Central Bank Digital Currency Business Strategy
Abstract
This study has focused on analyzing Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) on the banking and financial system. particularly in the context of the economics dissertation help. The use of CBDC is in the trial phase, and the banking system of none of the countries has implemented it completely. This has been the study’s primary limitation as it has restricted critical findings based on few recent ongoing studies. The data has been collected from secondary sources and follows the qualitative approach of research. The different sources used in the study are journals, websites, and academic articles, among others. CBDC is a new electronic form of cash and is different from the other digital currencies as it uses token-based currency. Different types of CBDC’s are wholesale vs. retail, account-based vs. token-based, direct, indirect, and hybrid models. Among the various kinds, the two most feasible are wholesale and retail. The retail CBDC is used for exchange purposes. On the other hand, wholesale is used by financial institutions. The future use of CBDC would result in changes in the business model followed both in the central banks and commercial banks. It has been further clear from the study that CBDC would not only impact the financial system of the country but also impacts the economic growth of the country significantly. The research in this area of study has been minimal; thus, it is improbable whether CBDC would replace the physical cash or not. However, it has been argued that difficulties associated with the flow of money may increase the possibility of encouraging CBDC in the banking system. Furthermore, many countries have initiated pilot projects on digital currency that may also influence the use of CBDC in the future.
Introduction
Background of the study

It has almost been more than 12 years since a newer electronic cash system termed Bitcoin has been introduced as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Everything got started in 2008 after a message was sent to the cryptocurrency mailing lists termed as Metzdowd.com. It was signed with the alias Satoshi Nakamoto. After that time, the growth of Bitcoin got exponentially as a value store for the means of payment of transactions (Barontini and Holden, 2019). This has increased the curiosity of the policymakers to explore as well as do adequate research to study the introduction of the Central bank digital currency. Blockchain technology might bring a revolutionary change to the present financial system and also central banking as it can give support to decentralized payments without making the requirement of third-party which control the payment network (Bordo & Levin, 2019). Regardless of the considerable volatility of the price, Bitcoin-like cryptocurrencies have attained more incredible popularity in individuals and institutional investors. There have been more than 4000 types of cryptocurrencies, whereas the market value of Bitcoin even increased and reached US$1 trillion, and Ethereum reached around US$172 billion (Ali, Barrdear, Clews and Southgate, 2014).
However, indifference to the bitcoin-like cryptocurrencies, stable coins such as Libra and USDT had tried to decline the volatility of the price of cryptocurrencies and even build connections in between cryptocurrencies and other main currencies like US dollars and others (Ali, Barrdear, Clews and Southgate, 2014). Such private cryptocurrencies have produced more significant concerns in central banks and also policymakers. Moreover, the Covid-19 pandemic has even made cash payments less appealing in emerging economies. As per a survey being conducted in October 2020, BIS found that more than 80% of the central banks were engaged in the investigation of the CBDC, wherein half has made progress the past conceptual; research to do experiments and run pilots. China is a pioneer country to experiment with CBDC, wherein it has run various pilot projects in multiple cities since 2020.
The central banks have recently started to issue digital retail currency (CBDC) on their own. Although the issue of electronic money by central banks was suggested at an earlier stage, the central bank itself was not embracing the concept (Bank for International Settlements, 2019). The design efforts were viewed as the main reason against making any decisions. However, it is only one decade since the concept of digital currency has been discussed widely by central banks, governments, and economists (Bank for International Settlements, 2018). Apart from the currency notes, every other application of the paper in the modern financial system, such as bonds, securities, communications messaging, transactions, and also correspondences, has been substituted by corresponding electronic as well as digital versions.
Moreover, the usage of physical cash in the transaction has also been in the stage of declining after it gets reinforced due to the prevalence of the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic. Such development has led to various central banks and government stepping efforts by exploring a digital version of the fiat currency (Rogoff, 2017). Some of the central bank’s interests are indigenous to pursue the particular objective of policies. For instance, the facilitation of a negative rate of interest of monetary policy (Barontini and Holden, 2019). Another driver was to give the virtual public currencies, which carry the legitimate advantage of private virtual money. At the same time, it avoids damaging the economic and social results of the private coins.
Aim of the Study
The study’s primary aim will be to assess the impact of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) on the banking and financial system.
Objective of the Study
The aim of the study is to assess the impact of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) on the banking and financial system. The objective of this study is to analyze the concept and trends concerning CBDC. This study has also evaluated the impact of CBDC on the banking and financial system. It has also given possible effects of CBDC on physical money/paper currency.
Research Problem, Significance, Question, and structure
It has been encountered that since none of the countries have officially issued Central bank digital currency yet and is in a trial phase, a lesser amount of research is being done on it. The researcher faced issues in this study as limited literature is being made wherein each of them is based on assumptions. There are no relevant cases related to CBDC, so it became problematic for the research to maintain the quality of the work. In addition to that, since the study aimed to assess the impact of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) on the banking and financial system, it lacks good practical references and evidence (Dow, 2019). Thus, it can be stated that the researcher faced challenges while dealing with this study. The significance of the research study is that it tends to provide more excellent knowledge regarding the Central bank’s digital currency. Since it is a new topic and not much research is done regarding this study, this study is of greater importance. This study will be giving in-depth knowledge to researchers, bankers, and also the public regarding these new currencies. This currency has not arrived in use but is going through a trial phase. This has led to limited knowledge regarding these digital currencies, wherein people are getting confused with digital payment. However, this study is even helpful as it differentiates between CBDC and digital income (Barontini and Holden, 2019). The detailed knowledge of types and models of central bank digital currency would be helpful as very few research studies possess such in-depth knowledge. The researcher has applied more excellent research knowledge to attain all of the data so that a new researcher would be getting every essential data in this study. This study is even of greater importance as it has explained its impacts on the financial and banking systems (Bindseil, 2020). Thus, the results of this study would be beneficial for the new researcher and especially the financial person who wants to understand it in detail.
The question of this research are as follows:
RQ1.
What is the impact of CBDC on the banking system?RQ2.
What is the impact of CBDC on the financial stability?RQ3.
What is the impact of CBDC on paper currency or physical currency?This study possesses a structure that is designed to meet the research study. It has six sets of chapters that include various sub-divisions, which helped attain the dissertation goals.

In this study, the first chapter, an introduction, has provided brief knowledge regarding the subject. The aims, as well as objectives of the study, have been integrated within this chapter which has helped in attaining a clear picture of the study. A literature review is the second chapter of this dissertation which will help elaborate topics in greater detail which will be considered secondary sources to ensure data reliability. Research methodology is the third chapter which reflects the approaches applied in the research study for practical analysis. The analysis and findings are the fourth chapters that explain data collected in a precise manner. The fifth chapter is named as a discussion that has helped in the practical study of the research as well as has also elaborated the output. The last chapter is the conclusion and recommendation chapter which has summarized the whole research work and even provides suggestions to increase the effectiveness of the future research.
Literature Review
Notion on Currency
It is stated by Bindseil (2020) that when societies started developing and people started getting evolved from hunting to gatherers, the need for materials began increasing. The people began to build houses, make furniture, wear clothes, etc. since it was not possible to produce and fulfill their needs individually, people began to purchase goods and services from one another(Raskin and Yermack, 2016). In the initial case before the invention of currency, people used to apply a barter system for the fulfillment of their needs. In this system, people use to make an exchange of one product for another. However, it had many limitations, and thus, people started exchanging things in terms of metals of shells (Reichlin, Turner & Woodford, 2019). As the system evolved, the metal currency grew, wherein gold and silver coinage were the main branches. However, in the eleventh century, China came up with paper currency for the first time (Bordo and Levin,2017).
Currency or money has arrived as the best solution to purchase the products. It is an economic unit that functions as a medium of exchange for transactions in an economy. It is a currency that provides services to reduce transactional costs. It has originated in commodity form, which possesses the physical property that needs to be adopted by the participants of the market as an exchange medium (Stein, 2012). The currency could be of different types that include market-determined, fiat currency, electronic cryptocurrencies, money substitutes, and fiduciary media, etc. Every government possesses its currency system. In the modern period, cryptocurrencies are getting evolved, which are developed to finance and make international exchange all around the world (Bindseil, 2020).
Currency is a liquid asset that is applied to settle the transaction. It executes its function dependent upon accepting its values in the government economy and even in the international market utilizing foreign exchanges. The present value of monetary curries is not derived through the materials applied to generate coins or notes. Matters are derived through preparedness to agree towards the displayed values and even rely on them for their usage in future transactions (Vasiliauskas, 2019). The primary function of currency is acknowledged as the medium of exchange that people and global economies aim to accept as the payment for present or future transactions. Thus, in the present modern economics, the currency is the monetary form that is issued by the sovereign or central bank exclusively. It is the responsibility of the central bank and the assets of the public holding the currency. When a currency is a fiat, then it is legal tender. The currency is generally issued by the people in paper form, but the current state does not define the characteristics of the currency (Stein, 2012).
