. Thus, the mental illness in single parents compromises the ability to progress in future of the children which makes it a key issue.
The presence of mental illness as challenge among single parents is also an issue because it compromises the ability of such parents to effectively take care of the children. This is because children are mainly dependent on their mothers or father to look after and support them in their effective development of growth (Mencarini et al., 2019). Moreover, the mental illness in single parents makes them lack concentration, effective cognitive condition mental stability and other to effectively think and process their ability to deliver required care to the children, in turn, making the children suffer from lack of enhanced support for their health and well-being (Pailhé et al., 2020). The mental illness among single mothers is also an issue because it leads to support the development of dysfunctional relation with the children by the parent. This is because of the hindered behaviour and emotion showcased by single parents towrads their children out of mental illness (Mencarini et al., 2019).
The mental illness in single parents has currently become an issue because it is not only affecting the family structure but also creating economic hardship for them which in turn is negatively affecting their ability to meet the demand and needs of the children. This is because single parents are the sole earners of the family and manage finances for the children to meet their needs. However, the presence of mental illness among single parents is making them mentally incapable to continue their work which lead them to face economic hardship (Rousou et al., 2019). The mental illness among individuals is stigmatised in some societies due to which the mentally ill persons are isolated and lack social support in overcoming their problems (Daliana and Antoniou, 2018). The presence of mental illness in single mothers would also make them lack effective social support in overcoming psychological distress which adversely impacts their social life (Mencarini et al., 2019). Moreover, single parenting families are increasing which is due to divorces among partners. The increasing number of single parents indicate the condition of mental illness among them would also be increased making it a key concern to be understood. Thus, the current study is going to shed light on the factors leading to mental illness among single parents along with ways to overcome them.
1.3 Significance of the Topic
The single parents act as the sole parental support for the child due to which hindrance in their mental ill health has a detrimental effect on the upbringing of the child (Wang et al., 2017). Therefore, discussion regarding the key mental ill health challenges faced by single parents are to be determined for better well-being of the children and health management of the parents. This is because it would help to understand the reason and prevalence of the mental challenges faced by single mothers and the way they can be managed to ensure their better well-being.
1.4 Gaps in the Topic
The existing studies explored the common mental ill health challenges faced by single parents without differentiating how the psychological health impact and challenges may different as per the gender of the single parent. This created a gap of failing to provide information regarding the specific mental ill health challenges faced by mothers and father separately as single parent. Moreover, the studies have failed to provide information regarding the way societal condition differently affect mother and father as single parents manage the development of their child which has potential impact on their mental ill health to be disrupted. The existing studies also lacked insight into the way the mental ill health challenges faced by single parents are to be managed to ensure their enhanced health and well-being.
1.5 Aim
The aim of the study is to explore mental ill health challenges faced by single parents globally.
1.6 Objectives
To identify the prevalence and nature of mental ill health challenges faced by single parents
To determine the factors responsible for creating mental ill health challenges experienced by single parents
To assess the impact of mental ill health challenges on single parents and their children
To analyse the strategies to be used in managing mental ill health challenges faced by single parents
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.0 Introduction
The current chapter is framed to provide an overview regarding the research topic which is important to establish effective understanding regarding the current study and debate the relevant topic. The review is also important to present the existing knowledge available regarding the topic and identify gaps that are required to be fulfilled. Thus, the literature review is to be performed to create effective clarity and focus regarding the study topic.
2.1 Concept of Mental Illness
Mental Illness is referred to the health condition in which changes in thinking, emotion or/and behaviour occurs among individuals that interferes with their work, social and family life. The common signs seen in mental illness are excessive paranoia, extreme and sudden mood changes, long-lasting sadness, dramatic change in behaviour and sleep pattern and social withdrawal (Horwitz, 2020). The mental illness adversely affects an individual by making them unable to manage stress and making healthy choices in life. The mental illness can affect individuals at any stage in life ranging from childhood through adolescent to adulthood (Carson, 2019). There are a certain type of mental disorder such as anxiety disorder, depression, eating disorder, post-traumatic disorder and psychotic disorder (Horwitz, 2020). The diagnosis of the mental illness is mainly made through medical examination based on psychological analysis tools and framework. The treatment for mental illness is dependent on the nature of serious and impact of the problem in individuals (Horwitz, 2020).
2.2 Factors affecting Mental Illness
The social, biological, genetic and environmental factors are responsible for influencing the presence of mental illness among individuals. In the study by Hyman (2018), it is mentioned that certain forms of mental illness are inherited in individuals through genetic traits present in the family. It makes the individuals remain vulnerable to develop mental illness irrespective of their lifestyle. For example, mental illness such as attention deficit disorder (ADHD), schizophrenia, major depression and others can be inherited through genetic traits between families (Faraone and Larsson, 2019). The study by Stack and Meredith (2018) informed that mental illness is influenced by changes in the brain chemistry of individuals in which the naturally occurring chemicals in the brain known as neurotransmitters that are responsible for carrying signals in the brain work in hindered manner. The environmental exposure to stressors such as workload, family problems, partner disputes and others influence development of mental illness such as stress and depression. In single parents, it is often seen that social and environmental conditions such as work pressure, family incompetency ad others influence them to be at increased risk of depression and stress (Irvine et al., 2021).
2.3 Model for Mental Illness
2.3.1 Biological Model
The biological model of mental illness is developed on the basis of assumption that neuroanatomy, brain and biochemicals are all physical entities that work together for mediating psychological processes (Woolfson, 2019). Thus, according to the model, the disturbances in the physical entities in the central nervous system is considered to be the cause of development of mental illness in single parents. However, various social and environmental factors are responsible for instigating the change in the neuroanatomy in the brain in single parents leading them to develop mental illness. The biological theory of mental illness mentions that common mental illness such as depression develops due to hindered level of serotonin in the brain. The model also mentions that psychological or mental illness are to be treated with surgery or drugs (Larkings and Brown, 2018). Thus, it indicates that the raised mental illness in single parents to be discussed are to be treated with effective medical treatment. However, it is argued that mental illness treated with drug therapy are tending to reoccur after the cessation of the medication (Woolfson, 2019). This indicates that in managing mental illness among any individuals drug therapy along with additional psychological therapies such as counselling, cognitive behaviour control therapies and others are to be involved.
2.3.2 Cognitive Model
The Cognitive model mentions the way thoughts and perception of people influence their lives. It is identified that often distress causes distortion in the perception of the people which lead to their unhealthy development of behaviour and emotions. This is because distorted beliefs influence the individuals regarding the way they process gathered information to develop thoughts (Young, 2018). Thus, it can be considered from the model that distortion in the perception of single parents regarding their life and livelihood may have led them to face unhealthy emotions and feelings which makes them mentally ill. The model mentions that people are required to learn to identify their distorted thoughts and evaluate them to rectify their thinking so that it relates closely to the reality. It is required because it leads to reduce distress and makes people be more functional in their everyday life with stable psychological conditions (Chavez-Baldini et al., 2021). Thus, the single parents to overcome the challenge of mental illness according to the model are to be made to identify the thoughts that are causing them distress and rectify their thinking to have improved psychological condition.
2.3.3 Behaviourism
In mental illness, the behaviour model mentions that maladaptive psychological behaviour is developed by person through the influence of one’s environment. Thus, the model focus on the practice of prioritising the change in behaviour on the basis of identifying the cause of the dysfunctional behaviour (Kartal, 2021). Therefore, according to the model, to tackle mental illness in single parents, focus on the key causes that led to their disrupted psychology and behaviour is to be identified and the treatment is to be based on the identified facts. The behaviourist model considers that the things which can be seen and observed are real. The mind, consciousness and Id are not able to be seen but they are can be seen through the way the people react, act and behave in the society. Thus, from behaviour, inferences of the mind can be developed but they are not the key things considered to be observed in the investigation to determine the nature and cause of mental illness. The model mentions that behaviourist assumes that the presented behaviour of an individual is learned habit and the behaviourist tries to determine the way they are learned (Spillane, 2021). Thus, in determining the mental illness challenges faced by single parents, behaviourism mentions that environmental experiences which led to the development of the behaviour are to be identified.
2.4 Theories of Mental Illness
2.4.1Psychodynamic Theory
According to Freud’s psychodynamic theory, the unconscious and conscious parts of the mind involves in conflict with each other which leads to the development of phenomenon known as repression. The repression is mentioned as the state in which the individual is unaware of the troubled motives, distress or desire, but they influence negativity in person (Fulmer, 2018). Thus, this aspect of the theory mentions that single parents who have mental illness may be unaware of the condition but shows negativity in their behaviour and emotional thoughts which hinders their well-being. The theory mentions that to develop enhanced mental ill health and overcoming repression, the individuals are to successfully overcome developmental conflicts such as hindered interpersonal relationships, trust and others (Cohen, 2020). This indicates that single parents to overcome mental illness are required to resolve their conflicts with personal relationships and partners. The criticism of the psychodynamic theory is that it is unfalsified and unscientific. Moreover, the theory is developed on the basis of single observed cases due to which it creates difficulty in testing the truth of the interpretation (Guntrip, 2018). Therefore, using the theory to explain mental illness in single parents would create hindrance in presenting empirical data of the mentioned unconscious mind that is leading to the illness.
2.4.2 Social Theory
The social perspective of mental ill health determines and understands the presence of the health issue within social contexts in which people live and uses effective evidence and practice for working with communities as well as individuals to assist in preventing mental ill health issues and ensure their recovery. The model also recognises other perspectives such as the biological model but considers that prevention, as well as recovery, can be achieved in best way through holistic participation of people and individuals (Saeri et al., 2018). This indicates that the inclusion of social network is to be made for assisting in preventing mental illness and recovery of the mental challenges faced by single parents as a result of their parenting condition and social life.
2.4.3 Labelling Theory
The Labelling theory mention that mental illness is result of the social interaction in which other individuals respond to people and they imagine on their own the meaning of the responses (Cohen, 2017). Thus, the theory deduces that mentally ill people develop the illness as a result of thinking of the labelled perspectives of others on them. It is evident as single parents are considered to be incapable of taking effective care of their child and labelled as lazy individuals. This causes the single parents to doubt their ability to take care of the child which makes them develop mental illness such as stress and depression (Cohen, 2017).
2.4.4 Humanistic Theory
The humanistic theory of mental ill health emphasises the significance of being one’s true self for supporting them to lead their life in most fulfilling way. The core belief of the theory is that people are basically good at heart and are able to make the right choices on their own (Lundström et al., 2019). The theory mentions that feeling of worthlessness makes individuals negatively impact their life and world around them. This is because the theory consider that the way a person views their world has a greater impact on their actions and thoughts (Bland and DeRobertis, 2020). It indicates that single parents by developing positive perceptions regarding the current condition and world around them would be able to avoid mental illness and related challenges. The humanistic theory educates an individual regarding the way to develop self-acceptance and avoid criticism to develop a safe place to work with personal growth (Bland and DeRobertis, 2020). Thus, to help single parents overcome mental illness challenges, the care is to be based on the perspective of humanistic theory so that it leads them to develop acceptance of their condition and overcome the illness by working towrads personal growth.
2.5 Concept of Single parents
Single parents are individuals to lives with their children or child on their own without having support from any spouse of live-in partners. The single parents are seen to remain overwhelmed by the responsibilities of juggling care of the children, maintaining steady job and managing household chores. It leads the single parents to develop mental illness challenges as they are unable to concentrate on their stabilising their mental ill health out of the increased parental pressure to care for the child (Nieuwenhuis, 2020). Moreover, the single parents develop mental illness such as depression out of stigmatisation in the society that a single individual cannot effectively meet all the needs and demands of the children required for their enhanced upbringing and well-being. It makes the single parents doubt their ability to fulfil responsibility for the children, which in turn, affects their mental ill health (Nieuwenhuis, 2020).
2.6 Factor influencing single parenting
The single parenting is influenced by hindered marital relationship, divorce, separation, unmarried couples, unintended pregnancy and adoption. The key event of the marital breakdown is known as separation and divorce is the legal consequence of the action (Whisenhunt et al., 2019). The divorce leads to single parenting as one individual is to take entire care of the child on whom main custodian of the child is provided whereas the other partner separated have minimum contribution out of being separated in raising the child (Fransson et al., 2018). The desertion is one of the ways in which single parenthood is established because it is the situation where the father or the mother leaves away from the marriage without leaving any support or assistance for the partner. It causes one of the partners to be alone and raise their children while acting as the single parent in the absence of the other parent (Whisenhunt et al., 2019). The death of a parent or unintended pregnancy in which one parent is left alone by other results in single parenting of the child (Fransson et al., 2018).
