Clinical Management of Postnatal Depression among New Mothers
Mental Health issue is referred to the problematic and concerning condition of a person regarding their emotional and psychological well-being. In the current decade, it is seen that mental health issues have become leading health concern among many individuals in different societies and is causing untimely death of people in communities. In the UK, it is reported that women are more likely to face mental illness compared to men and nearly twice of them prone to be diagnosed with depression and anxiety (mentalhealth.org.uk 2019). The presence of perinatal or postnatal depression is found to be common among women. This is evident as in the UK it is reported that 1 in 5 women develop some form of mental health issue during their pregnancy or following the birth of the baby (rcog.org.uk, 2017). In the study of Dhar and Barton (2016), it is mental that depression and cardiovascular disease are inter-related. This is evident as the study mentions that 90% of patients with history of cardiovascular disorder are found to be suffering from depression. For those researching these topics, seeking healthcare dissertation help can provide valuable insights and guidance.
The impact of new mothers suffering postnatal depression is not only limited to cause deteriorate emotional condition such as develop self-harm intentions but also affects them develop physical health issues such as cardiovascular diseases, weakened immune system, fatigue and others along with self-harm intentions (Fancourt and Perkins, 2017). This is evident from the study by Healey et al. (2013) informs that out of 73 women referred for postpartum depression 58% of them expressed intention to develop self-harm and kill themselves. In addition, the study by Stewart and Vigod (2016) informs that a 28-year old mother of three-month-old child reported of severe fatigue, low energy, irritability, insomnia and others due to postnatal depression. The presence of postnatal depression among new mothers is also seen to negatively affect the upbringing of the baby and create issues within the family (Gentile and Fusco, 2017). Thus, this assignment is developed to determine the way clinical management of postnatal depression among new mother can be done. In addition, the role of nurses and different health professionals are to be discussed and care plan along with best practices for the new mother is to be explained to control postnatal depression and cardiovascular issue as co-morbid health condition.
 clinical-management-of-postnatal-depression-among-new-mothers
clinical-management-of-postnatal-depression-among-new-mothers
While working as a student nurse in practice placement within the female ward, many patients with mental health problems and severe depression were provided to be cared. Among them, Bianka who is a new mother was referred to the mental health ward under the section 3 of Mental Health Act (MHS) 1983 to be treated for severe depression as key mental health issue along with management of her physical health problem that is heart disorder. This is because the heart problem was stable but her mental health condition of severe depression is leading to make her develop intention of self-harm and suicide. She is found to be aware of the mental health services as she was previously referred to the care for controlling her depression. The NEWS2 score of Bianka was found to be abnormal most of the time which raised the concern among the nurses that she is being provided effective care in controlling her complex health issues of severe depression and heart problem to ensure her well-being.
In a news article published by Oxford University, it is reported that cardiovascular disease is one of the leading cause of death among pregnant women in the UK. This is evident as 9 women per 100,000 population in the UK who are pregnant are reported to die each year as a result of cardiovascular health issue (ox.ac.uk, 2019). In addition, the study by Blais et al. (2019) informed that postnatal depression is seen to raise complication of heart condition and leads new mothers to develop cardiovascular diseases. Thus, it is utmost significant that proper monitoring of Bianka’s health condition is to be performed by the nurses so that her depression can be controlled and heart condition can be managed favourably so that her well-being is ensured and fatal conditions related to health condition can be avoided.
The Best Practice in healthcare refers to the systematic process in which identification, gathering, examination, dissemination and implementation of information is done along with healthcare intervention outcomes are monitored for patients based on their health condition (Abbott et al. 2018). The best practice for Bianka who had cardiovascular disease along with severe postnatal depression can be accomplished by following effective identification of the sign and symptoms regarding the complex health issue, implementation of proper treatment and taking proper prevention strategies. The best practice can be accomplished in health if the healthcare practitioners take proper initiative to early diagnose health condition of the patient and implement proper intervention along with monitor the health of the patients (Knights et al. 2016). This is because in this way the healthcare practitioners can timely detect and analyse the sign and symptoms regarding the patient’s health issue making them aware of the particular intervention to be provided for best approach. Therefore, in case of Bianka, to perform best practice the health practitioners initially require to identify and have knowledge of the underlying signs and symptoms of postnatal depression. Moreover, they are to detect the way these symptoms can lead to deteriorate heart condition of Bianka so that the health practitioners are aware of the intervention to be taken that would help her to resolve her complex health issue.