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
Vasiliauskas (2019) have defined currency as a liability or responsibility issued by the central banks, and it can help determine the term CBDC. A CBDC is an electronic form of cash that could be exchanged, similar to traditional money. It is a legal tender that is issued by the central bank in digital form. It is identical to fiat currency, exchangeable from one fiat currency to another, but its form is variant (Vlahovic, 2014). Although people exchange money through electronic means regularly through bank transfers, card payments, or digital wallets, however, there is a difference between CBDC with digital electronic payment. Although CBDC is a digital currency, it cannot be compared with the private digital currencies which people are using for decades. CBDC is a new type of token-based digital money.
Different types of CBDCs
Wholesale Vs. Retail
According to Bordo and Levin (2017), One of the effective ways to differentiate CBDC is utilizing their implementation model. CBDCs could be with retail or wholesale. In the retail model of CBDC, the access to the currency have broad to the corporate or business firms and also to consumers of all economic levels (Vlahović, 2014). On the contrary, in the wholesale model of CBDC, access to these currencies gets confined to only a limited group of financial banks and institutions. In the present stage, the wholesale efforts are highly relevant in the economies which possess developed interbank systems as well as capital markets. In addition to that, retail CBDC is expected in the upcoming economies with economic inclusion, which was expected (Ward, Clack, and Haig, 2016).
Account-based Vs. Token-based
It is stated by Graham and Leary (2018) that another way of categorizing CBDC is by classifying it based on account and token. In the account-based format, the CBDC ownership is associated with its identity, and wherein the transaction updates the payee and payer’s balance. Such arrangement possesses a system that is used for the sending of digital payments. However, on the token-based format, the CBDC’s ownership is associated with proof. The usage of cryptography helps in verifying digital signatures to execute as well as make verification of the transfer (Gu, Mattesini, Monnet, and Wright, 2013). Hence, transactions led to a change of ownership of a particular unit of the token. In such meaning, the tokenized format of CBDC helps in resembling the right of the currency. In the tokenized CBDCs, all forms of tokenized currency like cryptocurrencies and stable coins could be programmed. This token CBDC is termed as Programmable money in which various logics are applied in the definition of money itself and where rules applied in payments in between multiple peers could be automated (Graham and Leary, 2018).
Direct, indirect as well as a hybrid model
As per Gu, Mattesini, Monnet, and Wright (2013), The CBDC is also categorized based on the distribution models. In the direct CBDC model, all parties possess in the transaction have a bank account on the central bank. Payments will be made by simply transferring currencies from one account to another, and wherein every claim is backed by the central bank itself (Nyborg, 2016). The central bank issues currency and organizes a permission system to make a straightforward transaction. Moreover, the central bank even meets the requirement of Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-money Laundering (AML) compliances with indirect distribution models of CBDC. In the indirect model, the central bank passes the digital currency token to its commercial banks or fintech, which distribute currency and even handle requirements such as KYC and AML. The claims which are made regarding the money is highly dependent on either non-bank financial institution or non-bank financial institutions but is not reliant on the central bank. Such CBDC is also termed synthetic CBDC.
There are a more significant proportion of the central banks which are working upon the hybrid models in which central banks makes the distribution of the Central bank digital currency to an intermediary like commercial bank or fintech, which handles the transaction and also make KYC and AML requirements.
Significance of CBDC
Nyborg (2016) has stated that CBDC is of greater importance as it helps in providing convenience, efficiency, stability and gives access to retail payments. Although electronic payments have provided efficiency gains in the past few decades regarding commercial bank money, the providing of electronic payment directly in the form of the central bank’s capital is of more significant benefit. ( Mancini-Griffoli & et al., 2018) The CBDC will be helpful for retail payment as digital payment leads to issues of vanishing of the demands for the banknotes, unsatisfied access to household shares as well as business banking system as well as varying concentration on retail payment infrastructure. However, CBDC helps in making payment safer and effective. It also helps in bringing financial stability and also inclusion.
According to Kumhof and Noone (2018), The CBDC possesses the ability to enhance the efficiency as well as safety of retail as well as a more extensive value payment system. On the retail side, the focus will be on ways digital currency could enhance the efficiency of making payments during the point of sales, peer-to-peer or online. CBDC can also benefit wholesale and interbank prices as it could make faster settlements and extend the hours of settlements. These currencies even can help in removing lower-value coins by delivering the electronic changes. For instance, it was encountered in April 2017 when the Bank of Korea made a trial to make a coinless society by allowing customers to deposit their changes in prepaid cards rather than accepting the more minor changes through purchase. This had not only assisted in improving the payment system but even acted as cost-saving benefits as the country had saved £36.7million upon production of coins in 2016 alone.
Apart from that, it is also stated by Nessen, Sellin, and Sommar (2018) that CBDC is also helpful, which will be making feasible ideas for sovereign money. It will be creating a monetary system wherein banks will no longer be creating sight deposits and thus will make effective means of payment. CBDC will also be making the financial system safer, wherein it will be allowing individuals, non-bank financial institutions, and also private sector companies to get settle directly in the money of central banks rather than deposits of a bank (Meaning, Barker, Clayton, and Dyson (2018). This will significantly reduce the liquidity concentration and will even decrease credit risk in the system of payment. This will also reduce the systemic approach towards larger banks and thus will decline negative externalities that banks’ financial instability possesses upon society. Moreover, after the providing of the risk-free alternative to the deposits of banks, the shift from depositing in banks to digital cash would decline the requirement for government’s guarantees upon warranties and also the elimination of moral hazards from the financial system(Meaning, Barker, Clayton and Dyson, 2018).
According to Nessen, Sellin, and Sommar (2018), CBDC would also be helpful to bring transition towards a cashless society. Since terror funding, money laundering is some of the critical issues faced by the community, CBDC is helping to encourage a cashless society. Soon, CBDC will be replacing coins and notes, and wherein all money will be exchanged in digital forms (Kumhof and Noone, (2018). When the digital transaction enhances and cash withdrawal through ATMs will decline, society will become less cash. In this situation, the government would be trying to make cryptocurrency regulations that will be transforming the payment system. In such a situation, Central bank digital currency would be an effective alternative. Apart from that, it is stated that CBDC will be improving counterparty credit risks for the sake of cross-border interbank payments as well as settlements (Moore, 1988). However, the wholesale version of the CBDC would be acting as an alternative approach for the means of cross-border payments. The wholesale CBDC, which could be exchanged across borders, could improve the amount, counterparty credits, and settlement risks. This currency also improves counterparty credits and even assist in settling hazards. Mersch (2018) has stated that CBDC is of more excellent benefits as it helps in providing 24-hours availability, anonymity as well as the elimination of the counterparty credit risk.
CBDC Models and Designs
There are different design choices for CBDC that includes the determination of who shall be granted to get access to the anonymity degree as well as interest-bearing features (Mersch, 2017). Various research is performed to understand the technological and economic influence of the introduction of the CBDC. However, scholar states that trying to understand macroeconomic results of the adoption of CBDC issues an issue as there is no prevalence of the historical experiences (Meaning, Barker, Clayton, and Dyson, 2018). It is reviewed that the values attained by the government money are acknowledged by unique political and legal characteristics. The fiat currency could be quickly submitted by any of its parties as a way of final settlement of fees, fines, taxes, and privately incurred liabilities. The CBDC even possesses the same underlying values as other forms of money issued by the government. Thus, CBDC has complete faith in the state of giving (European Central Bank, 2019).
According to Galariotis, Makrichoriti, and Spyrou (2018), CBDC need to possess all the features so that the central bank can serve as a central counterparty for every payment that is being processed through CBDC. The virtual currency needs to be available to the public without making any restrictions and is considered as the legal tender for the nation. These virtual currencies should take variant forms linked with either prevailing payment infrastructure technology or crypto technology. The central bank will guarantee at-par convertibility of CBDC in cash of reserves (Lalouette and Esselink, 2018). In this regard, the central bank will, however, not provide leading facilities for the digital currency holders. The Central bank will be giving interest rates on the liabilities of CBDC with interest rate structures of government liabilities, financial stability objectives, and the central bank’s monetary policies. The availability of CBDC is initially limited to the predefined user’s group like commercial banks as well as Non-banking financial institutions or to the economic broader system in which access will be extended to the non-financial business and households in a later stage (Mersch, 2017).
Impact of CBDC on the banking system
As per Friedman (2019), The application of CBDC and its envisioned development would be bringing a more significant change in the business model of both central and commercial banks and ultimately to the banking ecosystem. It is reviewed that from the point of view of powerful banks, wholesale CBDCs are of more incredible help to attain the objective of achieving financial stability (Keister and Sanches, 2018). It is done by becoming a better channel for transmission to lend money and even assisted in preserving the monetary sovereignty of central banks. In the same line, the concept of the introduction of the interest-bearing CBDCs would be allowing the monetary policy to break the effective lower bound (Kihara, Koranyi, John and Chopra, 2019). When used widely, such innovation could be practical monetary policy tools for the central banks, mainly when individuals make preference to hold the cash because of prevailing of the negative rate of interest. The CBDCs can even help in shrinking the balance sheet of the commercial banks because of the conversion of the deposits of banks in the CBDCs (Galariotis, Makrichoriti, and Spyrou, 2018). The disintermediation degree of the banking system because of CBDC that are adopted largely apart from bank deposit would be affecting undoubtfully to commercial bank lending with the supply of liquid assets and will also involve market rates (Friedman, 2019). It is, however, found that various central banks have already shown their concerns regarding retail CBDC implementation and ways it could destabilize effects upon the financial system. Such apprehensions are linked with potential changes in bank funding costs and composition (Kirkby, 2018).
