Using MBTI in Candidate Assessment
Introduction
The selection of the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) based personality evaluate test has been performed for the purpose of utilisation in the assessment process of the selected company. This is meant to be the instrument of the psychometric measure through which the assessment of the potential candidates could be conducted. The MBTI had been developed by Katharine Cook Briggs and by her daughter, Isabel Briggs Myers as a personality inventory. It had been based on the psychological theoretical constructs of Carl Gustav Jung. This psychometric tool is employed to discover and understand the varied human personality traits so that such characteristics could be utilised for career development and leadership training. Apart from these, resolution of conflict is another process where the MBTI derived results can be utilised.
Description of used measures
Information derived from the MBTI is utilised by organisations to analyse and assess the strengths and weaknesses as well as methods of perception and processing of information associated with the targeted occupational candidates. In this context, the psychometric analytical measures have been 16 in number which have outlined the personality types and traits of the involved potential employees. These analytical measures and types are categorised further into four individual dichotomies which have been specified in the theories of C.G. Jung. The focus is primarily centred on formulation of better understanding of the methods of approaching and managing work and associated time by the potential employees. Furthermore, solving of problems and making of decisions to properly deal with stress factors have also been significant. For the BAE Systems, the utilised measures in the organisational assessment process, have reflected the fact that consistency and order could be recognised even in the seeming random behavioural variations demonstrated by the assessed individuals. The assessment has been premised on the perspective that basic differences in the individual preferences are formulated on the individual perceptions and judgements. Furthermore, according to Blodgett (2017), the measures applied have been reflective of another consideration. This could be identified as the probable methods of understanding the extent of awareness of the assessed personnel regarding external and internal influences such as ideas, feelings, people and material. This has been fundamental to the process of perceiving the extent of one of the dichotomies, namely, the assessment of Extraversion or Introversion, existing within the selected organisational human resources. This has been also indicative of the preferable methods of acquisition of personal stimulus, by the potential employees of the company.

Next, the judgemental preferences of the personnel under consideration, outlined through the MBTI assessment, have been reflective of the procedures and ways through which the personnel could arrive at different conclusions concerning their perception of their surroundings. This is directly related to the revelation of personal traits. This could further be indicative of the second dichotomy of Sensing or Intuition since this measure outlines the modes of information consumption and the processes of focusing on specific perceptions of reality and facts. According to Diekmann and König (2015), it is an apt observation that human beings systematically differ in their perceptions, in their conclusion formulations on such perceptions and in their application of meaning into such perceptions. The deciding factors are personal values, motivations, skills and interests which impart the combined formative influence on generation of reactions. As has been opined by Furnham (2017), in case of the selected organisation, this measure has specified the differential characteristics involving the potential employees who have been more dependent on their past experiences (this has been the Sensing process) and those who have valued their visions and ideals for the futures ( this has been the Intuition process). Next, the MBTI psychometric analysis has been suggestive of the development pattern of the points of focus of the assessed potential employees and the potential ones under the process of selection. This phase has been characterised by the gathering of responses through which the influence of the dichotomy of mode of Thoughts and Feelings could be determined. This psychometric analysis has been oriented towards outlining the traits of the potential employees under the selection and assessment process, regarding the possibilities that they could deal with the external reality as per their dominant feelings and also, concerning the probabilities that such under selection candidates could react to the external situations as per their existing notions of the personal value mechanism. In the second case, it has been necessary to understand the congruence in between the personal value mechanism and the external situations which are confronted by the potential employees of the concerned organisation. The description of the core aspects of such a phase could outline personal preferences of decision formulation, logical thinking abilities and the influence of personal concerns as the dominant factors. This has been also emblematic of the dichotomy of spontaneous reactions and propensity to seek factual clarities regarding external conditions. Finally, the psychometric analysis has also involved the assessment of the targeted personnel through the notions of the dichotomy of Perception formulation against Judgemental attitudes. This has been oriented towards demonstrating the conflict in between the self-management of life and the methods preferred by the different individuals to deal with their external realities. The focus is on the determining factors of judgement formulation on the basis of orderly approach and perception formulation based on spontaneous responses.
Discussion
The test involved the development and presentation of a survey questionnaire comprising of 70 questions to which have been presented to the selected test participants. The time duration involved was that of 45 minutes at most (for specific individuals who had taken time to put in their responses) and 30 minutes at least (for others who had been comparatively faster). This test had been developed as a personality trait analysis method. The participants had to study the questionnaire and put the individual responses at the appropriate sections of the answer sheet of the following format:
The participants were instructed to put their answers down in the corresponding grid boxes through the checkmark for either A or B. The assessed personnel had also been instructed to provide their answers in the form of their intuitive responses and were not required to formulate their responses through deliberate thinking. This had been necessary to evaluate their personality traits through identification of their basic preferences and emotional orientations. Some examples of such a questionnaire could be provided, in this context which, are as the following:
Example 1: (Test based analysis of the levels of practicality and sensibility in the test participants in comparison to fixed mindsets such as idealistic conceptions)
Q1: Do you think that you have greater inclination towards sensibility and practicality rather than idealism?
