Journey Through Depression
1. Introduction
1.1 Why I choose this subject?
I have encountered and furthermore saw among others the torment, misery and sadness brought about by the clinical condition “depression”. In spite of the fact that in my childhood and for a large portion of my adolescent years, I frequently felt dismal or lost, I was totally uninformed of this overwhelming psychological instability. Be that as it may, in my mid twenties I saw how incapacitating this sickness can be, as I spiralled downwards, getting hopeless and unmotivated; soon life had no delight and I was deadened. My circumstance deteriorated because of the absence of an accurate diagnosis and the non-existing widely inclusive medications offered by conventional medication. Seeking healthcare dissertation help could provide valuable insights into understanding and addressing such conditions more effectively. Also, the absence of information and in this manner absence of help from family, companions and society as a rule added to a sentiment of disappointment and misery.
Now, I comprehended that taking the allopathic course or tolerating the poor perspective on individuals from my prompt circle and society on depression was not going to support me. I was very crippled and forlorn, however a little sparkle of non-congruity and interest was started within me. The introduction of freshly discovered assurance assisted to show signs of improvement, feel much improved, live better and I started my explorative way of elective medications in the desire for finding better approaches to ease my manifestations of depressions. En route, I understood that I was not the only one in my affliction: some of my companions and a significant number of my associates were additionally persevering through the impacts of this dysfunctional behaviour, a couple of them in a much most exceedingly terrible situation.
Take a deeper dive into A Critical Analysis with a Focus on Depression with our additional resources.
Despite the fact that depression is a typical mental issue, and the quantities of individuals influenced by it keep on moving upwards, the treatment that are broadly utilized all throughout the globe is the potential short acting antidepressants prescription. This medication treatment not just presents various symptoms, including disturbance, uneasiness, acid reflux, discombobulation, a sleeping disorder and even an expanded danger of self destruction, however it too limits the opportunity of the person to accomplish a significant healing. Specialist Amit Goswami clarifies that when the cerebrum is changed with substances, one can't address the initial one as it does not exist anymore. Allopathic medication takes into consideration everybody the equivalent, as its center rule is that every organic framework are made equivalent, while energy medications are increasingly individualized and are customized.
Clinical depression is considered among the most common disorders. The prevalence of the psychological issues is rising among the common populace throughout the globe that demands immediate clinical consideration. The clinical manifestations of depression are depicted through varied ways in the daily life such as in the pattern of diet regimen, continued bitterness or loss of enthusiasm for every activity of daily life, reduced self esteem and confidence. The mood swings observed during the phase of depression can often lead to destruction or suicidal in nature (WHO, 2017). Depression is categorised based on the seriousness or severity of the condition and another condition known as dysthymia is a type of moderate or mild everlasting type of depression. The disorder not only hampers the quality of life of people but also shows its destructive impact upon the economical condition of the nation (Essau, and Chang, 2009). The most convenient forms of treatment for depression are antidepressants, behavioural interventions such as cognitive behavioural therapies along with modifications in the life style of patients (NHS Digital, 2019). In this regard, the concept of quantum medicine is considered to be an emerging one in the field of medicine to treat the condition of depression. This is considered under the practice of complementary or alternative medicine. The concept of quantum medicine is based on the fact that the body of living organisms is composed of electromagnetic waves or radiations that demonstrate changes along with the mental, physical or chemical alterations within the body (Chopra, 2015). It has been set up that a biophysical approach can be used to treat mild or moderate degree of depression and related issues as evident from the past confirmations (Chopra, 2015). The concept of complementary and alternative medicines is based on following concepts: bio electromagnetic therapies, nutritional healing, energy healing, relaxation techniques, herbal medications, behavioural interventions and mind body therapeutics (Chopra, 2015).
Health problems associated with behavioral factors like anxiety, depression, substances, or alcohol are major causes of mental health problems. Their treatment usually requires a holistic approach as they may require multiple approaches for treatment. However, they have been the main disabling factors of the healthcare sector all over the world. They have also made the primary care sector be stretching, causing many problems. Quantum medicine has been one of those sectors that have come hand in ensuring depression state in different people has been contained (Katon et al., 2008). The clinical setting determines the kind of depressive symptoms seen by staff in primary care. Children, adult, and adolescent patients have varied symptoms depending on the causes of their depression. Since 1997, there has been a constant rise in the number of depression cases reported in primary healthcare, with a yearly rise of 2%. The majority of the patients who have reported cases of depression see it as a recurrent or chronic illness that has always affected them. Most of those patients who have reported depression are adults and have shown a high risk of contracting this illness (Katon et al., 2002). Their recovery has been difficult, or the rate of recovery has been less. Some have indicated that they have been experiencing depression reoccurring when they seek clinical services.

Most national surveys have consistently indicated that many people in the U.K. receive mental healthcare services from primary care providers compared to specialized mental healthcare institutions. Primary care institutions have been identified as the major mental healthcare service providers for children, adolescents, and adults (Katon et al., 2002). People with mental disorders often find primary care easily accessible compared to specialized institutions. Many patients have indicated that it would be appropriate for healthcare institutions to have integrated services for primary care and mental health services. Through this, they will ensure both behavioral and medical health needs for patients are addressed without much difficulty. However, currently in the U.K., most systems are fragmented into mental health, substance abuse, medical, and social services delivered from specific geographical locations. The approach has made the clinical setup lead to increased cases of depression as patients would have to seek services over wide areas and in a more challenging manner. If the systems could be put together and collaboration be enhanced, it could make most of the activities easy, and the rate of depression would reduce in return (Katon et al., 2002). There have been reports through national surveys that indicate that most primary care institutions provide mental health services to their patients. However, the question that will arise is whether they provide it effectively that would lead to the complete recovery of the patients (Katon et al., 2002). The barriers to accessing comprehensive mental health services in the clinical practice and shortage of mental health care providers are the reasons for the rise of depression cases.
1.2 Rationale for the study:
Few evidences based on randomised control trials (RCT) and other case studies preliminaries have suggested that several individuals who are not able to access the mental health treatment for depression and other psychological disorders, who are not satisfied with the front line allopathic medication such as antidepressants due to its immense associated side effects had taken up the quantum medicine approach as an effective alternative therapeutic regime (Nahas and Sheikh, 2011). The approach is sustained because of the detailed investigation of the patient, i.e., from their nutritional propensity to their root causes and it offers to provide more benefits than harm within a huge population (Yanick, 2002). Therefore, the present study will conduct a qualitative meta-analysis on the efficacy of quantum medicine approach which involves the strategies of energy healing, relaxation techniques, mind body therapeutics and nutritional healing.
Qualitative meta-investigation is an endeavour to lead a thorough optional subjective examination of the primary subjective discoveries. Its motivation to give an increasingly far reaching portrayal of a marvel and an appraisal of the impact of the technique for examination on discoveries—and it is talked about within throughout the assignment. Therefore, the present investigation will discuss about the clinical consideration depression and its impact upon health of the individuals, its different forms and their symptomatic manifestations, the global prevalence of the clinical issue, a brief about the frontline method of treatment for depression (Hill, Knox and Hess, 2012). The next crucial part of the assignment will discuss about the concept of quantum medicine, the various approaches within the concept utilized for the patients of depression along with their efficacy rate based on randomized control trials and case studies. The study will also include systematic reviews as it is a significant step of the amalgamation procedure, the review studies evaluate the nature of the examinations they have taken into consideration. They would then be able to utilize this evaluation to appoint various preliminaries to consider discoveries. As a part of the investigation process improper quality investigations are once in a while downsized in significance or rejected from the review process. The precise process outlines all the accessible proof about a specific clinical research question, for this assignment depression is considered. In light of the proof at present accessible, it will offer a complete response on a specific inquiry concerning treatment, anticipation, reasons for illness, or damage (Gupta, and Sharma, 2016).
2. Literature Review
2.1 Clinical depression
The most common disorders of mental health according to the categorization of diagnostic is depressive disorder. As these two disorders are highly prevalent within the common people they are being referred as common mental disorders (WHO, 2017). An issue of mental health which is portrayed by perseveringly discouraged mind-set or loss of enthusiasm for exercises, causing noteworthy impedance in everyday life is a characteristic trademark for depression. Possible causes that are considered as trigger factor for depression is the mixture of mental, physiological and social origins of misery. With the progress of research studies in the field of mental health with respect to functioning of brain, it has been stated that the altered functioning of the circuits of neurons proposes that these elements may cause changes in cerebrum, The chronic presence of negative emotions such as bitterness or loss of enthusiasm that describes significant depression can prompt a scope of social and physical symptoms which characterizes the major depressive disorder. Among the symptomatic manifestations related to depression alteration within the pattern of rest, craving, vitality level, attentiveness and every day conduct or self-esteem are the prominent ones. Depression can likewise be related with considerations of self destruction (Otte, et al., 2016).
2.2 The depressive disorder incorporates two fundamental sub-classes
The episodes of major depressive disorder or depression include the adverse symptomatic behavioural changes as stated above but it varies with the seriousness of condition. Therefore, on the basis of seriousness of the disease it can be categorised into the state of gentle, moderate, or extreme; and Dysthymia can be considered to be chronic or interminable type of depression of gentle or moderate category. The manifestations of dysthymia are very much similar to episodes of depression; yet will in general it can be classified as less extreme and the duration is comparatively more (Essau, and Chang, 2009). A further significant feature with regard to depressive disorder is the association of the disorder with episodes of maniac disorder. The episodes of maniac disorder is characterized by raised disposition and expanded vitality, coming about in over-action, exerting pressure during discourse and diminished requirement for rest (Merikangas, et al. 2012).
Management of depression successfully in the primary care setup has a significant effect in the healthcare sector because of the interactions between physical and mental health. The majority of depression cases are associated with an increased number of unexplained medical symptoms, including fatigue and pain and general health outcomes that are poor (Katon et al., 2002). When depression goes without being treated, it becomes associated with independent morbidity. In return, it leads to prolonged recovery and a negative prognosis accompanied by other medical illnesses that increase premature mortality related to comorbid medical illness. Other than that, it leads to an increased number of functional impairments, which results in reduced work productivity. With people having depression through various factors, the quality of life for the patients and their family members reduces. A study conducted on the older adults’ primary healthcare indicated that those who participated and had depression had their quality of life declined (Katon et al., 2002). The quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) were drastically reduced, with diseases such as cancer, hypertension, emphysema, and chronic foot problems also rose. Also, depression can act as a barrier to developing productive and positive relationships between healthcare institutions and patients. PCPs rate patients who have depression to be difficult to handle, evaluate and treat compared with those with depression (Katon et al., 2002). When such patients are not correctly managed, they become unsatisfied, and their level of depression also elevates.
2.3 Global menace of depression
At a worldwide level, more than 300 million individuals are evaluated to experience the ill effects of depressive disorder which is proportional to 4.4% of the population of the globe in the year, 2015. The number of people with basic mental issue all inclusive is going up, especially in lower-salary nations, in light of the fact that the populace is developing and more individuals are living in the age when depression occurs most ordinarily. It speaks to an obstruction to manageable advancement in all districts. Depression hinders any individual from accomplishing their maximum capacity, hinders human capital, and is related with untimely mortality from self destruction and different associated sicknesses (WHO, 2017).
