Exploring the Link between Dementia and Elder Abuse: A Study on Care and Nursing Homes in England
Research Question:
What are the factors that underpin the abuse and neglect of elderly with dementia in care and nursing homes in England?
Introduction
Firstly, this proposal outlines the background and rationale for the study which would be to draw a link between risk of elder abuse and dementia. aims to provide the most valuable insights into healthcare dissertation help. Secondly, it outlines the aims and objectives of the study. These include finding the reasons behind abuse and neglect of elderly patients with dementia in care and nursing homes in England, highlighting the attitude and perceptions of the caregivers in relation to the delivery of care to older dementia patients and also reflecting the beliefs and thoughts of older dementia patients regarding neglect and abuse. The Literature search strategy through the use of databases, keywords, inclusion and exclusion criteria would subsequently be looked at. Additionally, ethics and anti-oppressive practice, project outline, and timetable will be discussed accordingly.
Background and rationale

Dementia is a disease that covers a wide range of symptoms associated with the decline in the normal functioning of a person. Symptoms of dementia usually vary; however, the core mental functions that are impaired significantly are language and communication, memory, judgment and reasoning, visual perception, ability to pay attention and keep focus. Dementia is progressive, and age is the main factor attributing to the onset of the symptoms. Dementia mainly has an impact on older people and the disease is characterised by loss of behavioural, social and cognitive functions (Wimo et al., 2013). According to Brooker and Latham (2015) with the progress of dementia and the related functional and cognitive disabilities, there is a necessity to have the provision of care and assistance for the patients. Hence the role of caregivers in care and nursing homes are of utmost importance of maintaining the quality of life for the patients. Elder abuse and neglect, especially of those suffering from dementia, has drawn interest in public discourse as this issue has been studied at large and attempts have been made to address the issues faced (Gibbs & Mosqueda, 2014).
Brayne (2016), estimated that, prevalence of dementia in England would increase drastically in the coming decades. There are about 676,000 individuals living with dementia in the England and these numbers are expected to double by 2040 (Parkin and Baker, 2016). Currently, dementia costs England about £19 billion per year and is set to increase up to £27 billion by 2040 (Department of Health, 2013). One-third of dementia sufferers live in care homes where they receive care to meet their daily needs (Alzheimer’s Society, 2013). With the rise in the number of older dementia patients and identification of the vulnerability of neglect and abuse (Bertrand, 2006), it is crucial to examine the issue of abuse in this subgroup of the older population in England. There is limited research on elder abuse in the case of those suffering from dementia in care settings although a small section of evidence indicates that it is nearly as widespread in all communities across the globe. There is concern among the health care domain that people with dementia may be at particular risk of elder abuse. However there is little data to confirm such fears. Though many older residents in UK care homes have a dementia, there is an increasing proportion of hospital patients suffering from the disease, data on the presence of a dementia do not frequently extend beyond with data covering elder abuse. This implies that it is hard for practitioners to know whether people with dementia face different risks than other vulnerable adults. There is also little information on what practitioners might be able to do to minimise risk and to respond to harm. It is proposed that individuals with dementia feature particular risks due to vulnerabilities although some of the risks are faced by older people more generally (Manthorpe, 2014). Cooper, Selwood and Livingstone (2010) highlight that dementia patients living in care homes and nursing homes are vulnerable to suffer from neglect and abuse, as they suffer from impairment leading to limitations in cognitive and physical functioning. However, they have received less attention from policy makers in health care system and researchers compared to cancer, heart disease, and HIV (Department of health, 2013). Additionally, many patients are not capable of reporting abuse and neglect fearing that such reporting can cause vengeance or disapprovingly influence their lives. Bertrand (2006) and Drossel, Fisher & Merser (2011) attest that the challenges, burdens, stresses and demands that associates with giving care in dementia are unique and such combined factors may increase the risk of abuse of elderly with dementia. Alzheimer's society (2013) state that there is a considerable concern by the public of abuse, 70% of adults in the UK says they are scared to move to care or nursing homes whilst 64% think that authorities are not doing enough to combat abuse in care and nursing homes.
Boye and Yan (2016) attest that there has been a gap in the literature that gives insight into the factors underpinning the abuse and neglect of elderly with dementia in care and nursing homes in England. There is a lack of substantial literature that thoroughly analyses these issues and gives researchers and policymakers in England an in-depth knowledge about the research topic. Against the backdrop of limited research on abuse and neglect of elderly dementia patients in health care organisations in England, the proposed research would explore the aspects leading to the abuse and neglect of elderly with dementia in care and nursing homes in England.
