Enhancing Service Quality through Self Machines
Abstract
Service quality poses as a topic, which has acquired an extensive inquiry for the past last decades, and in recent years, it has emerged in the form of self-machines that has profound impacts on the manner in which customers interact with organizations, in creating positive
service outcomes such as customer retention, customer loyalty, as well as behavioral intentions. In this regard, this study focuses primarily on Tesco Extra and the manner in which it uses self-machines, and on the other hand, the way in which self-machines play a significant role in the retention of customers at Tesco Extra. The data for this study were collected through online survey, social media, as well as emails. The results of the study thus reveal that there is a positive relationship between self-machines service, quality, behavioral intentions, and loyalty, which both directly and indirectly influence customer satisfaction, which lead to customer loyalty and retention. The results of this study provide sufficient insight for other organizations apart from Tesco Extra to invest in the new technology, to enhance the experiences of their customers, to enhance customer satisfaction, loyalty, as well as intentions.
Keywords: Self-service, customer satisfaction, behavioural intentions, self-service technology, self-machines, Tesco Extra

Introduction
Background information
Tesco Extra, a company incorporated in the United Kingdom introduced self-checkout machines that allow its customers to take the position and duty of the cashier, a process that involves scanning, bagging and thereby paying the items without the assistance of any other person (Orel & Kara, 2014). The uniqueness of the self-machines projects a situation in whereby one can make payment even using the coins or through banknote scanner. Self-machines have since garnered popularity within the continental Europe and across the American continent, with the United States leading the pack. Self-machines are devices that have been developed in the commercial world to save time that various purchasers use to get the products they need and find the amicable way of paying for them without facing difficulties (Considine & Cormican, 2016). This paper hereby bases the role that the machines have played in the food industry, and specific company that the paper will narrow down to is the Tesco Extra Company. There has been a steady rise of self-machines that food chains have adopted in their sale operations but there has not been modification in the operations since inception. Tesco was never left behind in the development that shifted people’s attention. It has come up with new approach of selling its groceries (Scherer et al., 2015).
The specific topic
The paper seeks to dig deep into the initiative that Tesco Extra food chain adopted within its operations as a measure to enhance service delivery to its customers. Any serious company boasts of its client base thus Tesco had the motivation not be left out in the fast growing competitive market within the entire food industry. The paper is designed to critically and analytically discuss the roles that the self-machines are likely to play insofar as customer retention is concerned. This paper will evaluate the possible benefits that the self-machines may have in the competitive business and the reaction that the stakeholders, chiefly the customer, pose to other food chains that either have also adopted the innovation or have not possibly introduced such in the market.
Importance of the problem
The decision by the food company to introduce the self-machine had a pressing reason behind it. Standalone self-service food kiosks have impacted the restaurant industry, improving operations and impacting customers’ purchasing habits. There was definitely a mischief to be cured. The paper herein relooks into such issues that may have created gaps, which Tesco Extra company in its wisdom, moved ahead of other players in the industry to fill (Voorhees et al., 2017). Firstly, it is noteworthy that this firm is not however the first one in the industry to introduce a self-machine. Groceria had actually come up with such a digital transaction platform to boost the customer services. The conspicuous challenge that the customers loyal to Sam’s Groceria faced had a big impact in its sales, leading to diminishing returns. The system that Food Chain Company associated with Sam faced was its inflexibility, in the sense that it was only accessible to customers who had the Sam’s Groceria Card (Wang et al., 2017). This surely limited the number of customers who were willing to purchase the commodities using different cards and even coins.
The pioneer innovation by Sam’s Groceria took the food industry by surprise. In fact, it registered many people within few months of inviting members to subscribe into the club membership (Demoulin & Djelassi, 2016). As this development continued, potential customers were discouraged by the strict requirement that the users of the cards must first apply for membership in the club so as to enjoy the services. The strict formality chased away the customers who had already shown the interest of using its self machines. Surely, a further expense requires on to pay an annual fee on top of the cub membership fee of $45. The customer base definitely had to shrink, the end result being felt in the decreased sales and revenue (Considine & Cormican, 2016).
Besides, Sam’s Groceria, Walmart too introduced a credit card that enabled the customers to digitally transact their purchases. The Walmart MasterCard and standard Walmart credit card hitherto offer 3% cash back on its website (Walmart.com) orders as well coupled with locomotive orders inside a pick up. Additionally, it offers 2% for gas purchases that the company makes either at Walmart or Murphy gas stations. A further one percent is granted on purchases that the customers make using the Walmart MasterCard or Walmart Credit Card (Considine & Cormican, 2016). Once the rewards are earned, customer receives his/her cash back bonus as a statement credit. The offers herein made by the company are not a walk in the park to the customers. The rationale behind some of the complaints that the customers make is that it is not easy to question the higher interest rates imposed by the company. In precision, food chain machines which also include ATMs are successful in many companies as they attempt to solve side problems efficiently and simply (Orel & Kara, 2014).
Aim
The basis of the research entails finding the rationale that drove the food chain to look for viable ways of attracting the customers to its food chains that are spread across the geopolitical regions that it enjoys customer base. In essence, it will highlight the viability of self machines and critically evaluate whether the original objective that the company had has succeeded.
Therefore, the aim of the proposed study is to analyze the roles that the improved innovation of the self machine as operated by the clients. The end objective is to place an emphasis on the impact that the self machines will have on the customer retention.
Research Objectives and research questions
The focus of the research is to highlight the emphasis of customer retention taking into cognizance of the self machines that were put in place to meet such important stakeholders in the food chain industry. An observer may make an inference that the company’s executive has the desire to place the company above its peers. The paper takes keen notice of interests that it had to mind this taking the risk in order to leave no stone unturned. The paper cannot over-emphasize the importance that due diligence play before a corporate body effects a radical change that is likely to happen.