The study by Nicholson et al. (2016) informs that untreated postnatal depression among new mothers makes them prone to experience the risk of cardiovascular disease such as ischemic heart attack. This is because the individuals with depression develop uncommonly sticky blood platelets which lead the blood to clot, in turn, causing patients to develop risk of heart attack (Roy, 2018). Thus, the nurses require educating Bianka and expecting mothers about signs and symptoms of depression and the underlying physical health issues such as cardiovascular disease to be faced by them. This is to be done to make mothers like Bianka to take early approach in availing care for their complex health condition which would also act as preventive strategy in offer timely care to the patients for their well-being. Moreover, severe depression which creates risk of cardiovascular disease for new mothers like Bianka can be prevented by referring the individuals to interpersonal therapy.
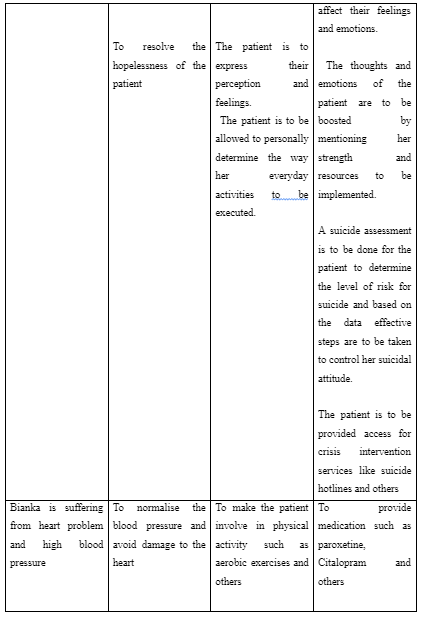
The interpersonal therapy is type of psychotherapy which focuses on people and improving their relationship (Stephens et al. 2016). This is because the therapy considers that all psychological problems are raised due to hindrance in personal relationships. This is evident from the study of Guille and Douglas (2017) where it is mentioned that interpersonal therapy helps to lower postnatal depression as well as improves social support, mother-baby bonding and martial functioning among women. The monitoring of heart condition of mothers through regular Electrocardiogram and blood pressure checking helps nurses to prevent cardiovascular disease and implement best practice for care (Şentürk et al. 2016). This is because this role of the nurses would help them to continuously monitor and detect any fluctuations of heart issues in patients like Bianka to take immediate care approach in preventing deterioration of heart health.
The serve depression and cardiovascular diseases in new mothers can be treated with implication of anti-depressant. However, the use of anti-depressants to control depression and blood pressure among expecting and new mothers is seen to cause complication in birth and babies (Bernard et al. 2019). The study by Pawluski et al. (2019) informs that the use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors such as paroxetine, Citalopram and others for controlling depression and cardiovascular issues in new mothers is safe. Thus, it may be used for Bianka to treat her severe depression in turn controlling cardiovascular complication. The nurses while offering anti-depressant to patients are to monitor the dosages and health condition to ensure no risk are being faced by the new mothers (Eke et al. 2016). This role is to be played by nurses for Bianka and new mothers so that changes in medication, as well as breastfeeding ways, can be informed to the patient to ensure good health of the mother and the baby.