Q2: Do you think that you have greater inclination towards idealism rather than sensibility and practicality?
Example 2: (Test based analysis of the levels of level headedness in the test participants in comparison to the probability of impulsive behaviour)
Q3: Do you feel that you are mostly level headed in comparison to the suggestion of being fundamentally impulsive in your behaviour?
Q4: Do you think that you could behave in a warm hearted and empathetic way even during adverse situations?
Example 3: (Testing for logical perspectives and rational thinking in comparison with the subjective drivers of decisions)
Q5: Do you perceive yourself to be a rational thinker?
Q6: Do you think yourself to be able to formulate logical perspectives regarding your work environment and situations?
Example 4: (Testing for the levels of ability in the test participants of paying attention to the minute details of work responsibilities)
Q7: Do you think that you are able to pay effective attention to the minute details of your tasks?
Q8: Do you think that you are better able to comprehend the fundamentals of your work responsibilities in comparison to others?
Example 5: (Testing of the ability of the participants to comprehend the greater overtones of sensibilities)
Q9: Do you think yourself able to comprehend the greater perspectives of your decisions at the workplace?
Q10: Do you consider yourself able to understand the bigger picture related to your designated task roles?
The test had been developed through a 3 phase based process. At the initial stage, the 16 different types of personality, outlined in the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator, were considered. At the second stage, for the purpose of the determination of the individual personality types of the individual participants in the test, the related questionnaire had been developed with 70 different questions. At the third stage, after the responses had been collected, the derived information was connected to the individual personalities through the process of correlating them to the questions which they had individually answered. This test could be commercially produced as well since this MBTI personality evaluation test is performed by about 80% of the Fortune 100 companies for the purpose of building stringing and effective working teams. The experienced and educationally eligible practitioner purchased the MBTI instrument from the authorised publisher. This had not been developed in house. The MBTI assessment tool is a restricted instrument and particular qualifications are required to administer such an instrument in terms of training and interpretation of the instrument. This could be obtained through MBTI certification guidelines programme. The MBTI Certification Program is exclusively provided by the Myers & Briggs Foundation. However, the MBTI Step III™ certification program is performed by the Centre for Application of Psychological Type (CAPT). The practitioners of this instrument are required to undergo the certification process conducted by the Myers & Briggs Foundation. This has been necessitated on the premise of ethical and accurate utilisation of the assessment indicators and to assist the clients with understanding and interpretation of the MBTI outcomes. The procedure targeted the applicant candidates for various posts of the BAE Systems. The design of the assessment tool has been undertaken to collect information regarding the behavioural traits and preferences of the potential employees under the judgement of the organisational selection process. This is not a normative measurement and is based on the group selection procedures so as to assist in the selection of working team members.
The MBTI instrument could be utilised for selection of occupational candidates specifically through the detailing the paths of perception and information processing propensities of different individuals. The differences of such behavioural traits also get reflected in the individual habits of employees. The BAE Systems requires taking into account the differences of the candidates prior to selecting them to perform specific task roles. This also assists in the integration of individuals into new work teams. Furthermore, the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator is the most extensively utilised personality assessment tool. According to Hancock (2016), approximately 3.5 million assessments are performed per annum globally. The key points of the MBTI are the behaviour, characteristics and preferences of the individuals. The assessment is based on the principles of the psychologist and researcher Carl Jung which identified the existence of innate drive towards growth and the individual actions and preferences are intrinsic to such urges. These points effectively enable the MBTI assessment measures to properly assist in the appropriate selection of right people for the right jobs. The psychometric assessment instrument can not be generalised and it is cost effective.
Test Procedures
The random sampling based method was applied to select 600 members of the BAE Systems out of the sampling frames which had been accessible. The research sample members were provided with the formulated questionnaire, the answer sheets and a specific cover letter within a postage envelope so as to notify them about the purpose and the rules of the test. The responses were collected through a 3 week data collection period. Not all of the selected participants responded to the initial request of survey and only 246 of the answer sheets had been returned by the end of the duration of the data collection schedule. This has been the evidence of the determined extent of 41% response rate. This attests to the observation that the degree of generalisation of selected samples to the research population for such tests could be altered when the sample size could exceed that of the number of 150 sample members. One reason for the comparatively low response rate could have been the length of the MBTI involving the four dichotomous scale dimensions. The eight different primary preference modes have been personality traits such as Extraversion (E)-Introversion (I), Sensation (S)-Intuition (N), Thinking (T)-Feeling (F) and Judging (J)-Perception (P). Furthermore, response bias could not be detected from the comparison between the late and early respondents. This had contributed to the perception that the number of answered questionnaire returned could be representative of the complete sample of selected personnel in terms of generalisation. Four temperate groups had been selected for the categorisation of the evaluated responses. These were Sensing and Judging (SJ), Sensing and Perceptive (SP), Intuitive and Thinking (NT) and Intuitive and Feeling (NF). These particular combinations comprising of the Myers-Briggs' dichotomous indices had been included to outline the temperament grouping which had been utilised by previous researches.