2.7 Demographics of Single parents
The single parents are present worldwide and in OCED countries nearly 3-11% of single parents are present among the households with the average ranging to 7.5% as determined in last report in 2011. It was reported that 23% parents in Australia, 27% parents in Canada, 7% parents in Mexico, 26% of parents in United States and 31% parents in Lithuania and 23% parent in New Zealand are single parents. It led to consider that on an average 31% single parent household are present in EU (OECD, 2021). In 2020, it is reported that the highest portion of single parents are present in Latvia along with Belgium, US and Lithuania. The percentage varied between 6-28% across different OCED countries with the lowest number of single parents present in Turkey and the highest number of single parents present in Lithuania (OECD, 2021). In the single households, most of the children are found to be living with their single mother compared to single gather. The proportion of children living with their single mother ranged on an average 5.60% whereas the children living with single father on an average is 1.21% (OECD, 2021). This indicates that the mothers are more affected to become single parents compared to fathers.
2.8 Parenting style
The single parents as well as double parents follow certain styles of parenting to manage the growth and development of the children.
2.8.1 Authoritarian
The authoritarian parenting style includes strict disciplinary parents who executes minimum to little negotiation with the child in managing and minding them. In this style, the communication with the child is mainly one way and rules to be followed are made by the parents only. In this style, the parents are less involved in nurturing the child and more involved in commanding them with presence of high expectation to be fulfilled by the child (Shaw and Starr, 2019). In the study by Yaffe et al. (2017), single mothers are found to be more authoritarian compared to the married mothers. It is evident as divorced and single mothers are found to score high in authoritarian scale (31.55) compared to the married mothers (27.05). This indicates that single mothers are stricter compared to the mothers with partners. The single mothers intend to be strict on their child to manage them in disciplined manner so that they are able to control the household and additional responsibilities without facing any hindrance. This is because presence of messy and uncontrolled child would lead the single mothers to face hardship to control and manage the child and other associated chores along with work in single handed manner.
2.8.2 Authoritative
The authoritative parents are those who set rules for the children but also considers the opinion of the children. They are seen to validate the feeling of the children while also mentioning the child that the adults are in-charge of their care and supporting decision making. These natures of parents invest increased amount of time and energy for the children to prevent them from developing behavioural problems. The parents following the style use positive disciplinary strategies for reinforcing good behaviour for the child. The parents representing the style are found to be self-disciplined and think for themselves along with the children (Bahrami et al., 2017). The study by Yaffe et al. (2017) mentioned that single mothers score 37.47 in respect to use of authoritative parenting compared to married mothers who score 34.15 in this respect.
2.8.3 Permissive
The permissive parenting style is the way in which the parents allow the children to make decision on their own without influence and provides limited direction or guidance to them. The permissive parents are found to be opposite to authoritarian parents and they act as a friend rather than a parent with the child. The communication in this style of parenting is often two-way in which the children are allowed to present their points with the parents. This nature of parents are warm and nurturing towards their child and the set minimal to no expectation to be fulfilled by the child (Hosokawa and Katsura, 2019). The single parents avoid being use permissive parenting style as they feel it would make them face hardship and lack of control to discipline the child alone. They also consider the permissive style would lead them to make the children more vulnerable to face behaviour and academic problem which eventually led them to get blamed as they being single are unable to manage the child (Tyler et al., 2019).
2.9 Theories of Single parenting
2.9.1 Social Learning Theory
The key focus of the Social Learning theory presented by Bandura is to make observation and imitate the emotions, behaviour and attitude of different people. Thus, it focuses on learning through the way of modelling and observing others. The children initially interact with the families and they through observation of different actions in the family learn the action of the care providers (Juffer et al., 2017). In case of single parents, the child has only one parental figure to look after them and they are to copy their actions. It is essential and vital that children are to be managed by both parents as otherwise they may develop Oedipus complex (Nathans, 2021). According to theory of Bandura, the parents are mainly responsible for teaching mannerisms to the children. The parents are required to be trustworthy to the child and it creates highly opportunity to developing good relationship with the individual (Baker et al., 2019). This indicates that the single parents are to be develop positivity in their behaviour as it would only help them to effectively support their child to form good relationship with them to support their enhanced growth and manner development. Therefore, a stable mental condition by the single parents is to be managed as it would help the children to observe them and develop positive behaviour.
2.9.2 Operant Conditioning Theory
The operant conditioning theory indicates that reinforcement and punishments are important for altering behaviour in children. The parents by using the methods would be able to strengthen the good behaviour in children and weaken the bad behaviour (Akpan,2020). The single parents are required to effectively manage the operant conditioning to manage the behaviour of the children. This is because the hindered management may lead to create problems in children to develop unwanted behaviour. Therefore, the single parents are required to use both reward and punishment in controlled manner so that they are able to make children learn good and avoid bad behaviour.
2.9.3 Attachment Theory
The attachment theory refers that attachment is one of the basic human need for securing relationship between a parent and child. Bowlby’s attachment theory explains the way children and parental relationship is built along with the way it influences emotional as well as social development of the child. There are mainly four stages of development mentioned in the theory and the stages initiate from infancy, pre-attachment, attachment in making and formation of reciprocal relationship in the end. In each of the stages, effective bond is gradually built between the parent and the child (Morelli et al., 2017). In case of single parents, the effective strong bond in unable to be developed as there are increased chances that the children are going to face hindrance such as social difficulties, mental problem, irrelevant development and others. Moreover, the single parents face increased mental illness which also leads them to effectively contribute towards supporting attachment of children with them (Malczyk and Lawson, 2017).
2.9.4 Deficit Theory
The Deficit Theory informs that single families are considered to be broken and somehow doomed to ensure effective management and development of their children. This is because single parents would be incapable to act in fulfilling the both the responsibility of mother and father required for the child (Savolainen et al., 2018). Thus, the theory mentions that it may lead to restrict growth and development in child who are managed by single parents. Therefore, single parent are to remain physical and mentally capable to act in overcoming the deficit as mentioned in the theory to support enhanced development of their children.
2.10 Advantages of single parent
The single parents are seen to face different advantages over double parenting. One of the advantages is single parents makes the living environment for the child less stressful and more secured. This is because the single parents without the partner avoid fighting in front of the children which helps to avoid necessary stress to be faced by them as well as children (Gupta and Kashyap, 2020). As mentioned by Wilkinson and Andersson (2019), single parents act as good role model for their children. This is because they make the children understand the way to be self-dependent and manage own work without assistance. The single parents also have the advantage to teach their children regrading importance of responsibility and independence in life. This is because single parents being busy in managing needs for the child leads the children to develop skills in controlling own actions in the family in support the single parents to allow taking good care of them. Single parents have the advantage to make the children easily learn shared responsibility for leading their life with the family (Gupta and Kashyap, 2020).
2.11 Impact of single parenting on the health of the single parents
The single parents are seen likely to suffer from mental ill health issues along with low economic condition, low social support and low livelihood. This is because single parents are seen to face burden of caring for the child along with managing entire household and job which leads them to develop mental pressure. It leads them to face negative feelings and emotions that adversely affects their mental ill health to support developing stress and depression (Abedini et al., 2017). As criticised by Muindi et al. (2020), single parents face economic issues which leads to negatively affect their health and well-being. This is because economic issues make the single parents face hindrance to understand regarding the way adequate finances required for supporting enhanced development of their child is to be arranged which in turn affect them to doubt and faced mental pressure regarding their capability of following role of parents.
The single parents face hindrance to make time for their children due to their busy schedule of managing work for earning mother to support the children’s upbringing and growth. It leads the parents face changes in time management and less interaction with the child which leads the parents to feel emotionally weak that they are unable to take enhance care of their child as needed (Jun-qing, 2020). As argued by Muindi et al. (2020), single parents are seen to develop problem in accepting new relations. This is because they face difficulty in bonding with the potential partners after caring for the child as they think it would led them to avoid making time for their children. The single parents are seen to face mental illness such as anxiety and stress as they struggle to make and spent quality time with the children. It makes them feel they are ignoring the required support for the child which affects them to develop negative psychological condition.
2.12 Gaps in Research
The existing study explains the basic overview of single parent and mental illness. However, the studies discussed lack to portray enough results regarding the way single parents faced mental illness challenges and way it interferes with tier life. Moreover, there is lack of information regarding the way mental challenges faced by single parents affect their life and management of the children. There is also lack of information regarding the strategies to be adopted by the single parents in overcoming the mental illness challenges to lead a healthy life with well-being. Thus, the study is to be further progressed to resolve the gaps and present more clarified understand regarding mental illness challenges faced by single parents and way it is to be managed for their well-being.
2.13 Summary
The chapter explained the concept of mental ill health and single parent along with factor affecting development of mental ill health challenges in single parents (stigma, responsibility, social life, etc) to provide clear understanding regarding the topic. Moreover, models and theories regarding single parenting (Albert Bandura-social learning theory, behaviourism, biological, psychodynamic, cognitive, and humanistic) and mental ill health is explained to present the theoretical basis of the topic. Further, the impact of mental ill health challenges of single parents and others through exploration of existing studies are made to present effects of single parenting on individuals.
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
3.0 Introduction
The chapter is going to present the specific techniques or procedures to be implemented for identifying, selecting, processing and analysing information regarding the study topic. The chapter is important to be developed as it helps to critically understand the way validity and reliability of the study to gather results.
3.1 Research Design
The systematic review is referred to reviewing the clearly formulated research question which uses reproducible and systematic methods for identifying, selecting and critically appraising relevant research along with collecting and analysing data from existing studies which are involved in the review process (Chen, 2017). In contrast, the narrative review is the review process in which a clarified question is answered by involving general discussion regarding a subject without any topical approach (Calati et al., 2019). In this study, the systematic review is to be used in formulating the research. The narrative review is not to be used because it does not show any attempt to locate the relevant literature which appropriately suits the study. Moreover, the searches made for identifying the paper in narrative review are not specified and leads to care potential bias in the presentation of results and findings in the study (Chen, 2017).
The systematic review approach is to be used because it strives to identify and analyse relevant studies regarding the topic in a comprehensive manner while using explicit search strategies. Moreover, it includes explicit description of the nature of the studies to be used and the limitation for the selection of the studies to inform the specific criteria with reasons to be followed in developing the study (Pati and Lorusso, 2018). The systematic review also helps to reduce bias in the studies and enhances transparency in the methodology as well as search strategy. This is because it informs way they are formulated and to be used. It leads to improve the replicability of the reviewed study. The systematic review allows rigorous critical appraisal of studies which results in formation of pooled estimate of intervention and its effectiveness in regard to the topic. The results developed through systematic review can be effectively applied in formatting evidence-based practice (Trindade et al., 2017).
3.2 Search Strategy
In the current research study, the electronic search strategy is to be implemented in gathering and identifying potential articles and journals in relation to the topic. The electronic search is preferred because it is cost-effective along with less time-consuming. Since less finances are present to be spent in developing the study and there is reduced amount of time left to be spent in meeting the deadline of the research, thus the electronic search strategy is appropriate for the study. The platforms to be used in executing the electronic search are MedLine, NCBI, PubMed and CINHAL. The PubMed along with Medline are to be used because they contain wide number of qualitative studies regarding the specified medical topics and helps in easily identifying them through use of simple medical terminologies present in the topic (Pubmed, 2021). The CINHAL platform is to be used because it helps in presenting comprehensive data from different research articles relevant to the explored topic in the study of interest (EBSCO, 2021). The NCBI is to be used because the platform contains different full-text medical articles from all over the world that could assist in effectively analysing the current topic of interest (NCBI, 2021).
In the study, the PEO framework is implemented for identifying the key search terms that can be used in the study. The identification of the search terms is made by referring to the study topic and evaluating few related articles regarding the study (Bailey et al., 2021). During the execution of the research, the search terms are expanded and refined based on the keywords to develop validated and relevant findings of data. The keywords to be used are “mental illness”, “mental challenges”, “single parents”, “single mother”, “single father” and others. The Boolean operators And and Or are to be used in connecting the keywords to formlate effective search terms which could help in refined collection of data for developing enriched execution of the study.
3.3 Selection of Articles
The inclusion and exclusion criteria in the study are to be specifically mentioned so that the aspects to be considered relevant and irrelevant in the study is effectively identified that is necessary to avoid any error in data collection process. In identifying the criteria, the PEO framework is to be used as it helps in systematic inclusion and exclusion of studies in the research.
3.3.1 Types of participants
In the study, the population to be focused are single parents who are equal and above the age of 18 years to 50 years. The wide age range is determined because it would help to explore the different mental illness challenges faced by young as well as adult single parents in managing their child and well-being. Moreover, both the single mother and father are to be focused in the study because it would help to identify the similarity and dissimilarity in the mental ill health challenges faced by single parents in respect to gender difference. On this basis, keywords are formulated to be used for researching in the platform such as CINHAL, Medline and others.
