Importance of Proper Patient Documentation in Nursing Care Management and Its Impact on Patient Outcomes
1.Calculations:
a)150 micrograms to Milligrams:
1 microgram = 0.001 Milligram
Therefore 150 micrograms = 150 x 0.001 = 150/ 1000 = 0.15 Milligram
b)150 micrograms to Grams:
1 microgram is 1/1000000g
Therefore 150 micrograms = 150 / 1000000 = 0.00015g
c)150 micrograms to Kilograms:
1 microgram = 1.0 × 10-9 Kilogram
Therefore 150 micrograms = 150 × 10-9 Kilogram = 0.00000015 Kilogram
2. a) 3000 micrograms to Milligrams:
3000 x 0.001 = 3000 / 1000 = 3 Milligrams
b) 3000 micrograms to Grams:
3000 / 1000000 = 0.003Gram
c)3000 micrograms to Kilograms:
3000 micrograms = 3000 × 10-9 Kilogram = 0.000003 Kilogram
3) a) 28500 micrograms to Milligrams
28500 x 0.001 = 28500 / 1000 = 28.5 Milligrams
b) 28500 micrograms to Grams:
28500 / 1000000 = 0.0285 Gram
c) 28500 micrograms to Kilograms:
28500 × 10-9 Kilogram = 0.0000285 Kilogram
4) a) 52000 micrograms to Milligrams:
52000 x 0.001 = 52000 / 1000 = 52 Milligrams
b) 52000 micrograms to Grams:
52000 / 1000000 = 0.052 Gram
c) 52000 micrograms to Kilograms:
52000 × 10-9 Kilogram = 0.000052 Kilogram
5) a) 106000 micrograms to Milligrams:
106000 x 0.001 = 106000 / 1000 = 106 Milligrams
b) 106000 micrograms to Grams:
106000 / 1000000 = 0.106 Gram
c) 106000 micrograms to Kilograms:
106000 × 10-9 Kilogram = 0.000106 Kilogram
Millilitres to Litres:
1)400
1 Millilitre = 0.001Litre
400 Millilitres = 400 x 0.001Litre = 400/1000 = 0.4 Litre
2)3800
3800 Millilitres = 3800 x 0.001Litre = 3800 /1000 = 3.8 Litres
3)23750
23750 Millilitres = 23750 x 0.001Litre = 23750 /1000 = 23.75 Litres
4)89200
89200 Millilitres = 89200 x 0.001Litre = 89200 /1000 = 89.2 Litres
2.Example of miscalculation of drugs and analysis of impact
The errors occurring while calculating the dosage of drugs are referred to as medication errors and it is considered to be a chronic problem in the field of healthcare. The miscalculations that occur within dosage of the drugs frequently remain overlooked and this can be related to inappropriate dosage calculation with respect to the body weight, age of the patients.
Example:
A pharmacist prescribed dosage of amoxicillin for a nine months old baby having body weight of 13 lbs. The instruction is to administer 333 mg of suspension of drug amoxicillin at routine intervals of 12 hours for the next 7 days.
Explanation:
The above dosage recommendation indicates that 666 mg of suspension of drug amoxicillin has to be administered to the baby each day, whose body weight is 13 lbs and age is nine months old. The prescription demonstrates two potential errors –
1) The dosage prescribed is higher than the UK practice guidelines as per the body weight of the patient (Saxena, 2014).
2) The dosage should be divided into two equal portions after the strict routine intervals of 12 hours but was prescribed to administer the full dosage twice.
Therefore, the correct calculation should be –
To convert the weight (in lb) to kg it should be divided by 2.2 13 lbs / 2.2 = 6.5 kg
As per British National Formulary for Children (BNFC) (2011 – 2012) guidelines children who are under 1 year age band should receive maximum of 62.5 mg of penicillin group of drugs (Paediatric Formulary Committee, 2012). However, in addition to this as per 2011 guideline any children having body weight less than 40 kg can receive amoxicillin suspension for any kind of indications up to 40–90 mg/kg/day (Saxena, 2014).
6.5 kg x 90 mg/kg = 585 mg per day.
Each dosage value will be = 585 mg / 2 = 292.5 mg every 12 hours.