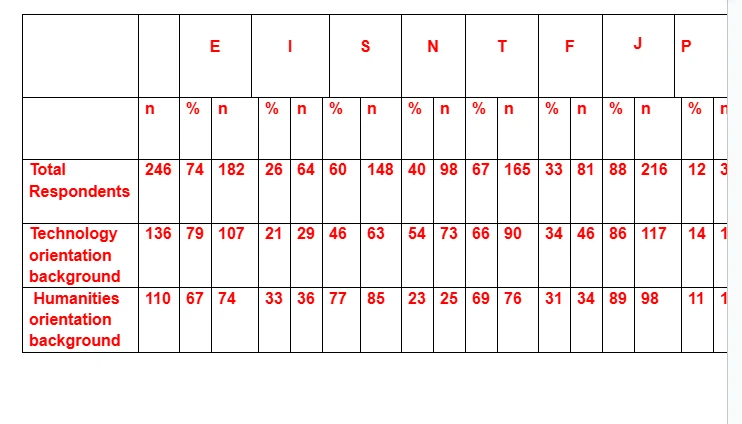
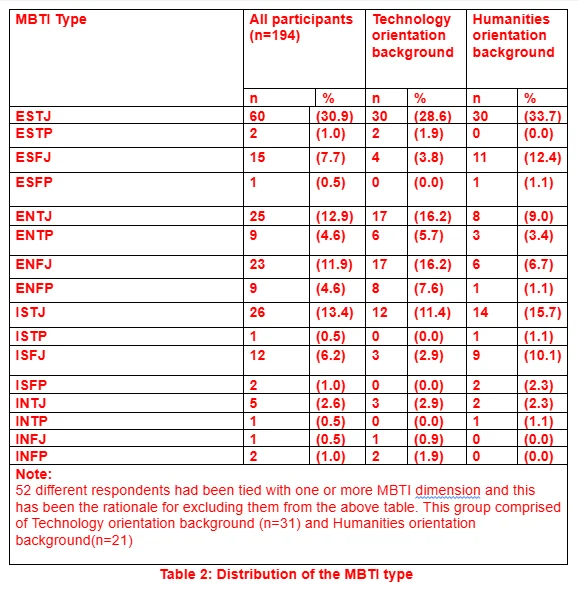
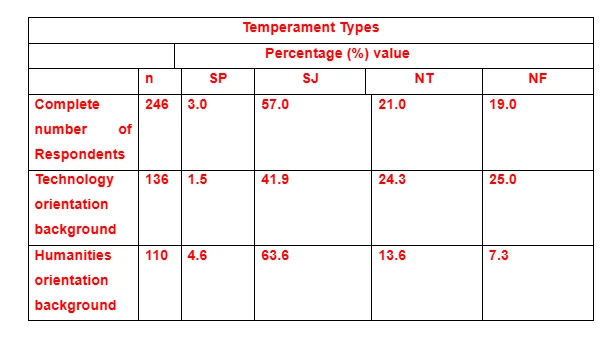
As could be ascertained from the analysis of the MBTI test derived data mentioned above, the distribution of the respondents within the 16 MBTI types of personality has revealed the prevalence of the preferences regarding the personality types of ISTJ, ENTJ, ESTJ, and ENFJ in greater proportion. The personality types comprising of the ESFP, ESFJ and ESTP had demonstrated lower prevalence in terms of occurrence. From an overall analytical perspective, the temperament type which was represented the most was that of Sensing-Judging (SJ=57%) and the rest had been Intuitive-Thinking (NT=21%), Intuitive-Feeling (NF=19%) and Sensing-Perceptive (SP=3%).