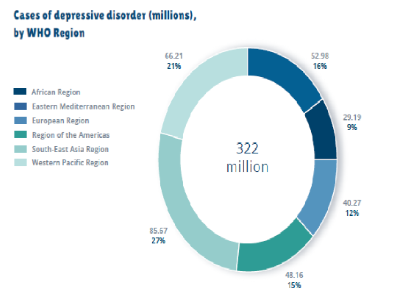
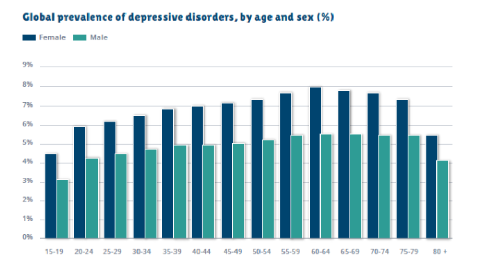
The incidence of depression is increasing among females (5.1%) than in comparison to the male counterparts (3.6%) (Refer, Fig: 2). The rate of prevalence differs by WHO Region, from a low of 2.6% among male group residing at the Western Pacific Locale to 5.9% among females residing at the regions of Africa. Moreover, it is evident that the rate differs by age, expanding among the aged population which was above 7.5% among females matured within the range of 55-74 years, or more 5.5% among the male counterparts. The incidence of depression additionally happens among youngsters and youths underneath the age of 15 years, yet at a lower level in comparison to the aged populace. Almost 50% of these individuals live in the Western Pacific Region and South-East Asia Region, mirroring the moderately bigger populaces of those two Locales which for example also incorporate India and China (Refer, Fig: 1). The all out evaluated number of individuals living with the said mental disorder expanded by 18.4% somewhere in between the range of 2005 and 2015 and this actually mirrors the general development within the populace of world, just as a proportionate increment within the range of age at which depressive disorder is predominantly increasing (WHO, 2017; Marshall, 2012). Moreover, in the United Kingdom, the rate of major depressive disorder is thought to be the second leading cause of morbidity and is one of the significant contributors to the number of suicide cases. The scenario is also similar in the United Kingdom with respect to the male and female ratio, which depicted that women are more likely to suffer from mental health related problems. About 10% of the mother and 6% of the father within the United Kingdom goes through the period of mental health problem within a given time frame (ONS, 2018; Patel, 2018).
Research Evidence for Collaborative Care
Different studies have shown how effective collaborative care can be for both small and large primary care institutions. With institutions having diverse health care setups providing services for free while others require payments, they will need to adjust differently depending on the patient population need to ensure everything takes place as required. However, when undertaking all these, its important that the safety of the patients and their general health be considered to have the best approach for treating their depression status (Glied, Herzog & Frank, 2010). Also, when treating depression, the healthcare professionals should focus on ensuring that they have other mental disorders and anxiety considered as they may be an obstacle towards achieving the best practices. Due to this general support on how effective depression management is through collaborative approaches in primary care and specialties, clinics could achieve effective results.
When collaborative treatment is involved for depressed patients, their results are likely to impress because the consideration and input from different professionals will make them succeed (Glied, Herzog & Frank, 2010). Compared to other approaches, it is important to note that this one seems to be systematic and comprehensive, and considerate of the prevailing conditions make different aspects a success. This approach's impact on the general healthcare systems is positive because it touches on the treatment requirements. Checking on the patient's symptoms will also help those concerned undertake various activities that are likely to ensure that people succeed in what they are undertaking under different circumstances (Glied, Herzog & Frank, 2010). Collaboration also encourages those involved in the treatment process to consider both the physical and social functioning of the patients and work towards the improvement of the quality of life. Since the approach involves both the patients and physicians, it could be important to ensure that different aspects of both parties will be considered, with several problems are going to be solved. The medical team's various aspects are likely to require the patient to affect the quality of services they are likely to receive (Glied, Herzog & Frank, 2010). There are different aspects of the treatment that need to be included when it comes to collaboration treatment.
When considering the cost-effectiveness of collaboration, it has a long-term impact that is likely to improve the general handling of the patients. Care of depressed patients is likely to be taken seriously, with the costs being incurred in the treatment process being one of the lowest because the concern for healthcare organizations would be having a better quality of life for patients (Ell et al., 2008). Cost of treatment in the clinical setup has been the main challenge that has been facing patients. It has contributed to the majority developing complicated conditions of depression due to a lack of early access to medical attention. But with the collaborative treatment cost-saving causes, there has been an improvement in how patients are accessing depression treatment approaches which helps them gain back their health. The health care system affording system achieves that, but several stages of depression can easily be detected because of how patients can access the services (Ell et al., 2008). Also, implementing the collaborative treatment will ensure primary caregivers can reach patients and accommodate them without much difficulties associated with depression. Due to the benefits of healthcare collaboration, there have been many institutions integrating services as they ensure patients have a better experience with the kind of services being provided. Through the collaborative approach, patients are improved by their social well-being taken seriously, which translates to the general benefits of how people should act. The satisfaction driven out of collaborative treatment makes both patients and physicians enjoy what they are doing and receiving.
There has been a recommendation from many studies about collaboration because of the evidence-based decisions the approach uses when handling patients. Mental health disorders require that a patient should receive services that will help improve their current conditions. When checking on the various programs with collaborative treatment approaches, the impact has been so positive that many patients have come out of the depression danger (Ell et al., 2008). Inclusion of all factors ensures that every aspect of the patient and those who are going to provide healthcare systems that are mindful of the well-being of the affected. Evidence-based practice is one of the ways through which different aspects of the patients are discovered (Ell et al., 2008). Therefore, undertaking various depression treatment programs should include having all the interested parties involved in the outcome. As primary care providers struggle to understand how to deal with depression, they must include all those experts that are likely to support them in various capacities for efficiency and improved outcomes.
Implementation of collaborative care on a large scale
Though different variations are in collaborative care program components, those programs that turn out to be effective depend on the core clinical principles and aspects. Failure to observe this, it is likely that people will get affected by different circumstances that may be external. The core components that patients will require, especially during chronic illness care, include; the usage of explicit treatment protocols and plans, reorganize the practice of the patient care to ensure their needs are met, especially those who require more time, accessing the required experts readily, and having supportive information system and strategies based on measurement care, stepped care and treatment target (Ell et al., 2008). Patient-rating scales are some of the systematic measurements for clinical outcomes applied on patients. The 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) for depression assists clinical officers in tracking patients and improving their state by proposing alternative treatment neds or adjusting the already undertaken procedures. Some points are critically considered forming a meaningful treatment approach where depression symptoms are experienced in patients forming the best approach for handling patients (Ell et al., 2008). The treatment takes place in a more targeted way where those involved ensure that various aspects of the patients are the main object and the areas where they are affected are what takes place. Despite the limited resources, psychiatric consultation is required to develop more focused solutions where patients are expected to respond positively to the treatment (Ell et al., 2008). Using the systematic treatment that targets it can help overcome the clinical inertia responsible for ineffective treatments. In the mental disorder diseases, there are many cases where people have been treated with different diseases and even misdiagnosed. Therefore, the primary care providers are made to be sure of what they are doing through an inclusive and easily applied approach.
There has been the large-scale implementation of evidence-based collaborative programs by different healthcare institutions to ensure that depression is treated correctly. Several health care organizations have undertaken large-scale implementations of evidence-based collaborative care programs for depression (Ell et al., 2008). Due to this, there are some cases of depression that have been dealt with more conclusively based on evidence-based treatment approaches. The approaches offer patients the kind of treatment according to the consideration reducing the number of days that patients are spending in seeking treatment services. Also, patients are incorporated in the decision-making process where various aspects of their condition are seriously considered before selecting the treatment process. Primary care providers at the community level have been involved in the decision-making process where various activities would help detect cases of depression before they get out of hand. However, there have circumstances as people are seeking medical services; they find themselves sinking further into depression because of how various activities (Ell et al., 2008). Implementation of the programs may be complex, but it helps patients achieve the quality of care they will always admire to get in healthcare facilities. It is also important to note that various healthcare organizations are aligned to accommodate arising challenges. Where healthcare professionals may be depressed because of the kind of work they constantly, they are given support services to help the cop with the conditions (Ell et al., 2008). Further, the combination of collaboration and evidence-based approach leads to effective handling of depression cases.
Effective Collaborative Care Programs Implementation
For effective collaboration care programs to be successful, the implementation process should be systematic and comprehensive to ensure every aspect required in the health sector is undertaken. Different organizations have employed collaborative care programs in their function and succeeded in providing effective treatment to different patients, especially the depressed category (Grypma et al., 2006). One of the key benefits obtained from the program is that it can be executed under different setups and deliver the required results.
To ensure effective implementation of collaborative care programs, it is important to fragment financial streams that will help integrate primary care and mental health services (Trivedi & Daly, 2007). Despite undertaking the financial integration procedures, it does not lead to effective clinical practices and integration because those involved are the ones who determine the kind of output that will be obtained. Having a support community and environment where people are collaborative will ensure primary care has all the kind of services that will provide the kind of care that leads to better services (Trivedi & Daly, 2007). With the combination of co-location, it is important to note that primary care providers will identify those factors that lead to depression and advise patients on avoiding them. This will ensure that behavioral health care is guaranteed, leading to improved health outcomes in the population and patients. Through this, the medical fraternity could cap depression instead of concentrating on factors that may not help.
To achieve effective treatment, it could be necessary that healthcare organizations move from episodic acute care where healthcare provided is in the form of ‘behavioral health urgent care.’ However, it should be based on the presentation of the care based on the population where the signs they indicate will determine the kind of treatment they will receive (Trivedi & Daly, 2007). This systematic approach will be used, and patient problems will be resolved, resulting in proper support. It is required that a clinical tracking system or a registry should be created where patients will be identified, preventing them from receiving any inappropriate treatment. Also, effective support would result in stepped care that would result in a better quality of care for the patients. This will lead to better handling of patients in both the primary care and specialty clinics (Trivedi & Daly, 2007). Therefore, it could be important to ensure the accomplishments benefit the patients positively.
Depression management caregivers should understand that in the treatment process, those initial treatments may not be sufficient enough to resolve the problems that the patients are facing at any particular moment (Trivedi & Daly, 2007). Treatment adjustments, systematic tracking of outcomes, and patient consultations may help them achieve the desired outcome, which is the patients' general well-being. Also, it will be easy for caregivers to provide proper treatments based on the guidelines as they could access the systems easily and locate the important information (Trivedi & Daly, 2007). They will also be able to focus on those patients who have not improved to the required standards.
Clinical flexibility is achieved when mental health providers ensure primary care has effectively collaborated. Free flow of information where communication with patients is kept open will help ensure efficiency in providing healthcare procedures. Mental health providers should keep the communication channels flexible, regularly accessible, and effective to ensure therapy sessions can be undertaken without even visiting the patients physically. Patients can be allowed to use technology in attending sessions and also make necessary clinical appointments (Trivedi & Daly, 2007). Further, they should ensure that evidence-based therapies should be used in behavioral activation, motivational interviewing, problem-solving, and brief cognitive-behavioral therapy. It is through this that primary care practice can achieve efficient service provision.
Integration of care is important as it will ensure sufficiency is achieved. Training for primary care and mental health specialists should be undertaken to ensure everything takes place more appropriately (Trivedi & Daly, 2007). Therefore, for effective implementation to occur, clinical support for both primary care and mental health specialty should receive finance, behavioral health, measured goals and objectives, operational support, and clear set standards that must be achieved. With the continuous support directed towards improving chronic illness care, it could be appropriate if large delivery systems could be used to manage the arrangements instead of using a fee-for-service medical approach that may be a barrier to most patients who may not afford it (Trivedi & Daly, 2007). However, it could be appropriate for all those involved to have a deep understanding of what they are expected to achieve.