3.3.2 Types of studies
In this research, the qualitative and quantitative primary studies are to be used in answering the research question. This is because it would help in presenting mixed primary data regarding the study topic that would led to provide stronger understand as well as interpretation of results. It is evident as statistical results gathered from the quantitative studies could be related with the qualitative studies to understand the reason behind the statistical different of various factors. Moreover, the mixed data would avoid the limitations to be faced on using either of the qualitative or qualitative studies (Powell et al., 2021). The secondary studies are excluded because they contain presentation of data from the perspective of the researchers which are influenced to some extent by the beliefs of the researchers leading to raise error in data presentation (Macieira et al., 2019). Thus, the studies that used meta-analysis, phenomenological design, grounded theory and others are avoided to be included in the current research.
The studies written and presented in English Language are to be included in the study because the current study is set in the UK where the key language understood and spoken is English and researcher belong from the place with understanding of the specific language. During the search, few Korean, Spanish and French articles related with the study are found, but they are excluded as the data from them could not be understood or interpreted in effective manner by the researchers involved in the study. The studies that are public on and after 2013 are included because such studies have updated, and recent information developed through advanced scientific experiments and logical research. The studies published before 2013 are exclude because such articles include backdated information which may be current eliminated through advanced experiments. The full-text articles are included as they provide comprehensive and detailed data regarding the study topic.
3.3.3 Study selection
The quality and scope of presentation of the topic in the included research influences the selection of studies to be made in the systematic review. The PRISMA flowchart helps in depicting flow of information in the study through various phases of systematic review. It assists in mapping out the number of records identified, and number of studies included and excluded during the research. The current systematic review led to inclusion of 10 articles listed from 2013-2021 for determining the mental illness challenges faced by single parents as a result of the parenting pressure. Among the 16 articles, 2 of them were qualitative studies and 14 of them were quantitative studies.
3.4 Quality assessment of Studies
In research, the quality assessment of the studies is needed to ensure credibility in the study. This is because credibility of the sources acts in the form of improved academic evidence which assists in baking up assertions mentioned within the study. However, without credibility in the study, it would fail to inform the reader that the study is correct for them to be considered for using as evidence in formulating practice (Voutilainen et al., 2017). According to Adib-Hajbaghery et al., (2017), credibility examination of qualitative studies is difficult to be performed in similar way. This is because each of the researchers in the qualitative studies have different opinions based on which they formulate the quality of the study which results to create difficulty in reaching a consensus. As argued by Halter et al., (2017), quality examination of studies is important to be established for analysing the transferability, validity, dependability and conformability of the researches. The assessment is also important as helps to determine the strength and weakness in the data presentation, research methods, data collection process and other in studies that in turn helps to improve trustworthiness in presenting the data within the findings (Voutilainen et al., 2017).
The quality assessment of the articles is to be executed by following the Critical Appraisal Skill Programme (CASP) tool. This is because it guides and directs the researchers about the way identified studies are to be critically analysed by following the main question presented in the framework (CASP, 2021). The CASP framework is seen to guide the researchers regarding the way methodology and data analysis method in the study is to be evaluated to understand the limitation faced in them and if it influenced the data in any way due to which the information from the study could not be used. The CASP tool act as valued guidance for the novice researchers because the constructive questions in the framework when follows ensures systematic analysis of the articles without any complication or problems (CASP, 2021). In the study, the use of scoring-based evaluation framework is avoided because many of the included articles contain study design which are not able to be appropriately scored due to their varied presentation (CASP, 2021). The CASP tool helps in analysis of theoretical as well as empirical data which is needed for presenting comprehensive review of the data from the articles (CASP, 2021). Thus, the CASP tool is to be used in critical analysis of the selected articles in the study.
3.5 Data Extraction
On the basis of research objectives and method for data analysis in studies, the nature of data extraction methods is seen to vary. It is important that specific study design is to be used for extraction of contextual data from studies. In extracting data, the first step includes identification of main characteristic of the study that are country which has been focussed in the study, qualification and name of the researchers, research settings, data of publication, data collection method, data analysis method and others. In quantitative studies, the statistical tools to be used in presenting the data are to be evaluated during data extraction to ensure they are credible and valid as they are being used in presenting the results. In order to answer the raised review question in enhanced way, separate data extraction template is to be created. This is because it would help in compiling key facts from existing studies that are included in the study. The effectiveness of the data extraction template is to be initially understood by using two articles as testers. The use of the articles in the template led to identify that the data extracted from them are appropriately relevant to the studies. The articles are randomly checked during inclusion in the data extraction to ensure their quality and level of error.
3.6 Data Synthesis
In the research, the data can be synthesised by using two key method that are integrative approach and interpretative approach. The focus of the integrative study is to summarise and compile the data on the basis of developed themes in the study. The themes developed allows making comparison of the collected data to ensure their suitability in the study. However, the interpretative approach involves focussing on key concepts within the research before execution of data synthesis (McDonald et al., 2018). In this study, neither of the two approaches are to be used. This is because interpretative approach is time consuming and creates violation of ethics during data presentation due to inclusion of the results based on the observation of the researchers (Rettie and Emiliussen, 2018). The integrative approach is not to be used because it is complicated and involve use of increased amount of time which is currently not available in performing the study (McDonald et al., 2018).
The thematic analysis method is to be used for data synthesis process in the study. This is because it is less time consuming and support simple way of analysing gathered data to be set within themes so that duplication of information is avoided (Vaismoradi and Snelgrove, 2019). The thematic analysis is also to be used because it provides flexibility to the researchers in analysing any data to be modified to be used in the study to ensure rich and detailed execution of the study (Vaismoradi and Snelgrove, 201). In performing thematic analysis, no supervision is required which indicates that no training or support is needed by the researchers in developing the study using the method. This nature of data analysis also allows in-depth presentation of data in clarified manner to resolve the raised questions in the study (Vaismoradi and Snelgrove, 201). The thematic analysis is to be performed by initially evaluating information of all the studies to develop common themes so that the data can be categorised accordingly. After the development of theme, the data are to be included accordingly and later methodologically analysed to resolve the raised question and meet the research objectives of the study (Vaismoradi and Snelgrove, 201).
3.7 Ethical Consideration
In research, ethical consideration is important because it ensures the study is been performed morally without any legal violation assuring the researchers are not going to face lawsuits in presenting the research (Yıldız, 2019). In ensuring ethical consideration in the study, the information to be identified from the existing researcher are to be paraphrased so that the meaning of the information remains same, but no plagiarism is faced on presenting them in the study. Moreover, the specific author along with the publication year of the articles from which the data is retrieved are to be mentioned for reference. It is to help the reader and others to recheck if the data is presented as mentioned in the study and not manipulated during its current presentation through the belief of the researchers. This is because manipulation of the results indicates violation of the true meaning of the data as presented and found through experimentation in existing studies.
In order to maintain ethical consideration, the studies to be included are to be ensured contains effective ethical approval. Further, the results are to be presented in such a way so that it does not harm the sentiments of any people. This is because it would help to establish beneficence and non-maleficence in which beneficial steps are to be taken for individuals through research and people are to be protected from any harm through the study. The researchers are to ensure that no person beliefs, feeling and thinking of them are to be influenced in gathering and presenting data for the study.
Chapter 4: Results and Findings
Theme 1: Prevalence of mental illness challenges faced by single parents
The single parents face different mental ill health challenges which are relative to the partnered parents and they may differ as per gender. In this context, the study by Kong et al. (2017) aimed to determine the mental ill health challenge of single parents and gender differences in the presence of the mental ill health challenges. For this purpose, 12,024 single and partnered parents are included in the study who are within 30-59 years of age and having children of 1-19 years of age. The mental ill health information was self-reported and multiple regression analysis is executed to explain fraction of covariates such as gender, age, socioeconomic status and others. The self-reporting of symptoms led to create limitation of objective evaluation of the symptoms from the perspective of the parents rather than through the use of medical knolwdege and expertise. The results revealed that single parents both mother and father expressed odd ratio of 2.02 in comparison to the partnered parent regarding mental ill health challenges. This indicates both single mother and fathers show higher mental ill health challenges compared to partnered parents. Among the single parents, suicidal intention (OR = 2.50, 95% CI 1.97–3.17) and depression (OR = 3.13, 95% CI 2.50–3.93) are the key mental ill health challenges being faced by them. In respect to poor socio-economic status, the single parent represented 50% higher mental ill health challenges compared to their richer counterparts. The strength of the study is that the self-reporting questionnaire is framed on the basis of DSM-IV that allows enhanced detection of depression.
Similarly, the study by Chiu et al. (2017) aimed to determine the self-related mental ill health status of single mothers and fathers in comparison to partnered parents. For this purpose, the study included 1058 single fathers, 5725 single mothers and 20,692 partnered parents in the study through Canadian Community Health Survey organised from 2001-2013. The results are gathered through multivariable logistic regression and odds of mental ill health among single fathers and mothers are compared to partnered parents. The findings revealed that single mothers and fathers show similar presence of poor mental ill health functioning (8.4% and 6.2%, respectively). The single fathers expressed a higher rate of mental ill health complications and physical health challenges compared to partnered fathers (OR 2.09, 95% CI 1.26 to 3.46). The limitation of the study is that it failed to inform the nature of mental ill health complications or challenges faced by single parents. However, the strength of the study is that it included a large population survey of mental ill health challenge prevalence in single parents which helped to mention the extent to which the problem is present in the society.
In comparison to the previous two studies, the current study by Kim and Yoo (2019) focused to identify the prevalence of mental ill health challenge in single mothers only compared to married mothers instead of referring to both the parents. The study analysed 1770 subjects who are gathered in 2016 from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. In gathering information, chi-square tests are executed to determine the general mental ill health attributes of the single mothers. The results revealed that single mothers are at increased risk of facing major depressive disorder in comparison to the married mothers. They represented a greater odd ratio of depression on adjusting with all covariates (odds ratio, 1.68; 95% confidence interval, 1.06–2.67). The limitation faced in the study is that it is executed in a single country and thus the gathered findings cannot be reciprocated in other countries. Moreover, the other limitation is that the study is focused on determining mental challenges in mothers only and not in both parents.
In contrast, the study by Kong and Kim (2015) aimed to understand the mental ill health challenges faced by single fathers in comparison to married fathers so that effective healthcare policies can be developed for them. For this purpose, the study included 58 single fathers and 228 married fathers in the study who are living in urban conditions. They were provided self-reporting questionnaires for mentioning their response and tool like Scale for Suicidal Ideation, Centre for Epidemiologic Studies–Depression, Global Assessment of Recent Stress, World Health Organization Quality of Life Assessment Instrument and the Korean version of the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test are used for further evaluation of their mental condition. The results revealed that single fathers expressed the poor quality of life (OR 7.30, 95% CI 2.82–18.74) along with higher depression (OR 3.85, 95% CI 1.29–11.45) and increased stress (OR 3.36, 95% CI 1.25–8.98) as mental ill health challenges compared to the married fathers. This indicated that single-parenthood leads to cause increased mental ill health challenges among the parents. One of the major limitations is that the sample collected in the study for executing the research is made from a single urban community due to which it reflected the local scenario rather than holistic view of the topic. The other limitation is that the sample size for the single fathers is too small and number of people in the comparative sample is hugely differentiated due to which the statistical power in explaining the results was somewhat limited.
The study by Atkins et al. (2018) aimed to investigate the experiences of mental ill health challenges faced by single black mothers. For this purpose, 210 back single mothers are included who aged within 18-45 years and reside in the urban communities. A descriptive and cross-section study design is used in framing the study and open-ended questionnaire is used for interviewing the black mothers and categorising their responses. The results revealed that 108 single mothers reported facing less somatic activity, 21 individuals increased inter-personal symptoms and 2 individuals faced lack of positive effect towrads their life. Nearly 48 individuals mentioned increased anger, 24 single mothers mentioned being depressed, 21 single mothers reported avoiding socialisation, 17 single mothers mentioned feeling lonely, 12 single mothers mentioned being stress and 16 single mothers mentioned being as mental ill health challenges faced due to their parenthood condition. This indicates that increased anger, sadness and depression are raised in single mothers as mental ill health challenges. The limitation of the study is that it used convenience sampling method for gathering sample which may have led to create bias in sample selection. It was found that 32 individuals did not respond to the questions which less loss of data to some extent in the study creating limitation towards its effective execution. Moreover, the study is set in urban condition and therefore the results could not be applied as evidence in explaining the prevalence of mental ill health challenges in single mothers in rural areas.