Past scientific evidence have revealed that dosage prescribed not in accordance to guidelines can result in several drug contraindications or negative reactions among children such as antibiotic related diarrhoea, convulsions, antimicrobial resistance (both at low and high dosage) without showing any benefits of the antibiotic prescribed (Saxena, 2014; Chung, 2007; Laxminarayan, 2013).
3 a) Prescribed dosage of Erythromycin, 40 mg/kg/dose for patient having body weight 74 Kg.
The maximum dosage in mg is –
74 Kg x 40 mg/kg = 2960 mg dosage of Erythromycin.
b) Mrs Smith is prescribed Ibuprofen 5mg/kg/dose and her body weight is 80 kg.
The maximum dosage of Ibuprofen that can be administered to Mrs Smith is –
The maximum dosage of Ibuprofen that can be administered to Mrs Smith is – 5mg/kg x 80 kg = 400 mg of Ibuprofen
3c) Chloe is 5 years old and was prescribed with a drug of dosage 5 mcg per kilogram body weight. The body weight of the child is 18 kilograms.
The drug dosage will be –
5 mcg prescribed for 1 kilogram body weight
Therefore, as the body weight is 18 kilograms, the child can receive maximum of 5 mcg x 18 kilograms = 90 mcg of the prescribed drug.
3d) Drug dosage as per body surface area:
Patient 1 weighs 75kg and is 1.6 metres tall. The drug dosage prescribed is 10mg/day.
As per the Mosteller formula, Body Surface Area (BSA) m2 (Mosteller, 1987)
= √ height (cm) x weight (kg) / 3600
Weight: 75kg; Height: 1.6 metres or 160cms
√ 75kg x 160cms / 3600 = √ 12000/ 3600 = √120/ 36 = 1.825 m2
If the dosage of drug is 10mg/ m2/day, then the dosage will be
1.825 m2 x 10 mg = 18.25 mg /day
Patient 2 weighs 20kg and is 0.7 metres tall. The drug dosage prescribed is 2mg/m2/day
As per the Mosteller formula, Body Surface Area (BSA) m2 (Mosteller, 1987)
= √ height (cm) x weight (kg) / 3600
Weight: 20kg; Height: 0.7 metres or 70 cms
√ 20kg x 70 cms / 3600 = √ 1400/ 3600 = √14/ 36 = 0.62 m2
If the dosage of drug is 2mg/m2/day, then the dosage will be
0.62 m2 x 2 mg = 1.24 mg /day
3e) Age of child = 6 years.
Recommended dosage 1 mg/years of age/day
1mg dose of drug for 1 year of child daily, then
For 6 years the dosage will be –
6 x 1mg = 6mg dose / day
3f) Age of child = 4 years
Recommended dosage 4.5 mgs/year of age/day
For 4 years the dosage will be –
x 4.5 mgs = 18/da
4.Volume of normal saline administered = 1.5 litres or 1500 mL
Time duration = 24 hours
The Drip Rate formula:
Drip Rate = Volume (mL) / Time (h) = 1500 / 24 = 62.5 ml / h (Park, 2013).
Therefore the patient will receive 62.5 ml of IV fluid every hour.
5. The given case scenario depicts that the patient, Emily is 88 years old. The patient is found to be in an independent state and her mental status is found to be alert. Respiration Rate (RR) of the patient was found to be 18 per minute scoring NEWS 2 score 0 (normal rate range 12 – 20 bpm); level of oxygen saturation is 80%, scoring NEWS 2 score 3 (normal level of saturation is ≥ 96); having blood pressure of 150/70, scoring NEWS 2 score 0 (normal systolic BP range 111 – 219); pulse rate of 92, scoring NEWS 2 score 1 (normal pulse rate range 51 – 90 bpm); and temperature of 37.5 ° C, scoring NEWS 2 score 0 (normal temperature range 36.1 – 38.0° C). The patient was found to be confused scoring 3 on NEWS 2 scale. Therefore aggregate NEWS 2 score of the patient Emily is 7 (Williams, 2019).