Implementing effective ways in a healthcare organization can take different forms with integrated care for behavioral health is one of the primary care problems. There are many ways to implement effective integrated care for behavioral health problems in primary care. There should be the inclusion of treatment manuals of various researches that are used in guiding healthcare professionals (Grypma et al., 2006). They should always ensure that any implementation is well understood as it will directly translate into the kind of services that will be obtained. There are various appropriate ways to ensure accountability for the participants, directly influencing better outcomes. They should also focus on core principles like tracking the desired outcomes carefully and providing measurement-based decisions at both the clinical and patient levels (Grypma et al., 2006). The process helps make the integration process easy with care programs living up to the promise of ensuring patients’ lives are improved.
To ensure that the implementation process for the evidence-based collaborative care programs take place without many challenges, it is better if they are broken down into small and medium practices that can easily be put in place (Grypma et al., 2006). Therefore having the financial practice would help a great deal in ensuring that fee-for-service healthcare programs are only implemented when necessary. Additionally, the introduction of changes would take place in a well-calculated approach that ensures health cares centers meet the demand of different stakeholders (Grypma et al., 2006). Different mechanisms, therefore, can be employed to ensure the successful undertaking of the programs.
Health care professionals should use structured rating scales commonly applied in mental disorders like the PHQ-9 in depression. Through this, they could ensure screening takes place timely, enabling patients to get insights into what they are expected and how their treatment is likely to progress without any problems (Grypma et al., 2006). Additionally, incorporating behavioral health ratings will ensure records are kept electronically, and the patient's history is well kept. This makes it easy for clinical managers and other health staff to follow history to improve patients' health without any problem.
Targeted treatment and stepped care where the various types of treatments ranging from referrals to mental health, psychosocial treatments, and medication can be adjusted according to the response that patients show that the desired outcomes are attained (Grypma et al., 2006). Also, incorporating evidence-based interview strategies could ensure the patient receives helpful support in the treatment process. The behavioral health problems would be addressed by training those involved on how they can apply them appropriately. Training of the health caregivers assists in the performance of core functions for the behavioral health care managers. They can engage in proactive outreach and adhere to treatment, understand the medical effects that arise, and undertake appropriate referrals and effective treatment of those involved. Sharing workflows and developing relationships with behavioral health providers, and giving referrals will help provide services (Grypma et al., 2006). Having active dialogue and collaborating between different parties will result in patients getting the quality care that could lead to desired health outcomes. Combining these strategies will make the handling of the patients efficient, and general patient care will improve despite the challenges that are likely to be faced.
The clinical harnessing of factors associated with mental health
Dealing with the effects of quantum medicine that have led to the increased clinical rise of depression can only be improved by having an intimate connection with the environment and ensuring that nature has been conserved. Clinicians and other historical factors have alluded to the fact that there are elements that contribute to imbalance and ill-health. There is evidence that some of the non-scientific approaches that go beyond the rudimentary medical theory have a positive impact on patients' healing process (Kardakis et al., 2018). Mental health has been impacted most, with several areas being one of the best approaches to better healthcare outcomes. This approach should be considered the modern way mental health can be handled and have the patient being in conditions that generally improve theire performance. Though different medical practices have been developed, the one that is efficient for most psychiatric disorders has a positive environment. Dealing with work-life balance challenges, increased concerns about negative psychological changes, stressful jobs, poor nutrition, decreased connection with nature, and having a more sedentary life are some of the things that will determine the kind of environment one lives (Kardakis et al., 2018). Therefore, as seen, several aspects of life are the significant determinants of mental health that one will keep in life.
Understanding the relationship between human health and nature plays a vital role in mental health as it directly impacts their performance. There are different characteristics of nature that have qualities that are distinct in ensuring that mental health is maintained; they include; Choleric [Fire (hot)], Melancholic [Earth (dry)], Phlegmatic [Water (moist)], and Sanguine [Air (cold)] (Kardakis et al., 2018). All the elements indicated above, if they are imbalanced, are likely to cause diseases in human beings. However, external elements can be used in the modification to ensure the imbalance is addressed and sustain the healthy lifestyle of the people. If any of the above factors misses or is imbalanced, there is a likelihood that they are likely to miss proper functioning, which could result in mental torture that leads to depression. Continuous lack of any of the above factors can lead to having serious disturbance within the body and result in deficiencies that ensure normal functioning of various factors (Kardakis et al., 2018). Having the elements working helps in attaining different factors associated with the mental health of a person. There is enough evidence that can directly be linked with the above mentioned factors directly impact the mental status of an individual.
Earth
The earth is what contains the general environment. when one is exposed to an environment that is friendly, it can act an intervention of therapy that courses healing of different individuals. There are circumstances under which different people find themsslves ion earth surrounding will depend on the mental status. There are general health benefits when one gets exposed to adequate nature (Kardakis et al., 2018). It is due to this that the increase of urbanization and industrization has negative impact on health. Most people are not finding enough space to have better development of thoughts that help them in undertaking different activities which assist in boosting mental health. People who have had interactive nature around thems they have been found to develop longtime mental benefits. Exposure to to fresh air and sunlight has its own benefits when it comes to psychosocial factors which assist in improving the mental well-being of an individual (Kardakis et al., 2018). Interaction with nature and biaodiversity has its own benefits on the development of microbiome which has positive influence on mental health of people. Though there are benefits that arise, interacting with soil and other things can lead to the potential exposure to contaminants like harmful pathogens and chemicals.
Out of nature, a clay art therapy has been developed where individuals who engage in this activities are found to be free from mental problems. Also, it has been found to improve the depression conditions which make them feel better and improve the quality of life. Therefore, engaging in earthly related conditions helps them general health effects. Having a sufficient greenspace assists majority of the people improve imagination, risk taking ability and self-discovery. Also, it has been established that engaging horticultural activities improves the mental health of different individuals. Patients who are assessed with mild depression are required to engage in horticultural activities that in return helps them improve their conditions. They are able to overcome their sick status and start having more improved mental conditions.
Increasing the exposure to nature through physical activities like walking, horticulture and exercises improves the mental status of different people compared to when they are least exposed (Kardakis et al., 2018). Generally engaging the in exercise the physical energy and mental imagination and engagement is much better than when one has limited interaction with the environment. studies in the UK indicate that nature interaction deals with depression much better when compared to quantam medicinal practice. It improves the self-esteem and healthy lifestyle of people making things much better than any form of therapies that one could be subjected. The undertakings not only doe they lead to improvement of the depression status but also mental disorders have been found to reduce (Kardakis et al., 2018). There also public health findings that have indicated that nature based exercises have got more improved health status. They have related the decrease of the number of mental health disorders to people interacting frequently with nature. It is due to these that nature plays a great role in the treatment of depression compared to clinical medicine.
Fire
The domain comprises direct subjection to sunlight, artificial light, heated objects, or heat on the human body. Light commonly held transcultural unscientific belief that a person's attitude enhances the weather is at bay and the sun is out (Kardakis et al., 2018). While constant exposure to sunlight and individual likings of pleasant temperature may improve moods, there is no consistent connection between seasonal differences and the occurrence of mood changes. However, vitamin D, which we get from sunlight, may moderate the impacts of direct exposure to light on mental health. On the contrary, the risk of depression is associated with low levels of vitamin D. The effect of supplementation of enhancing moods is still unknown (Kardakis et al., 2018). A study conducted on multiple sclerosis patients monitored prospectively for two years showed that sunlight's subjection was contrary to fatigue and depression scores. Ironically, the study showed that only when vitamin D levels are higher than 80 nm is when the depression scores improved. The results are, however, not significant when the sun exposure changes (Kardakis et al., 2018). That is to say that sun exposure reflected enhancement of energy and moods and not vitamin D.
A different facet of "light-based therapy" for mood moderation simulates dawn to re-energise cortisol and serotonin secretion and control the circadian rhythm. Various clinical attempts have revealed that this may be specifically important for the seasonal affective disorder (SAD). Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of between two and eight weeks have estimated the various impacts between high 1600- 10,000 lux bright light therapy and stimulating dawn thirty minutes before waking between 101 and 300 lux (Kardakis et al., 2018). The findings are conflicting, and the two might be effective in SAD, with more robust support for typical bright light therapy
A common health intervention that involves the use of heat is the sauna. Sauna needs a traditional variety of hot rocks and radiant heat to create moisture and modern invisible types that embrace far-infrared light. Presently, more assessment is needed regarding traditional sauna, even though new evidence proposes that infrared sauna enhances similar physiological advantages (Kardakis et al., 2018). While proof is still preliminary, there is a minimal number of managed researches conducted on occasion sauna bathing on health. Nevertheless, the primary physiological impacts of regular sauna baths have there for some time.
Recently, researchers conducted the first longitudinal studies on a large Finnish cohort (n=2315), and the findings showed positive results in a range of health domains (Kardakis et al., 2018). The health domains included respiratory disease, dementia, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, the physiological response to sauna bath correlates with low or moderate physical exercise intensity. Thus, it suggests beneficial improvements related to sauna baths correspond to likeable advantages realised during regular physical exercise. Even though recent in-depth research lacks especially for mental health complications, typical benefits seem to be related to the growing activity of the thermoregulatory system (Kardakis et al., 2018). Therefore, it is sensible to presume that similar advantages are achieved from various modalities of atmospheric bathing from various cultural activities. The cultural traditions include 'sweat lodge" in the native American "hammam" in the Islamic and the "Onsen" from the Japanese, all of which appreciate long-term honour for their regenerative capacity.
One specific feature of classic sauna that needs more interrogation mental and general health conditions is the typical use of cold exposure after the subjection to heat (air/cold showers/snow after the sauna). A study of 2015 involving three thousand participants aged between 18-60 years living with severe comorbidity and no regular exposure to cold showering were exposed to random cold and hot shower as a control group for thirty-one consecutive days (Kardakis et al., 2018). Later sixty days of bathing with cold water at their discretion for the intervention group. The main findings from this study were related sickness and illness lead to absence from work. The results further showed a 30% reduction in absence for disease to hot and cold showers compared to the control group. However, there were no sick days for adults with severe comorbidity. This study suggests that it is essential to investigate sauna bathing and subjection to cold baths, especially considering the popularity of sauna baths globally.
However, one small research analysed the acute body temperatures and not the long-term impacts. Still, it did not examine qualitative variations in the view of enjoying sauna when exposed to the cold bath. A different study of 2016 discovered that when patients with chronic heart disease get exposed to a cold bath, it is safer for their health, but the practice needs a lot of caution (Kardakis et al., 2018). However, the study did not consider factoring in qualitative factors of subjection to cold described as extracting distinguished regeneration in current ethnographic literature. At the same time, it focused on this review while outside (in direct contrast to heat-based therapy). There are many possible applications of cold medicine (cryotherapy) for several health complications.
