Case Studies Interpretation
Interpretation of Cases 1- 3:
Three adult individuals had conducted the biochemical screening of their blood based parameters. The details of their parameters along with the reference ranges are given below in a table format:

All the previously mentioned parameters are evaluated for the liver functioning test. The unusual values of the liver enzymes or proteins demonstrate about the working status of the liver and the degree to which the liver is harmed. The biochemical screening of the individual indicated for the case study 1 that the parameters of Alanine aminotransferase, Aspartate Aminotransferase and Albumin are all inside the typical range expect Bilirubin which is higher for the case patient 1-3. For those involved in related research or needing further insights, seeking healthcare dissertation help can provide additional support and guidance. .
The Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or SGPT is an essential enzyme synthesized by the hepatocytes. If there should arise an occurrence of extreme liquor consumption or HCV disease, the death of the hepatocytes happens at an a lot quicker rate than the typical and in the end the ALT level gets elevated in the blood. The raised degree of ALT points towards about the injury of the liver still it has been additionally seen in few situations where the liver is harmed to a more prominent degree yet the ALT level is ordinary so the utilization of ALT is restricted. Almost around 33% of the person who are contaminated with HCV shows typical degrees of ALT. This might be on the grounds that the HCV advancing are moderately slow and the degree of fibrosis are probably going to be typical (Custro, et al, 2001).
Liver makes two primary proteins: Albumin and Globulin. Low levels may indicate possible damage to liver or sickness related to it (Chan, et al, 2015). AST is another enzymes produced in the liver. High blood levels of AST could be an indication of harm or disease in liver or muscles of the body. A below level of albumin indicates about lack of healthy nutrition. It can likewise imply that you have liver illness or an inflammatory malady (van Beek, et al, 2013). Albumin plays a key role in numerous capacities, such as keeping up pressure within blood vessels and in the transportation of substances, for example, medications and hormones. So when its level is low, the blood will be unable to circulate essential materials effectively (Chan, et al, 2015). Doctors characterize hypoalbuminemia as a disorder or gathering of side effects such as damage to liver, kidney, enteropathy related to protein loss and malnutrition (Chan, et al, 2015). Bilirubin is released when red blood corpuscles breaks down. For the most part, the liver clears bilirubin out of our system. In the event of elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood, an issue called jaundice should be addressed during clinical investigation urgently (Mizukawa, et al, 2011). The patient showed the liver functioning enzymes within the typical range however, the Complete Blood Count (CBC) and the symptomatic manifestations has to be considered for accurate interpretation as because nausea, reduction in body weight, anorexia and emesis prior two weeks of jaundice confirmation indicates about billiary blockage as a consequence to damage to liver due to gallstones (Castera, et al, 2012; Lee, et al, 2009). Similar manifestations happening consistently for over about fourteen days preceding the presence of jaundice recommend a malignant biliary impediment, persistent hepatitis, or substance exposure (particularly liquor) (Castera, et al, 2012). Intermittent brief scenes of nausea, anorexia or emesis reaching out over months to years, particularly when joined by right upper quadrant stomach torment, suggests gallstones (Castera, et al, 2012). An ascent in serum bilirubin up to 2 mg/dl every day is correlated with extra hepatic impediment, yet a more prominent pace of increment recommends hemolysis, hepatitis, or liver damage. The serum bilirubin of patients with pure biliary hindrance does not exceed over 30 mg/dl; a higher value indicates hepatocellular jaundice also. The CBC may give proof to hemolysis by exhibiting anemia in a patient without loss of blood or a typical blood smear showing spherocytes or other strangely formed erythrocytes. Leukocytosis and neutrophilia are irregular in viral hepatitis, but normal in cholangitis and alcoholic hepatitis. Eosinophilia in addition to jaundice is suspicious for poison hepatitis or a premise of hypersensitivity (Lee, et al, 2009). Case patient of jaundice without the presence of bilirubin in the urine has either hemolysis or a hepatic deformity concerning take-up of bilirubin or conjugation. Prominent existence of proteinuria indicates towards the condition, amyloid (Mizukawa, et al, 2011; Shapiro, et al, 2010). The accurate diagnosis of symptomatic manifestations is considered to be significant because clinical symptoms related with jaundice regularly guides to achieve a diagnostic conclusion. Stomach torment much of the time goes with jaundice and its character may highlight a particular analysis. Despite the fact that hepatocellular jaundice is usually without any acute sensation of pain, a dull pain or "stagnant sensation" in the right side upper quadrant may point towards acute hepatitis of any reason (Mizukawa, et al, 2011). Pain sensation related with alcoholic hepatitis, particularly when joined by fever, jaundice, and leukocytosis, might be adequately serious to eventually result in an intense surgical process of abdomen (Mendenhall, et al, 1982). Pain sensation radiating in the right upper quadrant of stomach for a prolonged period in an episodic manner and particularly when emanating to the right scapular region, right shoulder, or around the upper stomach and also affecting the girdle territory proposes gallstones. Consistent epigastric or right upper quadrant torment conceivably emanating to the back proposes malignancy of the tip of the pancreas (Shapiro, et al, 2010).