Theme 2: Impact of mental ill health challenges of single parents on the family and parents
The mental ill health challenges present in single parents are seen to have adverse impact on the families and their children. Therefore, related studies are to be explored to develop overview regarding the impact of the condition of the individual associated with single parents. In the study by Daryanani et al. (2017), the aim is to develop overview regarding the mental ill health challenges of the single mother effect on the children. For this purpose, 368 adolescent and their single mothers are included in the study for a baseline to two-year follow-up collection of results regarding the research. Out of the 368 participants who participated in Time 1 assessment, only 287 individuals were finally involved and completed Time 2 assessment where 224 completed Time 3 assessment. The time 1 assessment differed on the grounds of demographic information from Time 2 assessment and third. The results mention that children who are raised by single mothers having mental challenges faced increased stressors in life and expressed higher rumination levels in the first-year follow-up study. Moreover, greater range of depression and rumination is seen in children of the single mother on the 2nd year follow-up study. This indicates that the single parents with mental ill health challenges create negative psychological impact on the children due to which they also expressed mental ill health issues such as depression, stress and rumination. The limitation of the study is that relative lack of single fathers’ inclusion due to which generalisation of the results for all single parent families could not be established. The other limitation is that cognitive vulnerabilities created by stress amount the young due to their single mothers are not mentioned in the study.
In comparison, the study by Golombok et al. (2016) aimed to determine the impact of single parents on their relationship with the children and their psychological adjustment. The study included 52 single parent families with children 4-9 years old. The use of standardised interview is made along with observations was done and survey questions were provided to gather responses from the selected participants. The results revealed no significant changes in parenting qualities for children among single parent families compared to married parents. Moreover, no differences in cases of adjustment among the children in the single parent families and no psychological problems are found to be raised among children of the single mothers. This indicates that single parent does not create any mental challenges as mentioned in the previous studies on the children. The limitation faced in executing the research is that the sample size is extremely small due to which greater statistical variation in the result could not be reached.
The study by Matijasevich et al. (2015) aimed to mention the longitudinal patterns of depression in mothers and its impact on the psychiatric disorder of the children. For this purpose, the cohort study of 421 birth are followed and included. The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) is used for detecting depression in mothers at 3, 12, 24, 48 months and 6 years from the birth of the children. The results revealed that depression symptoms in mothers ranged from low trajectory (34.8%), moderate-low (40.9%), increasing (9.0%), decreasing (9.9) to the high trajectory (5.4%). The presence of psychiatric disorders in children was seen to raised from low to the high trajectory depression in single mother. This indicates that depression in single mothers has the addictive effect to result in facing hindrance with psychological ability in children. The limitation of the study is that to detect the level of depression in children, the responses from the mothers are to be expected which may lead to hindered response and few mothers may not wish to reveal regarding the mental issues of their children.
Theme 3: Factors influencing mental illness challenges in single parents
The mental illness challenges in single mothers are influenced due to presence of different factors for which discussion is to be developed so that the condition leading to the situation can be identified. In this respect, the study by Meier et al. (2016) is explored that aimed to explain the relation of employment and mental ill health of single mothers. This study included information from 2010,2012 and 2013 rounds regarding ATUS that involved question of Subjective Well-Being Module. A total of 34,565 women and men of 15 years and older are included to complete the module over the three cycles of ATUS. The results were developed by examining the emotions of the single mothers in regard to broader spectrum of parenting activities. It was reported that single mothers expressed higher level of sadness, lower happiness, increased fatigue and stress compared to the partnered mothers and those who are not employed. The employed single mothers are found to happier and less stressed or sad. This indicates that employment is one of the key factors that influence mental ill health challenges of single mothers as its presence enhanced their health whereas its absence makes mothers develop increased low mood and depression. The limitation of the study is that it focused on single mother perspective and not on perspective of single father due to which holistic influence of employment as factors for mental ill health challenges in single parents cannot be determined.
In comparison, the study of Kim and Kim (2020) aimed to determine wide number of factors that are responsible for negatively influencing the mental ill health and quality of life of the single mothers compared to the married or partnered mothers. For this purpose, data from 195 single mothers and 357 married mothers are included in the study. The quality of life is assessed based on the World Health Organization Quality of Life-abbreviated form (WHOQOL-BREF). The results revealed that older age, education, increased income and status of employment (β = 8.452, p = 0.037) are positively related to the enhanced quality of life of the single mothers. The residential instability (public rental housing: β = - 10.779, p < 0.001; Jeonse rental housing: β = - 0.324, p = 0.01), alcohol addiction and health problem are related with mental ill health challenges among the single mothers. The higher education among single mothers is seen to be independently related with their enhanced mental ill health. The limitation faced in the study is self-reporting of data which led to hindered objective analysis of facts due to possibility of exaggeration of responses by participants. The other limitation is that the sample selection is done from a single community due to generalisation of results in respect to region could not be achieved. The cross-sectional design led to create hindrance in developing effective causal relationship between variables.
The study by Liang et al. (2018) emphasised that single parenthood has common risk of facing mental ill health challenges such as depression, stress and anxiety. The aim of the study is to identify the psychosocial factors that are resulting to create mental ill health challenges among single parents. For this purpose, data from National Psychosocial Burdens Prevalence Study organised in 2015 is included. It led to the inclusion of 6925 single mothers with up to 3 children and they are randomly gathered from 271 paediatric clinics. The use of Parenting Stress Index (PSI), Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-4) and Perceived Stress Scale (PSS-4) are executed to gather detailed information need for the study. The results mentioned that 30% of the single mothers in the selected population are depressed, 37% are facing stress which is twice the number of partnered mothers. The factors such as inadequate social support, financial issues, partner maltreatment or abuse in childhood of the parents influenced them to be at risk of showing increased mental ill health challenges. This informs that single mothers are disposed to depression and face economic, social and environmental adversity that results in the mental ill health challenges. The limitation faced in the study is that the gathered information are self-reported which may led to presentation of errored data as there are changes of exaggeration of facts during self-reported by the participants out of lack of enhanced knolwdege regarding the way it may affect the research.
In contrast, the study by Melhado (2017) aimed to determine the factors that responsible in causing stress as mental ill health challenge among the single fathers. For this purpose, the study included 14 single fathers who are involved in a semi-structured interview for gathering information regarding the factors influencing their negative mental ill health condition. The interview transcripts are appropriately collected and involved in Nvivo for effective analysis. The findings mention that single fathers experience mental ill health challenges while caring for the child due to factors such as intense requirement of care delivery to the child, absence of mother to assist them, housing, finances, medical insurance and incapability in forming effective communication with the children. The lack of social support for the single fathers was a major factor that led them to feel increasingly stress with managing care of the child and contribute to managing the family. The limitation faced in the study is use of qualitative approach in executing it because it led to inclusion of smaller sample size and lack of quantitative information to be gathered which are needed for effective analysis of the evidence of the results. Moreover, the small sample size led to create barrier in the generalisation of the results for diverse population.

In comparison, the study by Atkins et al. (2020) aimed to determine the factors that are key contributors of depressed mood as mental ill health challenge in single black mothers. For this purpose, the study used cross-sectional design and descriptive analysis. An open-ended questionnaire is developed to gather responses from selected participants. Nearly 210 back single mothers are included in the study who are between 18-45 years of age. The results revealed that 319 responses are collected from the participants and 115 of the responses mention financial complication is major factors that contribute to the depressed condition in the single mothers. The results also mentioned that daily parental hassle and medical condition are key factors that contribute to raise mental ill health challenge of depression and stress among the single black mothers. The limitation faced in the study that cause effect relationship between identified factors and depression in single parenthood could not be identified. Moreover, it was seen that 37 women did not provided any response and many provided single response regarding the study due to which lack of adequate data collection for enriched execution of the study could not be reached. The other limitation is that the study is set in urban community condition and thus the results could not be generalised in rural context.
Theme 4: Strategies to overcome mental illness challenges in single parents
The mental ill health challenges experienced by single parents can be managed with implication of effective strategies under the assistance of different individual. In this regard, the study by Fonagy et al. (2016) aimed to explain the impact of psychotherapy for parent-infant for parent who has mental ill health problem or challenges compromising their well-being. For this purpose, 38 parent-infant are included in experimental group and control group respectively. The outcome of the impact is assessed on the basis of the baseline and at 6- and 12-months respective follow-up results. The primary outcome for the study determined was infant development whereas the secondary outcome of the study is determined on the basis of infant-parent interaction, maternal representations, maternal reflective and others. The results revealed that increased favourable outcome was seen in parent and infant group for experimental group who were provided psychotherapy regarding parental stress, parental representation, maternal mental health and others. This indicated that psychotherapy improves the parent’s psychological well-being, in turn, making them form enhanced relationship with their children. The limitation of the study s that the sample size is small due to which generalisation of results was harder to be reached. Moreover, the study focussed only on the aspect of the mother and does not mention the way the therapy could be effective in influencing father’s mental health which is equally involved in caring for the infant or child for supporting their growth and development.
In comparison, the study by Atkins (2016) aimed to mention the actions executed by black single mothers in overcoming depression as mental ill health challenge to be able to take effective care of their children and manage their family. The study mentioned that it included 208 community residing single mothers of black origin who were suffering from depression. The participants led to provide 333 response regarding the topic, out of which 327 response was valid to be included in the research. The results revealed that 63% mentioned escape and avoidance way, 18.3% mentioned social justice use, 3.7% informed resolving raised problem through effective planning. 1.8% mentioned self-controlling and 12.2% mentioned positive reappraisal of own role are effective way of controlling mental ill health challenges among single black mothers. The limitation initially identified is that the cultural focus of the research is regarding women in black community due to which the results developed could not be generalised for commonly for single mothers of all culture. Another limitation is that the study is quantitative analysis of facts due to which the subjectivity of the results could not be presented in the research which is important for understanding the actions that led to the choice of response among black single mothers for managing mental ill health challenges faced by them.
The study by Bailie et al. (2012) aimed to determine the relative impact of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) in helping parents with depression to have better mental health condition to care for the children. For this purpose, 16 parents are included in the study who are provided MBCT as intervention for depression and later interviewed to determine the effect of the therapy. The results revealed that higher emotional reactivity, empathy, acceptance, greater family involvement, emotional stability and comfort along with recognising own needs was able to be made by the single parents who were provided MBCT. This indicated that MBCT is effective on parents in lowering their depressed symptoms and improve their contribution to provide effective care to the children. The limitation faced is small sample size like the previous studies which made is harder for the gather results to be generalised. The examination of causality could not be performed which acted as limitation for the study as the mechanism of MBCT implication in managing depression in parents could not be determined.
Chapter 5: Discussion of Findings
The critical analysis of existing literature gathered in the study led to develop detailed knowledge and understanding regarding mental ill health challenges in single parents. The information initially mentioned the nature and prevalence of mental ill health challenges among single parents. In this respect, the study Kong et al. (2017) presented information regarding overview of the prevalence of mental ill health challenges focussing on both single mother and father as parents whereas the studies by Chiu et al. (2017), Kim and Yoo (2019) and by Atkins et al. (2018) focused to present information regarding single mothers as parents only and study by Kong and Kim (2015) focused to present information regarding single father as parents only. In all these studies, it is identified that single mothers, as well as single fathers, are equally prone to develop mental ill health challenges compared to partnered parents in managing their children. All the studies mentioned common prevalent mental ill health challenges faced by single parents are suicidal intension, depression, anxiety and stress.
The fact regarding suicidal ideation as mental ill health challenge among single mothers is evident from the study of Chau et al. (2014) where it was mentioned that single mother shows 3-fold increased risk of executing suicide. This is because they are unable to cope the responsibilities of managing the children and other activities alone. Thus, effective care for the single mothers are to be taken to lower their suicidal ideation to support their well-being. The depression is mainly a mood disorder which affects an individual to feel sadness, lost or anger in their daily life which interferes with their thinking ability and make them show hindered behaviour (Johnsen et al., 2018). The depression is mentioned to be present as major mental ill health challenge among single mothers and it interferes with their quality of life. The fact is evident as it is also supported by the study of Rousou et al. (2019) where it is mentioned that depression is high risk in single mothers as they have to manage wide number of responsibilities without any assistance. It makes them develop stress and anxiety which they are unable to cope leading the single mothers slowly into depression. The study by Kong et al. (2017) mentioned use of DSM-IV as effective in detecting the mental ill health challenges among single parents. This is effective as DM-IV is considered as clinically significant diagnostic system for the detection of wide number of psychiatric issues such as depression, stress and others (Zheng et al., 2019).