The topic herein paints the picture of purposive plan that views the rationale that the company rolled out for purposes of customer retention. The paper assumes that it had the actual goals that Tesco Extra formulated at the very early stages of this noble objective. The paper also reasons on the probability of success that the company may have relied on and at the same time; analyze the customer review regarding the quality of self machines in the market.
Though minimally, the paper, in the course of discussion may do comparison with other food chains that it had almost the same standing within the market politics. In case there is change (which can as well be notable) that can be measured.
The research will be premised on the following questions:
Did Tesco Extra sufficient conduct due diligence while implementing the self machine?
What was the main driving factor to adopt self machines?
Has the role of the self machine become realty to retain its customer base?
Literature Review
Literature review herein considers the theoretical background of the topic “the role of self-machines for customer retention in Tesco Extra,” that the paper intends to analyze in a critical perspective. The key factors that result from the theoretical trajectory, will then inform the path of intellectual reasoning. Beside, this part will dwell on what other public intellectuals have written about the issue of self machine in food chain industry coupled with the end result, target being on the client retention. Furthermore, literature review will focus on whether the holdings of the pundits have been fulfilled by the ever-changing market dynamics. The critique will be the extent to which their probable ideas have passed the test of time regarding their suggestions.
Theoretical framework
During the last decade customers’ interaction with firms has changed, as a result of self-service technologies. The self-service technology (SST) which refers to activities or benefits based on technology that are carried out by the consumers themselves, have become very common in the 21st century most notably in the food sector (Orel & Kara, 2014). This development has revolutionized the sector that many did not imagine could be used by entrepreneurs and venture capitalist to make profits; a great contributor to the government thus influence being felt in all aspects. The theoretical aspect that the paper places emphasis is grounded on the 4 tenets of functionality of the machines, the design, security and lastly the customization. In brief, though it will be discussed later, customization implies the guide that the workers and staff in general should familiarize themselves with (Kokkinou & Cranage, 2015).
The concept of self-machines
This paper will rely on the study that has shown that the replacement of IT service capabilities with SST is acceptable to technology based knowledge workers. Given the increasing technology development, it is important to understand the potential impact of SSTs on consumers’ assessments and intentions towards the firm. According to (Zhu et al., 2007), speed, control, reliability, ease of use and enjoyment are the most important attributes to consumers in evaluating SSTs. Among various types of SST, retail self-checkouts have grown at a fast pace over the past five years (Holman & Buzek, 2007). In their argument, Lusch and Vargo (2009), argues that SSTs lead to active customer participation in the co-production of service which is a component of value co-creation and is critical for providers, with consumers making an important contribution to service productivity. The wide range of SSTs available include automatic teller machines (ATMs), pay-at-the pump automated machines, internet banking, automated airline ticketing, in-store kiosks and the self-checkout systems (Cunningham et al., 2008). The innovation has proved that customers seem happy with the levels of functionality and security in the organizations SSTs. However the study highlighted an issue with the design and customization of the SSTs in the organization. Generic SST quality measurement, such as SSTQUAL, simply does not transcend industries and contexts (Tsou & Hsu, 2017). SST being a recent service delivery method, comparatively little research has been done on it (Beatson et al., 2008). Its success from the customers perspective is not yet clear according to Marzocchi & Zammit (2006) and is raising significant research issues (Dabholkar et al., 2003) hence there is a difficulty in finding a specific literature due to its recent introduction (Marzocchi & Zammit, 2006). However, while most studies focus on reasons for adoption and intention to use SSTs, limited research on its impact on customer satisfaction and retention exists (Weijters et al., 2007). Most empirical research has focused on experimental conditions using student samples or critical events analysis as primary sources of data but studies on SST usage in a real life scenario are still lacking. Hence, this study contributes to bridge this literature gap, focusing not only on understanding SSTs in the service encounter but also on its impact on customer satisfaction and retention. What is critical to SST adoption in finance is not critical to adoption in retail, finance, or technology. While there are factors that should be considered baseline factors to adoption some factors are more important than others depending on context. It is clear from the results of this study, when compared to previous studies, that contextual or environmental factors determine SST adoption (Kelly, et al., 2017).
However, this study focuses on a single multi-national financial services organization which Tesco fits. An extension of the sample is required to further improve the quality of results. Future research should consider broadening the scope to include more organizations within the knowledge worker technology sector. Furthermore, this study, like previous studies, employs deductive reasoning methods assuming no cultural differences existed between environments. Future studies might consider inductive methods in an attempt to isolate some of these issues. It is important to highlight that SST quality measurement is not the only factor relevant to adoption of SST within the business context. Orchestration of SST, or the streamlining and integration of applications, is also important. The demand for support is also important when considering investment in SST, because if demand is low the most cost effective mechanism maybe to continue with traditional support representatives (Reinders et al., 2015).