Though it is known that elderly patients suffering from dementia are commonly subjected to mistreatment and abuse in hospitals or care homes, little has been done to address the physical, emotional, and psychological abuse. The vulnerability of this population towards abuse is more as the patients are not able to express their feelings and experiences. A rising public concern can only be formed when there is enough guiding knowledge on the reasons behind such abuses. Risks for abuse can be reduced if there is provision for training, support, legal protection and ongoing supervision. The healthcare sector calls for research to highlight the underlying factors behind such patient abuse. The proposed research would examine the literature related to maltreatment of elderly dementia patients in care and nursing homes and thereby argue for the policy which can have the basis of a multi-systems approach. The research could identify areas for future research in dementia care domain and evaluate current healthcare policies in England. The research aims to identify factors that protect the health of elderly suffering from dementia and help this population to live with dignity, security, and confidence in care and nursing homes. There would be a positive change brought in healthcare settings in terms of care service provided to this population (Cahill, O'Shea & Pierce, 2012).
Aim
The general aim of the proposed research is to collate, study and summarize the published literature on the factors that underpin the abuse and neglect of elderly patients, aged 60 years and above, suffering from dementia in care and nursing homes in England. The study would inform further research in this particular area.
0bjectives:
- To examine the experiences of elderly dementia patients subjected to neglect and abuse in care and nursing homes in England.
- To explore how abuse and neglect are defined and the prevalence of abuse and neglect in care and nursing home in England for elderly patients with dementia.
- To identify the factors behind abuse and neglect of the elderly with dementia in England.
- To explore the attitudes of health care providers towards the elderly with dementia patients in care and nursing homes in England.
- To access policies and legislations currently in place safeguarding elderly with dementia in care and nursing homes in England.
Literature search strategy
Databases
A comprehensive search in electronic databases for peer-reviewed articles and other sources of secondary data would be conducted for the proposed study. Electronic databases are the rich source of information on varied topics, and they are reliable and authentic (Bryman, 2015). For the proposed research the databases that would be searched for relevant information are PubMed, CINAHL, Cochrane, and Medline. These databases are updated on a regular basis and therefore have all recent information on the concerned domain. The proposed search would be supplemented by a thorough search in the search engine Google Scholar for identifying pertinent gray literature on the research topic. Google Scholar is a source of books, journal articles, reports, abstracts, conference papers and proceedings that throw light on the relevant research topic (Bryman, 2015).
Keywords
Keywords refer to the search terms used in the due course of literature search in electronic databases for retrieving required information. The keywords represent the main ideas and concepts generated from the research question (Flick, 2015). The keywords for the proposed research are “abuse, neglect, treatment, maltreatment, dementia, elderly, older, patient, England, care home, nursing home, health, hospital, healthcare, family, types of abuse, reporting ”
Inclusion criteria
The articles published after the year 2006 would be considered for the proposed research in order to get recent and up-to-date relevant information
The articles providing information for sufficiently addressing the research question would be considered for the proposed research in order to have a focused approach
Exclusion criteria
The articles published before the year 2006 would not be considered for the proposed research
The articles not providing information for sufficiently addressing the research question would not be considered for the proposed research, such as child abuse, an older adult without dementia and outside England.
Ethics and anti-oppressive practice

Ethical issues can be defined as judgements which are morally involving issues which are right from wrong, ought or ought not or actions which are good or bad (Kimmel, 2007). Ethical issues revolve around asking sensitive questions to older patients and their families as dementia is a medical condition that affects mental status. In the proposed research will only consider articles and data that address issues regarding the discussion of sensitive incidence like neglect in care practice with the older dementia patients. Autonomy, that is respect for the person, is to be exhibited while questioning them. Informed consent would be taken from the participants prior to research. Many patients with dementia have the capacity to consent to participation in research. However it is vital to understand that people suffering from dementia have difficulties with attention span, comprehension, communication and memory. For this reason extra care would be taken to ensure that the information presented is understood by the patients. Their pace is to be respected. Printed information can be helpful as a support to memory. Additionally, allowing the individual the right to choose whether to participate in research is termed as beneficence, which ensures well-being while participating in a study. The principle of non-malfeasance requires researchers to do no harm to participants, articles that maintain confidentiality and anonymity of participants will be considered. The principle of justice is the ethic of fairness, information needs to be collected in a fair process. Ethical concerns are also present regarding the dignity of the staffs supposed to deliver care to older dementia patients and are involved in the data collection process. Their modesty is to be taken care of while collecting information from them (O'Leary 2013).
To support the above, The Mental Capacity Act 2005 have a legal obligation to protect vulnerable individuals who suffers from mental impairment such as dementia from anything that will serve as a harm to their health.