The way prevalent mental ill health challenges affect single parents are to be understood so that the adversities of the problem and the need of its management can be determined. Daryanani et al. (2017) mentioned that rumination is one of the key adverse impact of the mental ill health challenges of single parents on their children. The rumination is the process of making continuous thinking regarding same thoughts that are sad or dark which makes the individuals involved in rumination develop prolonged depressed state or develop impaired ability to process emotions (Carone et al., 2020). Moreover, the depression in single parents are seen to influence development of depressed state among the children too (Daryanani et al., 2017). This indicates that hindered psychological health of the single parents also have adverse effect on the mental well-being of their children. The fact is supported by the study of Nieuwenhuis and Maldonado (2018) where it is informed that lower psychological ability of single parents creates mental pressure on the children during their upbringing as they are incapable to develop healthy communication with their parents. The lack of emotional support leads the children to become also depressed and show symptoms of rumination.
In contrast, the study by Golombok et al. (2016) highlighted that mental ill health challenge of the single parents create no negative impact on the children and family. However, it is rejected by the explanation in the study by Matijasevich et al. (2015) where it is mentioned that depressed state of single parents has negative impact on the mental efficiency of the children. The existing 16 studies which are been explored, it is found that 10 of them supported mental health among parents to some extent influence well-being in children. Moreover, no other existing study apart from Golombok et al. (2016) is found that mentions mental ill health challenge of single parents does not affect the mental cognition and expression of behaviour in children. Thus, a confusion is raised, and further exploration of facts are required to determine the actual effect of the problem on families. Further, studies are explored to highlight some key factors that are leading to support development of mental ill health challenges in single parents.
The study by Meier et al. (2016) emphasised that employment condition is responsible in influencing mental ill health challenges in single mothers. It is evident as employed single mothers are mentioned to be happier and with better mental efficiency compared to unemployed mothers. This is because employment ensure the single parents have adequate financial ability in spending money needed for proper upbringing of the child and ensure them meeting all their needs without facing economic turmoil (Damaske et al., 2017). However, unemployed mothers are seen to face hindrance in managing adequate economic resources needed for their living which makes them worried and gradually develop mental ill health challenges out of frustration regarding the way to meet the needs in the family (Richter and Lemola, 2017). In contrast, the study by Kim and Kim (2020) highlighted education, social status and age are additional factors as per employment which is also highlighted in the previous study to influence mental ill health challenges in single mothers. The presence of increased education makes the single mothers have effective knowledge and skill to analyse the way they can manage their children upbringing without hindrance to support their well-being. Moreover, the high educated single mothers or parents face less chances of poverty which makes them economically confident to take care of the child without worrying, in turn, makes them develop mental stability. It is evident as higher educated single mothers have well opportunity to find jobs needed for earning finances in setting effective parental support for the children’s well-being and upbringing (Härkönen, 2018).
The study by Kim and Kim (2020) also mentioned that housing condition has adequate influence on the mental ill challenges among single mothers. This is because lack of stable housing condition makes single mothers remain stressed regarding the way to ensure safe living space for their children where they can be born and brought up effectively. The study also highlighted addiction problem to be key issue in presence of mental ill health challenges among single parents. This is evident as alcohol addiction leads to hinder the normal mental analysis ability of single parents in turn making them feel mentally challenged in developing decision to care for their children (Kim and Kim, 2020). In contrast, the study by Liang et al. (2018) highlighted that lack of social support along with partner maltreatment or abusive childhood of single parents influences their development of mental ill health challenges. This is because lack of social support makes the single parents feel lack of assistance from others in the society to be capable single parent in caring for the children. It also makes them doubt their efficiency in upbringing the children which leads to negatively affect their psychological thinking and gradually affects their mental health to be challenges to develop depression and stress. The fact is supported by the study of Damaske et al. (2017) where it is mentioned that lack of social support to single mothers hindered their ability to care for the children and negatively affect their mental health.
The presence of partner violence and abuse for the single mothers makes them mentally unable to be confident and safe to ensure effective care for the child. They develop fear of their children to be taken away by their partners which leads to their stress and depression (Wuest et al., 2021). The study by Kim and Kim (2020) and Liang et al. (2018) both emphasised that abusive childhood of single parents may influence their development of mental ill health challenges. This is evident as abuse in the early stage of life create emotional turmoil on the individuals and affects their ability to cope complex situation to be reduced out of the emotional condition. The inability to escape from the emotional condition makes the single parents to be increasingly depressed which affects their ability to take care for the child.
The study by Atkins et al. (2020) has highlighted that medical condition of single parents makes them face mental ill health challenges while caring for the children. This is because the single parents feel they due to their hindered health are being incapable to deliver adequate support needed by the child for their enhanced upbringing. In addition, the study mentioned daily hassle for parental duties among single parents lead them to develop mental ill health challenge. It is evident as daily hassle of the parental responsibilities makes the single parents unable to have stable emotional health and affect their ability to maintain effective sleep schedule, energy intake and others which contributes to their mental ill health. The fact is also supported by the study of Li (2020) where it is mentioned that single parents are to have increased energy in performing parental duties which they are incapable to maintain at all time. It leads them to develop mental ill health considering they are incapable to fulfil minimum needs of their children due to lack of support and being single.
The strategies to overcome mental ill health challenges among the single parents are explored so that it can be implemented to ensure them better well-being and mental health. In this respect, the study by Kirby et al., (2019), mentioned use of psychotherapy including parent and children at the same time. This is because the therapy would help the parents and children explore each other mental health condition and way they can support one another in overcoming the mental ill health problem to support each other well-being and good health. In contrast, the study by Bailie et al. (2012) mentioned use of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) for the single parents to be effective in controlling their mental health. This is because MBCT would help single parents to be conscious regarding their mental issues and way they can control them to develop enhanced phycological health needed in supporting care for the children. However, the study by Atkins (2016) mentioned use of common techniques in overcoming the mental ill health challenges among the single parents. The study mentions use of self-control of emotion with personal and social support along with plan effective to control negative emotions to lead a better mental health. Moreover, it mentions avoidance of complex thoughts is to be made as a way to overcome increased mental ill health challenges by single parents.
Chapter 6: Conclusion and Recommendations
Conclusion
The above discussion mentions that mental ill health in single parents is one of the current health issues being faced in the UK as well as globally. In the Europe, UK is one of the countries with highest number of single parents caring for their children. This is because increased number of partners are found to be living alone with their children due to mutual separation, divorce, death, family issues and others. However, the single parenting is seen to cause hindrance to the psychological health of the individuals which is creating obstacles towards enhanced child management and care by the single parent families. The mental ill health challenges faced by single parents is a key concern as it is negatively affecting their social life. Thus, the topic is been focussed in the study so that through effective research adequate information can be gathered regarding it.
The background regarding the topic is developed by exploring existing studies which mentions that mental ill health challenges are faced due to various reason. The biological model mentions that change in the brain functioning and chemical release in the brain leads to mental ill health challenges among individuals. The cognitive model mentions that mental ill health challenges leads single parents or any individuals to show disturbed thoughts and actions which hinders them in managing well-develop social life. The psychodynamic theory mentions that by overcoming repression and develop awareness regarding the disturbed mental health condition, the single mothers can take effective action in controlling the mental ill health challenges. The single parents are mentioned to require making time, controlling everyday action, managing social actions and others to care for the children which is seen to create mental burden on them in performing effective care. The information in the study is gathered by executing systematic review of articles. The CASP framework is used for critical analysis of selected articles in the study to ensure their level of validity and reliability to be included in the study. The articles in the study are selected by using inclusion and exclusion criteria and the data analysis is performed by using thematic analysis method. A total of 15 articles related to the study are chosen and 4 key themes are used for categorically present the gathered data from the articles.
The information from selected articles mention that mental ill health challenge among the single parents is widespread. The mental ill health challenge mainly faced by them are stress, depression, anxiety, suicidal thoughts and others which disrupt the single parent’s effective focus on managing appropriate care for their children. The depression is the most common mental ill health challenge faced by the single parents. The presence of mental ill health challenges among the single parents is seen to affect the children as well as family condition. This is because it is seen that children with mentally ill single parents expressed higher chances of developing depression. Moreover, the presence of mental ill health challenged single parents fail to show effective concentrated care on their children. The children show increased presence of stress and rumination who have mentally ill single parents suffering from depression, anxiety and others.
The factors such as education, housing condition, employment, social support availability and financial condition affected the development of mental ill health challenges among single parents. This is because highly educated single mothers are found to be more planned and disciplined in managing their children whereas the uneducated single mothers face hindrance with managing childcare which leads them to experience mental ill health challenges out of being unable to play their appropriate role in enhanced upbringing of the children. The single parents mainly mothers with employment are less likely to suffer mental ill health challenges compared to unemployed single mothers as they have enhanced financial efficiency and ability to arrange required resources needed to support enhanced well-being and upbringing of the child in single handed manner. The strategies mentioned to be implemented in managing mental ill health challenges faced by single parents are use of psychotherapy and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy. The use of social support planned actions and others are general strategies to be applied by single parents to overcome their mental ill health challenges while managing duties in single parenthood.
Recommendations
Accessing support system: The single parents to overcome or avoid mental ill health challenges are recommended to access a support system who can assist them in watching and caring for the children when in need. Moreover, the support system that are family and friends are required to support single parents in executing errands and sharing information regarding personal emotions so that the individual avoid being lonely and isolated. This is because loneliness and isolation complex the mental health condition in any individuals as assistance required to overcome the negative emotions are not available. The single parents are recommended to join single-parent support group to access assistance regarding the way to cope with parental needs and car for the child while being alone. This is because it forms a basis of communication and interaction of thoughts between single mothers and acts as system of support in single parenting.
Develop disciple: The single parents are recommended to make their child follow certain rules and duties as per their age. This is because it would make the children self-dependent along with assist the single parents to overcome duties which they are no more require to concentrate, in turn, making them feel relaxed to some extent. The following by the rules of single parent’s children is important because it would make them disciplined and create expected behaviour of the child without hindrance.
Maintain daily routine: A daily routine for work management at home and job is to be maintained by single parents. This is recommended because it would make the single parent avoid facing confusion and worried regarding which duties to be performed at what time due to which they often become stress and show mental ill health. Therefore, a consistent routine would help the with effective time management and ensured duties to be organised so that it does not create fear and stress among the single parents regarding they are not methodically performing all their duties of caring for the child and being a terrible parent.
Involvement in counselling session: The single parents are recommended to access help of mental health professional to overcome mental ill health challenges. This is because they are going to involve the single parents into require counselling session and talk therapy required by them to overcome negative emotion and develop positivity. The involvement in counselling session is also recommended as it would make the single parents understand the way they can answer queries regarding family management single-handily without panicking or fearing that create emotional stress.
Avoid feeling guilty: The single parents are seen to feel guilts of not providing the utmost care required by their children out of lack of support of partner. This feeling of guilt is to be avoided so that a sense of well-being among the single parents can be created which is needed for supporting their better focus on life and manage negative emotion to think in positive way leading to avoid facing mental illness.
Limitations
The limitation faced in the study is lack of time and adequate finances due to which more enriched gathering of data could not be established. The other limitation is that most of the facts shared are focussed on single mother more than the single fathers. This is evident as impact of mental ill health on the single mother is more focused compared to single father as parents due to which the range of mental health problem faced by single fathers could not explored to wider extent. Since parents indicates both mother and father, thus more focus on the mothers led to limited presentation of information. The secondary research design used lead to create limitation of results that are not directly gathered from participants which would have provided more current view regarding the topic.
Future Scope of the study
The study could be used in developing understanding regarding the way mental ill health challenges develop and managed in single parents mainly the mothers. However, in future, the current study is required to be extent to equally explore the impact of mental ill health challenges among single fathers and mothers as they both act as the parents to take care of the child in lack of partner. The study is to be further focused to gather more primary data directly from individuals so that current prevalence of the condition focussed in the topic can be understood.
References
- Abedini, Z., Mirnasab, M. and Fathi Azar, E., 2017. A Comparative Study of Identity Styles, Quality of Life and Behavioral Problems between Single Parent and Two Parent Adolescents. Journal of Education and Learning, 6(2), pp.235-245.
- Adib-Hajbaghery, M., Adib, M.E. and Eshraghi Arani, N., 2017. Evaluating the quality of randomized trials published in Persian nursing journals with more than 10 years of publishing using the CASP checklist. Iran Journal of Nursing, 30(109), pp.1-9.
- Agnafors, S., Bladh, M., Svedin, C.G. and Sydsjö, G., 2019. Mental health in young mothers, single mothers and their children. BMC psychiatry, 19(1), pp.1-7.