2.1.2 Self machines service Quality
Service quality is a standard of excellence that fulfils customers’ needs and contributes to achieving customers’ satisfaction. Service quality has become an important and vital issue of organizational success in today’s dynamic and global competitive retail business environments (Anitsal & Flint, 2006), customers focuses their priority on service quality when they spend their money; they obviously try to maximize the value in return and satisfaction for every single unit of money they spent (Pefok & Andrey, 2010). Service quality incorporates procedures related to service delivery and outcome, a number of researches have been conducted to analyze the structure and proper understanding of service quality. Service quality is a strategic tool and essential in gaining several operational and competitive advantages, superior service quality satisfies customers’ through increasing higher value perception and it is also closely tie with higher rate of return on investment (Jain & Gupta, 2004). Companies that emphasize on superior service quality achieve average 17.4% return on investment whereas companies with poor service quality achieve only average 4.5% return on their investment and superior service quality increased market share five to six times more and faster. SST service quality is being offered by organizations to improve the customer experience, decrease the expenses which directly or indirectly relate to their employees, attain customer retention and to bring technological advancements in their business (Tsou & Hsu, 2017). According to (Weijters et al., 2007), it is argued that SSTs provide inexpensive transactions, opportunities for co-creation, customization, and reduction of heterogeneous service encounters hence helps service firms increase the efficiency and quality of services and also minimize costs related to their operations (Anitsal & Schumann, 2007). Service suppliers like hotels, banks, and restaurants etc. are continuously employing SSTs to replace their customary means of service delivery to achieve quality services promoting customer retention (Anitsal & Flint, 2006). Boon-itt (2015) notes that increasingly, customers are looking to solve problems or answer questions they have about your product or service quickly and easily right at the very moment they have that need, with as little friction as possible. However, Smith & Wong (2016) also state that in many cases they do not want to have to search too much or talk to a human being to do so or at least not yet. The paper therefore focuses prominently on the factors that the self machines have contributed in retaining the customers, without forgetting that their sole objective of continuity of the business by the firm is maintained.
Notably, service quality conceptualization includes procedures related to the delivery of the service, as well as service outcome. A number of studies such as that of Boon-itt (2015) note that to inspect the service quality paradigm and conclusively, it has been noted that it entails 5 dimensions, which include reliability, responsiveness, assurance, tangibility, and empathy. Literature provides several measurement scales to measure service quality construct. In determining the SST service quality, the “SERVQUAL” scale was introduced to involve a face-to-face environment of the service process, and it was used with a three-dimensional service quality model named the technical quality, corporate image, as well as functional quality. There other models developed by researchers to measure service quality and customer satisfaction, include the Technical-Functional Quality Model, the Satisfaction-Service Quality Model. SERVPERF and the Attributes model. Among all of these models SERVQUAL and SERVPERF are widely used to measure service quality because both models are relatively easy to understand and use, it is easy to analyze collected data and they are also time and cost-effective. Similarly, another model provided by Considine & Cormican (2017), initiated a three-dimensional model, used for service quality and it included physical quality, corporate quality, as well as interactive quality. Physical quality relates to the physical products that are offered in the service production process, while delivering services to customers (Tsou & Hsu, 2017). As such, in various customary service instances, measuring service quality have majored on the interaction of clients with various organizational staff, as well as other market mix variables.
Customer loyalty towards Self-machines
Customer loyalty increases the probability of purchase, as well as frequent buying of the offerings of Tesco Extra. Today, buyers are faced with a lot of products and their expectations about the quality of goods and services is very different from the past. Due to these facts, buyers will choose the goods and services that are more consistent with their needs and expectations. The key factor in gaining customer satisfaction and loyalty, is providing appropriate services. customer loyalty increases probability of purchase and frequent buying of firm’s offerings. Customer loyalty refers to the mindset of consumers who have a favorable approach regarding a company, whereby, they promise to buy the company’s products/services, and also purpose to endorse the offerings of the company to others. The Service Profit Chain exhibits that it is important for the service firms to increase the satisfied and loyal customer base in order to attain growth and profitability. Customer loyalty increases with service firm’s value by analyzing the service quality, value, and loyalty chain in context of electronic service delivery context. Service quality enhances customer loyalty, which is notably expressed in the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB). TPB postulates that behavior results from attitude perceived behavioral control, as well as subjective norms (Parasuraman & Colby, 2015). In this regard, it forms the foundation of the customers’ satisfaction, loyalty, as well as attitude towards self-machines. Tesco Extra needs to embrace self-machines, in order to obtain a loyal customer base, and to attain growth, as well as profitability. Companies like Tesco Extra can retain customer loyalty through customer satisfaction by providing exceptional service to customers, which in turn, can lead to growth in market share (Das, 2015). Furthermore, TPB provides a significant link between customer satisfaction, favorable attitude, and loyalty, which are of great importance towards increasing customer loyalty (Tsou & Hsu, 2017).
Behavioural intention and SST service quality
Literature notes that consumer behaviour relates to the Theory of Reasoned Action, which relates behavioural intention with actual behaviour. This theory note that customer attitude towards novel technology usage influences behavioural intention. In order to determine the post purchase behavior of customers, several advanced models employ customer assessment of SSTs service quality in terms of satisfaction and behavioral Intentions (Chen et al., 2009). Certain indications show clearly whether a customer will leave or stay with the firm, make positive remarks, endorse the firm’s products, pay high prices and remain committed towards the firm in terms of loyalty. According to (Venkatesh et al., 2012) the research conducted to explore customers’ intentions to use SSTs revealed that various factors and attitude drive customers’ behavioral intentions towards SSTs (Weijters et al., 2007). In this regard, numerous prevailing models the assessment of SST service quality by customers, based on factors such as satisfaction and behavioural, as they determine whether customers will remain loyal to a company, endorse its products or services, and make positive remarks (Chen et al., 2018). Demoulin & Djelassi (2016) research work revealed that past usage, situational factors, and perceived behavioral control are the important elements of behavioral intention towards SSTs.