Fever habitually joins jaundice brought about by acute hepatitis, despite the fact that it as a rule endures close to a couple of days. Fever related with chills generally focuses to biliary hindrance, particularly because of stones or injury and, less regularly, because of carcinoma. Moreover, the case patient of jaundice requires intensive documentation of all past and current medication and poison exposures specifically about torment relievers, sedatives, and anti-conception medication pills or different estrogens and other homemade organic compounds that the patient may neglect to make reference to as they might be hepatotoxins (Jain, et al, 2017). Apart from medication consumption of alcohol, particularly ounces consumed every day rather than measurement of number of drinks. Surgical history, regardless of whether later or remote might be ensured in the reason for jaundice (Shapiro, et al, 2010). A family ancestry of jaundice, liver illness, or iron deficiency (particularly in case of splenectomy) ought to be looked for. A positive family ancestry of liver infection may involve the hereditarily transmitted nonhemolytic hyperbilirubinemias (i.e., Crigler–Najjar, Dubin–Johnson, Gilbert's, or Rotor's disorders), non cancerous repetitive intrahepatic cholestasis, hemochromatosis, Wilson's ailment, alpha-1 antitrypsin inadequacy or inherited spherocytosis in the differential determination (Strassburg, et al, 2010).
.Therefore, for the first and second case study showed exceptionally high value of bilirubin with respect to normal range should be correlated with the clinical manifestations of the patient along with detailed background history of medication, lifestyle and previous surgical procedures. Moreover, for further confirmation CBC, biochemical examinations of urine, ERCP or CT scan are recommended. For the third case study, apart from high bilirubin the value of albumin is lower than reference range therefore the nutritional history of the patient and urine analysis for kidney functioning should be correlated for accurate interpretation (Jain, et al, 2017). . .
Interpretation of Case study 4
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to The Importance of Case Studies in Nursing.
The adult was a 58 yrs old male, with BMI of 34.5 kg/m2, waist circumference of 104 cm (41 inches), Blood pressure of 145/88 mmHg, diagnosed with diabetes recently and therefore prescribed with medication metformin and other aspects are unremarkable apparently came for routine health screening. The patient had a history of alcohol consumption of 8-10 U/week approximately. The details of the liver functioning enzyme parameters along with the reference ranges are given below in a table format: .




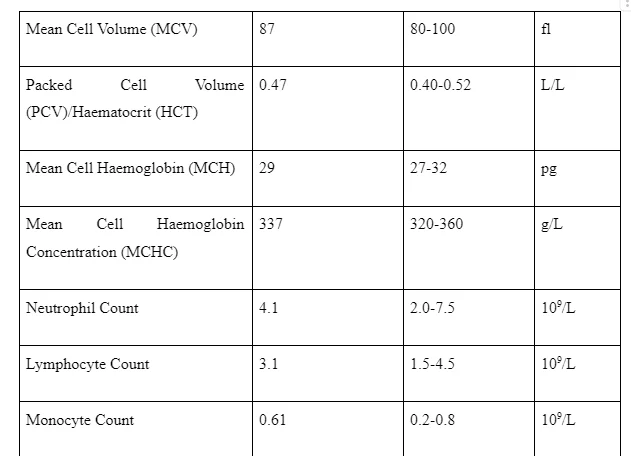



The unusual values of the liver enzymes or proteins demonstrate about the working status of the liver and the degree to which the liver is harmed. The biochemical screening of the individual indicated for the case study 4 that the parameters of Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) and Bilirubin are all exceptionally high with respect to reference range expect Albumin.