Apart from the above, it is stated by Kay (2018) that CBDCs, which are highly dependent on the extends of their application, could cause a reduction in the transactional demands for the deposits of the bank. Since the transaction in CBDC declines the risk of settlement and even minimizes the need for liquidity for the transactional accommodations, moreover, providing the genuine risk-free alternative to the deposits of the bank could lead to change which is away from the residues from banks (Kihara, Koranyi, John and Chopra, 2019). It even can reduce the requirement for the government, which gives assurances on the deposits. At the same time, the declined disintermediation of banks executes its issues. When banks start to fall their promises over the period, then their ability to make credit creation gets constrained (Kim and Kwon, 2019). As central banks could not give credit to their private sectors, the influence upon the bank credit roles requires to have understood appropriately. Moreover, as banks do not possess a significant volume of lower costs transactions deposits, the rate of interest margins arrives under stress which could lead to enhancement in the credit costs. Hence, the potential costs of disintermediation state that it is essential to design and also apply CBDC in such a way that it generates demands for CBDC through bank deposits (Keister and Sanches, 2018).
As per Kim and Kwon (2019), CBDC even possesses other risks which need to be materials. The presence of CBDC even makes it practical for depositors to attain balance when there is an imbalance on any of the banks. The deposit flights could be faster as compared to the withdrawal of cash. Moreover, the availability of the CBDCs would recline panic runs as depositors possess knowledge that can be withdrawn quickly (Kimball, 2015). One of the results could be that banks need to be motivated to hold a more significant liquidity level that results in lower bank returns. Since CBDCs are currency and do not pay interest, so their impacts on deposits of the banks are limited. The depositors who need CBDCs for transactions likely sweep the day-end balances towards interest-earning accounts of deposits (Masciandaro, 2018).
Consequences of the CBDC model on the financial system
According to Kimball (2015), CBDC and also its envisaged development affects both central as well as commercial business models of banks and also banking ecosystem. From the central bank’s point of view, wholesale CBDC can assist in achieving and maintaining financial stability by being an effective mode of the channel of transmission and also lend markets which help in preserving the monetary sovereignty of the central banks(Kirkby, 2018). In the same line, the introduction of interest-bearing CBDCs permits monetary policy to break the practical lower bounds. When it is used widely, then such innovation leads to an effective monetary policy tool for the central banks, mainly when individuals like to hold cash because of the prevailing negative rate of interest (Qian, 2019).
Central Bank Digital Currencies Working Group (2019) has stated that CBDCs can shrink the balance sheet of the banks because of the conversion of the deposits of banks in CBDCs. The degree of disintermediation of the system of banking because of CBDCs, which are mainly adopted despite banks deposits, would undoubtfully impact the lending of commercial banks, supply of liquid assets, and also market rates. It is stated by Dow (2019) that there are some of the central banks have already shown concerns regarding the implementation of retail CBDC and could possess destabilizing impacts upon the financial system. Such apprehensions are linked to change in the compositions and funding costs for banks (Qian, 2019).
Since there is no clear view regarding the successful future of CBDC models, envisaged technology and IT infrastructure which support CBDCs are beads on either distributed ledger technology or possess balance in between newer DLT solutions and also database platforms.

It is stated by Masciandaro (2018) that there is no one scholar view upon the implication and introduction of the CBDC that would entail financial stability. The specificity of the theoretical types upon CBDCs strengthens the number of scholarly discussions (Dow, 2019). Thus, the influence of CBDC’s upon financial stability are grouped mainly in different groups that include CBDC’s effect upon financial stability, CBDC’s impacts on interest-bearing, and also study on the effects of non-interest bearing CBDC’s upon economic strength. However, it is stated by Bech and Malkhozov (2016) that the impact of CBDC’s upon financial stability was hindered due to the absence of clarity regarding future CBDC that would be in particular economy and actors it might reach. Thus, the lack of understanding upon design and application of CBDC outlaid in the ambiguity of effects of CBDC that would lead to demand and supply of money and credit and financial stability. It is stated by Belke (2018) that CBDC is in complexity wherein the introduction of CBDC accounts at central banks declines the supply of the private credits which are delivered by the commercial banks. This enhances the rate of nominal interest, which decreases the reserve-deposit ratio of commercial banks (Nelson, 2018). The application of CBDC would improve the probability of the panic and difficulties of banks in which cash reserves of commercial banks would drastically contract, and banks might have issues paying to their depositors. This has affected the financial stability negatively, affected economic activities for longer terms, and even possess impact capital stocks as well as output levels (Bech and Malkhozov, 2016). Since CBDC had led to the provision of credit to private actors, it might have the possibility to compete with bank deposits which upon implementation of CBDC have influenced the present bank set-ups and also financial intermediations which possess spillovers upon pricing, stability, and also bank’s fund compositions(Nelson, 2018).
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
Introduction
Research methodology is termed as the system that is applied to make a practical selection, process, and also data analysis associated with the study. It monitors researchers to make effective conduction of research and also assists in achieving the aim as well as the objective of the research study (Silverman, 2011). The study aims to assess Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) on the banking and financial system. Thus, this chapter has explained research philosophy, research approaches, methods, designs, data collection tools, and data analysis tools. This chapter has also presented regarding ethical consideration and also stated research limitation and time framework.
Research Philosophy
Research philosophy is stated as a process where data are gathered, evaluated as well as applied for the means of research. It is expressed as a technique and function used to make the effective selection, identification, and analysis of data. It directs its researchers to conduct research study conductions and assist in attaining the research aim and objectives of the study (Allwood, 2012). There are two types of philosophy which include positivism and interpretivism. Since the study aims to assess Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) on the banking and financial system, this study has applied Interpretivism philosophy. This philosophy was used to gather non-numerical data to attain the research findings. This philosophy also helped in building links with data and also make usage of subjective approaches (Fellows and Liu, 2008). The application of bottom-up approaches, which is associated with interpretivism philosophy, has assisted in making this research study more robust and flexible. Even though research could have made the application of research philosophy but since CBDC is a new concept and no practical impacts have been encountered, so researcher-made usage of subjective data. This study even does not accept positivism philosophy as it is not flexible and also rigid (Saunders & et al., 2012).
Research Approach
Research approaches are the procedure that possesses a plan and design that have steps to make a broader assumption to detail data collection methods, analysis, and also explanation. There are two types of research approaches that include inductive and deductive approaches. An inductive approach is an approach in which data are gathered and possess theory as an outcome of data analysis (Allwood, 2012). The deductive approach, on the other hand, is linked with theory development and tests that are used in terms of quantitative methods. Since the study aims to assess the impact of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) on the banking and financial system, so this study has made the application of the inductive approach to have an in-depth expansion of theory and development(Crowther & Lancaster, 2009). This approach was also applied to produce meaning utilizing data collected through different patterns and linked with ideas. Inductive approaches were also used as they would help in giving subjective perspectives and even expand newer phenomena utilizing different perspectives.
Research methods
Research methods are the process that is used to gather data for analysis to attain newer data. Qualitative and quantitative research are two methods wherein qualitative methods give focus on subjective data. On the other hand, quantitative methods are methods that emphasize personal data and also help in attaining objective outcomes (Crowther & Lancaster, 2009). Since the study aims to assess the impact of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) on the banking and financial system, so this study has made the application of qualitative methods. Qualitative methods are applied as it gives main focus upon subjective data and also focuses upon non-numerical data. This methodology was applied as it assisted in linking with approaches that made usage of textual data, which are gathered utilizing secondary data. This method was even used as it helped in interpreting data by lessor errors (Fellows and Liu, 2008). Such methods have enabled the researcher to deal with problems and even assisted in attaining findings utilizing generalization. However, the researcher could have applied quantitative research methods, as numerical data made this study complex, so the researcher made the application of qualitative research methods (Creswell, 2013). Furthermore, since the researcher did not want to formulate and test hypotheses, so quantitative methods were not giving more importance.
Research Designs
Research designs refer to a strategy that integrates various components of study in a very logical manner and even ensures effective addressing of the issues of research (Richie & Lewis, 2013). Exploratory, descriptive, and explanatory design are the three types of research designs (Blaxter, Hughes and Tight, 2016). Since, aim of this study is to assess the impact of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) on the banking and financial system so this study has made the application of descriptive designs. This design has helped in explaining data and focuses on problems utilizing data collection. It has also assisted in exploring data and give additional information. Moreover, this research has shown significant focus on issues and analytics, this application of such design has assisted in attaining richer insight to understand CBDC.