- Akpan, B., 2020. Classical and Operant Conditioning—Ivan Pavlov; Burrhus Skinner. In Science Education in Theory and Practice (pp. 71-84). Springer, Cham.
- Atkins, R., 2016. Coping with Depression in Single Black Mothers. Issues in mental ill health nursing, 37(3), pp.172-181.
- Atkins, R., Gage, G., Kelly, T.A., Joseph, P.V., Johnson, S., Ojo, K. and Williams, W., 2018. Exploring expressions of depression in black single mothers. Issues in mental health nursing, 39(11), pp.935-945.
- Atkins, R., Luo, R., Wunnenberg, M., Ayres, C., Lipman, T.H., Pena-Cardinali, V., Hayes, L. and Deatrick, J.A., 2020. Contributors to Depressed Mood in Black Single Mothers. Issues in mental health nursing, 41(1), pp.38-48.
- Bahrami, B., Dolatshahi, B., Pourshahbaz, A. and Mohammadkhani, P., 2017. Determinants of Authoritative Parenting Style in Iranian Mothers. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal, 15(4), pp.317-324.
- Bailey, J., Tod, A., Robertson, S. and King, R., 2021. Exploring advanced nursing practice in stroke services: a scoping review. British Journal of Neuroscience Nursing, 17(Sup2), pp.S8-S14.
- Bailie, C., Kuyken, W. and Sonnenberg, S., 2012. The experiences of parents in mindfulness-based cognitive therapy. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 17(1), pp.103-119.
- Baker, E.R., Jensen, C.J. and Tisak, M.S., 2019. A closer examination of aggressive subtypes in early childhood: Contributions of executive function and single-parent status. Early Child Development and Care, 189(5), pp.733-746.
- Bland, A.M. and DeRobertis, E.M., 2020. Humanistic perspective. Encyclopedia of personality and individual differences, pp.2061-2079.
- Calati, R., Ferrari, C., Brittner, M., Oasi, O., Olié, E., Carvalho, A.F. and Courtet, P., 2019. Suicidal thoughts and behaviors and social isolation: A narrative review of the literature. Journal of affective disorders, 245, pp.653-667.
- Carone, N., Lingiardi, V., Baiocco, R. and Barone, L., 2020. Sensitivity and rough-and-tumble play in gay and heterosexual single-father families through surrogacy: The role of microaggressions and fathers’ rumination. Psychology of Men & Masculinities.
- Carson, S.H., 2019. 14 creativity and mental illness. Cambridge Handbook of Creativity, pp.296-318.
- CASP 2021, Critical Appraisal Skill Programme (CASP) tool, Available at: https://casp-uk.net/ [Accessed on: 30 June 2021]
- Chau, K., Kabuth, B. and Chau, N., 2014. Gender and family disparities in suicide attempt and role of socioeconomic, school, and health-related difficulties in early adolescence. BioMed research international, 2014.pp.8-12.
- Chavez-Baldini, U., Nieman, D.H., Keestra, A., Lok, A., Mocking, R.J., de Koning, P., Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V., Bockting, C.L., van Rooijen, G., Smit, D.J. and Sutterland, A.L., 2021. The relationship between cognitive functioning and psychopathology in patients with psychiatric disorders: a transdiagnostic network analysis. Psychological medicine, pp.1-10.
- Chen, C., 2017. Science mapping: a systematic review of the literature. Journal of data and information science, 2(2).pp.78-90.
- Chiu, M., Rahman, F., Kurdyak, P., Cairney, J., Jembere, N. and Vigod, S., 2017. Self-rated health and mental health of lone fathers compared with lone mothers and partnered fathers: a population-based cross-sectional study. J Epidemiol Community Health, 71(5), pp.417-423.
- Cohen, B.M. ed., 2017. Routledge international handbook of critical mental health. Routledge.
- Cohen, E.D., 2020. The Psychoanalysis of Perfectionism: Integrating Freud’s Psychodynamic Theory into Logic-Based Therapy. International Journal of Philosophical Practice, 6(1), pp.15-27.
- Coles, R.L., 2017. Single fathers and their children. Fatherhood: Contemporary theory, research, and social policy, pp.37-57.
- Daliana, N. and Antoniou, A.S., 2018. The mental health of single-parent families in relation to psychological, societal and financial parameters.pp.77-101.
- Damaske, S., Bratter, J.L. and Frech, A., 2017. Single mother families and employment, race, and poverty in changing economic times. Social science research, 62, pp.120-133.
- Daryanani, I., Hamilton, J.L., McArthur, B.A., Steinberg, L., Abramson, L.Y. and Alloy, L.B., 2017. Cognitive vulnerabilities to depression for adolescents in single-mother and two-parent families. Journal of youth and adolescence, 46(1), pp.213-227.
- EBSCo 2021, CINHAL, Available at: https://www.ebsco.com/products/research-databases/cinahl-complete [Accessed on: 30 June 2021]
- Faraone, S.V. and Larsson, H., 2019. Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Molecular psychiatry, 24(4), pp.562-575.
- Fenner, P. and Mohamad, Z.B., 2019. “What We Have Shared Is Actually a Big Secret”: Group Art Therapy With Divorced Single Mothers in Malaysia. Art Therapy, 36(2), pp.59-67.
- Firth, J., Siddiqi, N., Koyanagi, A., Siskind, D., Rosenbaum, S., Galletly, C., Allan, S., Caneo, C., Carney, R., Carvalho, A.F. and Chatterton, M.L., 2019. The Lancet Psychiatry Commission: a blueprint for protecting physical health in people with mental illness. The Lancet Psychiatry, 6(8), pp.675-712.
- Firth, J., Siddiqi, N., Koyanagi, A., Siskind, D., Rosenbaum, S., Galletly, C., Allan, S., Caneo, C., Carney, R., Carvalho, A.F. and Chatterton, M.L., 2019. The Lancet Psychiatry Commission: a blueprint for protecting physical health in people with mental illness. The Lancet Psychiatry, 6(8), pp.675-712.
- Fonagy, P., Sleed, M. and Baradon, T., 2016. Randomized controlled trial of parent–infant psychotherapy for parents with mental ill health problems and young infants. Infant mental ill health journal, 37(2), pp.97-114.
- Fransson, E., Låftman, S.B., Östberg, V. and Bergström, M., 2018. Wellbeing among children with single parents in Sweden: Focusing on shared residence. The triple bind of single-parent families: Resources, employment and policies to improve well-being, pp.145-167.
- Fulmer, R., 2018. The Evolution of the Psychodynamic Approach and System. International Journal of Psychological Studies, 10(1).pp.78-89.
- gingerbread.org.uk 2021, Single parents, Available at: https://www.gingerbread.org.uk/what-we-do/media-centre/single-parents-facts-figures
- Golombok, S., Zadeh, S., Imrie, S., Smith, V. and Freeman, T., 2016. Single mothers by choice: Mother–child relationships and children’s psychological adjustment. Journal of Family Psychology, 30(4), p.409.
- Guntrip, H.Y., 2018. Personality structure and human interaction: The developing synthesis of psychodynamic theory. Routledge.
- Gupta, A. and Kashyap, S., 2020. Growing up in a Single Parent Family; A Determining factor of Adolescent’s Well-being. Advanced Journal of Social Science, 7(1), pp.138-144.
- Halter, M., Pelone, F., Boiko, O., Beighton, C., Harris, R., Gale, J., Gourlay, S. and Drennan, V., 2017. Interventions to reduce adult nursing turnover: a systematic review of systematic reviews. The open nursing journal, 11, p.108.
- Härkönen, J., 2018. Single-mother poverty: How much do educational differences in single motherhood matter. The Triple Bind of Single-Parent Families: Resources, Employment and Policies to Improve Wellbeing, pp.31-50.
- healthofchildren 2021, Single-parent families, Available at: http://www.healthofchildren.com/S/Single-Parent-Families.html [Accessed on: 30 June 2021]
- Horwitz, A.V., 2020. Chapter One. A Concept of Mental Disorder. In Creating Mental Illness (pp. 19-37). University of Chicago Press.
- Hosokawa, R. and Katsura, T., 2019. Role of parenting style in children’s behavioral problems through the transition from preschool to elementary school according to gender in Japan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(1), p.21.
- Hyman, S.E., 2018. The daunting polygenicity of mental illness: making a new map. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 373(1742), p.20170031.
- Irvine, A., Rawlinson, C., Bor, W. and Hoehn, E., 2021. Evaluation of a collaborative group intervention for mothers with moderate to severe perinatal mental illness and their infants in Australia. Infant Mental Health Journal.3(1). pp.45-90.
- Johnsen, I.O., Litland, A.S. and Hallström, I.K., 2018. Living in Two Worlds–Children's Experiences After Their Parents' Divorce–A Qualitative Study. Journal of pediatric nursing, 43, pp.e44-e51.
- Juffer, F., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.J. and van IJzendoorn, M.H., 2017. Pairing attachment theory and social learning theory in video-feedback intervention to promote positive parenting. Current opinion in psychology, 15, pp.189-194.
- Jun-qing, F., 2020, August. The Causes and Solutions on the Problems of Child Rearing in Single-Parent Family. In 2020 4th International Seminar on Education, Management and Social Sciences (ISEMSS 2020) (pp. 1231-1234). Atlantis Press.
- Kartal, H.B., 2021. An essay on the background of experimental psychology and behaviourism. Psychology Research on Education and Social Sciences, 2(1), pp.55-59.
- Kim, G.E. and Kim, E.J., 2020. Factors affecting the quality of life of single mothers compared to married mothers. BMC psychiatry, 20, pp.1-10.
- Kim, K.J. and Yoo, J.H., 2019. Single Mothers and Mental Health in South Korea: The Seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survery, 2016. Korean Journal of Family Practice, 9(4), pp.331-335.
- Kirby, J.N., Sampson, H., Day, J., Hayes, A. and Gilbert, P., 2019. Human evolution and culture in relationship to shame in the parenting role: Implications for psychology and psychotherapy. Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice, 92(2), pp.238-260.
- Kong, K.A. and Kim, S.I., 2015. Mental health of single fathers living in an urban community in South Korea. Comprehensive psychiatry, 56, pp.188-197.
- Kong, K.A., Choi, H.Y. and Kim, S.I., 2017. Mental health among single and partnered parents in South Korea. PloS one, 12(8), p.e0182943.
- Larkings, J.S. and Brown, P.M., 2018. Do biogenetic causal beliefs reduce mental illness stigma in people with mental illness and in mental health professionals? A systematic review. International journal of mental health nursing, 27(3), pp.928-941.
- Li, Q., 2020. Mothers left without a man: Poverty and single parenthood in China. Social Inclusion, 8(2), pp.114-122.
- Liang, L.A., Berger, U. and Brand, C., 2018. Psychosocial factors associated with symptoms of depression, anxiety and stress among single mothers with young children: a population-based study. Journal of affective disorders, 242, pp.255-264.
- Lundström, L.G., Aasa, U., Zhang, Y. and Sundberg, T., 2019. Health care in light of different theories of health—A proposed framework for integrating a social humanistic perspective into health care. Journal of integrative medicine, 17(5), pp.321-327.
- Macieira, T.G., Chianca, T.C., Smith, M.B., Yao, Y., Bian, J., Wilkie, D.J., Dunn Lopez, K. and Keenan, G.M., 2019. Secondary use of standardized nursing care data for advancing nursing science and practice: a systematic review. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 26(11), pp.1401-1411.
- Malczyk, B.R. and Lawson, H.A., 2017. Parental monitoring, the parent-child relationship and children's academic engagement in mother-headed single-parent families. Children and Youth Services Review, 73, pp.274-282.
- Matijasevich, A., Murray, J., Cooper, P.J., Anselmi, L., Barros, A.J., Barros, F.C. and Santos, I.S., 2015. Trajectories of maternal depression and offspring psychopathology at 6 years: 2004 Pelotas cohort study. Journal of affective disorders, 174, pp.424-431.
- McDonald, E.W., Boulton, J.L. and Davis, J.L., 2018. E-learning and nursing assessment skills and knowledge–An integrative review. Nurse education today, 66, pp.166-174.
- Melhado, S., 2017. Identifying Stressors experienced by single fathers who are parenting in New York City. Walden University, 2017, pp.1-144.
- Mencarini, L., Pasqua, S. and Romiti, A., 2019. Single-mother families and the gender gap in children’s time investment and non-cognitive skills. Review of Economics of the Household, 17(1), pp.149-176.
- Morelli, G.A., Chaudhary, N., Gottlieb, A., Keller, H., Murray, M., Quinn, N., Rosabal-Coto, M., Scheidecker, G., Takada, A. and Vicedo, M., 2017. A pluralistic approach to attachment. The cultural nature of attachment: Contextualizing relationships and development, pp.140-169.