Regarding specific impacts of sauna on mental health outcomes, there is irresistible anecdotal proof from old folklore but few sociological or scientific proof. However, from the same discussion above of the Finnish cohort, there is a strong relationship between constant sauna bathing and depletion of psychotic disorders from a study follow-up with a median of 25years (Kardakis et al., 2018). Still, currently, it is the only longitudinal proof available. Furthermore, different researches have proposed a positive impact from "jjimjilbang," a Korean sauna, and depletion of pain intensity in chronic situations like hypertension headaches. Considering the prevalence of unreliable reports on the association between improved mental health and sauna, this is a good investigation line that needs enough attention from worldwide scientific research, most especially in the light of current positive results regarding the application of whole-body hyperthermia (WBH) to reduce primary depressive disorder (Kardakis et al., 2018). WBH requires the application of sustained heat for between 1-2 h to increase the body temperature and other times through a machine that heats in the tent that protects the body.
An earlier uncontrolled review discovered that a single session of WBH lowers depressive signs in people suffering from depression. Therefore, researchers find whether this impact would overshadow a fiction control condition- a complement method that does not require heat. Researchers examined a sole acute treatment in seven weeks, randomised, twin-blind review having 30 adults with primary depressive disorder (MDD) (Kardakis et al., 2018). The findings showed that compared to the sham group (copying all characters except the heat intensity), only a single WBH therapy treatment revealed significantly lower depression scores that remained constant for a 6-week post-intervention study period.
Water
Water as a domain summary the factors related to the effects of direct water consumption and subjection to water like physical activities that are water-based, balneotherapy (disease treatment by showering in natural springs water, and use of general hydrotherapy. Every mammal needs water for survival, where the human body comprises 60% water (Descilo et al., 2010). Apart from the benefits of being hydrated for an intracellular function, proper electrolyte balance, and extracellular communication, there are various cognitive and mood effects of dehydration. Mild and moderate dehydration can lead to headaches, dry mouth, dizziness, and rapid heartbeat. While, acute dehydration can result in life-threatening medical attention, which can alter a person's mental state (Descilo et al., 2010). Researchers conducted novel research analysing mild dehydration (that occurs due to moderate exercise) on thirty females with good health concerning the mental health impacts. The participants managed three 8-h, placebo-controlled activities requiring various hydration conditions (regarding the diuretic-induced situation or exercise). During the experiments, most cognition aspects did not feel any impact. However, the significant effects at 1.36% reveal a reduction in mood, but increased the view of task difficulty, reducing concentration and increasing headache symptoms (Descilo et al., 2010). It is related to dehydration levels when at moderate, but various studies will force the body beyond 1.50% dehydration because of increased adverse outcomes.
Apparently, in many cultures, the therapeutic use of water is evident, mainly in the natural springs water spa in hot springs. A study comparing paroxetine in treating common anxiety disorder and balneotherapy (a cultural practice for immersing a subject in natural springs, mineral water, or mud) in spa resorts confirmed a significant spa treatment advantage the anxiety scales (Descilo et al., 2010). Those treated with balneotherapy showed remission and higher sustained response rates. Compared to the muscle-relaxation method used for stress relaxation, short-term balneotherapy is better when provided with a higher subjective rating when healthy participants relax. Another study was also crucial in lowering salivary cortisol.
Apart from acting as a stress reliever, balneotherapy has proven to enhance life quality and improve chronic pain symptoms of patients with fibromyalgia (a condition associated with widespread pain all over the body, mental distress, sleep disorder, and fatigue). A one-week study done at the Dead Sea showed significant improvements in participants' happiness and general health measures (Descilo et al., 2010). Balneotherapy also has positive impacts on fibromyalgia patients. Three-week treatments on fibromyalgia patients on balneotherapy produce substantial progress on the consequence measures that include depression, pain, quality of life, stress, and other fibromyalgia impacts (Descilo et al., 2010). From both the studies, a follow-up investigation confirmed physical improvements for more than four months on average. However, short-term psychological gains from both the research suggest the advantages of constant balneotherapy in controlling fibromyalgia. The traditional application of modern steam rooms also gives a great therapeutic interface with water and heat.
While the in-depth water exploration-based its physical activities aside from the auspices of this analysis, a few novels use of intensive water-based activities are worthless. Recently, a study analysed Deptherapy, a United Kingdom-based charity that gives a scuba diving experience to support military veterans who had life-changing injuries from the wars (Streeter et al, 2010). The study examined fifteen male veterans in an uncontrolled form retrospectively and prospectively on a scale of quantitative consequences of the mental health and functional capabilities impacts. The veteran participants recorded an improvement on a scale of psychosocial health, depression, insomnia reduction, and enhancements of anxiety levels. Various studies have suggested that a combination of scuba and medication may positively impact these veterans (Streeter et al, 2010). Researchers further suggest that for injured veterans, this activity helps them, especially when underwater, as they will feel they are weightless. The researchers concluded that scuba diving could benefit injured veterans as it helps them in chronic pain relief and stress alleviation. Surf therapy is another water-based application that has worked to enhance participants' health (Streeter et al, 2010). It is a form of adventure, especially for young people who have not healed from other forms of therapy. However, this form of therapy gives a range of additional advantages (apart from direct impacts from immersion in water) involving escalated atelic skill development and increased mindfulness, general physical activity, and sunlight and fresh air exposure (Streeter et al, 2010). Researchers have confirmed that surf therapy effectively treats conditions such as suicidal thoughts, depression, and anxiety. Researchers are still conducting more research on modalities and mechanisms that can enhance the treatment of mental illness.
Surprisingly most people do not know that dehydration and anxiety are related. Inadequate water in the brain changes how one response to stressful situations. Conversely, having a sufficient water supply in the body keeps your body in good shape and free from mental health issues (Streeter et al, 2010). Even though more study is needed on the relationship between water and stress, current research suggests that staying hydrated help reduce stress.
Air
The domain is under the factors related to the impacts of direct subjection to fresh air, effective and conscious breathing, some exercises involving breathing (for example, yoga, also known as pranayama). We can achieve this through constant breathing-focused biofeedback methods. These techniques can help in reducing perceived stress and anxiety. For example, controlling natural breathing coordinates the electrical activity in the human piriform (olfactory) cortex and regulates limbic-related areas in the brain (the areas include hippocampus and amygdala, which are the main areas in the brain affected with stress, anxiety, and memory (Lim et al., 2012).
One main recognised environmental factor affecting physical health includes constant subjection to air pollution, a common problem in the modern world—increased exposure to air pollution associated with possible effects on the central nervous system (Lim et al., 2012). For example, a longitudinal study of 600 elderly Koreans found that constant exposure to air pollution increases depressive symptoms. Furthermore, a cross-sectional study suggests that smoke from second-hand cigarettes relates to the escalating depressive symptoms, especially in smoking naïve people. Still, after several adjustments to the demographic range, the findings were the same (Lim et al., 2012).
As per the World Health Organization, for every ten people, nine inhale polluted air, resulting in more than seven million deaths annually. Studies have associated the adverse constant air pollution with respiratory issues, neurovascular, cardiovascular diseases. New preclinical proof states that air pollution may lead to microglial activation, cerebrovascular dysfunction, and neuroinflammation (Caddick, Smith & Phoenix, 2015). The effects can also lead to altering the blood-brain barrier. Air pollution can also lead to devastating impacts on mental health. Most population in the world lives in areas where air pollution is more than the required from WHO guidelines (Caddick, Smith & Phoenix, 2015). A study model using a mouse as the subject investigated an extended period (one year) of exposure to filtered air and fine ambient airborne material particulate impacted stress-related animal behaviour and mental responses (Caddick, Smith & Phoenix, 2015). Findings collected confirmed that mice subjected to long periods of air pollution showed more stress-like impairment and responses in longitudinal learning and memory when contrasted with the second group subjected to filtered air.
The kind of air we inhale and the way we inhale it can influence our well-being and health. While dysfunctional and functional inhalation is hard to define, dysfunctional breathing is a term explaining breathing difficulties that include irregular, shallow, restricted, or rapid breathing. Effects of dysfunctional breathing include a range of psychological and physical health conditions. Mainly, people recognise dysfunctional breathing as a symptom of anxiety or depression (Caddick, Smith & Phoenix, 2015). People with chronic breathing problems have a high correspondence with anxiety and depression.
Patients with medical conditions in the United States gave reported Breath regulation techniques (BRTs) and Mindful breath awareness (MBA) as one of the most used mind and body therapy. It is also the second most applied complementary approach (second after all, the natural dietary substitutes combined with these methods). Therapists mostly use MBA and BRT as complementary and psychological treatments for mental health issues, including mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT), cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT), and general mind-body practices (Matzer et al., 2014). The standard mind-body practices include Taiichi, yoga, relaxation training, qigong, relaxation training, and mindfulness, among other forms of meditation. Researchers have conducted an assessment on all these clinical studies and suggested various reviews.
Clinical examinations that have emphasized BRTs as a direct intercession for common mental health issues are breathing exercises for yoga. BRTs and MBA are essential to various features of yoga exercise. For instance, yoga participants do the yoga postures with a combination of MBA and breath coordination movements (Matzer et al., 2014). Specifically, pranayama, a yoga BRT, meditation methods, and relaxation techniques mainly apply breath to focus and relax the mind. These techniques also help keep the body in shape, lower blood pressure and relieve depression. In addition, breath is one of the best powerful tools against stress.
Various clinical studies have confirmed yoga BRT is effective in lowering the intensity of depression symptoms. One randomized control trial applying a yoga BRTs method, a technique called Sudarshan Kriya Yoga (SKY), confirmed that the technique is similarly effective as the electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) and a primary prescribed drug (imipramine) which is a pharmacological antidepressant for depression mostly patients take it for a whole month (de Manincor et al., 2016). Other assessments applying identical yoga BRTs techniques discovered decreased depression symptoms in participants who consumed alcohol after a detox program. Other impacts included reducing depression symptoms in traumatic survivors and decreasing posttraumatic stress (PTS). Most current research that applies MBA into various yoga features has discovered advantages for reducing anxiety and depression symptoms and improving the general health of the participants (Descilo et al., 2010). Colleagues and Streeter have also found primary proof that yoga practices that are breath centred increase gamma amino-butyric acid (GABA) brain levels related to depression symptoms.
Some researchers have assumed that neurophysiological methods discuss the advantages of breath-centred yoga exercises in various ways and primarily comorbid medical states. The medical conditions include mental health issues founded on the idea and proof that yoga exercise decreases the allostatic load in stressful situations and rejuvenates body balance and homeostasis in the human system (Lim et al., 2012). These researchers hypothesise that breath-centred yoga exercises help correct reduced activity of the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) by stimulating the vague nerves and the primary peripheral way of the PNS. The breath-centred yoga activities also helped raise the reduced GABA levels and decrease the allostatic burden of stress. PTS, anxiety, chronic pain, depression demonstrate mental and medical conditions that arise from stress have low heart rate variability (HVR) and reduced GABA energetic activity (Tarlaci, 2010).
Consequently, reactions to pharmacological agents that raise actions of the GABA system have shown the development of depressive symptoms in response to breath-centred yoga exercises. Current studies state that depression issues represent stress disorders. Future studies should cover the gaps in explaining and opening ways to develop an antidepressant treatment to work and correct underlying neurochemical imbalances and not just depression symptoms.