Data Collection Methods
The data collection method is stated as an essential element of study that impacts a particular manner. There are two sources of data that includes primary and secondary data. Primary data is termed as firsthand data, which are collected through direct quotations, which include surveys, questionnaires, interviews, and even observations (Bryman & Bell, 2011). This data is necessary and assists in effectively generating data. It is objective and is gathered directly utilizing sources. Such primary information is advantageous as it gives up-to-data data related to research topics linked to secondary data. Nevertheless, the longer time to collect and the higher costs are the main disadvantages of the primary data sources (Creswell, 2013). Secondary data, on the other hand, are already present data which are written by different authors wherein data are gathered through articles, magazines, books, journals, etc. Since, the aim of this study is to assess the impact of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) on the banking and financial system so this study has collected data only utilizing secondary sources, wherein none of the primary data were inferred in this research (Blaxter, Hughes, and Tight, 2016). The researcher had gathered secondary sources through journals, government reports as well as articles. This study has made the application of database through different scholar sites, which includes Emerald Insights, Google Scholar, and also Microsoft Search. The secondary data is advantageous as it is less costly and assist in collecting secondary data. Collecting these data also does not need more time and even requires lower costs (Panneerselvam, 2014). Although, researcher could have applied primary data sources in this study but in present context since, there is only a limited amount of scientific data involved regarding CBDC, researchers have used only subjective data. Google scholar search engines have been applied to attain academic search.
Data Analysis
Data analysis is an essential element of a research study in which a data analysis tool is critical to attaining findings and conclusions. It is used to evaluate gathered data utilizing sources to achieve the results of the research. The practical usage of data analysis is advantageous as ineffective data analysis could negatively influence the validity and reliability of the study of research (Bryman & Bell, 2011). There are various types of data analysis tools such as thematic analysis, content analysis, grounded theory, etc., Since, aim of this study is to assess the impact of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) on the banking and financial system so this study has applied thematic data analysis to analyze secondary data utilizing published sources. This study has used these analysis methods to make a practical evaluation of the secondary data and identify patterns and themes associated with data collection. It has also helped in making understanding the research findings regarding CBDC (Panneerselvam, 2014)
Ethical Consideration
Ethics is an essential part of a research study, which is used to gather primary and secondary data. This study has effectively applied ethical data wherein all of the secondary data regarding CBDC were gathered utilizing academic papers. The collected data are reviewed in an efficient manner in which no data got plagiarized. Moreover, each of the secondary data regarding CBDC applied in this study was acknowledged in which each of the references has been cited utilizing reliable sources. The secondary data, collected through authentic and valid sources, were neither manipulated nor any data were added without in-depth study (Richie & Lewis, 2013).
Time Horizon
Time Horizon is the schedule to perform the work on time. There are two types of time horizons which include longitudinal and cross-sectional time horizons. This study has applied a longitudinal time horizon to acknowledge the impact of CBDC on banking system. It was used because of its flexibility to collect data utilizing secondary sources and also reviewed topics in the particular time frame. This time horizon was beneficial as it helped strengthen data using a specific period (Silverman, 2011).
Research Limitation
It was reviewed that researchers have faced issues while collecting research studies. This research study has faces problems to gather information regarding CBDC as very lesser data are present regarding it. Moreover, most of the sources that reveal the data regarding CBDC were highly paid sources. The limitation of the time has also allowed the researcher to make an in-depth analysis of the study.
Chapter 4: Findings
Impact of CBDC on financial/banking system
Digital currencies are nowadays gaining more attention globally. This is because the use of digital currencies enables improving the efficiency of the financial system. The improved efficiency is in direct payment where there is no involvement of third party/go-betweens. This, in turn, makes the payment process more accessible and flexible, along with security (Bank for International Settlements, 2021). In this regard, the Brookings Institution (2021) highlighted in its report that digital currencies such as Bitcoin do not replace other official physical currencies but are likely to pose challenges for the Federal Reserve or the other central banks. This has ultimately raised the need for developing own e-currency by the central banks (Brookings Institution, 2021).
CBDCs represent the digital currency developed and issued by the central banks. In other words, CBDC is the digital token issued by the central bank and is regulated by the monetary reserves of the territory (Bastos, 2019). The increasing attention towards digital currency has made central banks think of developing their e-currency. In this regard, the Brookings Institution (2021) mentioned that very few banks are focusing on digital currencies. So far, very few central banks such as Tunisia and Ecuador have developed/issues their digital currency to the public. This digital currency would enable the public to use electronic deposits during transactions (Brookings Institution, 2021). In this regard, it has been argued by Rodeck & Curry (2021) that physical/paper currency is used globally despite this people nowadays prefers conducting transaction online using credit cards or phone. This, in turn, indicates that the currency issued by bank reserves already exists in electronic form. Additionally, most of the currency produced by the central banks, also known as wholesale central bank money, is made in electronic format. Thus, cash or physical money moving in the system is just a tiny fraction and is likely to impact the banking/financial system (Bank for International Settlements, 2018)
Digital currencies such as Bitcoin have no physical form and exist only virtually. The information is stored in the cloud, thus reducing the importance of banks for daily transactions. The use of digital currencies enables the customers to handle the transaction activities themselves quickly, and therefore it helps avoid bank charges. Thus, the operations of banks relying on revenue would be impacted significantly (Badea & Claudia, 2021). In this regard, Ostroff (2020) has stated that central banks issuing their digital currency would help them protect their market share from losing to Bitcoin. In addition, issuing digital currency would help the bank to pursue a negative rate of interest. The negative interest rate of the banks allows it to charge the customers for depositing. Despite this, it can impact the role of the banking/financial system. According to the report of The Economist (2021), the use of official digital currency in central banks poses the threat of minimizing the role of traditional banks as lenders. Besides, it can impact the functioning of conventional banks drastically if the depositors withdraw money from conventional banks and starts depositing in central banks. CBDC attracts more financial resources towards central banks. Thus, CBDC facilitates the growth of major banks, but it is likely to impact the functioning of commercial banks.
The use of digital currency in banks helps in reducing the transaction costs as acquiring/sharing of information becomes more straightforward using the new blockchain technology. The use of innovations/technology in the payment system helps enhance the speed of different cross-border and domestic transactions. The improved speed of transaction reduces the cost associated with it. Besides, digital currency would also broaden its access as people belonging to rural households can easily use the payment system. Therefore, CBDC can improve the efficiency of the payment system effectively (Fernández & Gouveia, 2019). For instance, in India, CBDC would enable people to conduct any small transaction using the decentralized payment system and no involvement of commercial banks (Singh, 2021). The use of CBDC would also increase access to people as compared to the traditional payment system. Advanced technology in digital currency makes it easier for people to send or receive money without any time constraints. This is thus worthy for the future as it enhances the payment system (Koumbarakis & Dobrauz-Saldapenna, 2019).
However, the use of new blockchain technology also brings specific challenges that can impact the banking system. In this regard, Calle & Eidan (2020) has highlighted that the decentralization of central banks can affect the stability of the financial market. The decentralization of banks means that financial products are readily available on the blockchain network and are open for use to all public. For example, securities such as bonds and stocks or other assets are available on the public blockchain, and the technology is more efficient in creating capital markets. Besides, it does not involve intermediaries, that is, banks (Calle & Eidan, 2020). Thus, getting loans/credits become more accessible at a low rate of interest. Besides, it also reduces the chances of fraud as customer information is stored in the cloud, and it is safer and easier to share. Blockchain technology has recently gained increased attention in the past few years. Thus, the use of blockchain technology in digital currency significantly impacts the baking industry by influencing the different services provided by the banks (CB Insights, 2021). The decentralized payment system would thus create problems for central banks, and it not only impacts the monetary system and economic growth of a country.
According to Viñuela et al. (2020), traditional banks have been the economy’s critical drivers for centuries. However, the recent concept of digital currency and now CBDC has become the threat or the risk factor for the growth of the traditional banks. In the past years, technology has gone through many drastic changes. Despite the change, the banking principles have remained the same. The banks give credit, creates new assets, and again provide new funds to the borrower. Commercial banks (or national banks) are responsible for holding the reserves concerning the customer’s deposit. In this, the customers can access only a tiny fraction of currency notes or coins. There was no specific limit fixed for money circulation in the economy. The central and commercial banks were responsible for handling the need for creating money for the economy (Viñuela et al., 2020). However, according to the report of OECD (2020), the introduction of digital currency has disrupted this principle of the banking system entirely. This is because one of the physical currencies is converted into digital currencies. It does not require storage in banks as it further moves to Federal Reserves. This indicates that CBDC would affect the normal functioning of the banking system. The CBDC would also affect economic growth. This is because people would no longer depend on banks for loans to start a business. Besides, commercial banks also cannot rely on consumer deposits to finance any credit. Thus, it would impact the growth of traditional banks and affect economic growth. Besides, CBDC also increases the risk of cyber-attack on central bank digital wallets, which can impact the entire economy. Moreover, CBDC increases the possibility of state intervention on transaction activities of people, for example, auto-taxation and different taxes based on region. Furthermore, it disrupts the overall financial equilibrium of the economy as it would enable the government to control the citizen’s money (Bank for International Settlements, 2018).
CBDC feasible in nature or affecting the financial stability
The importance of digital currencies has increased with digital advancement in the banking system worldwide. In this regard, the central bank issue fiat money in digital format by CBDC. In a study, it has been observing that around 80% of the central banks of the world are now focusing on CBDC. In this, the US Federal Reserve has already progressed by introducing the pilot project in CBDC (Csis, 2020). In the present trends, two types of CBDC feasible are wholesale CBDC and Retail CBDC. In the wholesale CBDC, access is limited. This system is used for cross-border transactions. On the other hand, the retail CBDC in the digital format of the cash can be accessed universally. In this system, there are mainly three types they are indirect, direct, hybrid. (Rba.gov.au.2020; Bis.org., 2018).