Customer satisfaction on SST service
Satisfaction is contemplated as the extent to which a customer provides positive sentiments towards a service encounter. It is concerned with a situation in which a customer is effectively compensated in a buying circumstance for an exchange of a cost (Chen et al., 2018). The loss of interpersonal aspect of service encounters may have an impact on consumer satisfaction and retention (Beatson et al., 2007). Thus, it is important to understand not only the motives that drive consumers to use SSTs in general but also its potential impact on consumers’ assessments of their experience with the organization and consumers’ future intentions (Beatson et al., 2006). In assessing the impacts of quality, customer satisfaction, as well as value on the behaviour of a consumer, sustainable competitive advantage remains the key aim for a business. Beatson et al. (2007) investigated the relationship among electronic service quality and customer satisfaction and found electronic service quality is positively related to customer satisfaction. If the use of self-service machines generates customer satisfaction i.e. if customers are pleased with the performance of the SST based on attributes they consider important, then it may impact greatly on the consumers’ intention to repatronise the store, thus establishing a feature differentiating the retailer from its competitors (Marzocchi & Zammit, 2006). In order to enhance productivity and improve customers’ satisfaction, companies integrate SSTs based on convenient and novel service channels while serving the customers (Demirci Orel & Kara, 2014). The study of Deng et al. (2010) showed that customer satisfaction, trust and switching cost boosted customer loyalty. This assessment is based on the characteristics of a product/service in providing a pleasant experience, which is consumption-related. Value Perception Theory denotes that satisfaction should be regarded as an emotional response that is initiated through cognitive evaluation (Parasuraman & Colby, 2015).
Hypothesized model
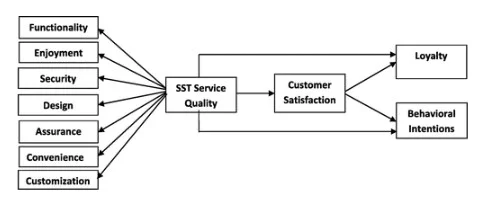
Introduction
Generally, this used qualitative research, based on people’s ideas, opinions, as well as beliefs towards the subject. In this regard, the research involved interviews, involving in-depth information. Overall, this chapter will explore on the research design to be used, will give an overview of the research approach and the research type to be used. Thereafter, the chapter will provide the rationale of the research paradigm, methodological approach, methods, and technique samples amongst other factors.
Research design, Research approach, and Research type
This study involved qualitative research, which aided in answering the study questions, using questionnaires. The data for this research were collected via online survey using emails, as well as social media. In this regard, purposive sampling was employed. The technique of purposive sampling is non-probability sampling, as it is regarded as the most effecting when studying knowledgeable experts (Orel & Kara, 2014). This type of sampling is based on certain characteristics of the participants and the general objective of the study (Parasuraman & Colby, 2015). The advantage of this sampling, making it the reason it will be adopted is that it is easier to generalize the study sample, as compared to random sampling whereby, not all participants may be having all the characteristics that may be required for the study (Taylor et al., 2015). In the process of data collection, the ethical issues were addressed by assuring the participants regarding their response confidentiality. The users of self machines at Tesco Extra from the big cities in the UK. Notably, big cities werebe targeted, owing to the fact that technological advancement often comes to big cities in any country. The total number of respondents to be used were 150, of which 70 per cent of them were male whilst 30 per cent of them were female.
Rationale
This study used qualitative research. The motivation behind adopting qualitative research is that it that, based on its nature, whatever differentiate humans from the rest of the world is the ability to talk. In this regard, as this study purposes to seek answers to various questions on individual experiences, the information it needs to gather from the participants, which aid in fulfilling some objectives (Kumar, 2019). The qualitative research was in form of questionnaires, whereby, it involved closed questions, as the participants were many in number (150) and open questions will not be necessary, to keep time. Closed questionnaires are easier and also quicker for the participants to answer. In addition, the answers of different participants can be easily compared; they can easily be coded and analyzed statistically. Moreover, the participants are likely to answer sensitive topics (Bulmer, 2017).
Research procedure
Data was collected through emails and social media platforms, owing to the fact that it would be difficult reaching the huge number of participants. Through social media platforms such as Facebook, the participants were easily engaged in answering the questionnaire, to enable Tesco Extra to obtain a deep understanding of their views regarding self machines (Quinlan et al., 2019). Moreover, the company would be able to obtain some other its customers’ email addresses, and this will enable it to send out questionnaires to them, which will be filled out, and after a few days, it will be required of the participants to send them back for analysis. Notably, social media and emails are the most significant equipment that will be used in conducting this particular research. Finally, the data collected will be analyzed using thematic analysis (Wodak & Meyer, 2015). After collecting data, statistical analysis will be performed, in order for the hypothesized relationship to be tested. The result of the study were aligned with important managerial, as well as practical implication that can guide in understanding consumer attitude towards using self-machines. Thereafter, an analysis was conducted, where thematic analysis is notably, one of the most effective forms of analysis in qualitative research, as it pinpoints, examines, and records themes that are derivable within data. These themes aid in providing a description of a particular phenomenon, which are associated with the study’s research questions. One of the motivations towards adopting thematic analysis is that it is flexible and provides a theoretical freedom. Of importance, is the fact that it provides a detailed account of data (Bulmer, 2017).
Access to data and Research Ethics
Ethical consideration is a critical issue in conducting a research. Firstly, there was informed consent, prior to conducting the research, whereby, the participants were given an opportunity to knowingly, and voluntarily give their consent to participate in the research (Kumar, 2019). In this regard, in an instance where a participant changed his or her mind in the course of the study, in case he or she had provided some vital information, they were discarded. Secondly, there wasbe respect for confidentiality and anonymity, whereby, the participants were assured that once their provided data were analyzed, they were discarded, to avoid the access to a third party. Notably, when these concerns were looked into, the research ran smoothly, and there was ease access to data from the participants (Quinlan et al., 2019).