The primary strength of the MBTI is that it brings out the information which could assist the organisations to assemble effective teams on the basis of the knowledge of how individuals function. This also highlights the factors of effective collaboration potential for every team member and also brings forth the efficiency which any candidate could bring to the task, after selection into the respective task roles. Furthermore, the MBTI provides information on personality types which assist the team leaders and process managers to select the most effective communication modes on an individual basis. The MBTI assessment further contributes in employee motivation through providing accurate preferences and personality type based data and this enables the human resource management personnel to determine to engage with the employees or occupational candidates on differential levels of psychological approaches, including both the logical and emotional levels. The major weakness of the MBTI personality assessment tool is that it only provides information on preferences and personality based interactive propensities of the subjects. No complete or holistic psychological profiling or accurate emotive inclination of the subjects could be generated. Morris (2016) states that it is necessary to outline that MBTI is open ended since no right or wrong answers, in definitive terms, are to be found within the theoretical perspectives since this test does not disclose every characteristic about the evaluated subjects. According to Moyle and Hackston (2018), reliability could be determined to be the consistency associated with any test or assessment measure concerning the definitive point of interest which has been brought under measurement. This could be better elaborated as the similar measure of outcomes which could be generated by testing or measuring any specific focus of interest at least twice.Rashid and Duys (2015) has observed this to be test-retest reliability which is at the core of significance of the accuracy of any scientific measurement or testing process. This could be envisaged as the terminal decisiveness associated with measuring of the inherently ambiguous factors of individual personality. The reason of such ambiguity could be ascribed to be the qualitative nature of every personality. Thus, the involved psychometrical instruments are short sighted concerning the generation of the consistency which could be expected from objective measuring processes. However, as has been observed by, there are standards of psychological instruments, which, could be generally acceptable to the scholars and these standards are adherents to the reliability factors of any such assessment outcome. Ressia (2016) has stated that the MBTI assessment instruments both meet and exceed such standards of reliability. The facts are as the following:
1: Through involving the continuity of achieved scores, in congruence with the other psychological assessment tools, the achieved reliability is mostly of greater accuracy than the other psychometric instruments.
2: Through retests, the type preferences did match up to 90% of the preferences which had been demonstrated in the previous, first tests.
3. Furthermore, changing types on the retest, the participants exhibited low clarity of preferences and this involved the specific dichotomous pairing such as E-I or S-N.
The reliability factor is greater across the constituents. However, it is to be noted that caution has to be exercised with actual evaluation of the outcomes of the MBTI instrument based tests where the reliability factor could be reported to be lower due to the dearth of available data. Validity is the extent or degree of compatibility of any measurement outcome with that of the existing meaning of what has been measured. The expected accuracy level is the most significant aspect in this regard when the MBTI personality test could be utilised to reflect the real world factuality. In this respect, the MBTI could be reflective of the validity of understanding the behaviour of the assessed people to extensive degrees, in terms of differentiation between the attitudes, values and behaviours of individuals. According to Rashid and Duys (2015), the validity of MBTI instrument based psychometric measurement could be categorised into three distinct patterns. The first one is the validity of the separate scales of preferences. The second one is the validity of the four different pairs of the individual dichotomies. The third one has been the entire combination particularity of differential preferences. The most authentic source of journal articles relating to Myers-Briggs Type Indicator has been the Journal of Psychological Type. The theoretical constructs suggested by C. G. Jung are also enumerated in this literary source. The journal articles are deliberative of the singular research studies, reviews of integrative and collective research and thesis papers on theoretical research which are called by Furnham (2017) as action research.

Conclusion
The preceding psychometric assessment procedure, utilising the MBTI instrument, has been performed to assist the occupational selection process of the BAE Systems. This has involved the evaluation of the psychometric measurement tool applied and linkages with the usefulness regarding the selection of potential employees have been established as well.
Recommendation
MBTI could be further utilised to identify the probable sources of motivational energy and generation of focus within the individuals who could be assessed. The BAE Systems could utilise this instrument of personality measurement to further develop effective leadership through understanding the processes through which individuals process information which they derive from external sources such as from their work environments. Furthermore, the factors of how individuals formulate their decisions and how they could operate during stressful situations are also important to be understood by the BAE Systems. In this respect, the BAE Systems could concentrate on the delineation of the leadership traits. These, in the assessed individuals, could outline the personnel who could be brought into the psychological category of Extraverted Intuitive Feeling Judging. The personnel who could be related to such a psychological group are identified as having extraverted feelings with introverted intuition and these employees could prove to be effective leadership material for the other employees of the BAE Systems.
Reference List
Blodgett, J., 2017. Exploring the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator.
Diekmann, J. and König, C.J., 2015. Personality testing in personnel selection: Love it? Leave it? Understand it!. In Employee Recruitment, Selection, and Assessment (pp. 129-147). Psychology Press.
Furnham, A., 2017. Myers-briggs type indicator (mbti). Encyclopedia of personality and individual differences, pp.1-4.
Moyle, P. and Hackston, J., 2018. Personality Assessment for Employee Development: Ivory Tower or Real World?. Journal of personality assessment, 100(5), pp.507-517.
Rashid, G.J. and Duys, D.K., 2015. Counselor cognitive complexity: correlating and comparing the myers–briggs type indicator with the role category questionnaire. Journal of Employment Counseling, 52(2), pp.77-86.
Ressia, S., 2016. Personality test. In Encyclopedia of Human Resource Management. Edward Elgar Publishing Limited.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