The support network of the patient is significant to arrange effective treatment and management of their health condition. This is because the family members, as well as their friends in the support network, can be involved in supporting care practices for the patients and take care decision on their behalf to ensure positive care services are provided satisfactorily to the individuals (Hetherington et al. 2018). As asserted by Li et al. (2017), the presence of a supportive family helps in early detection and care for severe depression among new mothers. This is because the family members through proper observation can detect the changes in the behaviour of the mothers and accordingly they involve healthcare practitioners at the early stage on detection of signs of health issue for the care of their member. Moreover, they participate in supporting the patient’s care to ensure their well-being. The involvement of family support for the new mothers helps her to get relived of care of older children and household work as well as have assistance in caring for the new child (Hetherington et al. 2018). This encourages the mother to less lonely and overburdened with work, in turn, making them develop better emotional health. Thus, the family support network is important for Bianka so that her worry regarding caring for the children and babies along with household work can be resolved in turn making her depression to be lowered as she feels supported and less lonely.
In the social support network for new mothers, the fathers are required to be ready in sharing the care of the newborn so that increased pressure on the mother can be avoided which often leads to their depression (Da Costa et al. 2019). Thus, Bianka’s husband is to be involved in supporting care of the newborn and the older children to make her feel relieved of care burden and feel less depressed for managing her responsibilities. In some cases, it is seen that the new mothers are unable to detect signs of depression and therefore suffer from the condition. However, few mothers are found to be active in detecting their signs of depression which leads them to seek medical services for their care (Hetherington et al. 2018). The stigma regarding mental health is seen to bar new mothers in accessing care for depression due to fear of judgement and isolation from society (Moore and Ayers, 2017). Therefore, new mothers like Bianka may avoid seeking care for their mental condition out of fear of stigma and lack of awareness regarding health issues. In this condition, the support network of patients like Bianka is able to help them access proper care at the right time. This is because family and friends along with carers for new mothers may support them to overcome the fear of stigma regarding depression and arrange as well as schedule necessary treatment for them to overcome depression (Brittain et al. 2017). The lack of supportive social network leads the new mothers to face lack of support in detecting and coping with severe depression (Hetherington et al. 2018). This is because the new mothers feel vulnerable of their lives and lack assistance as well as lonely in taking care of the newborn, older children and household work making them develop the further depressive mood.
The patients when detained under section 3 of the Mental Health Act (MHA) 1983 are to be provided effective care and treatment in the hospital-based on meeting few criteria and condition. The detention under the Act for treatment is allowed for 6 months and it can be renewed (legislation.gov.uk, 1983). This indicates that Bianka is to be detained for care regarding severe depression in postnatal condition irrespective of her wish in the mental health ward. The section 117 of MHA informs that patients hospitalised more than six months are to be provided accommodation in the community to help them lead normal life (legislation.gov.uk, 1983). The section under the Act informs that if Bianka stays more than six months in the hospital then authorities are to arrange proper accommodation in the community to ensure she can lead a normal and healthy life with continuation of care.
The different health professionals who may be involved in offering care to new mothers like Bianka for managing severe depression and cardiovascular diseases include nurse, general practitioner, cardiologist, psychiatrist, occupational therapist and dieticians. The nurses have the role to ensure the best care is provided to the patients by considering their needs and demands. In order to execute the role, the nurses are to be informed in details regarding the mental and physical health condition of the patient (Higgins et al. 2018). This is because the information would lead the nurse caring for Bianak to understand the nature of care to be provided so that her depression is lowered and the cardiovascular condition is improved to ensure better health condition. The occupational therapist has the role in case of patients with severe depression to restructure their life so that the individual develops proper activities and avoid depressive ideas (Felice et al. 2018). Thus, the role of occupational therapist for Bianak is to determine the way her everyday activities and way of living life is to be changed to improve her mental health.