Limitations
Notably, this research had certain limitations, which may impact on the generalizability of the results. The main limitation is with the sample selection. As the research was done with individuals living in the UK cities, it is evident that the research was not able to get significant information from customers located in remote areas, yet they may have had a different attitude concerning the use of self machines. In this regard, there was limited insights in determining the attitude of all customers in terms of loyalty, as well as behavioral intentions on the use of self-machines.
Conclusion
This chapter makes it evident that Tesco customers would rely heavily on self-machines and in facilitating data collection, it is worth noting that qualitative research was regarded as the most significant approach. Data was collected through online survey, by use of emails, as well as social media, and in addition, this was conducted using purposive sampling. It should also be noted that this study adhered to significant ethical standards, which ensured its success. The following chapter, which is on the results of the study, would then bring forth the results collected from the data obtained through online survey, social media, and emails.

Results and Discussion
Introduction
This chapter presents the results of the study, derived from the online survey, emails, as well as social media for Tesco customers. This will be accompanied by the discussion of the results, which will be backed up by information from the literature. In this regard, this chapter will first provide the results and this will be followed by a vital and critical discussion on the same, as presented below:
Results of the data collection
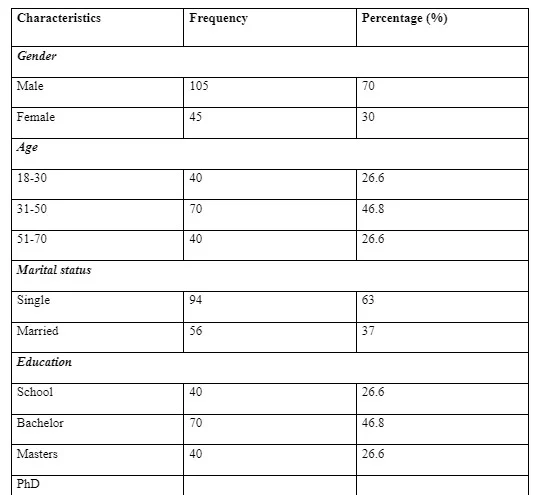
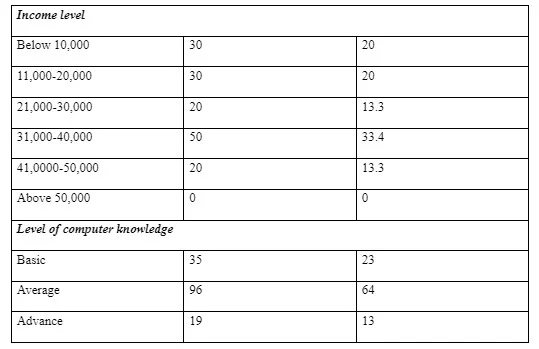
The total number of participants that were used in this study were 150, of which 105 of them will be male whilst 45 of them were female (equivalent to 70 per cent male, whilst 30 per cent female). The majority of the respondents had master’s degree, and with an average of 64 per cent of them having an average level of computer knowledge. 23 per cent of the participants had basic, and 13 per cent of them had advanced computer knowledge. In addition, it is also evident that the marital status of the participants were that 63 per cent of them were single, whereas 37 per cent of them were married. It is also significant to note that based on the ages of the participants, it is evident that 40 participants were within the age bracket of 18 to 30 years, whereas 70 of the participants fell between the ages of 31 to 50. Moreover, 40 of the participants fell between the age brackets of 51 to 70 years. Worth noting also, is the fact that regarding the level of education of the participants, 40 of them had just attended secondary school, whilst 70 of them had their bachelor, and the remaining 40 of them had Phd. Finally, it is also evident that 30 of the participants had their income level below 10,000, 30 of them also had their income level between 11,000-20,000, 20 of the participants had their income level between 21,000-30,000, whereas 50 of the participants had their income level between 41,0000-50,000. No participant had an income earning of above 50,000. Overall, upon the collection of data, it is evident that the study generally brought forth significant practical, as well as managerial implications, which aided in understanding the attitude of the customers on the use of self-machines and the roles of self-machines in enhancing customer retention.
The demographic characteristics of the participants
The participants were asked the type of services, which they need for self-service machines and it is evident that 15 of the participants used self-machines for ATM service. In addition, 30 of the participants used self-machines for pay-at-the pump automated machines, whereas 40 of the participants used self-machines for in-store kiosks. It should also be noted that 50 of the participants use self-machines for self-checkout systems, whereas 60 of the participants use the self-machines for online bill payment. 30 of the participants use self-machines for online shopping, whereas 60 of them use the self-machines for online learning. Overall, it is evident that all of the participants used self-machines for given purposes and others for various services and for this reason, they maintained their loyalty towards Tesco Extra, owing to the fact that they were able to fulfil their satisfaction.
The participants were also asked on the reasons why they were loyal, owing to the use of self-machines and 40 of the participants noted that self-machines were convenient for them to use, as they prevent time wastage. Moreover, 50 of the participants noted that they enjoyed using self-machines, and others (60 of them) indicated that they had guaranteed security, which they opted for, instead of having the Tesco staff attend to them. Moreover, 40 of the participants indicated that the functionality of self-machines is sufficient, which drives them into being loyal to the company. Moreover, other participants indicated that the self-machines are designed in a way, which attract them into using them.