2.4 Possible routes of depression
2.4.1 Etiology of Depressive disorder
An intricate course of biological related procedures has been embroiled with regard to the etiology and the phenomenon involved during the depressive disorder. However, such research had not generally explained whether such procedures are fundamental causal variables, connects, or results of despondency. The pathways are interrelated with several components of hereditary vulnerabilities, structure and function of the brain, neuroendocrine and neurotransmitter involved procedures and the pathways involved in relation to the immunological mechanism. Moreover, it has been also observed that considerable progress have been made in the individual following aspects such as environmental factors, individual factors and the related biological factors that give expanded hazard for despondency. Considering the heterogeneity of the depressive disorder, it is not amazing that the exploration of investigation till date has neglected to join on a solitary arrangement of the biological phenomenon that is identified with the beginning and course of depression. Be that as it may, there are several scientific evidences that are related to cerebrum, the central and peripheral nervous system (Saveanu and Nemeroff, 2012).
2.4.1.1The time process and the phenomenon of depression
Time of beginning of significant depression in association to age may have both clinical and etiological ramifications. According to clinical observations, prior time of beginning is related with a more terrible course of despondency with more prominent odds of repeat, chronicity, and destruction. Moreover, with regard to etiological factors, first beginning of depression at various ages for instance during childhood, immature, grown-up and more seasoned grown-up may reflect to some degree distinctive causal components. It has been also observed that several people may encounter a solitary significant episode of major depressive disorder following an intense stressor and recuperate with little ramifications for future powerlessness. Unfortunately it has been also observed that among several people of around 50–80 percent who had suffered from one major episode of the disorder will have repetitive scenes and frequent subclinical symptomatic manifestations with the danger of repeat dynamically expanding with every scene of significant episodes (Saveanu and Nemeroff, 2012).
The prognosis of depressive disorder at the phase of childhood is comparatively uncommon; though numerous cases had been observed among several preadolescents including preschoolers have huge disguising manifestations of dysphoria and misery. In general, maximum analyzed forms of depression initially show up among the populace of youth and early adulthood particularly among those conceived in later decades. For instance, when several investigations was conducted within the populace of community, up to 33% of youths met standards for the clinical consideration of major depressive disorder (MDD). The age of the individual with the first beginning phase of the disorder, has both etiological and clinical implications. Similarly diagnosed cases of depressions with immature beginning among the populace of youths incorporates a critical extent among both the groups of treatment and community diagnosed individuals who are more likely to suffer from intermittent scenes and with high chances of relapse (Saveanu and Nemeroff, 2012). The depressive phenomenon in the phase of childhood is considered to be a blend of subgroups:
- Individuals with genuine hereditarily familial beginning stage for the repetitive episodes of depression;
- Individuals who are presented to noteworthy psychosocial harassment, for example, misuse, parental abuse, culpability, and family disturbance who keep on encountering social maladjustment and other issue in their life from early childhood, however not turned up into depressive condition into adulthood and
- Individuals with inevitable bipolar disorders.
The beginning phase of depression among the adult populace is significant for a few variables. The first significant reason is that expanding paces of depression among adolescent groups as of late infer, in addition to other parameters, that the etiology is considerably psychosocial, with noteworthy social moves in ongoing decades that have made upsetting encounters and diminished assets had added to the onset depressive encounters. Another issue is the gigantic difference in paces of disorder among the young ladies and men with respect to the initial symptomatic manifestations of the disorder. The sensational increments of the phenomenon among the young ladies showing prominent contrast with regard to the pace observed among young men obviously demands investigations based on etiological models that can clarify the basics of such contrasts. For instance, various models accentuate hereditary, hormonal, stress introduction and stress forms, social molding of qualities and vulnerabilities, and adapting techniques based on sexual orientation (Saveanu and Nemeroff, 2012).
Perinatal Depression
The stages of childbearing years among several women during the phase of pregnancy specifically, have pulled in unique consideration as for the event of depression and about its latent capacity impacting the development of the baby. It has been observed that a majority of ladies experiences mellow "blues" following the parturition of a newborn child (Brummelte, and Galea, 2016). Moreover, somewhere in the range of 10 and 20 percent of new mothers experience the clinical symptomatic manifestations of depressive disorder that may lasts from few numbers of weeks to a year. Comparatively to a lesser degree under 0.5 percent, experience intense episodes of psychosis related with the depression. An enormous scope epidemiological review conducted currently had analyzed paces of the mood swings and depression among ladies who are not pregnant in contrast to past-year pregnant ladies and highlighted in their findings that hardly any distinctions in general in state of mind had been observed among the study populace of both categories (Vesga-Lopez et al., 2008). Moreover it should be taken into consideration as stated by the researchers of the study that the paces of major depressive disorder were comparatively much higher among ladies who have given birth in contrast to ladies who were not pregnant. For all ladies pregnant in the previous year, their phase of depression was related with factors for instance not being hitched, suffered significantly due to any emotional trauma and unpleasant life occasions in the previous year, and also due to poor health. However, a woman experiencing the sensational hormonal changes during and after pregnancy has concentrated as the significant reason behind hormonal and biological etiological components of post birth depression. Among the other parameters in addition to biological risk factors for depression, the other factors such as stress of the society, the members and the attitude of the family, degree of support obtained from the society and family, worse economic status of the individual all might act as trigger factors for depression. Although the studies related to post partum depression is scarce, there are some studies that had reported about the episodes of depression among fathers but not as high as reported among new mothers. In this regard, it must be mentioned about the study findings of Paulson, et al, 2006 who conducted study on depression among two parents household and recruiting samples based on randomized control trials with about 5000 families. The study findings highlighted about the paces of depression of about 14% among mothers and 10% among fathers. The expanded level of symptoms of depression following the birth of a baby is related to factors such as considerable amount of adjustment in day to day life that enhances the level of stress. Therefore, the worth of the relationship of the mother with her child and the association of depressive disorder acts as causal factors for elevated level of depression among new fathers (Brummelte, and Galea, 2016).
2.4.1.3Biological factors in association with depression
The biological factors include endocrine, neurological, immunological and both combined factors for neuro and hormonal known as neuroendocrinological factor. These factors play a significant role in the process of advancement of severe category of depression and this are in well association with stress and psychological processing of data. The related etiologies are developmental factors and gender of the individual (Lohoff, 2010).
Hereditary factor
It should be taken into consideration that depression is significantly associated with gene or hereditary structure of family. An audit of twin investigations reported that around 33% of the risk probabilities for MDD among grown-ups are acquired due to hereditary contrasts among people. This figure is considerably lower than for some other mental issue, for example, schizophrenia or bipolar issue. Therefore, the danger of acquiring MDD increments about 2.5 to multiple times for the individuals who have a relative of first degree with similar incidence of depression, while having a profound threat to life with regard to episode relapse chance from five to sixteen or multiple times in a couple of months after the first episode. Hereditary impacts get altered due to sexual orientation and formative stages, and they show their impact upon the internal physiological state and mental attributes as well as the categorization of the individual's response towards their environment. A few hereditary polymorphisms have been connected to expanded danger of depression with regard to strain. The principal role among these is played by the serotonin framework (5-HT). This is because, the serotonin, a neurotransmitter applies impacts on an expansive scope of physiological capacities, for example, feelings, rest, circadian rhythm, thermoregulation, hunger, animosity, sexual conduct, torment affectability, and sensorimotor reactivity (Stuart-Parrigon and Stuart, 2014). Shortfalls in the focal 5-HT framework, for example, diminished 5-HT focuses, hindered take-up capacity of the 5-HT transporter, modified binding with 5-HT receptor, and exhaustion of tryptophan, have been considered to be connected with various mental issues and psychological disorders specifically with depression. The findings of several studies regarding the functioning of serotonin framework and associated polymorphism had highlighted that this system is related to transformation of the data with regard to psychological threat. This study is a decent choice with respect to evaluation of neurobiological mechanism operation during strained environmental conditions among the depressed individuals (Lohoff, 2010).
Functioning of the neuroendocrine system
Key parts of the neuroendocrine system are the HPA axis, locus coeruleus-norepinephrine (LC-NE) frameworks and the related corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH), which incorporates limbic and cortical pathways interconnected bidirectionally through different hormonal routes and neurotransmitter. The essential glucocorticoid hormone is cortisol, which triggers a course of capacities that are versatile in the intense periods of reaction in response to stress and which regularly resolve rapidly through inhibitory criticism forms in the HPA pivot. Depression has been connected with raised concentration of cortisol and related neurohormones (Penninx, et al. 2013). Various examinations have demonstrated more significant levels of cortisol and variations from the norm in cortisol regulations among individuals who are depressed in contrast to people who are not suffering from depression. Moreover, patients suffering from depression demonstrate more slow recuperation of cortisol levels because of psychological strain in comparison to control group (Burke et al., 2005). People who show irregular regulation of cortisol considerably even after treatment are bound to backslide and for the most part have a more unfortunate clinical forecast than patients whose cortisol level came back to typical after treatment. Apparently supported hypercortisolism harms the emotional framework, eventually resulting in the demise of cells in hippocampus region with summed up impacts on the circuits responsible for basic regulation of feeling. Several evidences are available with regard to GR polymorphisms related with expanded danger of acquiring significant episodes of MDD (van Rossum et al., 2006) and contrasts can also be observed with regard to treatment for depressive disorder.
Immunological System in relation to Depression
Several studies on current models had recommended that incessant pressure enacts the immunological system in such a way that it prompts aggravation, and that interminable irritation thus prompts side effects of depression. In spite of the fact that the subjects of these impacts are yet to be unraveled, proof demonstrates that incessant pressure is related with expanded degrees of both depression and C Reactive Protein (CRP). Levels of Interleukin (IL)-6 and CRP are raised in people presented to incessant stress (Slavich, and Irwin, 2014). The provocative response may likewise add to indications of depression by activating sickness in conduct, disturbances for hunger drive, social action and rest. On the other hand, depression might be associated with inciting the physiological process of inflammation. A current meta-examination reported about three causal models: depression to the process of inflammation, inflammation to depression and bidirectional affiliations (Howren, Lamkin, and Suls, 2009). Further research utilizing imminent longitudinal structures is expected to explain the causal associations among stress, inflammation and depression.
Environmental and Individual trigger factors
The models for etiology are in association with depression are to a great extent considered to be “diathesis-stress” models which highlights the fact that upsetting encounters acts as a trigger factor for the onset of depression among individuals as those are thought to be more susceptible because of psychosocial and biological attributes and conditions (Saveanu and Nemeroff, 2012).
The stressors related to environment, in association with the depressive disorder incorporate intense life occasions, interminable pressure, and revelation to vulnerability at the childhood phase. Moreover, the trigger factors for individual related with depression incorporate intellectual, relational, and character factors. These varied forms of environmental, biological and individual vulnerabilities in combination add to the advancement of depression and furthermore might be influenced by state of depression as happens in a bidirectional procedure.
The other psychological disorders that are associated with depression include addiction disorder, anxiety, personality and conduct disorder in relation with other associated clinical issues. The association of other psychological disorders along with depression makes the treatment management more difficult (Saveanu and Nemeroff, 2012).
Protective or resilience factors
The protective factor is the parameter that is associated with the environment or individual with regard to the decreased chance of acquiring depression whereas the resilience factor is referred as the process where an individual is able to overcome the hazard factor and the associated adverse outcomes which helps them to achieve the positive outcomes. These factors may include the biological, environmental and the psychological factors for instance, warm attachment between among family adults and connection between them, positive personality characteristics, caring attitude of adults towards their children, proper development of cognitive function and intelligence level, achievements and motivations at schools and community level and certain neurochemical, neurohormone and peptides (Saveanu and Nemeroff, 2012).