The occupational therapist have the role to inform nurses caring for Bianka regarding the different services such as bathing, dressing, caring for newborn, helping her take care of her older children and others they are to be provided in supporting her daily living so that eventually her depression is lowered. The dieticians have the role to inform about dietary intake and nutrition required by the patients (Saligheh et al. 2017). The dietician for Bianka has the role to inform the diet to be taken by her and foods to be avoided to improve her cardiovascular health. In addition, the dietician has the role to inform exercises and physical activity to be performed by Bianka to lower her depression and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. This is because it is seen that certain exercise can enhance the physical activity of new mothers which improves their mood and reduces the risk of heart issues (Saligheh et al. 2017). The general practitioner for Bianka has the role to assess her overall health condition and inform intervention to be provided to her to control her mental and physical health.

The psychiatrist has the role to analyse the mental condition of Bianka to inform the nature of intervention required by her and to be provided by the nurses to lower her depression. It is seen that psychiatrist by analysing new mothers often involve them in taking Cognitive Behaviour Therapy for long-term and Interpersonal Therapy for short-term to cope with severe depression after the birth of baby (Du Preez et al. 2016). The cardiologist has the role to execute screening of heart condition and determine the nature of care needed by the patients (Hare et al. 2019). The study by Hare et al. (2019) informs that cardiologist has the role to routinely screen patients for depression as it creates risk for cardiovascular diseases. However, the study by Sepulveda (2019) informed that cardiologist often neglects to check mental health condition of new mothers and pregnant women while diagnosing their heart condition. This leads pregnant women to face hindered physical health. Thus, this informs that cardiologist for Bianak have the role to screen her depression and assess her cardiovascular health to determine the nature of care to be provided by the nurses to ensure her better heart condition.
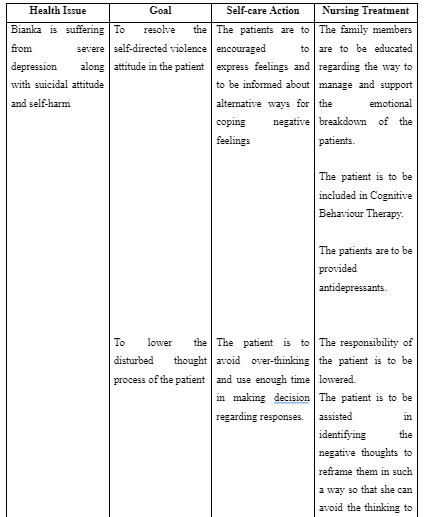
In order to build effective care support for Bianka, a proper care plan is to be developed for her by considering her complex health issue of severe depression along with the cardiovascular disease. The care plan is referred to the written statement for an individual developed by assessing their needs identified during health diagnosis and evaluation (Higgins et al. 2018). The care plan for Bianak is going to focus on certain variable like daily support, living arrangement, mental health condition, physical health goals, support network assistance and others. The NICE guidelines mention that risk assessment of patient is to be executed to determine the probable risk regarding health to be faced by the patients and the way they are to be resolved to ensure quality healthcare (NICE, 2015). Therefore, risk assessment of community condition and social support network for Bianka is to be performed to determine the nature of services to be provided to her to offer her risk-free care. The care plan for Bianka is to involve the inclusion of her family members and husband who would offer her support to do everyday chores and share the care of the older children as well as the newborn. This is required to meet the goal of lowering her depression as sharing her responsibility would make her control her emotional breakdown caused due to work load and loneliness of executing duties.
The care plan of Bianka also requires including Cognitive Behaviour Therapy for long-term condition along with Interpersonal Therapy for the short-term condition. This is because CBT allows therapeutic care to be provided to the individual by adjusting with the change in the pattern of the behaviour with the progress of each session (Freedland et al. 2015). Therefore, the therapy would gradually try to fit in resolving the negative feeling into positive emotion, in turn, allowing better mental health condition of the patient. In addition, interpersonal therapy would help Bianka to improve her relationship with family members which would eventually make her feel included in the community and access support to care for the newborn that in turn would lower her depression caused due to overthinking and overburden with responsibilities.