Discussion
The results of this chapter make it evident that self-machines have played a significant role in customer retention, and for this reason, they are regarded as vital aspects in the day to day lives of the customers. Notably, self-machines have been widely accepted by individuals around the globe and not only in Tesco Extra, owing to the fact that due to technological innovations, this trend has been having an ever-increasing rate (Anitsal & Flint, 2006). Of importance to note, is the fact that as self-machines continually grow into becoming an important trend in the service delivery in Tesco Extra, it is worth noting that it has become of significance to investigate the impacts of self-machines on service quality, whilst considering customer satisfaction, loyalty, customer retention, as well as behavioral intentions (Boon-itt, 2015).
Based on the results derived from this study, it is evident that the acceptance rate of self-machines is generally high, thereby, implying that customers are ready to adopt various technology mediated encounters, whilst embracing change, as most of them would prefer getting their services done by use of new, as well as exciting ways (Boon-itt, 2015). This is owing to the fact that customers would always want to be served in ways in which they feel excited, and comfortable, and for these reasons, they prefer using self-machines, as the most effective way of getting their services done. As such, it is notable that this research purposes to provide a practical insight, meant for various service firms, and to various employee-mediated interfaces, in order to improve their service delivery to their customers (Considine & Cormican, 2016).
Service quality is a standard of excellence that fulfils customers’ needs and contributes to achieving customers’ satisfaction. Service quality has become an important and vital issue of organizational success in today’s dynamic and global competitive retail business environments (Anitsal & Flint, 2006), customers focuses their priority on service quality when they spend their money; they obviously try to maximize the value in return and satisfaction for every single unit of money they spent (Pefok & Andrey, 2010). Service quality incorporates procedures related to service delivery and outcome, a number of researches have been conducted to analyze the structure and proper understanding of service quality. As such, the results of this study indicate the positive, as well as significant relationship between self-machines service quality and the manner in which it relates to customer loyalty (Considine & Cormican, 2016). Notably, the results purpose to elaborate the fact that the higher service quality that is offered by self-machines enhanced the loyalty of the customers towards continually adopting the use of self-machines and their retention to a given organization. Findings according to literature suggests that the conceptual framework proposes the positive link between self-machines, customer satisfaction, as well as loyalty. Certain indications show clearly whether a customer will leave or stay with the firm, make positive remarks, endorse the firm’s products, pay high prices and remain committed towards the firm in terms of loyalty. According to (Venkatesh et al., 2012) the research conducted to explore customers’ intentions to use SSTs revealed that various factors and attitude drive customers’ behavioral intentions towards SSTs (Weijters et al., 2007). For this reason, companies like Tesco Extra can retain customer loyalty through customer satisfaction by providing exceptional service to customers, which in turn, can lead to growth in market share (Das, 2015).
The wide range of SSTs available include automatic teller machines (ATMs), pay-at-the pump automated machines, internet banking, automated airline ticketing, in-store kiosks and the self-checkout systems (Cunningham et al., 2008). The innovation has proved that customers seem happy with the levels of functionality and security in the organizations SSTs. However the study highlighted an issue with the design and customization of the SSTs in the organization. Customer loyalty increases the probability of purchase, as well as frequent buying of the offerings of Tesco Extra. Today, buyers are faced with a lot of products and their expectations about the quality of goods and services is very different from the past. Due to these facts, buyers will choose the goods and services that are more consistent with their needs and expectations (Considine & Cormican, 2016). The key factor in gaining customer satisfaction and loyalty is providing appropriate services. Notably customer loyalty increases probability of purchase and frequent buying of firm’s offerings.
Based on the findings of this study, it is also significant to take note of the fact there is a positive, and also a significant relationship, which exists between the self-machines service quality and behavioral intentions of the customers. Various scholars such as Considine & Cormican (2016) bring forth the idea that there is a positive influence of technology readiness, which affects the behavioral intentions of the customers, as well as their satisfaction. In addition, it is evident that e-service quality, also positively influences the behavioral intentions of the customers through enhancing indirect impact of satisfaction, which then leads to customer retention, and ultimately, customer loyalty. Whilst considering a structural path analysis, it is easily observable that customer satisfaction purposes to partially mediate the existing relationship between self-service quality and customer behavioral intentions (Demoulin & Djelassi, 2016). In addition, results also provides significant evidence that customer satisfaction also purposes to partially mediate the existing relationship between self-machines service quality and the loyalty of customers at Tesco Extra Company. For instance, self-check-out systems at Tesco Extra has a service quality, which has positive impacts on the customer loyalty, as it mediates the effects of customer satisfaction.
It is significant to take note of the fact that in the present digital environment, service organizations such as Tesco Extra are increasingly using various new technologies in providing fast, and also easy service interface for a variety of their customers. Owing to this way, it is evident also that banks are also purposing to provide internet, as well as mobile banking services to a variety of their customers, in order for them to be able to handle their financial transactions wherever they are for instance, at their homes or even offices. Moreover, it is also clear that Automated Teller Machines have been installed by various banks, in order for them to conveniently serve various customers (Kokkinou & Cranage, 2015). Notably, by use of ATM, it is clear that customers would feel a great sense of independence whilst carrying out their transactions for instance in funds transfer, online bill payment, and also whilst disbursing cash among other services. In this regard, they do not have to wait for a very long time, for service personnel of a given organization in question, owing to the fact that the services can be provided through technological interface instead of the employees of the organization (Lusch and Vargo, 2009).
Overall, it is significant to take note of the fact that self-machines have resulted in customer facilitation in Tesco Extra, great cost reduction, as well as a convenient service environment for the users. Notably, various organizations have been able to provide facilities, which aid in online shopping from their website. Moreover, it is also evident that there is the pure e-commerce business, which also aids companies in selling their product through online platform and by use of a technological interface (Marzocchi and Zammit, 2006). In this regard, the companies provide full information regarding the prices of products, the type and also the quality of the said product. In this regard, customers are able to purchase these kinds of products by just sitting at their homes of even offices. Tesco Extra has also made payment to be easy online by use of either a debit or a credit card, and as such, the firm is able to deliver its products to various customers at their convenience through their own use of a sufficient delivery system. Overall, it is worth noting that self-machines have enabled greater flexibility, based on time, as well as place, owing to the fact that customers now find it easy and also convenient for them to shop from their desired organization without spearing any of their additional time (Orel & Kara, 2014).