- Muindi, A., Ireri, N. and Menecha, J., 2020. The Prevalence of Psychological Problems of Students from Single Parent Families and Their Academic Performances: A Case of Mukaa Sub-County, Makueni County, Kenya. Journal of Sociology, Psychology & Religious Studies, 2(1), pp.30-50.
- Nathans, S., 2021. Oedipus for Everyone: Revitalizing the Model for LGBTQ Couples and Single Parent Families. Psychoanalytic Dialogues, 31(3), pp.312-328.
- NCBI 2021, NCBI, Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ [Accessed on: 30 June 2021]
- Nieuwenhuis, R. and Maldonado, L., 2018. The triple bind of single-parent families: Resources, employment and policies to improve well-being. Policy Press.
- OECD 2016, Family size and household composition, Available at: https://www.oecd.org/els/family/SF_1_1_Family_size_and_composition.pdf [Accessed on: 30 June 2021]
- Pailhé, A., Panico, L. and Heers, M., 2020. Being born to a single mother in France: trajectories of father’s involvement over the first year of life. Longitudinal and Life Course Studies, 11(1), pp.123-149.
- Pati, D. and Lorusso, L.N., 2018. How to write a systematic review of the literature. HERD: Health Environments Research & Design Journal, 11(1), pp.15-30.
- Powell, K.R., Deroche, C.B. and Alexander, G.L., 2021. Health data sharing in US nursing homes: A mixed methods study. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 22(5), pp.1052-1059.
- PubMed 2021, PubMed, Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ [Accessed on: 30 June 2021]
- Rettie, H. and Emiliussen, J., 2018. Practical impressions of interpretative phenomenological analysis from the novice’s standpoint. Nurse researcher, 26(2).
- Rousou, E., Kouta, C., Middleton, N. and Karanikola, M., 2019. Mental health among single mothers in Cyprus: a cross-sectional descriptive correlational study. BMC women's health, 19(1), pp.1-11.
- Saeri, A.K., Cruwys, T., Barlow, F.K., Stronge, S. and Sibley, C.G., 2018. Social connectedness improves public mental health: Investigating bidirectional relationships in the New Zealand attitudes and values survey. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 52(4), pp.365-374.
- Savolainen, J., Eisman, A., Mason, W.A., Schwartz, J.A., Miettunen, J. and Järvelin, M.R., 2018. Socioeconomic disadvantage and psychological deficits: Pathways from early cumulative risk to late-adolescent criminal conviction. Journal of adolescence, 65, pp.16-24.
- Shaw, Z.A. and Starr, L.R., 2019. Intergenerational transmission of emotion dysregulation: The role of authoritarian parenting style and family chronic stress. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 28(12), pp.3508-3518.
- Spillane, R., 2021. Thomas Szasz: From social behaviourist to dramaturgic-existentialist. Existential Analysis, 32(1), pp.139-153.
- Stack, R.J. and Meredith, A., 2018. The impact of financial hardship on single parents: An exploration of the journey from social distress to seeking help. Journal of family and economic issues, 39(2), pp.233-242.
- Tarar, A.H., Asghar, H., Ijaz, M.M. and Tarar, M.A., 2021. Psychological Well Being and Adjustment Of Single Parents: Psychosocialand Economic Challenges. PAFMJ, 71(Suppl-1), pp.S76-81.
- Tarar, A.H., Asghar, H., Ijaz, M.M. and Tarar, M.A., 2021. Psychological Well Being and Adjustment Of Single Parents: Psychosocialand Economic Challenges. PAFMJ, 71(Suppl-1), pp.S76-81.