When depression is treated in primary care, it usually goes underdiagnosed, undetected, and undertreated. The continuous undertaking of such activities leads to clinically caused depression be on the rise. Despite those who aim to cap its effect, they cause further harm while achieving the patients' general well-being (Katon et al., 2002). Men, older adults, patients who come from minority communities, and those patients with medical comorbidities are at a higher risk of their depression not being detected or not effectively attended, resulting in more harm. Despite those in the clinical practice being attentive in their activities, they find it challenging to achieve the end goal effectively (Katon et al., 2002). The national mental health task force recommended a need for healthcare professionals in primary care to ensure they undertake routine diagnosis of adult patients. In a clinical setup where systems have been developed to provide effective treatment of patients, the depression treatment must be included as it will help ensure the patients' general well-being
There are brief methods through which screening of depression can take place. Asking simple questions like whether the patient often feels depressed or sad, and the patient will answer by either indicating yes or no. One of the medically ill patients is tested within any community. There is a sensitivity percentage of 70% and specificity of 90%; this is based on the answers obtained from the patients. The Patient Health Questionaire-2 (PHQ-2) has two questions that ask about the mood of depression (Katon et al., 2002). One of the questions is whether the patient has often been bothered with his depression, feeling down, or any form of hopelessness in the past weeks. Another question is whether the patient has been concerned with the pleasure of doing this or little interest in the past months. Undertaking such short screenings will enable healthcare staff to understand the state of patients when they come to seek primary care service (Katon et al., 2002). However, because the clinical practice has been split into various sectors, it is difficult for depression to be detected. For patients with Such brief screening tools, office staff or physicians can easily administer such brief screening tools during a primary care visit. Through the positive responses to the questionnaires, the healthcare providers can evaluate depression in a patient and provide the necessary support. However, some patients will not respond positively to address the negative responses; it could be necessary if the clinicians could ask other additional questions to bring out the possibility of depression (Katon et al., 2002). Also, it could be essential if the clinicians could engage in care or functional impairment that may seem to be inconsistent with the objectives of the medical illness.
3. Treatment of Depression
3.1 Frontline treatment for depressive disorder
3.1.1 Diagnostic criteria
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is characterized by the experience of miserable state of mind or anhedonia (lost intrigue or joy) persevering almost throughout the day, consistently for in any event fourteen days, which recognizes it from an intermittent dismal disposition or absence of intrigue that goes on for a couple of hours or days. For a conclusion, four extra manifestations are required, including weight reduction or increase; rest disturbances; easing back down or accelerating of physical developments; weariness or loss of vitality; considerations of uselessness; trouble with dynamic; and intermittent contemplations of death or self destruction. Manifestations should cause noteworthy trouble or weakness at the time of working and ought not to be inferable from tranquilize misuse, prescription changes, or ailments (for instance hypothyroidism). People with MDD may likewise encounter somatisation, huge nervousness, and even psychosis; it builds the danger of self destruction and mortality related with other clinical and mental conditions (Mitchell, Vaze, and Rao, 2009).
Clinical introduction presents noteworthy diagnosis since people do not encounter any different symptomatic manifestations. In addition to seriousness side effect, recurrence, and length can vary across people and vacillate after some time in a similar person. Some may have exceptionally diligent manifestations that do not dispatch over a significant stretch of time, and others may have numerous long periods of reduction of symptomatically signs between discrete scenes (Gotlib, Lewinsohn, and Seeley, 1995). For the most part two out of five individuals with MDD start to recuperate inside a quarter of a year of beginning; recuperation starts inside one year of beginning for four out of five individuals. The more drawn out the phase of the episode of depressive disorder, the more extended time will be required for recuperation. The category of gentle to moderate manifestations during a time of depressive disorder recuperation is an incredible indicator of whether MDD will happen once more. Additionally a few perceived subtypes of despondency may require explicit treatment, including psychotic depression (visualizations or potentially hallucinations that happen just with regards to the depressive scene) and atypical depression (typical or overstated disposition reactivity and frequently altogether expanded rest and craving) (Mitchell, Vaze, and Rao, 2009).
The national health service (NHS) has approved some treatments that can treat depression depending on the different levels. However, though medical approaches are part of the approved methods, it has not proved effective compared to pf psychotherapies. Due to these reasons, sometimes quantum medicine has not been the best approach for treating depression. Instead, under other circumstances, there have been cases where the rate has risen instead of decreasing. Psychotherapies have shown strong evidence that they can deliver mental health care and primary care for people with depression (Katon et al., 2002). If incorporated into clinical practice, it could be the best approach through which dealing with depression can be accessible in the primary care and the healthcare sector in general. Evidence-based approaches have indicated that treatment of depression can use both pharmacological approach and nonpharmacological options to ensure different aspects of depression are addressed (Katon et al., 2002). However, pharmacological sometimes leads to increased levels of depression because they do not accommodate the fundamental factors that affect patients. Where nonpharmacologic treatment approaches are used, it could be necessary if the PCPs ask patients about those who initiated the treatment and why the mode was preferred. Also, they should inquire why psychotherapy approaches are not part or part of the depression because they are why depression is treated in a patient (Katon et al., 2002). Tracking depression rating scales through the patients’ clinical outcomes, like looking into the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), is essential to give a pointer on what should be done. Also, it could be crucial if primary care provides could keenly consider clinical outcomes in the treatment processes and relate them to factors like blood lipids and blood pressure to ensure the safety of the patients. Any treatment adjusted should be done systematically on the patient and aim to improve the initial conditions. Therefore, approaching the medication should always depend on the evidence and psychotherapies that would increase the general quality of life for the patients (Katon et al., 2002). When providing any form of treatment, it could be essential to understand the previous conditions that the patient has gone through and the levels that his/her depression levels are to ensure effectiveness.
For effective depression management to take place in primary care, some steps need to be followed. They are as follows; diagnosis and detection, engagement in treatments and patient education, initiating evidence-based pharmacotherapy or psychotherapy, monitor and focus on ensuring that the treatment is adhered to, evaluate the treatment’s effectiveness, lastly check on the side effects that arise (Katon et al., 2002). However, because most primary care institutions do not engage in mental health services, they find it challenging to adhere to the treatment requirements. Patients respond to various treatments at different levels; treatment trials for depression have shown that specialty care and primary care setups indicate that initial costs are between 30-50% effective. This does not depend on the kind of treatment that has been selected. However, there is an improvement that happens as patients continually adjust and healthcare professionals give them better attention (Katon et al., 2002).
Usually, when patients seek medical attention, the information found is scanty and cannot be used to select the best treatment. However, considering the history of the patient and his family would play a significant role in helping to get the best treatment approach (Katon et al., 2002). However, in the initial process of selecting the treatment plan, clinicians must use the existing guidelines while considering the patient’s treatment history as it will assist in arriving at the best decision. They should always strive to ensure that they adjust and intensify the treatment to improve its efficiency if the initial treatment fails to work as they had planned. Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression (STAR-D) data on trials indicate that most patients fail to respond to the initial medication effectively but improve with continuous adjustments that healthcare professionals prescribe (Katon et al., 2002). Some of the things that will enhance include agents, doses, and the kind of treatment used for the patient. Those patients indicating severe depression levels should be recommended to receive advanced treatment. At this stage, they would be advised to visit specialty mental health services where additional and advanced treatments may be undertaken. Despite all these, treatment will generally depend on the response that those in the healthcare sector will give to patients.
3.1.2 First line psychotherapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) assesses, challenges, and adjusts useless considerations that continue during the phase of depression. Interventions related to behavioural therapies are likewise used to increment charming exercises to treat anhedonia. CBT can be directed in individual or gathering positions. It is for shorter time span (for instance 20 meetings) and issue centred. The most read psychotherapy for despondency; CBT has the biggest load of proof for its adequacy (Carter, McIntosh, Jordan, Porter, Frampton, and Joyce, 2013).
Supportive form of therapy is the underlying treatment for youth with brief, mellow form of depression without self-destructive approach or psychosis. Treatment proceeds for up to 8 meetings until abatement. Supportive psychotherapy incorporates, however is not restricted to, undivided attention and reflection, rebuilding of expectation, critical thinking, adapting aptitudes, and systems for keeping up cooperation in treatment, psychoeducation, and family and school inclusion (Luty, Carter, McKenzie, Rae, Frampton, Mulder, and Joyce, 2007).
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is viable as a single therapy with regard to despondency during youth. CBT centers on distinguishing subjective bends that may prompt discouraged state of mind and furthermore uses issue - unravelling conduct actuation and feeling guideline abilities to help oversee and battle with the depressed state of mind. Psychotherapies that meet standards as proof based medicines for geriatric gloom incorporate CBT, social treatment, subjective bibliotherapy, critical thinking treatment, short period psychodynamic treatment, and memory treatment (Carter, McIntosh, Jordan, Porter, Frampton, and Joyce, 2013).
Subtleties of note:
• Individual treatment is regularly more powerful than within gathering.
• Effect size is by all account large for clinician-diagnosed despondency than self-evaluated depression.
• Elder adult age is related with lower viability (yet at the same time viable) (Carter, McIntosh, Jordan, Porter, Frampton, and Joyce, 2013).
Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) has demonstrated successful approach for treating paediatric form of despondency; concentrating on helping people showing declination in relational clashes by showing them relational critical thinking abilities and helping them change correspondence designs. Psychotherapy is by all accounts progressively compelling for youth ages within 12 to 18 years (Luty, Carter, McKenzie, Rae, Frampton, Mulder, and Joyce, 2007).
Problem-solving therapy (PST) instructs to characterize individual issues, build up various arrangements, distinguish the best one and execute it, at that point evaluate its adequacy. A moderate proof base, yet demonstrated to be successful for moderate form of despondency. Examination demonstrates that these medicines are reliably more successful than hold up list or other negligible contact medicines. Meta-examinations that look at the viability of CBT, IPT, and PST demonstrate no huge contrasts in adequacy between these medicines (Luty, Carter, McKenzie, Rae, Frampton, Mulder, and Joyce, 2007).
3.1.3 First line pharmacotherapy
Antidepressant medication determination ought to be individualized dependent on clinical components, including profile of adverse reactions, co morbidity, bearableness profile, past reaction, potential medication sedate collaborations, persistent inclination, and cost. No antidepressant medication has been plainly demonstrated to be better than another; all FDA-endorsed antidepressant drugs ought to be considered conceivably suitable for first-line treatment (Sewitch, Bexton, Rahme, Galarneau, and Blais, 2009).
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), bupropion, mirtazapine, and a few more up to date medications are commonly utilized as first-line prescriptions in light of the fact that their security and bearableness might be desirable over patients and clinicians contrasted with those of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) (Alexopoulos, 2011).
Mirtazapine and other blended objective drugs can be especially valuable in cases of depressive disorder related with sleep deprivation and weight reduction because of reactions of sedation and expanded hunger. Bupropion's blended impacts on monoamines (counting dopamine) might be useful for patients with dormancy and expanded craving (Alexopoulos, 2011). Bupropion has likewise indicated guarantee for issues like lack of ability to concentrate consistently, clutter, nicotine compulsion and a few appetitive issue. Youth with moderate to extreme form of depression could be contended for pharmacologic treatment. (In gentle cases, psychotherapy might be viewed as first-line treatment.) Fluoxetine and escitalopram are the main FDA-affirmed antidepressants for youths; fluoxetine is the main FDA-endorsed antidepressant medication for young people. Different SSRIs (sertraline or fluvoxamine) are frequently recommended dependent on comorbidities, symptom profiles, and individual or family ancestry of reaction to a particular drug. Paroxetine is infrequently utilized for the paediatrics cases; absence of information shows viability and generally higher symptom trouble (Sewitch, Bexton, Rahme, Galarneau, and Blais, 2009).