Conclusion
Based on the provisions provided in this chapter, it is evident that sufficient information on data collection has been provided, in line with a discussion, backed up with vital information from the literature. In this regard, it is evident that the information provided in this chapter are in line with the literature review findings. This chapter has been able to answer the research questions, and also meet its aim. The following chapter, which is the conclusion chapter will provide a vivid, definitive and clear summary of the provisions in the entire paper, as provided below.
Conclusion
Theoretical implications
This study provides significant contributions, based on the existing literature. In line with this, the major contribution of the study is that it provides empirical evidence of mediating the impact of customer retention, owing to the use of SSTs service quality, in addition to customer loyalty, as well as behavioural intentions. Notably, this posits on the terms of how and why self-machines quality have impacted on the behavioural intention and loyalty of customers (Orel & Kara, 2014). As such, it is evident that this study adds onto the literature on self-machines service quality and the existing relationship that Tesco has with its customers. Hence, the aforementioned model used in the literature review provides a significant insight on the self-machines literature whilst relating it to service marketing research. Evidently, based on previous studies; customer retention, loyalty, and satisfaction is regarded as a mediating variable that exists between service quality and self-machines quality settings (Smith & Wong, 2016). Notably, the results of those previous studies indicate that there exists a positive relationship between self-machines quality and loyalty, as well as behavioural intentions. In this regard, it is also evident that the results, derived from this study also confirm the existing relationship, as previously explored.
Satisfaction is contemplated as the extent to which a customer provides positive sentiments towards a service encounter. It is concerned with a situation in which a customer is effectively compensated in a buying circumstance for an exchange of a cost (Chen et al., 2018). The loss of interpersonal aspect of service encounters may have an impact on consumer satisfaction and retention (Beatson et al., 2007). Thus, it is important to understand not only the motives that drive consumers to use SSTs in general but also its potential impact on consumers’ assessments of their experience with the organization and consumers’ future intentions (Beatson et al., 2006). In assessing the impacts of quality, customer satisfaction, as well as value on the behaviour of a consumer, sustainable competitive advantage remains the key aim for a business. Beatson et al. (2007) investigated the relationship among electronic service quality and customer satisfaction and found electronic service quality is positively related to customer satisfaction.
Practical/managerial implications
This study imposes significant practical, as well as managerial implications, which aid in understating customer attitude in the use of self-machines in terms of customer loyalty, customer retention and behavioural intentions. It is then important for Tesco Extra Company to pay intensive efforts in a bid to understand the factors, which may possibly create satisfaction or even dissatisfaction amongst its customers that use the self-machine systems (Considine & Cormican, 2016). Service quality incorporates procedures related to service delivery and outcome, a number of researches have been conducted to analyze the structure and proper understanding of service quality (Beatson et al., 2006). Service quality is a strategic tool and essential in gaining several operational and competitive advantages, superior service quality satisfies customers’ through increasing higher value perception and it is also closely tie with higher rate of return on investment (Jain & Gupta, 2004). In this regard, Tesco Extra Company is obligated to maintain a high standard of service quality, through emphasizing on security, as well as privacy measures in attaining great confidence on the technological interface. In addition, it should be noted that the more the self-machines are of great quality, the higher the rate of customer retention whilst adopting the self-machines. It is also worth noting that Tesco Extra should take the initiative of driving positive intentions of its customers towards adopting self-machines through enhancing consistent monitoring, as well as evaluation (Chen et al., 2018). Notably, these steps would aid the company in providing necessary information on the improvement of service delivery to its customers, which would then result into customer retention through use of self-machines. It is advisable for all organizations in the retail industry to employ the use of self-machines, which notably provides great autonomy to its customers (Considine & Cormican, 2016). In line with this, it aids in enhancing the technological interface, thus, enabling greater ability in providing customized services to its loyal customers.
The results of this study are also noted to provide significant insight for Tesco Extra to invest more into newer technologies, with an aim of enhancing customer loyalty and customer retention. This is owing to the fact that the future of Tesco Extra rely heavily on the kind of technological innovation, which the company brings in bettering the services it provides to its loyal customers (Chen et al., 2018; cited in Considine & Cormican, 2016). Putting into consideration, the coming technological era, it is worth noting that it will require firms to pay much attention towards improving customer experience, whilst using advanced technological interface. In addition, reputed firms should as well be obligated to take the necessary initiatives in improving technological literacy among their consumers, and should as well take aggressive steps in letting their consumers know of the systems that they have introduced, or which they intend to introduce sooner or later (Anitsal & Flint, 2006). This poses as an important factor, which would facilitate the success of a company and it will also purpose to improve the loyalty, as well as positive behavioural intentions of the customers.