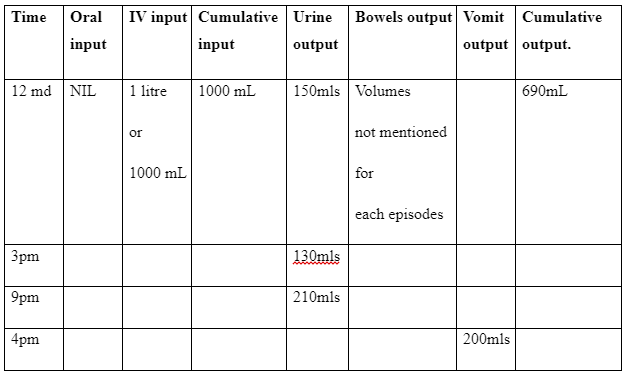
7. Normal output of urine should be 1ml/kg of body weight per hour. Here Christine has shown output of 490 ml of fluid within 9 hours. According to NICE, (2013) guidelines, the daily fluid or water administration can be up to 25 – 30ml/ kg /day. However, Christine was administered with 1000ml of IV fluid for 24 hours for 74.39 Kg of body weight.
Body weight of Christine is - 11 stone 10lbs
1 stone = 6.35 Kg
11 stone = 69.85 Kg; 10 lbs / 2.2 = 4.54 kg
Total Body weight in kg = 69.85 Kg + 4.54 kg = 74.39 kg
Therefore, as per the normal condition, 490 mL (little less) of fluid can be given out by Christine of weight 74.39 kg within 24 hours. As per the NICE, (2013) guidelines, the fluid that should be administered is around 223.17 mL of fluid as per the body weight of the patient.
8. The process of maintaining documentation or records of the patients by the nurses contributes significantly to the care management of the patients. It is the professional accountability of the nurses to maintain the health records accurately as it involves a wide range of important information related to health of the patients. It is a part of good nursing practice and without record there is no proof available that care has been offered in a timely manner to the patient that can create legal issues during the time of crisis (Mutshatshi, 2018).
9. The improper documentation of the health records of patients is associated with poor care service to the patients, long duration of stay at hospital and even death of patients. Moreover, it is considered as a professional misconduct as it enhances the chances of medico-legal risk when the care service could not be tracked down if required (Mathioudakis, 2016).
References:
- Saxena, S., Ismael, Z., Murray, M.L., Barker, C., Wong, I.C., Sharland, M. and Long, P.F., 2014. Oral penicillin prescribing for children in the UK: a comparison with BNF for Children age-band recommendations. Br J Gen Pract, 64(621), pp.e217-e222.
- Paediatric Formulary Committee, 2012. British National Formulary for Children 2012–2013. London: British Medical Association, the Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain, the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, and the Neonatal and Paediatric Pharmacists Group.
- Chung, A., Perera, R., Brueggemann, A.B., Elamin, A.E., Harnden, A., Mayon-White, R., Smith, S., Crook, D.W. and Mant, D., 2007. Effect of antibiotic prescribing on antibiotic resistance in individual children in primary care: prospective cohort study. Bmj, 335(7617), p.429.
- Laxminarayan, R., Duse, A., Wattal, C., Zaidi, A.K., Wertheim, H.F., Sumpradit, N., Vlieghe, E., Hara, G.L., Gould, I.M., Goossens, H. and Greko, C., 2013. Antibiotic resistance—the need for global solutions. The Lancet infectious diseases, 13(12), pp.1057-1098.
- Mosteller, R.D., 1987. Simplified calculation of body-surface area. The New England journal of medicine, 317(17), pp.1098-1098.
- Williams, B., 2019. The National Early Warning Score 2 (NEWS2) in patients with hypercapnic respiratory failure. Clinical Medicine, 19(1), p.94.
- Mutshatshi, T.E., Mothiba, T.M., Mamogobo, P.M. and Mbombi, M.O., 2018. Record-keeping: Challenges experienced by nurses in selected public hospitals. Curationis, 41(1), pp.1-6.
- NICE Guidelines, 2013. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg174/documents/intravenous-fluid-therapy-nice-version2 (Accessed on 20.08.2020)
- Park, K., Lee, J., Kim, S.Y., Kim, J., Kim, I., Choi, S.P., Jeong, S. and Hong, S., 2013. Infusion volume control and calculation using metronome and drop counter based intravenous infusion therapy helper. International journal of nursing practice, 19(3), pp.257-264.
- Mathioudakis, A., Rousalova, I., Gagnat, A.A., Saad, N. and Hardavella, G., 2016. How to keep good clinical records. Breathe, 12(4), pp.369-373.
Dig deeper into Importance of Establishing Estimated Delivery Date with our selection of articles.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