The high level of ALT arise an occurrence of extreme liquor consumption or HCV disease and points towards about the injury of the liver (Custro, et al, 2001). AST is another enzymes produced in the liver. High blood levels of AST could be an indication of harm or disease in liver or muscles of the body (van Beek, et al, 2013). Bilirubin is released when red blood corpuscles breaks down. In the event of elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood, an issue called jaundice should be addressed during clinical investigation urgently (Mizukawa, et al, 2011).
While investigating the blood plasma parameter it was observed that the case patient had elevated levels of GGT, Glucose (Fasting), Cholesterol and Triglycerideswith respect to normal range. The Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) is a settled prescient biomarker of the serum for liquor related liver damage, hepatitis and bile duct related infections. The raised degree of GGT likewise shows an assortment of ailing conditions, for example, the cardiovascular malady, the state of diabetes, metabolic syndrome (MetS). Despite the fact that GGT is found inside numerous tissues of the body however liver is viewed as the primary source (van Beek, et al, 2013). On the off chance that any of the above condition is harming the liver the estimation of the parameter GGT increments and the higher value signify more prominent degree of harm to the liver (Koenig, et al, 2015). Lipids are one of the vital components which control cell activities and homeostasis. Liver assumes a fundamental job in lipid digestion, a few phases of lipid production and transportation. However, there is conspicuous decrease in plasma cholesterol and triglyceride (TG) levels among patients with acute hepatitis and hepatic damage with respect to decreased biosynthesis of lipoprotein. For decreased liver biosynthesis limit, low degrees of TG and cholesterol are generally seen in constant liver maladies (Milić, et al, 2014). High triglycerides are frequently indicates of different conditions that elevates the risk of coronary disease and stroke, obesity and metabolic syndrome. Therefore, it is suspected that the patient was also suffering from metabolic syndrome along with alcohol related liver damage as the HDL level is low which is considered as another indication (Almeda-Valdés, et al, 2009). The CBC may give proof to hemolysis by exhibiting anemia in a patient without loss of blood or a typical blood smear showing spherocytes or other strangely formed erythrocytes. Eosinophilia in addition to jaundice is suspicious for poison hepatitis or a premise of hypersensitivity but the patient did not demonstrate eosinophilia in the haematology assessment (Lee, et al, 2009).
While investigating the blood plasma parameter it was observed that the case patient had elevated levels of GGT, Glucose (Fasting), Cholesterol and Triglycerideswith respect to normal range. The Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) is a settled prescient biomarker of the serum for liquor related liver damage, hepatitis and bile duct related infections. The raised degree of GGT likewise shows an assortment of ailing conditions, for example, the cardiovascular malady, the state of diabetes, metabolic syndrome (MetS). Despite the fact that GGT is found inside numerous tissues of the body however liver is viewed as the primary source (van Beek, et al, 2013). On the off chance that any of the above condition is harming the liver the estimation of the parameter GGT increments and the higher value signify more prominent degree of harm to the liver (Koenig, et al, 2015). Lipids are one of the vital components which control cell activities and homeostasis. Liver assumes a fundamental job in lipid digestion, a few phases of lipid production and transportation. However, there is conspicuous decrease in plasma cholesterol and triglyceride (TG) levels among patients with acute hepatitis and hepatic damage with respect to decreased biosynthesis of lipoprotein. For decreased liver biosynthesis limit, low degrees of TG and cholesterol are generally seen in constant liver maladies (Milić, et al, 2014). High triglycerides are frequently indicates of different conditions that elevates the risk of coronary disease and stroke, obesity and metabolic syndrome. Therefore, it is suspected that the patient was also suffering from metabolic syndrome along with alcohol related liver damage as the HDL level is low which is considered as another indication (Almeda-Valdés, et al, 2009). The CBC may give proof to hemolysis by exhibiting anemia in a patient without loss of blood or a typical blood smear showing spherocytes or other strangely formed erythrocytes. Eosinophilia in addition to jaundice is suspicious for poison hepatitis or a premise of hypersensitivity but the patient did not demonstrate eosinophilia in the haematology assessment (Lee, et al, 2009).