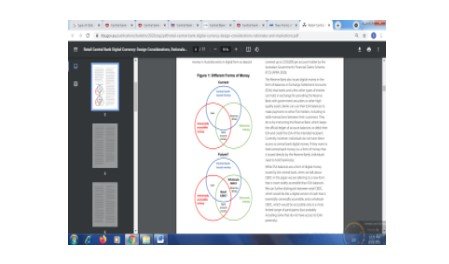
The retail CBDC is one of the forms of cash which can be accepted in the digital format and can be widely used for the store of value and exchange. In this, the unit for the account would be in the design of sovereign currency, for instance, the Australian Dollar. Moreover, the CBDC can be convertible in another form of cash at par. Apart from this, it can also be used as legal tender (Rba.gov.au.2020).
This CBDC can be offered to the public in a different form. In this, the first form is a deposit account, and another is digitally issued tokens. In the first form, the business and individuals can open a deposit account in the central bank. Moreover, with the deposit account, the account holders can get quality service. On the other hand, the other form is a digital token. These tokens are the alternative to coins and banknotes. In addition, the central bank issues this token that is distributed by the commercial banks. The significant difference in this type is the verification required for its usage.
Additionally, the authenticity of the CBDC token is checked. Besides, these tokens are spent or not is also appropriately checked. Apart from this, in a deposit account, verification is required on the account holder’s side. In this, the warranty is done by KYC (Know your customer) ((Deliotte, 2020).

Figure 2: Cash, electronic payment instruments, and retail CBDC
The above figure highlighted the difference between the present electronic payment system and CBDC. The direct claim of cash is processed by the central bank. On the other hand, the insistence on a deposit account is processed by a commercial bank. Commercial bank backs these claims by holding some reserves in the central bank (Bis.org. 2021).
The wholesale CBDC is majorly used for payment and settlement in various financial institutions. This model of CBDC can be used to improve efficiency and help manage the risk during the settlement process. In the present scenario, the wholesale CBDC is not allowed for the financial market participants. These are not allowed to hold an account in the central bank. Moreover, the wholesale CBDC is not permitted for money transfers.
On the other hand, it can be used in transferring the asset in the form of securities. Two parties can use the wholesale CBDC if they are trading on the support, for instance, securities for cash. In this scenario, the delivery and payment for the investment will occur instantaneously with the help of wholesale CBDC. The wholesale CBDC is present use the domestic payment and cross border payment (Deloitte, 2020). In the current period, 60 central banks are trying to understand the CBDC in digital price transformation. In this regard, 36 central banks are using wholesale and retail CBDCs.
Moreover, 18 central banks are majorly focused on the retail CBDCs. The CBDCs have increased the efficiency of the domestic payment, which has improved the financial stability. For instance, in Sweden, the Riksbank has currently introduced a concept of E- Krona. In this scenario, the use of cash has significantly declined. The main aim of introducing this system is to find an alternative way of payment. Moreover, this will enhance the payment system and ensure financial stability (Deloitte, 2020).
Impact of CBDC on paper currency or physical money
The financial system has gone through many changes in the past. In this regard, for instance, the securities and bonds have been replaced in electronic form. In the present global Covid-19 pandemic, the importance of digital currency has increased drastically. This has also forced the central banks to think about a new way of the payment system. In this regard, the new CBDC system can replace paper currency with the help of creating a cashless economy (Rbi.org, 2021).

Figure 3: CBDC retail project that is furthest in their development as of 2020 by country Source: (Statista, 2021
From the above figure, it is clear that the sand dollar of Bahamas is the most developed CBDC around the globe as of 2020. Moreover, China is planning to introduce digital currency known as e-CNY by the year 2022. The above figure highlighted those different countries that are working on digital currency. As a result, is it possible that physical money may be replaced in the future (Statista, 2021)? Moreover, people are using the online platform to process their payments as per their comfort. Apart from this, the paper currency can be a shift by the CBDC to reduce the dependence on natural resources. In this regard, the reliance on digital currency will be increased to meet the climate goals of various countries in the future (Gansbeke, 2021).
CBDC is a new type of digital currency that helps differentiate from the settlement balance and reserve of the commercial bank held in the central bank. CBDC has various designs based on access, operational availability, degree of anonymity, and others. CBDC has an enormous impact on the payment system, which overcomes the cons of the fast payment systems (Rbi.org, 2021).
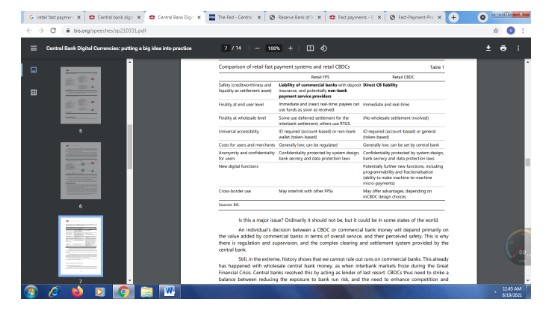
Figure 4: Comparison of retail, fast payment system, and retail CBDC (Source: Bis.org, 2021)
In figure 4 above it highlights the critical difference between the Fast payment system (FPS) and CBDC. It has been highlighted that the safety level is higher in CBDC than FPS because the payment liability is directly transferred to the central bank. This makes the payment system faster and effective for the account holders (Bis.org., 2016; Bis.org., 2021).
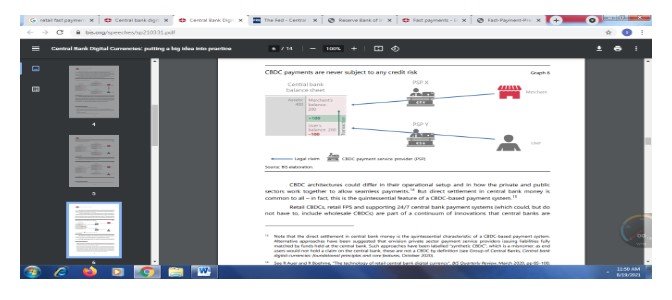
Figure 5: CDBC payment system
In figure 5, it shows that the CBDC can make the payment system simpler. CDBC help to reduce the credit risk and make the payment system more reliable for the users. Moreover, the CBDC system is safer because it is backed by the central bank, which helps settle direct claims, which is less time-consuming (Bis.org., 2021).
Besides, the payment of CBDC will have a significant impact on the bank deposit. In this regard, the direct CBDC will make the system simpler. In addition, it will reduce the bank deposit because there is no intermediary between them. The central bank will have direct control over the overall system. This, in turn, can demotivate some account holders from using CBDC. Apart from this, the bank which offers a low interest rate in comparison to the CBDC rate will observe a decline in the bank deposit significantly. In the case of digital cash, it will be of no use for providing bank loans which are the banks’ core assets. This, in turn, will reduce the lending capacity of banks. This scenario can be observed in the small banks, which depend on the return generated on lending. In addition, this will also increase the cost for the bank in the long run. Moreover, the CBDC rate can serve as the base for the bank rates, which can be used by the bank for the proper execution of the funds for the lenders (Baer, 2021).
Chapter 5: Discussion
Over the past years, digital currencies and CBDC have gained importance due to their potential to impact the banking/financial system of the economy. Throughout the findings, it has been evident that CBDC may not replace official currencies, but it may pose particular challenges to the central banks (Brookings Institution, 2021). The use of CBDC promises improved financial services and greater transparency. Despite this fact, CBDC’s future still depends on the benefits and risks associated with it. In this regard, it has been evident that very few central banks have started using or focusing on CBDC. For instance, the central banks of Tunisia and Ecuador are the ones who have begun issuing their e-currencies to the public (Brookings Institution, 2021). The cash hold or used by the public is significantly less, and the majority of the cash is deposited in the banks that are in electronic form. This cash is used by people globally through online transactions. It can be understood from this that before developing CBDC public are still using the electronic structure of physical currency. Thus, it has been argued that CBDC would have less impact on the financial system (Brookings Institution, 2021; Bank for International Settlements, 2018).
The use of blockchain technology in digital currency is the factor that impacts various services offered by banks. CBDC would result in the decentralization of the central banks. Blockchain technology helps in displaying financial products such as stocks and bonds over the public blockchain network. This effectively improves the capital market and does not require the involvement of a middleman (CB Insights, 2021). Besides, the participation of banks would make it easier for people to get loans quickly. Again, using CBDC would also help in reducing the chances of fraud as the financial information of the customers is more secured in the cloud. Thus, it has been clear that the decentralized structure of central banks due to using CBDC would impact its functioning significantly (Calle & Eida, 2020; CB Insights, 2021).
Digital currencies like Bitcoin have to some extent, impacted the importance of banks for performing daily transactions. In this regard, issuing its digital currency by the central bank would help protect its market share. In this regard, it has been evident from the study’s findings that CBDC would impact the functionality of major banks, but it also facilitates growth in the long run (Badea & Claudia, 2021; Bank for International Settlements, 2018). The data collected also reflected the fact that CBDC would also impact the growth of the economy. Thetraditional/commercial banks are the drivers of economic growth. The adoption of CBDC in the central banks would be a threat to the development of these traditional banks. The commercial and central banks are responsible for handling the monetary needs of the economy.