The Equality Act 2010 makes it mandatory for health and social care professionals to consider service users’ cultural background, diversities, beliefs and protect their dignity. The proposed research would take into consideration studies involving people from all ethnic backgrounds, minority groups, disabled individuals, all ages, and all socioeconomic background.
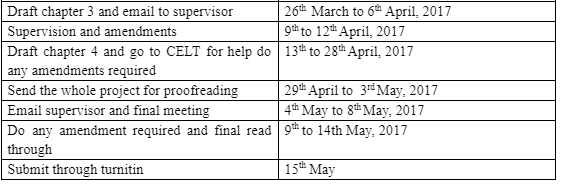
Project outline
Chapter 1- Introduction, Background and Rationale, Literature search strategy, Ethics and anti-oppressive practice considerations, project outline.
Chapter 2- Literature review which includes:
- Definition of abuse, neglect and dementia
- Prevalence
- Staff attitudes
- Reaction of patients
- Preventative policy and strategy
Chapter 3- Application of theory to practice through analysis of theoretical models and case studies and analysis of relevant legislation and policies:
- Agency link (case study) - Park view nursing home
- Mental capacity act, (2006)
- Safeguarding Adult (2010)
- Human Rights Act (1998)
- Deprivation of Liberty Safeguards (DoLS)
- The National Dementia Strategy (2009)
Chapter 4- Conclusion, Recommendation, Reflection

References
- Alzheimer’s Society (2013) ‘Low expectations attitudes on choice, care and community for people with dementia in care homes document purpose title publication date target audience Acknowledgements’.
- Bertrand, R.M. (2006) ‘Are all caregivers created equal? Stress in caregivers to adults with and without dementia’, Journal of Aging and Health, 18(4), pp. 534–551. doi: 10.1177/0898264306289620.
- Boye, F. and Yan, E. (2016) ‘Abuse of older persons with dementia: A review of the literature’, Trauma, Violence, & Abuse, . doi: 10.1177/1524838016650185.
- Brayne, C. (2016) ‘Dementia prevalence in England, 1990-2010: The cognitive function and Ageing study (2016 AAAS annual meeting (February 11-15, 2016))’, .
- Brooker, D. and Latham, I. (2015) Person-Centred dementia care: Making services better with the VIPS framework. London, United Kingdom: Jessica Kingsley Publishers.
- Bryman, A. (2015) Social research methods. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press.
- Cooper, C., Selwood, A., Blanchard, M., Walker, Z., Blizard, R. and Livingston, G. (2010) ‘The determinants of family carers’ abusive behaviour to people with dementia: Results of the CARD study’, Journal of Affective Disorders, 121(1-2), pp. 136–142. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2009.05.001.
- Department of Health (2013) ‘Dementia - A state of the nation report on dementia care and support in England’,
- Drossel, C., Fisher, J.E. and Mercer, V. (2011) ‘A DBT skills training group for family caregivers of persons with dementia’, Behavior Therapy, 42(1), pp. 109–119. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2010.06.001.
- Flick, U. (2015) Introducing research methodology: A beginner’s guide to doing a research project. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
- Gibbs, L.M. and Mosqueda, L. (2014) ‘Medical implications of elder abuse and neglect’, Clinics in Geriatric Medicine, 30(4), pp. xv–xvi. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2014.08.015.
- Humphreys, S. (2010) ‘The equality act, 2010’, Research Ethics, 6(3), pp. 95–95. doi: 10.1177/174701611000600306.
- Kimmel, A.J. (2007) Ethical issues in behavioral research: Basic and applied perspectives. 2nd edn. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing.
- Manthorpe, J. (2014) ‘The abuse, neglect and mistreatment of older people with dementia in care homes and hospitals in England: The potential for secondary data analysis: Innovative practice’, Dementia (London, England)., 14(2), pp. 273–9.
- Matthews, B. and Ross, L. (2014) Research methods a practical guide for the social sciences. Harlow: Longman.
- Mental capacity act (2005) Legislation uk. Available from: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2005/9/contents [Accessed: 2nd December 2016].
- O’Leary, Z. (2013) The essential guide to doing your research project. 2nd edn. London: SAGE Publications.
- Parkin, E. and Baker, C. (2016) ‘The commons library and its research service’, Dementia: policy, services and statistics, .
- The British Psychological Society and SCIE (2007) ‘Dementia A NICE–SCIE guideline on supporting people with dementia and their carers in health and social care’, .
- Wimo, A., Jönsson, L., Bond, J., Prince, M. and Winblad, B. (2013) ‘The worldwide economic impact of dementia 2010’, Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 9(1), pp. 1–11.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2012.11.006.
Continue your exploration of Role of Effective Communication in Vital Signs Monitoring with our related content.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