The above discussion informs that Bianka is suffering from severe depression along with has developed self-harm and suicidal attitude. The major approach to be used in resolving mental health issue of Bianka is Interpersonal Therapy and Cognitive Behaviour Therapy as it allows proper control of depression. The family members have the role to offer care, show emotional support and share responsibilities of Bianka to improve her mental as well as physical health condition. The psychiatrist, cardiologist, nurses and psychotherapist are the professionals required in caring for Bianka. The care plan indicates that Bianka is involved in CBT and Interpersonal therapy, have antidepressants and have support from family to ensure proper recovery from the complex health issue.
Take a deeper dive into Clinical Intervention and Prevention Strategies for Bipolar Disorder in Young People with our additional resources.
References
Abbott, A., Schröder, K., Enthoven, P., Nilsen, P. and Öberg, B., 2018. Effectiveness of implementing a best practice primary healthcare model for low back pain (BetterBack) compared with current routine care in the Swedish context: an internal pilot study informed protocol for an effectiveness-implementation hybrid type 2 trial. BMJ open, 8(4), p.e019906.
Bernard, N., Forest, J.C., Tarabulsy, G.M., Bujold, E., Bouvier, D. and Giguère, Y., 2019. Use of antidepressants and anxiolytics in early pregnancy and the risk of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension: a prospective study. BMC pregnancy and childbirth, 19(1), p.146.
Blais, L., Ahmed, S.I.S., Beauchesne, M.F., Forget, A., Kettani, F.Z. and Lavoie, K.L., 2019. Risk of postpartum depression among women with asthma. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice, 7(3), pp.925-933.
Brittain, K., Mellins, C.A., Phillips, T., Zerbe, A., Abrams, E.J., Myer, L. and Remien, R.H., 2017. Social support, stigma and antenatal depression among HIV-infected pregnant women in South Africa. AIDS and Behavior, 21(1), pp.274-282.
Carson, N., 2019. Antidepressant use during breastfeeding. Prevention, 10, p.1-19.
Da Costa, D., Danieli, C., Abrahamowicz, M., Dasgupta, K., Sewitch, M., Lowensteyn, I. and Zelkowitz, P., 2019. A prospective study of postnatal depressive symptoms and associated risk factors in first-time fathers. Journal of affective disorders, 249, pp.371-377.
Dhar, A.K. and Barton, D.A., 2016. Depression and the link with cardiovascular disease. Frontiers in psychiatry, 7, p.33.
Du Preez, A., Conroy, S., Pawlby, S., Moran, P. and Pariante, C.M., 2016. Differential effects of ethnic density on the risk of postnatal depression and personality dysfunction. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 208(1), pp.49-55.
Eke, A.C., Saccone, G. and Berghella, V., 2016. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) use during pregnancy and risk of preterm birth: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 123(12), pp.1900-1907.
Fancourt, D. and Perkins, R., 2017. Associations between singing to babies and symptoms of postnatal depression, wellbeing, self-esteem and mother-infant bond. Public health, 145, pp.149-152.
Felice, E., Agius, A., Sultana, R., Felice, E.M. and Calleja-Agius, J., 2018. The effectiveness of psychosocial assessment in the detection and management of postpartum depression: a systematic review. Minerva ginecologica, 70(3), pp.323-345.
Freedland, K.E., Carney, R.M., Rich, M.W., Steinmeyer, B.C. and Rubin, E.H., 2015. Cognitive behavior therapy for depression and self-care in heart failure patients: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA internal medicine, 175(11), pp.1773-1782.
Gentile, S. and Fusco, M.L., 2017. Untreated perinatal paternal depression: Effects on offspring. Psychiatry research, 252, pp.325-332.
Guille, C. and Douglas, E., 2017. Telephone delivery of interpersonal psychotherapy by certified nurse-midwives may help reduce symptoms of postpartum depression. Evidence-based nursing, 20(1), pp.12-13.
Hare, D.L., Stewart, A.G., Driscoll, A., Mathews, S. and Toukhsati, S.R., 2019. Screening, Referral and Treatment of Depression by Australian Cardiologists. Heart, Lung and Circulation. pp.23-45.