In this regard, the CBDC is likely to disrupt the financial system. CBDC would replace banks as no storage place is required, and all the currencies move to federal reserves. Besides, CBDC would also reduce the dependency of the public on banks for credit as all the activities are handled digitally. This impacts the functioning of the banks and thus economic development (Viñuela et al., 2020). The possibility of cyber-crime also increases with the increased use of digital currencies. This, in turn, also impacts the economy and services provided by the central banks. Moreover, with the reduced functioning of the banking system, the chances of state interference in public transactions increase. This would increase government control over public money, thus likely to disturb the entire financial system of the country (Viñuela et al., 2020; Bank for International Settlements, 2018).

Figure 6 (a): Project initiated by central bank globally (Source: Deloitte, 2020)
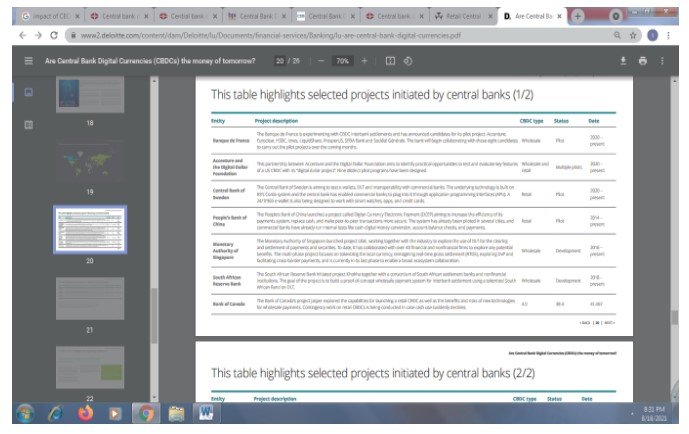
Figure 6 (b): CBDC Projects initiated by various central banks worldwide (Source: Deloitte, 2020)
The two figures above depicted that the uses of CBDC have increased enormously globally with the increase in the number of CBDC projects.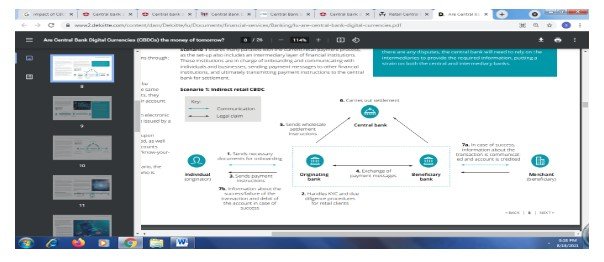
Indirect retail CBDC (Source: Deloitte, 2020)
In the indirect retail CBDC, many parallels are connected with the present retail payment system. This system includes various financial institutions, which form an intermediary layer. These institutions play a pivotal role in communicating with businesses and individuals. Moreover, these institutions are in charge of processing various payment transactions. Apart from this, the financial institutions ultimately process the transaction to the central bank for the final settlement (Deliotte, 2020).

Figure 8: Direct retail CBDC
(Source: Deloitte, 2020)
Direct retail CBDC is another form of retail CBDC. In this system, the business and individual hold a private account in the central bank. In this form of CBDC, the role of intermediaries is removed, which is of no use. In this, the central bank performs all the critical functions related to payment services. This system will have a significant impact on the present structure. Moreover, this will increase the central bank’s responsibility to a large extent (Deliotte, 2020; Bis.org., 2020).
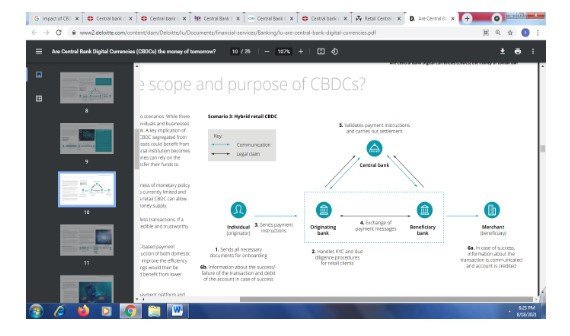
Figure 9: Hybrid retail CBDC (Source: Deloitte, 2020)
The hybrid retail CBDC is a blended version of the wholesale and retail CBDC. This type of financial institution is the intermediary layer of the system. In addition, businesses and individuals have a direct link with the central bank regarding their transactions. Moreover, this system has a crucial implication where different intermediaries kept the balance sheet of any individuals segregated from the system. This, in turn, increases the profitability of the business illegally. For instance, an institution that has becomes insolvent, in this scenario, the financial institution can act as intermediaries for getting the claim from the central bank. This can result in economic instability for the institution in the future (Deliotte, 2020).
The types of CBDC highlighted above signify that it has increased the effectiveness of the banking system. The retail CBDC can be used by the central bank to distribute and control the money supply in the market digitally. The retail CBDC motives to adopt the cashless transaction. Moreover, this will also help in developing trustworthiness among the users. This is turn, will motived individuals to uses this system as an alternative for cash transactions (Deliotte, 2020; Bis.org., 2020).
On the other hand, the wholesales CBDCs can be used for domestic payments. In the current scenario, the transaction value in wholesale CBDCs is considerable. Moreover, it has quick settlement timeframes. The system has great importance in the business, so these wholesalers, CBDCs, are executed by the central bank. This system is operated on the real-time gross settlement (RTGS) for processing the payment by the bank (Deliotte, 2020; Bis.org., 2020).

Figure 10: Wholesale CBDCs for cross border payment (Source: Deloitte, 2020)
Figure 9 depicts that the overall system of CBDCs in wholesale in cross-border payment. In this figure, it has been highlighted that this system includes several jurisdictions and intermediaries in the payment system. The Monetary Authority of Singapore has implemented the project “Ubin” that primarily focuses on the wholesale CBDCs in 2016. This project was initiated for a cheaper and faster cross-border transaction, including foreign currency (Deloitte, 2020). In the present digital era, every country is working towards developing a new system of digital currency. In this regard, CBDC is one of the primary steps toward creating a cashless economy. This new system of CBDC will help in bringing significant changes to the banking system. This system will reduce the role of intermediaries, making the system more efficient (Rbi.org, 2021). In this regard, various countries, for instance, the Bahamas have introduced a CBDC system of its own. In the present pandemic, the importance of CBDC system is gradually increasing. Besides, in a study it has been found that Bitcoin mining consumption is around 110 terawatt hours of electricity in a year (Gansbeke2, 2021). This can hinder in achieving the climate goal set by different countries in future. In this context, the new CBDC system has been developed to overcome the cons of the different digital currency.
Apart from this, different countries are working in enhancing payment system to make it simpler to use by the customer. In this regard, different countries run project on pilot basis to improve the financial payment system of the country. This is turn will open opportunities to grow fast than the other in this competitive world. Moreover, the CBDC system will have huge effect on the bank deposits. In this regard, it will reduce the role of the commercial bank. This is turn can create obstacle in the overall development of the country in the future (Baer,2021).
In my opinion the CBDC will change the banking system worldwide. In this regard, it will make the system faster in comparison to today’s banking system. In my opinion the world in changing faster with change in technology and thus changing the banking system would be effective. In the present scenario, the world is moving toward digitalization which will change every sphere of human life to greater extent. In the research, it has been observed that the smaller countries for instance Bahamas have lot of advancement in the CBDC system. Moreover, in my opinion, the CBDC system will gradually reduce the role of intermediary which in turn will make the system more effective and productive in the long-run.
Chapter 6: Conclusion
CBDC is gaining importance with the technological advancement in the banking system worldwide. In a global scenario, there is a paradigm shift in the overall banking system, which has made the system more efficient and productive for the account holders. This system has a long-term impact on the financial system of the country. This study aims to analyze the impact of CBDC on the financial/banking system. With this aim, the study has used a qualitative research approach for data collection. The study has been based on previously published literature as it would be cost-efficient and effective in finding accurate answers to the research questions. Under this approach, different secondary sources of information have been used that include academic articles, authenticate websites, and reliable journals, among others.
CBDC has made the payment procedure easier and flexible for the users. In addition, this has also made the banking system secure to use and made the settlement process faster. In a study, it has been observing that different types of digital currency, for instance, Bitcoin, cannot replace paper currency. In this regard, the need for e-currency emerged to improve the financial system of an economy. In this scenario, the central banks of various countries are developing digital currency for the general public. In the present trend, people like to do online transactions through different payment modes like FPS and others.
Apart from the digital currency, for instance, Bitcoin also does not have any physical presence. This makes it less effective for the bank to use it for their lending and settlement daily. The digital banking system based on CBDC makes the overall system easy to use for the customers. In addition, it also helps to reduce the transaction cost for the account holders. This is turn, hurt the earning of the banking in the long run. In addition, it also reduces the earning capacity of banking, which significantly impacts the bank rate. Besides, the pros there are some positive sides of digital currency as it helps the bank to safeguard their market share. The CBDC also has a significant impact on the economy of the country. In this regard, CBDC will have a massive effect on the functionality of the commercial bank, where the customer will tend to withdraw money from their account and shift to CBDC. This, in turn, will have an enormous impact on the financial system of the country.