- Trindade, E.P., Hinnig, M.P.F., Moreira da Costa, E., Marques, J.S., Bastos, R.C. and Yigitcanlar, T., 2017. Sustainable development of smart cities: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 3(3), p.11.
- Tyler, D., Donovan, C.L., Scupham, S., Shiels, A.L. and Weaver, S.A., 2019. Young children’s sleep problems: The impact of parental distress and parenting style. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 28(8), pp.2098-2106.
- Vaismoradi, M. and Snelgrove, S., 2019, September. Theme in qualitative content analysis and thematic analysis. In Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung/Forum: Qualitative Social Research. 20(3). pp.56-98.
- Voutilainen, A., Saaranen, T. and Sormunen, M., 2017. Conventional vs. e-learning in nursing education: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nurse education today, 50, pp.97-103.
- Wang, D., Li, S. and Hu, M., 2017. Comparisons of the influence of raising people's identity on mental health between two-parents family children and single parent family children by propensity score matching. Wei sheng yan jiu= Journal of hygiene research, 46(5), pp.709-716.
- Whisenhunt, J.L., Chang, C.Y., Parrish, M.S. and Carter, J.R., 2019. Addressing single parents’ needs in professional counseling: A qualitative examination of single parenthood. The Family Journal, 27(2), pp.188-198.
- Widan, R.J. and Greeff, A.P., 2019. Aspects of Social Support Associated with Adaptation in Middle-Class, Single-Mother Families. The American Journal of Family Therapy, 47(3), pp.148-164.
- Wilkinson, R. and Andersson, M.A., 2019. Adolescent socioeconomic status and parent-child emotional bonds: Reexamining gender differences in mental well-being during young adulthood. Society and mental health, 9(1), pp.95-110.
- Woolfson, A., 2019. The biological basis of mental illness. Nature, 566(7743), pp.180-182.
- Wuest, J., Ford-Gilboe, M., Merritt-Gray, M. and Varcoe, C., 2021. Exemplar: Building on “Grab,” Attending to “Fit,” and Being Prepared to “Modify”: How Grounded Theory “Works” to Guide a Health Intervention for Abused Women. In Developing Grounded Theory (pp. 90-107). Routledge.
- Yaffe, Y., 2017. Do single mothers differ from non-single mothers in their parenting styles? A brief report study. Interdisciplinary Journal of Family Studies, 22(2).
- Yıldız, E., 2019. Ethics in nursing: A systematic review of the framework of evidence perspective. Nursing ethics, 26(4), pp.1128-1148.
- Young, D.K.W., 2018. Cognitive behavioral therapy group for reducing self-stigma for people with mental illness. Research on social work practice, 28(7), pp.827-837.
- Zheng, Y., Severino, F., Hui, L., Wu, H., Wang, J. and Zhang, T., 2019. Co-Morbidity of DSM-IV personality disorder in major depressive disorder among psychiatric outpatients in China: a further analysis of an epidemiologic survey in a clinical population. Frontiers in psychiatry, 10, p.833.
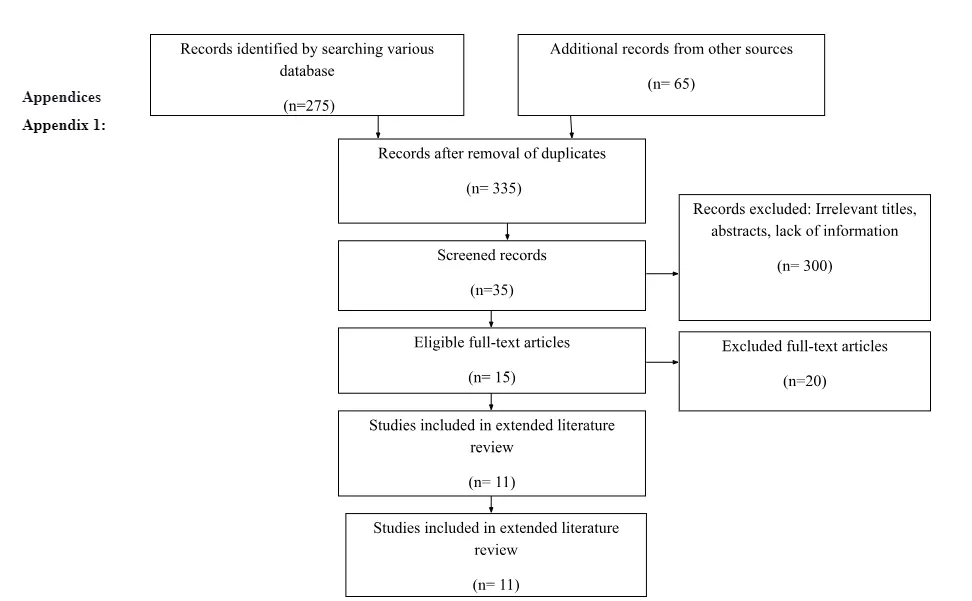
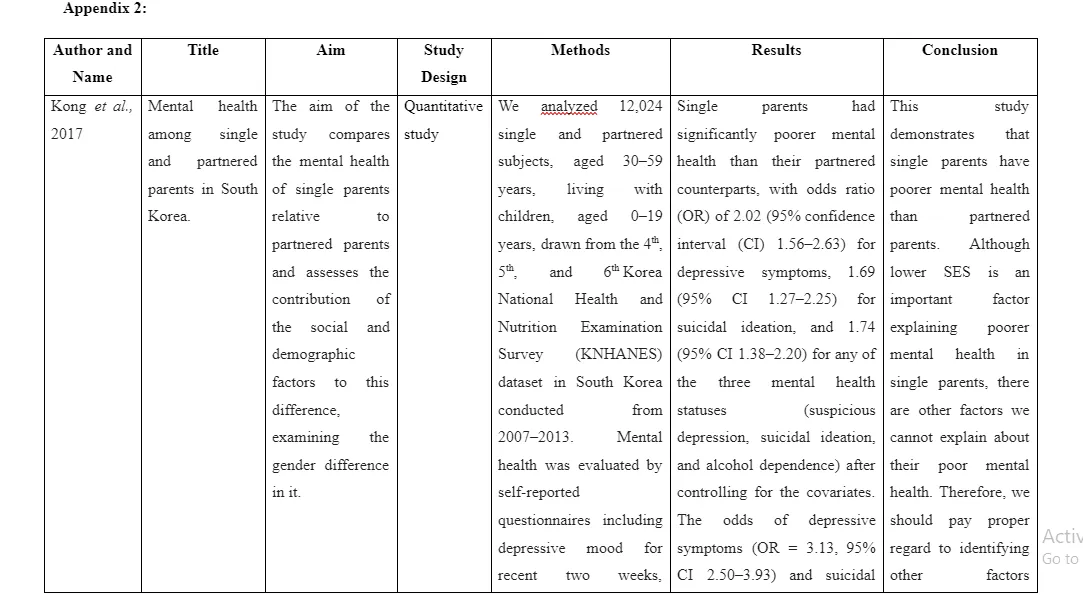
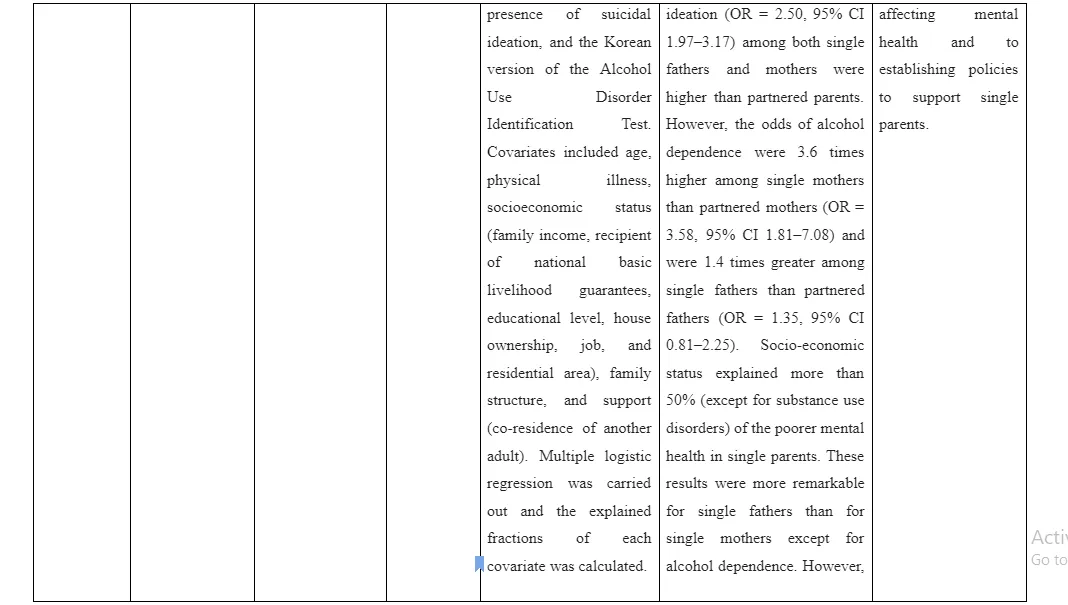
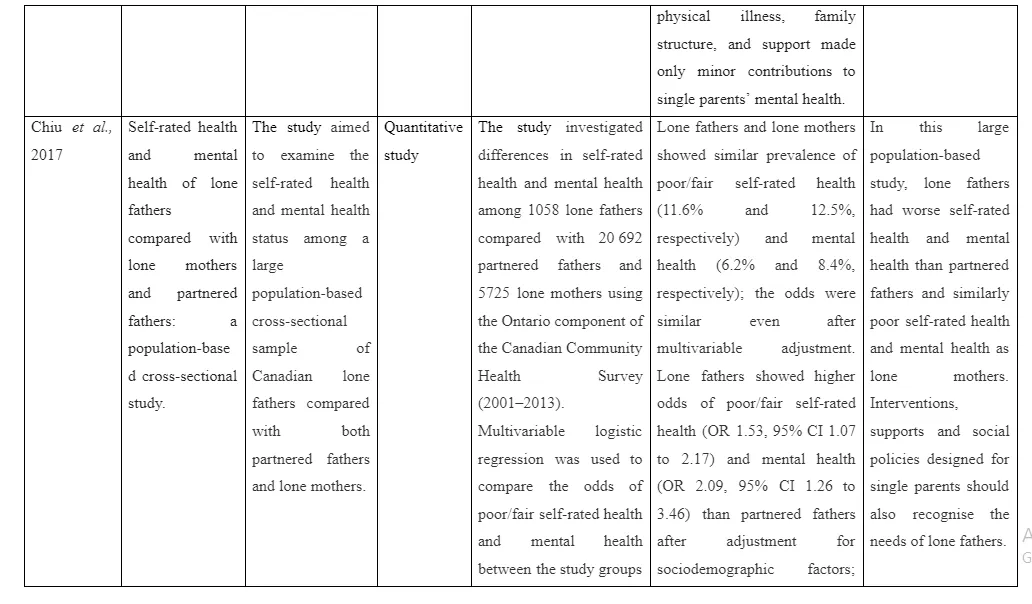

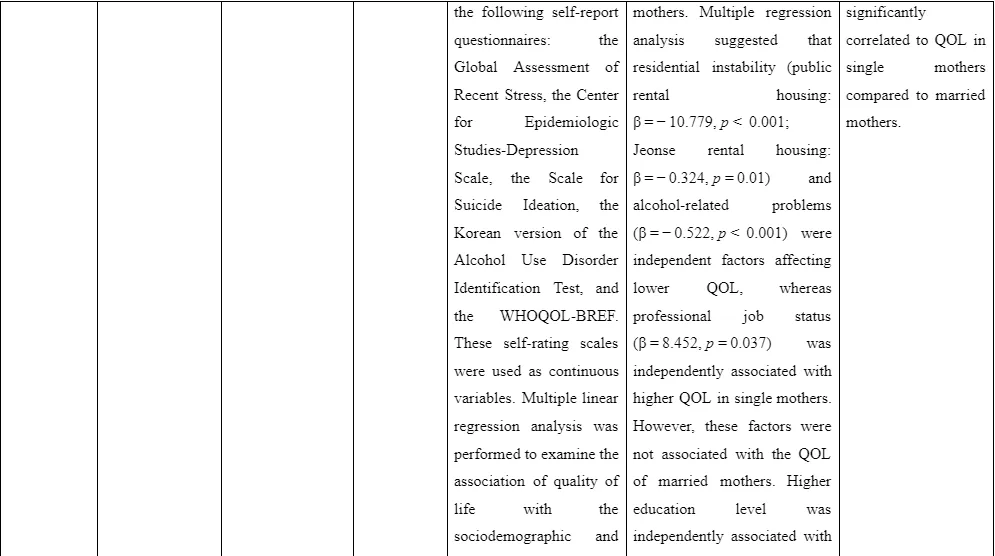
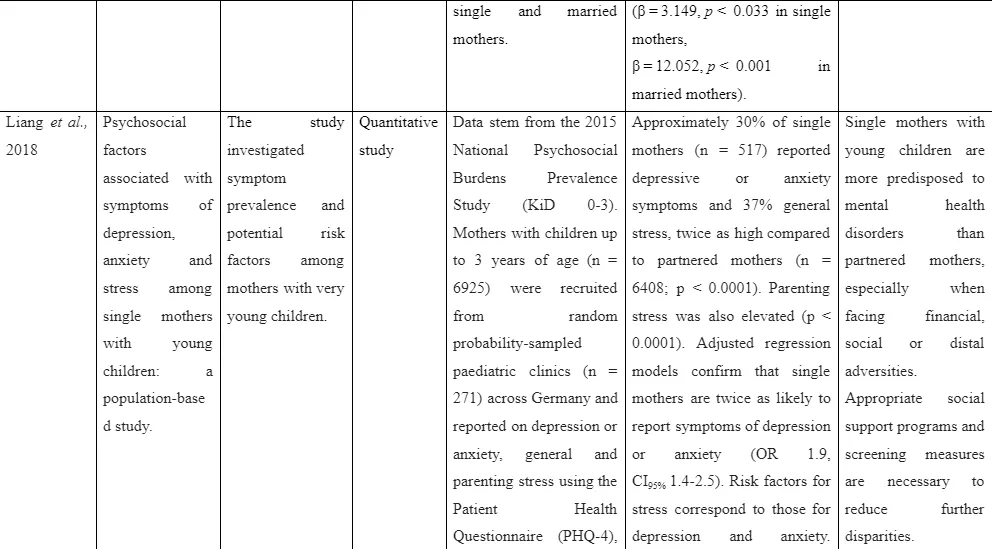
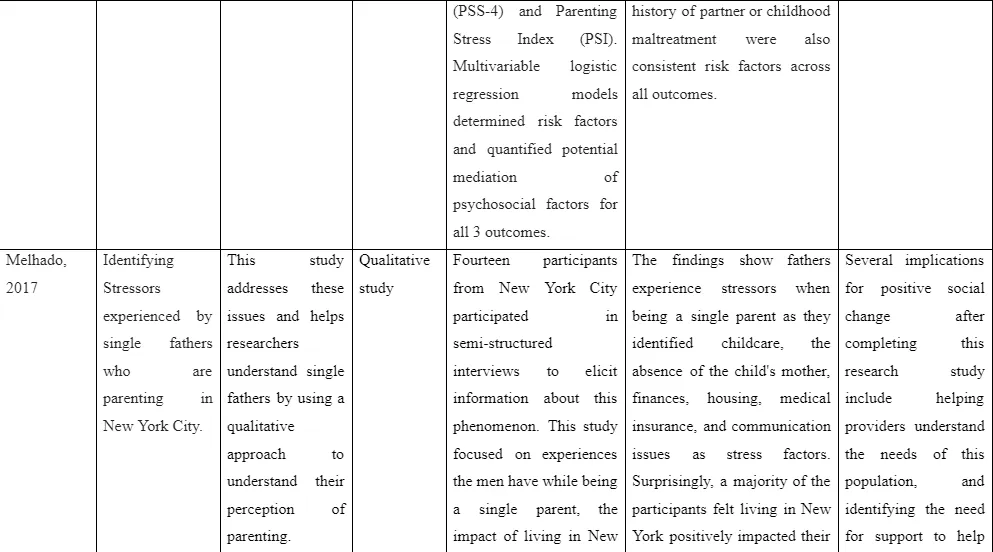

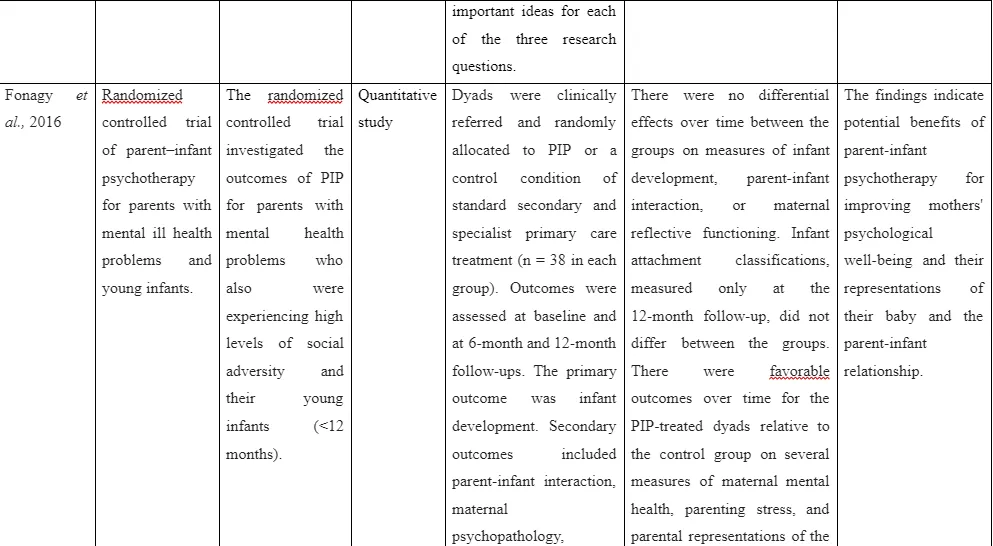



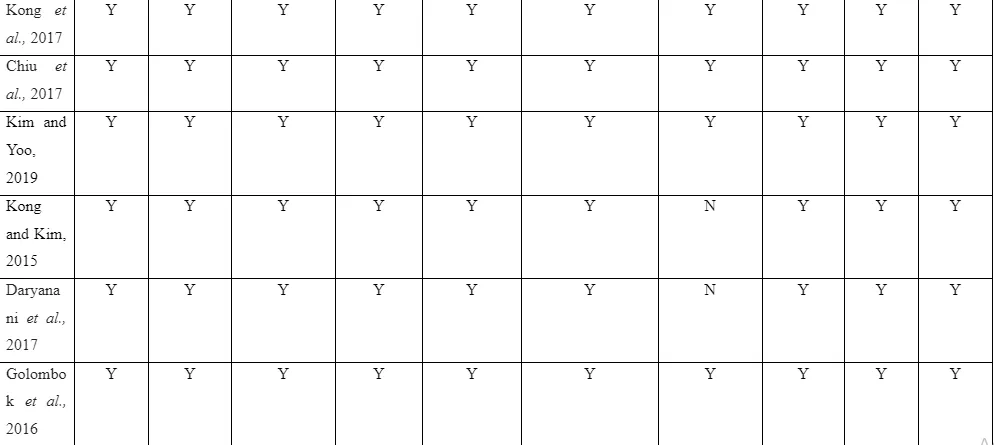
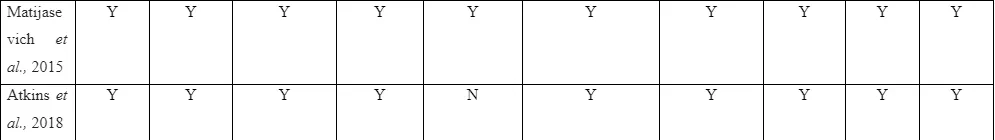
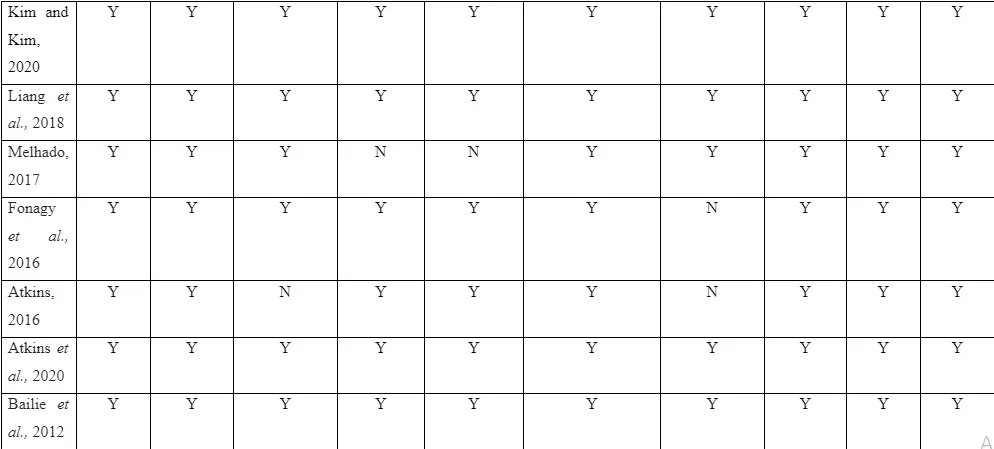
Dig deeper into Managing Coronary Heart Disease Patients with Depression with our selection of articles.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