Around 66% of patients demonstrating serious forms of depression might react to stimulant treatment. Be that as it may, more established depressed individuals are especially powerless against the antidepressant medications, particularly cardiovascular and anticholinergic symptoms, which can bargain consistence and adequacy. A 2006 Cochrane audit did not bolster any one medication class as more viable than another; however TCAs were less very much endured (Flint, and Rifat, 2001).
A general guideline: Start low, go moderate, and stand by longer for adequacy. More seasoned grown-ups frequently require indistinguishable medication dosages from for more youthful grown-ups (Alexopoulos, 2011).
Particular serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), tricyclic antidepressants, and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are proof based. The reaction profile of SSRIs is likely best; fluoxetine is less perfect because of its long half-life (in case any prescription changes are required), as is paroxetine because of anticholinergic attributes and prominent medication tranquilize associations. Reaction profiles and drug or clinical ailment associations are a specific worry that ought to be inspected cautiously (Flint, and Rifat, 2001).
Depression treatment has got various challenges, and the more those concerned address various negative concerns, the more improved the quality will be. Research condition of various types of treatments and what occurs in the actual implementation of the treatment poses a significant gap, especially in primary care (Unutzer et al., 2008). Though many treatments have proven effective in treating depression, studies in the U.K. have indicated that patients do not receive adequate treatments that can lead to comprehensive healing. Over 10 million people in the U.K. receive prescriptions for antidepressants yearly; primary care healthcare professionals usually give this. However, many patients have not been taking the medication consistently because they have side effects or some reservations (Unutzer et al., 2008). They do not take serious follow-ups with primary care providers in case a change of treatment is required. Since only a few patients have access to evidence-based psychotherapies under the primary care setup, you find several of them going through depression without any help. Also, there are circumstances under which patients have continuously taken inappropriate doses due to clinical inertia and lack effective treatment intervention because the initial treatments may not be working appropriately (Unutzer et al., 2008). Due to the little uptake, the small percentage of patients who have started their depression treatment at the primary care has shown significant improvement. Even at the specialty clinics, some patients have shown improvement in mental health despite patients having severe illness and received treatment that is more consistent with the required guidelines recommended for the whole process (Unutzer et al., 2008). The patients who get referrals to psychotherapy receive inadequate treatment trials, and their response rate may be low. However, the cost of treatment and lack of evidence-based psychotherapy are some barriers they have to overcome.
Challenges that face the primary care setup, like conflicting demands and time constraints, are the main barriers to the effective treatment of depression. Healthcare professionals always have limited time to train on diagnosing and treating depression and other forms of mental illness. However, it is good if the primary care institution provides treatment for depression patients because they may feel free to discuss family problems, emotional distress, and their behaviuoral problems (Unutzer et al., 2008). After all, the stigma found is related to mental health concerns and disorders where the PCPs may not seriously consider the health problems.
Efforts associated with improving and managing mental disorders and depression in primary care usually focus on educating primary care providers, screening, developing treatment guidelines, and referring patients to mental health specialists if they have advanced conditions. Despite the well-intended actions, they have not effectively addressed the burden of depression and other mental disorders handled at the primary care level. It could be important for mental health specialists to be co-located with other healthcare improvement activities and primary care (Unutzer et al., 2008). Primary care should have clinical social workers, psychologists, and psychiatrists on their premises to ensure patients receive complete guidance and diagnosis regarding mental health-related services. However, currently, it is hard to find a clinic where various health services are located, making clinical practices insufficient despite the struggle to ensure improved care outcomes (Unutzer et al., 2008).
3.1.4 First line blended treatment
Meta-investigations demonstrate that joining pharmacotherapy and CBT prompts better transient results, with little to medium-impacts sizes, contrasted with either treatment alone. A comparable example is watched for joining any psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy, in spite of the fact that the proof base is not sufficiently enormous to look at explicit psychotherapy medicines other than CBT. The mix of drugs and CBT has been demonstrated to be progressively strong in intense treatment of immature MDD than either single therapy in two enormous United States preliminaries. Accord rules prescribe psychotherapy as an adjunctive treatment to prescription in more established grown-ups (Kemmeren, van Schaik, Smit, Ruwaard, Rocha, Henriques, and Zukowska, 2019).
3.1.5 Adjunctive interventions
Physical activities intercessions treat despondency through steady and continuous exercise (e.g., 60 minutes, 3 times each week for 10 to 14 weeks); more successful than no treatment and not any more powerful than pharmacotherapy or psychotherapy. The quantity of great examinations is constrained. Electroconvulsive treatment (ECT) is a proof based mediation for extensive form of depression; utilized most much of the time among more seasoned people. Potential clinical confusions demonstrate alert is justified. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation might be considered more effective in this field (Veale, Le Fevre, Pantelis, De Souza, Mann, and Sargeant, 1992).
3.1.6 Complementary and alternative mode of interventions
Third-wave subjective and conduct treatments, which incorporate broadened social initiation, acknowledgment and commitment treatment, and serious memory preparing might be promising yet have a little proof base. More examinations are required, however internet and other modernized medicines hold guarantee as proof based medicines of depression (Freeman, Fava, Lake, Trivedi, Wisner, and Mischoulon, 2010).
3.1.7 Contraindications with the frontline treatment options
It is suggested patients taking antidepressants and SSRIs (particularly youthful grown-ups) be firmly observed by human services workers, family, and parental figures for forthcoming suicidality, antagonistic vibe, unsettling, lunacy, and bizarre changes in their conduct, particularly inside the initial period and not many long periods after the treatment or when measurements of medication dosage is balanced (Flint, and Rifat, 2001). It is also suggested that kids and young people taking antidepressants and SSRIs be firmly observed by medicinal services suppliers, family, and parental figures for developing the same symptomatic manifestations. CBTs should be adjusted (counting guardians, among different components), and conduct and intellectual social intercessions may improve temperament in right on time (and possibly moderate) phases of dementia (in both the patient and parental figures). Psychopharmacologically, SSRIs and different medications with no critical anticholinergic impacts are viewed as first-line medicines. Reactions related with tricyclics incorporate sedation, anticholinergic impacts (drying of mouth, obscured vision, obstruction in the passage of bowel, retention of urine, unsettling, disarray), cardiovascular impacts (tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, arrhythmias), prostatism, narrow scope of glaucoma and gaining weight. Reactions related with specific serotonin-reuptake inhibitors incorporate initiation, tremor, disturbance, dazedness, a sleeping disorder, queasiness, looseness of the bowels, issues related to sexual functioning, cerebral pain, hyponatraemia, weight reduction and rash. Hyponatraemia is an uncommon yet conceivably genuine unfavourable impact of antidepressants. Healthcare service workers may presume hyponatraemia if patients create disarray, laziness, muscle spasms, queasiness and seizures. On the off chance that hyponatraemia happens and then healthcare providers need to stop the usage of antidepressants immediately. Tricyclics are related with higher paces of unfavourable impacts than specific serotonin-reuptake inhibitors, however the thing that matters is little and of unsure clinical hugeness. Reactions will in general lessen after some time, apart from the gain in weight and dysfunctioning of the sexual system that may continue longer than the other symptoms. Health care practitioners should stop treatment step by step, as antidepressants can cause resurge of the associated side effects. Withdrawal manifestations incorporate uneasiness, disturbance, a sleeping disorder, tremor, tipsiness, paraesthesia, emotional episode and rhinitis. These adverse reactions are often noticed with medications having a short half life, for example, paroxetine (Latendresse, Elmore, and Deneris, 2017).
Treatment for the depressive disorder can include a blend of way of life changes, talking treatments and medication. Talking treatments, for instance the cognitive behavioural therapies (CBT), are regularly utilized for mild or moderate forms of chronic depression, for which the symptomatic manifestations are not alleviating. Antidepressants are additionally prescribed in some cases. For cases of moderate to serious forms of depression, a blend of talking treatment and antidepressants is frequently suggested. In the event that anyone is having a serious despondency, they might be eluded to an expert psychological wellness group for intense behavioural therapies along with recommended medicines. Several individuals suffering from depression gets benefitted by making way of life changes, for example, getting more exercise, eliminating the habit of liquor consumption, quitting the habit of smoking and up taking healthy diet regimen. Moreover, it had been also observed that going through a self improvement guide along with joining a care group are additionally advantageous for the individuals suffering from the pangs of depression. These measures assist those individuals with increased superior comprehension about what makes them feel discouraged and also imparting their encounters to others in a comparative circumstance can likewise bring steadiness in their thought process (NHS Digital, 2019).
3.2 The approach of quantum medicine
The approach of quantum medicine is considered to be a budding technology in the field of medical science and this thought is considered to be under the branch of complementary or alternative forms of medicine. The essential concept behind the treatment approach is that body of every human being comprises the flow of electromagnetic radiations within and outside the body and this play a major role for the associated changes in mental, physical and chemical areas. The treatment benefits from the low dosage electromagnetic radiations that interact with the organs of the body. This fundamental approach is considered to be very new in the branch of medicine (Chopra, 2015).
By connecting material science and the biological science behind the living creatures would nowadays can be considered as powerful active procedures continued by an endless progression of vitality, substance or matter and data inside certain space-time quanta characterized as morphogenetic fields (Yanick, 2002). Life is not considered to be within harmony process or in the state of equilibrium which is depicted as dissipative structure. An increasingly unique definition or hypothesis supplanted the old static idea of homeostasis and the procedure meant to keep solidness through the incorporation of powerful changes which as of late has been characterized as allostasis. Allostatic load is the measurement of the exertion because of the aggregate sum of pressure or stress the entire framework needs to adapt to keep up the process of allostasis. Allostasis lead to fortify the potential for wellbeing toward salutogenesis while allostatic load lead to a reduction of potential for wellbeing toward pathogenesis. Allostasis and allostaic load are in a unique relationship which can be termed as dynamic as a declaration of the progression of data because of versatile elements (Yanick, 2002). Therefore wellbeing and illness could be better comprehended as a statement of the allostasis/allostatic load elements. The streams of data within an organic or biological framework can be concentrated either by an atomic and chemical portrayal with the utilization of electromagnetic signs during discharge and preparing approach. It has been observed through various evidences, within the past few decades, that electromagnetic radiations are endogenously produced at various level in numerous cell parts and it constitute a functioning job in synchronizing either internal cell work at infinitesimal level either as fundamental versatile reaction of organs, device and entire living being (Pandarakalam, 2018). In this system all the versatile reaction both at minute and at naturally visible level, i.e., macroscopic level and all encompassing, could be recognized by their particular electromagnetic signs outflow. Every particular versatile response, being one of a kind for any individual gets distinguished on the basis of their own particular and individual electromagnetic radiations which can be associated likewise with their emotional or psychological patterns. Therefore, it has been established that a biophysical approach can be utilized to treat mild or moderate level of depression and associated issues based on past confirmations (Pandarakalam, 2018).