Moreover, it will reduce the role of the commercial bank in the overall system. Digital currency will have a significant effect on the financial system in which will help in reducing the cost for the bank. In addition, this will make the system simple to use as it is based on blockchain technology. Moreover, this advanced technology will help in improving cross-border transactions and reducing the settling time for the bank. This, in turn, enhances the bank's productivity and expands its access to a large number of people.
CBDC will make it easier for people to access the different financial products, which in turn help in improving the financial system. In addition, this system is safer to use by the customer. On the other hand, this advanced CBDC system will significantly impact the market’s stability. In this regard, the whole monetary system will be affected by these significant changes introduced by the central bank in the payment system. This, in turn, will hinder economic growth and development in the long term. Besides this, CBDC has one of the significant drawbacks that it is the issue related to cyber security. In this regard, the CBDC system is digitalized and open to the general public for their use. This has increased the probability of cyber-attack on the banking system. This will have an enormous impact on the country's economic system, where all the customer's vital data will be in danger. In this regard, the central bank must check all the loopholes before introducing any new digital currency for their customers.
Based on the above discussion, it has been evident that the CBDC would effectively improve the payment and transaction system; thus, it can ensure financial stability in the future. Digital advancement has raised the importance of digital currencies in the banking/financial system. In this regard, some pilot projects on CBDC are in observation globally. From the review of works of literature, it has been clear that there are different types of CBDC. However, among the different types, only wholesale CBDC and retail CBDC are practically feasible for the banking system. The retail CBDC is accessible universally; however, the wholesale CBDC is limited in access. Retail CBDC is most viable because this digital currency is similar to a sovereign currency and can be exchanged and convertible.
On the other hand, wholesale CBDC is mainly preferred by the financial institutions to make payments and manage the settlement process. However, it is currently not used for the participants of the financial market instead used in cross border and domestic payments. Besides, wholesale CBDC also involve jurisdictions and intermediaries in the payment system. For instance, the project Ubin of Singapore was initiated towards wholesale CBDC to make cross-border transactions cheaper, faster, and flexible. The study has further highlighted the pros of CBDC over the secured payment system that further indicates its impact on the payment system. The data collected reflected that CBDC is safer than the fast payment system as payment is directly transferred to the banks. Thus, in this regard, it can be understood that CBDC would provide more safety to account holders' money and ensure a better and faster payment system.
Another impact of CBDC has been evident concerning a bank deposit. The CBDC of central banks would reduce the overall bank deposit of the traditional/commercial banks. This is because of the lack of intermediary between them, and the central bank would have no control over the financial system. This, in turn, is likely to influence the account holders to withdraw their deposits from commercial banks. The CBDC rate of interest would have a significant impact on the warranty of the account holder. The study's findings further highlighted that with the reduced deposit, the banks would reduce their lending capacity. Besides, this would also impact the revenue of banks that operates based on the generation of customers lending. Therefore, ultimately it would result in reduced performance and increased costs of the banks.
Based on the review of different works of literature, it has been clear that cashless or digital money has a meaningful impact on the banking or financial system. However, it is unlikely whether the use of CBDC would replace the physical currency/paper currency or not. Furthermore, this would entirely depend on the impact of negative aspects associated with the flow of cash that attracts illegal transaction activities in the economy.
References
Ali, R., Barrdear, J., Clews, R., and Southgate, J. (2014). The Economics of Digital Currencies. Quarterly Bulletin of the Bank of England, 54(3), pp.276–286.
Allwood, C. M., 2012. The distinction between qualitative and quantitative research methods is problematic. Qualitative & Quantitative, 46, 1417–1429.
Badea, L. & Claudia, M. P. M., 2021. The Economic and Environmental Impact of Bitcoin. IEEE, Vol. 20, pp.01-10.
Baer, G., 2021. Central Bank Digital Currencies: Costs, Benefits and Major Implications for the US Economic System. [Online] Available at: https://bpi.com/central-bank-digital-currencies-costs-benefits-and-major-implications-for-the-u-s-economic-system/ [Accessed on 19 August, 2021]
Bank for International Settlements (2019). Big Tech in Finance: Opportunities and Risks; BIS Annual Economic Report 2019; Bank for International Settlements: Basel, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 55–80.
Bank for International Settlements, 2018. Central bank digital currencies. [Online] Available at: https://www.bis.org/cpmi/publ/d174.pdf [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
Bank for International Settlements, 2021. Digital currencies and the future of the monetary system. [Online] Available at: https://www.bis.org/speeches/sp210127.pdf [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
Bank for International Settlements. (2018). Central Bank Digital Currencies. Bank for International Settlements. [Online]Available at: https://www.bis.org/cpmi/publ/d174.pdf [Accessed 17 August 2021].
Barontini, C., and Holden, H. (2019). Proceeding with Caution – A Survey on Central Bank Digital Currency. BIS Papers No 101. [Online]Available at: https://www.bis.org/publ/bppdf/bispap101.pdf [Accessed 17 August 2021].
Bastos, V., 2019. Central Bank Digital Currencies: Advantages, impact, and privacy concerns. [Online] Available at: https://zerocap.com/cbdc-advantages-privacy-zerocap/ [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
Bech, M., and Malkhozov, A. (2016). How Have Central Banks Implemented Negative Policy Rates? BIS Quarterly Review, March 2016. [Online]Available at: https://www.bis.org/publ/qtrpdf/r_qt1603e.htm [Accessed 17 August 2021].
Belke, A. (2018). Helicopter Money: Should Central Banks Rain Money From the Sky? Intereconomics, 53(1), pp. 34–40.
Belke, A., Gros, D., Osowski, T. (2017). The Effectiveness of the Fed’s Quantitative Easing Policy: New Evidence Based on Interest Rate Differentials. Journal of International Money and Finance, 73, pp. 335-349.
Bindseil, U. (2020). Tiered CBDC and the Financial System, The European Central Bank, Working Paper Series, Number 2351. [Online]Available at: https://www.ecb.europa.eu/pub/pdf/scpwps/ecb.wp2351~c8c18bbd60.en.pdf [Accessed 17 August 2021].
Bis.org., 2016. Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures. [Online] Available at: https://www.bis.org/cpmi/publ/d154.pdf [Accessed on 19 August, 2021]
Bis.org., 2018. Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures. [Online] Available at: https://www.bis.org/cpmi/publ/d174.pdf [Accessed on 18 August, 2021]
Bis.org., 2020. Central bank digital currencies: foundational principles and core features. [Online] Available at: https://www.bis.org/publ/othp33.pdf [Accessed on 18 August, 2021]
Bis.org., 2021. Central bank digital currencies: putting a big idea into practice. [Online] Available at: https://www.bis.org/speeches/sp210331.pdf [Accessed on 19 August, 2021]
Bis.org., 2021. Central bank digital currency: the quest for minimally invasive technology. [Online] Available at: https://www.bis.org/publ/work948.pdf [Accessed on 18 August, 2021]
Blaxter, L., Hughes, C. and Tight, M., 2016. How to Research (third edition). Buckingham: Open University Press.
Bordo, M. & Levin, A. (2019). US Digital Cash: Principles & Practical Steps; Technical Report; Hoover Institution: Stanford, CA, USA, 2019.
Bordo, M., and Levin, A. (2017). Central Bank Digital Currency and the Future of Monetary Policy. [Online]Available at: https://www.hoover.org/sites/default/files/bordolevin_bullets_for_hoover_may2017.pdf [Accessed 17 August 2021].
Brookings Institution, 2021. Digital currencies: Implications for central banks. [Online] Available at: https://www.brookings.edu/events/digital-currencies-implications-for-central-banks/ [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
Bryman, A., & Bell, E., 2011. Business Research Methods (3rd ed.) Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Calle, G. & Eidan, D., 2020. Central Bank Digital Currency: an innovation in payments. [Online] Available at: https://www.r3.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/r3_CBDC_report.pdf [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
CB Insights, 2021. How Blockchain Could Disrupt Banking. [Online] Available at: https://www.cbinsights.com/research/blockchain-disrupting-banking/ [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
Central Bank Digital Currencies Working Group. (2019). Key Aspects Around Central Bank Digital Currencies. CEMLA Center. [Online]Available at: https://www.cemla.org/fintech/docs/2019-06- KeyAspectsAroundBankDigitalCurrencies.pdf [Accessed 17 August 2021].
Creswell, J. W., 2013. Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. London: Sage publications.
Crowther, D., & Lancaster, G., 2009. Research Methods A concise introduction to research in management an Oliver, P., 2003. The Student’s Guide to Research Ethics. Maidenhead: Open University Press.
Csis.org. 2020. Central Bank Digital Currency, Design Choices, and Impacts on Currency Internationalization. [Online] Available at: https://www.csis.org/analysis/central-bank-digital-currency-design-choices-and-impacts-currency-internationalization [Accessed on 18 August, 2021]
Deloitte, 2020. Are Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) the money of tomorrow? [Online] Available at: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/lu/Documents/financial-services/Banking/lu-are-central-bank-digital-currencies.pdf [Accessed on 18 August, 2021]
Dow, S. (2019). Monetary Reform, Central Banks, and Digital Currencies. International Journal of Political Economy, 48(2), pp. 153-173.