Looking for further insights on Care planning process in the healthcare practice? Click here.
References:
- Custro, N., Carroccio, A., Ganci, A., Scafidi, V., Campagna, P., Di Prima, L. and Montalto, G., 2001. Glycemic homeostasis in chronic viral hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. Diabetes and metabolism, 27(4), pp.476-481.
- Chan, A.W., Chan, R.C., Wong, G.L., Wong, V.W., Choi, P.C., Chan, H.L. and To, K.F., 2015. New simple prognostic score for primary biliary cirrhosis: albumin‐bilirubin score. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology, 30(9), pp.1391-1396.
- van Beek, J.H., de Moor, M.H., de Geus, E.J., Lubke, G.H., Vink, J.M., Willemsen, G. and Boomsma, D.I., 2013. The genetic architecture of liver enzyme levels: GGT, ALT and AST. Behavior genetics, 43(4), pp.329-339.
- Castera, L., 2012. Noninvasive methods to assess liver disease in patients with hepatitis B or C. Gastroenterology, 142(6), pp.1293-1302.
- Lee, J.H., Yoon, J.H., Lee, C.H., Myung, S.J., Keam, B., Kim, B.H., Chung, G.E., Kim, W., Kim, Y.J., Jang, J.J. and Lee, H.S., 2009. Complete blood count reflects the degree of oesophageal varices and liver fibrosis in virus‐related chronic liver disease patients. Journal of viral hepatitis, 16(6), pp.444-452.
- Mizukawa, B., George, A., Pushkaran, S., Weckbach, L., Kalinyak, K., Heubi, J.E. and Kalfa, T.A., 2011. Cooperating G6PD mutations associated with severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia and cholestasis. Pediatric blood & cancer, 56(5), pp.840-842.
- Lucey, M.R., Mathurin, P. and Morgan, T.R., 2009. Alcoholic hepatitis. New England Journal of Medicine, 360(26), pp.2758-2769.
- Shapiro, S.M., 2010, June. Chronic bilirubin encephalopathy: diagnosis and outcome. In Seminars in Fetal and Neonatal Medicine (Vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 157-163). WB Saunders.
- Jain, A., Mehta, N., Secko, M., Schechter, J., Papanagnou, D., Pandya, S. and Sinert, R., 2017. History, physical examination, laboratory testing, and emergency department ultrasonography for the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis. Academic Emergency Medicine, 24(3), pp.281-297.
- Strassburg, C.P., 2010. Hyperbilirubinemia syndromes (Gilbert-Meulengracht, Crigler-Najjar, Dubin-Johnson, and Rotor syndrome). Best Practice & Research Clinical Gastroenterology, 24(5), pp.555-571.
- Koenig, G. and Seneff, S., 2015. Gamma-glutamyltransferase: a predictive biomarker of cellular antioxidant inadequacy and disease risk. Disease markers, 2015.
- Milić, S., Lulić, D. and Štimac, D., 2014. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity: biochemical, metabolic and clinical presentations. World journal of gastroenterology: WJG, 20(28), p.9330.
- Almeda-Valdés, P., Cuevas-Ramos, D. and Aguilar-Salinas, C.A., 2009. Metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Annals of hepatology, 8(S1), pp.18-24.
- Theise, N.D., 2013. Histopathology of alcoholic liver disease. Clinical liver disease, 2(2), p.64.
- Clinical Biochemistry Reference Ranges Handbook, NHS, 2019 (accessed on 1.04. 2020).
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