Limitations and future research
It is significant to take note of the fact that this study brought forth certain limitation that notably had their effects on the results generalizability (Considine & Cormican, 2016). Worthy of noting, the major limitation, which it showed was with the sample selection. Owing to the fact that the data for this study were collected through online survey, emails, as well as social media, it is worth noting that other users of self-machines in Tesco who do not use the aforementioned data collection methods were not considered, yet they would have different perception regarding the use of self-machines, other than those provided in the results section (Anitsal & Flint, 2006). This then presents the fact that the results of this study provided limited insight on the perception of the customers’ attitude in terms of behavioural intention, retention, as well as loyalty on the use of self-machine systems. This then creates the need for a diversified research method, which would be able to reach all the required participants for such kind of study (Boon-itt, 2015). Moreover, it is worth noting that this study was generally qualitative in nature, and as such, there were limitations on the survey-based data collection method. In this regard, there is need for further research that employs the use of different methodological approaches such as the use of qualitative research, and even quantitative research (Anitsal & Flint, 2006). In addition, there is need for other forms of variables to be included and this includes the corporate image of the service providers, which needs to be employed in the current model used in this study, as a mediator variables, purposely for future research (Considine & Cormican, 2016).
Bibliography
- Anitsal, I., & Flint, D. J. (2006). Exploring customers’ perceptions in creating and delivering value: Technology-based self-service as an illustration. Services Marketing Quarterly. 27(1), 57–72.
- Beatson, A, Coote, L, Rudd, J (2006). Determining consumer satisfaction and commitment through self-service technology and personal service usage. J Mark Manag 22:853-882.
- Boon-itt, S. (2015). Managing self-service technology service quality to enhance e-satisfaction. International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences, 7(4), 373-391.
- Bulmer, M. (2017). Sociological research methods. Routledge.
- Chen, Y., Yu, J., Yang, S., & Wei, J. (2018). Consumer’s intention to use self-service parcel delivery service in online retailing: An empirical study. Internet Research, 28(2), 500-519.
- Considine, E., & Cormican, K. (2016). Self-service technology adoption: An analysis of customer to technology interactions. Procedia Computer Science, 100, 103-109.
- Considine, E., & Cormican, K. (2017). The rise of the prosumer: An analysis of self-service technology adoption in a corporate context. SciKA-Association for Promotion and Dissemination of Scientific Knowledge, 5(2), 25-39.
- Demoulin, N. T., & Djelassi, S. (2016). An integrated model of self-service technology (SST) usage in a retail context. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 44(5), 540-559.
- Demoulin, N. T., & Djelassi, S. (2016). An integrated model of self-service technology (SST) usage in a retail context. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 44(5), 540–559.
- Kelly, P., Lawlor, J., & Mulvey, M. (2017). Customer roles in self-service technology encounters in a tourism context. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 34(2), 222-238.
- Kokkinou, A., & Cranage, D. A. (2015). Why wait? Impact of waiting lines on self-service technology use. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 27(6), 1181-1197.
- Kumar, R. (2019). Research methodology: A step-by-step guide for beginners. Sage Publications Limited.
- Lusch, R, Vargo, S (2009). Service-dominant logic-a guiding framework for inbound marketing. Mark Rev St. Gal.6: 6-10.
- Marzocchi, G, Zammit, A (2006). Self-scanning technologies in retail: determinants of adoption. T Serv Ind J, 26(6):651-669.
- Orel, F. D., & Kara, A. (2014). Supermarket self-checkout service quality, customer satisfaction, and loyalty: Empirical evidence from an emerging market. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 21(2), 118-129.
- Parasuraman, A., & Colby, C. L. (2015). An updated and streamlined technology readiness index: TRI 2.0. Journal of service research, 18(1), 59-74.
- Quinlan, C., Babin, B., Carr, J., & Griffin, M. (2019). Business research methods. South Western Cengage.
- Reinders, M. J., Frambach, R., & Kleijnen, M. (2015). Mandatory use of technology-based self-service: does expertise help or hurt?. European Journal of Marketing, 49(1/2), 190-211.
- Scherer, A., Wünderlich, N. V., & Von Wangenheim, F. (2015). The Value of Self-Service: Long-Term Effects of Technology-Based Self-Service Usage on Customer Retention. MIS quarterly, 39(1).
- Smith, L. C., & Wong, M. A. (Eds.). (2016). Reference and Information Services: An Introduction: An Introduction. ABC-CLIO.
- Taylor, S. J., Bogdan, R., & DeVault, M. (2015). Introduction to qualitative research methods: A guidebook and resource. John Wiley & Sons.
- Tsou, H. T., & Hsu, H. Y. (2017). Self-Service technology investment, electronic customer relationship management practices, and service innovation capability. In Marketing at the Confluence between Entertainment and Analytics (pp. 477-481). Springer, Cham.
- Tsou, H.-T., & Hsu, H.-Y. (2017). Self-Service technology investment, electronic customer relationship management practices, and service innovation capability. In Marketing at the Confluence between Entertainment and Analytics. (pp. 477–481). Berlin: Springer.
- Voorhees, C. M., Fombelle, P. W., Gregoire, Y., Bone, S., Gustafsson, A., Sousa, R., & Walkowiak, T. (2017). Service encounters, experiences and the customer journey: Defining the field and a call to expand our lens. Journal of Business Research, 79, 269-280.
- Wang, Y., So, K. K. F., & Sparks, B. A. (2017). Technology readiness and customer satisfaction with travel technologies: A cross-country investigation. Journal of Travel Research, 56(5), 563-577.
- Weijters, B., Rangarajan, D., Falk, T., & Schillewaert, N (2007). Determinants and outcomes of customers’ use of self-service technology in a retail setting. Journal of Service Research. 10(1), 3–21.
- Wodak, R., & Meyer, M. (Eds.). (2015). Methods of critical discourse studies. Sage.
- Zhu, Z, Nakata, C, Sivakumar, K (2007). Self-service technology effectiveness: the role of design features and individual traits. J Aca Mark Sci 35:492-506.
Continue your exploration of Emergency wake up device for truck drivers at loading with our related content.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