European Central Bank (2019). Transmission mechanism of monetary policy as explained by ECB, European Central Bank. [Online]Available at: https://www.ecb.europa.eu/mopo/intro/transmission/html/index.en.html. [Accessed 17 August 2021].
Fellows, R. and Liu, A., 2008. Research Methods for Construction. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell. Fernández, S. & Gouveia, O., 2019. Central Bank digital currencies: features, options, pros and cons. [Online] Available at: https://www.bbvaresearch.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/WP_Central-bank-digital-currencies-ICO.pdf [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
Friedman, M. (2019). Monetary and fiscal framework for economic stability. Am. Econ. Rev., 38, 245–264.
Galariotis, E., Makrichoriti, P., and Spyrou, S. (2018). The Impact of Conventional and Unconventional Monetary Policy on Expectations and Sentiment. Journal of Banking and Finance, 86, pp.1–20.
Gansbeke1, F.V., 2021. Why Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC) Now And What They Could Mean For Climate Change? (1/2). [Online] Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/frankvangansbeke/2021/06/27/why-central-bank-digital-currencies-cbdc-now-and-what-could-they-mean-for-climate-change-12/?sh=10b5b65c24a8 [Accessed on 19 August, 2021]
Gansbeke2, F.V., 2021. Why Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC) Now And What They Could Mean For Climate Change? (2/2). [Online] Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/frankvangansbeke/2021/06/27/why-central-bank-digital-currencies-cbdc-now-and-what-they-could-they-mean-for-climate-change-22/?sh=1ad6ef702f23 [Accessed on 19 August, 2021]
Graham J. R., and Leary M. T. (2018). “The Evolution of Corporate Cash”. Review of Financial Studies, 31(11), 4288-4344.
Gu C., Mattesini F., Monnet C., and Wright R. (2013). “Banking: A New Monetarist Approach”. Review of Economic Studies, 80, 636-62.
Kay, B. (2018). Implications of Central Banks’ Negative Policy Rates on Financial Stability. USA Journal of Financial Economic Policy, 10(2), pp. 310-320.
Keister, T., and Sanches, D. (2018). Should Central Banks Issue Digital Currency? Bank for International Settlements. [Online] Available at: https://www.bis.org/events/eopix_1810/keister_paper.pdf [Accessed 17 August, 2021].
Kihara, L., Koranyi, B., John, M., and Chopra, T. (2019). How Does Negative Interest Rates Policy Work? [Online] Available at: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-ecb-policy-ratesexplainer/explainer-how-does-negative-interest-rates-policy-work-idUSKCN1VY1D2 [Accessed 17 August, 2021].
Kim, Y., and Kwon, O. (2019). Central Bank Digital Currency and Financial Stability, Bank of Korea. [Online] Available at: https://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3330914 [Accessed 17 August, 2021].
Kimball, M. (2015). Negative Interest Rate Policy as Conventional Monetary Policy. [Online] Available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/002795011523400102 [Accessed 17 August, 2021].
Kirkby, R. (2018). Cryptocurrencies and Digital Fiat Currencies. Australian Economic Review, 51(4), pp. 527–539.
Koumbarakis, A. & Dobrauz-Saldapenna, G., 2019. Central Bank Digital Currency: Benefits and Drawbacks. SSRN Electronic journal, pp.01-20.
Kumhof, M. and C. Noone, (2018). “Central bank digital currencies - design principles and balance sheet implications”. Bank of England, Staff WP No. 725.
Lalouette, L. and H. Esselink (2018). “Trends and developments in the use of euro cash over the past ten years”, ECB economic bulletin, June 2018.
Mancini-Griffoli, T. & et.al. (2018). “Casting Light on Central Bank Digital Currency”. IMF Staff Discussion Note, 18/08.
Masciandaro, D. (2018). Central Bank Digital Cash and Cryptocurrencies: Insights from a New Baumol–Friedman Demand for Money. Australian Economic Review, 51, pp. 540-550.
Meaning, J, J. Barker, E. Clayton, and B. Dyson (2018). “Broadening Narrow Money: Monetary Policy With A Central Bank Digital Currency”. Bank of England Staff Working Paper No. 724.
Mersch, Y. (2017). “Digital base money: An assessment from the ECB perspective”. speech, Helsinki, 16
Mersch, Y. (2018). “Virtual or virtueless? The evolution of money in the digital age”. Lecture.
Moore, B. (1988). Horizontalists and Verticalists: The Macroeconomics of Credit Money, Cambridge.
Nelson, B. (2018). Financial Stability and Monetary Policy Issues Associated with Digital Currencies. Journal of Economics and Business, 100(C), pp. 76-78.
Nessen, M., P. Sellin and P.A. Sommar (2018). “The implications of an e-krona for the Riksbank’s
Nyborg, K. (2016). Collateral frameworks: the open secret of central banks. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
OECD, 2020. Digital Disruption in Banking and its Impact on Competition. [Online] Available. at: https://www.oecd.org/daf/competition/digital-disruption-in-banking-and-its-impact-on-competition-2020.pdf [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
Official Monetary and Financial Institutions Forum, London, 8 February 2018.
operational framework for implementing monetary policy”. Economic Review, 2018:3,
Ostroff, C., 2020. Why Central Banks Want to Create Their Own Digital Currencies Like Bitcoin. [Online] Available at: https://www.wsj.com/articles/why-central-banks-want-to-create-their-own-digital-currencies-like-bitcoin-11603291131 [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
Panneerselvam, R., 2014. Research Methodology. New Delhi: PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.
Qian, Y. (2019). Central Bank Digital Currency: Optimization of the Currency System and Its Issuance Design. China Economic Journal, 12(1), pp. 1–15.
Raskin, M., and Yermack, D. (2016). Digital Currencies, Decentralized Ledgers, and the Future of Central Banking. National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc., NBER Working Papers, 22238. [Online] Available at: https://ideas.repec.org/p/nbr/nberwo/22238.html [Accessed 17 August, 2021].
Rba.gov.au.2020. Retail Central Bank Digital Currency: Design Considerations, Rationales, and Implications. [Online] Available at: https://www.rba.gov.au/publications/bulletin/2020/sep/pdf/retail-central-bank-digital-currency-design-considerations-rationales-and-implications.pdf [Accessed on 18 August, 2021]
Rbi.org, 2021. Central Bank Digital Currency – Is This the Future of Money. [Online] Available at: https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/BS_SpeechesView.aspx?Id=1111 [Accessed on 19 August, 2021]
Reichlin, L., Turner, A., Woodford, M. (2019). Helicopter money as a policy option, Vox EU CEPR Policy Portal. [Online] Available at: https://voxeu.org/article/helicopter-money-policy-option [Accessed 17 August, 2021].
Richie, J. & Lewis, J., 2013. Qualitative Research Practice: A Guide for Social Science Students and Researchers. London: Sage. business consultancy. (2nd ed.). Oxford: Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann.
Rodeck, D. & Curry, B., 2021. Digital Currency: The Future Of Your Money. [Online] Available at: https://www.forbes.com/advisor/investing/digital-currency/ [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
Rogoff, K. (2017). The Curse of Cash: How Large-Denomination Bills Aid Crime and Tax Evasion and Constrain Monetary Policy; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2017.
Saunders, M. & et al., 2012. Research Methods for Business Students, 6th ed. New York: Pearson Education Limited.
Silverman, D., 2011. Qualitative research - 3Rd Ed. London: Sage publications ltd.
Singh, A., 2021. RBI’s digital currency plan: Challenges, risks, and benefits. [Online] Available at: https://www.theweek.in/news/biz-tech/2021/07/26/rbi-digital-currency-plan-challenges-risks-and-benefits.html [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
Statista, 2021. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC) retail projects that are furthest in their development as of 2020, by country. [Online] Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1229713/countries-with-most-mature-retail-cbdg-worldwide/ [Accessed on 19 August, 2021]
Stein, J.C. (2012). Monetary policy as financial stability regulation. The quarterly journal of economics, 127(1), pp.57–95.
The Economist, 2021. When central banks issue digital money. [Online] Available at: https://www.economist.com/special-report/2021/05/06/when-central-banks-issue-digital-money [Accessed on 18 August, 2021].
University Press, Cambridge.
Vasiliauskas, V. (2019). Central Bank Digital Currencies, Bank for International Settlements. [Online] Available at: https://www.bis.org/review/r190527b.htm [Accessed 17 August, 2021].
Viñuela, C., et.al., 2020. The Future of Money and the Central Bank Digital Currency Dilemma. Sustainability, Vol. 12, pp. 01-22.
Vlahović, A. (2014). Challenges to the Implementation of a New Framework for Safeguarding Financial Stability. Journal of Central Banking Theory and Practice, 3(3), pp.19–52.
Ward, T., Clack, S., and Haig, B. D. (2016). The Abductive Theory of Method: Scientific Inquiry and Clinical Practice. Behavior Change, 33(4), pp.212–231.
Take a deeper dive into Can They Do to Improve the Situation with our additional resources.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