Healey, C., Morriss, R., Henshaw, C., Wadoo, O., Sajjad, A., Scholefield, H. and Kinderman, P., 2013. Self-harm in postpartum depression and referrals to a perinatal mental health team: an audit study. Archives of women's mental health, 16(3), pp.237-245.
Hetherington, E., McDonald, S., Williamson, T., Patten, S.B. and Tough, S.C., 2018. Social support and maternal mental health at 4 months and 1 year postpartum: analysis from the All Our Families cohort. J Epidemiol Community Health, 72(10), pp.933-939.
Higgins, A., Downes, C., Carroll, M., Gill, A. and Monahan, M., 2018. There is more to perinatal mental health care than depression: Public health nurses reported engagement and competence in perinatal mental health care. Journal of clinical nursing, 27(3-4), pp.e476-e487.
Higgins, A., Downes, C., Carroll, M., Gill, A. and Monahan, M., 2018. There is more to perinatal mental health care than depression: Public health nurses reported engagement and competence in perinatal mental health care. Journal of clinical nursing, 27(3-4), pp.e476-e487.
Katzmann, J.L., Mahfoud, F., Böhm, M., Schulz, M. and Laufs, U., 2019. Association of medication adherence and depression with the control of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and blood pressure in patients at high cardiovascular risk. Patient preference and adherence, 13, p.9.
Knights, J.E., Salvatore, M.L., Simpkins, G., Hunter, K. and Khandelwal, M., 2016. In search of best practice for postpartum depression screening: is once enough?. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology, 206, pp.99-104.
Li, Y., Long, Z., Cao, D. and Cao, F., 2017. Social support and depression across the perinatal period: A longitudinal study. Journal of clinical nursing, 26(17-18), pp.2776-2783.
Möllerberg, M.L., Årestedt, K., Swahnberg, K., Benzein, E. and Sandgren, A., 2019. Family sense of coherence and its associations with hope, anxiety and symptoms of depression in persons with cancer in palliative phase and their family members: A cross-sectional study. Palliative medicine, 33(10), pp.1310-1318.
Moore, D. and Ayers, S., 2017. Virtual voices: social support and stigma in postnatal mental illness Internet forums. Psychology, health & medicine, 22(5), pp.546-551.
Nicholson, L., Lecour, S., Sliwa, K., Wedegärtner, S., Kindermann, I. and Böhm, M., 2016. Assessing perinatal depression as an indicator of risk for pregnancy-associated cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular journal of Africa, 27(27), p.119.
Pawluski, J.L., Brain, U., Hammond, G.L. and Oberlander, T.F., 2019. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor effects on neural biomarkers of perinatal depression. Archives of women's mental health, 22(3), pp.431-435.
Saligheh, M., Hackett, D., Boyce, P. and Cobley, S., 2017. Can exercise or physical activity help improve postnatal depression and weight loss? A systematic review. Archives of women's mental health, 20(5), pp.595-611.
Şentürk, Ş., Kağıtçı, M., Balık, G., Arslan, H. and Kır Şahin, F., 2016. The Effect of the Combined Use of Methylergonovine and Oxytocin during Caesarean Section in the Prevention of Post‐partum Haemorrhage. Basic & clinical pharmacology & toxicology, 118(5), pp.338-343.
Sepulveda, A.A., 2019. A Call to Action: Addressing Maternal Mental Health in Pediatric Occupational Therapy Practice. Annals of International Occupational Therapy, 2(4), pp.195-200.
Stephens, S., Ford, E., Paudyal, P. and Smith, H., 2016. Effectiveness of psychological interventions for postnatal depression in primary care: a meta-analysis. The Annals of Family Medicine, 14(5), pp.463-472.
Stewart, D.E. and Vigod, S., 2016. Postpartum depression. New England Journal of Medicine, 375(22), pp.2177-2186.
Appendix
Appendix 1:
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