3.3 Quantum based views on depressive disorder
The science of psychiatry defines that condition of depression is secondary to the primary cause of mood fluctuations or disturbances. It is evident that our thought process relates to varied experiences within one’s own life. However, if the thought process is not in the right track then there are high chances of encountering faulty feelings and eventually negative experiences in life. It is evident that in the progressive stages of depression our mind or brain becomes negatively programmed just like computer. According to the concept of quantum thinking the unconscious state of mind is an origin of parallel or quantum thinking and the state of cognitive depression is related to the total misarranged state of quantum thinking (Malik, and Lindesay, 2009). In this regard, it must be mentioned that the state of depression or related cognition is divided into three groups: a) spontaneous generation of negative thoughts; b) a series of expectations that is considered to be unrealistic; and c) an array of cognitive distortions which is described as below:
Illogical Conclusion
Assuming a conclusion though there is scarcity of information with regard to the circumstances and also even when few evidences are against the conclusion.
Choosy conception
Individuals focus on the details of the situation and loose focus or ignore the details of the specific features of the situation.
Oversimplification
This is meant by formulation of generalised comment on the basis of a single incident.
Shortening and Exaggerating
The importance of the procedure is shortened while the errors related to it are exaggerated.
Absolutistic
The concept of dichotomous thinking is based on the concept to direct all the encounters in two opposite directions or categorizations for instance either unblemished or imperfect (Malik, and Lindesay, 2009).
These kinds of thought mechanism are prevalent among all individuals who are suffering from the pangs of depression. Based on the model of cognitive depression the thoughts feed the other related thoughts of depression and they generate and perpetuate the non biological factors (NBD) (Pandarakalam, 2018). The concept of cognitive based distortions is considered to be extremely organised but it is not convenient to demonstrate the concept on the basis of dysfunctional state of transmission of neurotransmitter and the conscious state of mind. The most suitable way to describe the condition is on the basis of quantum misinterpretation which is based on the incidents of de arranged thought process (Tarlacı, and Pregnolato, 2016).
Over the past few years, random controlled trials have led to an established robust evidence-based approach referred to as collaborative care of depression. Recent studies have indicated that colloborative approaches are effective in treating depression, anxiety disorders, and comorbid medical disorders like heart diseases and diabetes (Unutzer et al., 2008). When undertaking such activities, it could be important that primary care providers collaborate with the care team where the depression care managers normally include clinical social workers, medical assistants, and other mental health care providers to help ensure a comprehensive treatment process takes place. Also, the inclusion of a psychiatric consultant will be helpful as they will help in providing depression management in the primary healthcare setup (Unutzer et al., 2008). When the depression care managers are involved in the primary care, they can describe the best close and pro-active follow-up, patient education, and evidence-based psychosocial treatments, including problem-solving treatment and behavioural activations. In addition, the depression care manager may facilitate referrals to have other additional services that may be required. There will be a need for the designated psychiatric consultant to regularly review the patient under the manager's care and suggest areas, where he thinks could be appropriate for improvement. Further, where the is a need for focused treatment, the psychiatric should play an important role in ensuring the treatment achieves the best results (Unutzer et al., 2008). Availability of the psychiatric consultant should be easy as the care manager may have questions that he may ask regarding specific patients. The team members should know what takes place as it will assist in undertaking various activities both in the short and long run as they have a very important role.
Stepped care principles need to be systematically intensified, changed, and stepped up if effective collaboration can be achieved. However, the process applies when the patient is not improving with the treatment he is going through. Undertaking this ensures that evidence-based approach treatment is employed as it will require changes based on the patient's reactions (Unutzer et al., 2008). Because stepped care focuses on using limited resources like management and specialist consultations for those patients who cannot be managed effectively based on primary care provision alone, making it more cost-effective. Patients undergoing depression care education undergo this systematic approach provides an effective approach where all the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) that help in tracking all the symptoms and develop an appropriate through which the patient’s quality of life could improve. Side effects could also be easily managed to make the treatment process favorable for the patients (Glied, Herzog & Frank, 2010). Additional treatments are recommended for those patients who continually show depressive symptoms even after initial treatment. Therefore it’s a worthy consideration for depressed patients who need to increase their quality of life.
Where depression is not followed keenly together with treatment, there is a probability that they may not achieve the required results. The treatment gains will begin to reverse, leading to more difficulties (Glied, Herzog & Frank, 2010). Such negative reactions are some of the negative reactions that are likely to ensure that they continually have close supervision from caregivers. It will be easy to deal with unpleasant reactions from poor care that may arise from the medication. Depending on the patient's state, the frequency through which patients are being attended will change because there is a collaboration from different areas (Glied, Herzog & Frank, 2010). Reoccurring depression could be avoided if patients are given proper medication that could help them undertake different activities. Dealing with depression and many other mental disorders requires a collaborative approach in the healthcare sector.
3.4 The concept of quantum approach to understand depression
To evaluate the concept of depression it is very important to understand that human beings are not electrical models whereas they are gifted with aesthetic dimensions.
Mind Consciousness and the Para psychodynamics
According to the concept of mind based on Newtonian theory, there is no existence of any subject beyond the objective world. Depending on that concept the NBD related to depression becomes difficult to comprehend and its significances are also taken into consideration (Pandarakalam, 2018). According to the opinion and beliefs of classical physicist, no two bodies can occupy the same space simultaneously within the same time frame and it is considered to be scientific block to relate the association of the non physical factors with brain (Goswami, 2011).
Up to this point, the comprehension of life and all the more explicitly the functioning of cerebrum and how it capacities was depended on standards of old style or Newtonian physical science concept. With progresses in logical seeing, such standards were considered to be incorrect, to a great extent because of their contention with the idea of subatomic particles. Old style physical science advances the understanding that universe and everything in it depends on material things and cooperations between them. The modern trend understanding in physics has nearly changed those ideas after the establishment of quantum material science (Pandarakalam, 2018). New understanding accentuate on the job of non-physical attributes like discharged vitality which frames the electromagnetic range. This offers an option for a calculated system and the logical depiction as for an auxiliary demonstration of the cerebrum structure and functions dependent on self coordinated neuroplasticity (Pandarakalam, 2018). Our universe is comprised of matter and vitality the principal properties of which are portrayed by quantum physics hypothesis (Tarlacı, and Pregnolato, 2016)). According to the study of Haemeroff and Penrose it could be stated that conscious mind encounters assume a significant operation for activity of the laws of universe. Further, they likewise credit that superposition of quantum happen inside the neurons microtubules. The properties of quantum have been more than once confirmed which incorporate arbitrariness or acausality, wave or molecule duality, Heisenberg's vulnerability rule and quantum connection or non-locally or quantum rationality. Despite the fact that these quantum properties are unusual, abnormal and illogical, they help in understanding the strange idea of conscious mind. However, there might be various prospects on how these peculiar elements of the mind could turn up into physical reality and show up throughout the everyday life (Ab Latif, and Ggha, 2019). The interrelated and covering thoughts related with cerebrum according to quantum properties are graphically depicted below in the diagram (Refer: Fig 3).
The etiology concerning the dysfunctioning of brain in general differs with such a degree, that each mental disorder could be related with interesting inclinations. Interruptions in transmission of signals through neurons are frequently viewed as significant answer for different mind issues. The transmission of signals in cerebrum is helped to their objectives through the complex neurocircuit associations by methods for explicit pathways (Tarlacı, and Pregnolato, 2016). Axons were had all the earmarks of being guided by four consolidated activities like short and prolonged attractions and short and prolonged repulsion. The phenomenons are additionally referred as contact-attraction and chemo-attraction and contact- repulsion and chemo- repulsion. Our brain comprises of billions of neurons which are connected within via trillions of associations with structure hard wired cerebrum hardware. Therefore, that type of circuits could profoundly alter in their systems administration via conveying signals dependent on singular association to outside condition. Indeed, even the quantity of these circuits fluctuates with time because of neuroplasticity (Ab Latif, and Ggha, 2019).
Contrasts among individuals and variable ecological association conceivably lead to tremendous variety in neurochemistry. Along these lines, because of large variety of neurocircuit organizing, there are chances that the equivalent mental problem could have different starting points among people. However, our current therapeutics, ordinarily a similar treatment management are utilized among people with various etiology, which is set apart with low achievement rate. A possible explanation may be considered such as because of huge number of circuits in mind and the incapabilities to discover the specific area of the faulty circuit (Ab Latif, and Ggha, 2019).
4. Five bodies of consciousness
The fundamental instructing of all vitality medication is that the origin of a sickness may reach out past the physical body into the energy contained bodies. This educating underlies the explanation behind proposing a development from a progressively static methodology of treating just the different parts of the human body under a biomedical program to a unique quantum idea of finding and expelling disease from the energy contained bodies. The objective is to turn out to be completely alive by recapturing by and large wellbeing and vitality. It is obvious to comprehend that physical harm must be treated by physical, surgical, and other biomedical applications (Leigh, 2018). Be that as it may, the issues related with clinical medications utilizing just this methodology as recognized seem to be:
Private everyday issues experiences of an individual cannot be handily submitted to biomedical tests and diagnosis;
Awareness, goal and calculated innovativeness isn't all around recognized through exploratory setting;
The concept of biomedicine does not address full body-mind-soul mending;
Treatment of separate physical body organs does not really mend the individual of sickness;
A materialistic way to deal with the universe does not think about its free-streaming, unfurling improvement towards an obscure future (Leigh, 2018).
Issues with narrow scope of treatment with biomedical applications are reported by the vitality advisors. Scientist, Goswami depicted that the “physical body” act as a cover for what is in actuality can be considered as a complicated human being. Individual mindfulness can be felt in the different vigorous bodies as imperativeness, physical sensations, psychological feelings, supramental instinct, and otherworldly completeness, all of which mirror a person's vitality reality (Goswami, 2011). Moreover, when an individual offers attention to the potential capacity of brain for growing individual vitality, he or she has a more noteworthy chance of tending to the issue prior to the arrival at a genuine physical sickness.
The five groups of vitality are generally given as:
a) The physical body, where portrayals are made of the unobtrusive bodies.
b) The vital body, which conveys the diagrams of organic capacities, mentioned within the physical as the various organs.
c) The mental, offering significance to the vital and the physical, of which the cerebrum makes a portrayal.
d) The supramental, giving settings to mental significance, essential capacities, in addition to the movement of the physical body.
e) Atlast, the bliss body, the boundless concept of being, where the prospects are also boundless, yet where the other four bodies apply dynamic limitations (Leigh, 2018).
Every one of these bodies is quickly portrayed as far as the terms of energy:
4.1 The Physical Body
The physical body is what we are comprised of and are totally observed to live. The fundamental frameworks inside the physical body are musculoskeletal, respiratory, cardiovascular, lymphatic, nervous, digestive, endocrine and reproductive systems; medicines can be applied to fix injuries related to physical body or inward, through addressing any dysfunctioning of organs. Medications are all around offered by biomedical administrations. The physical body is thought to be exceptional to every individual as a result of its structure and this also takes into consideration the profiling of deoxy ribonucleic acid (Leigh, 2018).
4.2 The Vital Body
The vital body comprises of the plans related to the body which are acquired from the morphogenetic field. This hypothesis was created by Rupert Sheldrake, who perceived that "memory is inherent in nature", and that it has a reverberation which progresses over time. Therefore, vital body is impacted by broadening examples of molding, which impact the development or improvement of interior systems of the body. Moreover, the occasions are deciphered as sentiments. Just like the physical body, vital body may also have either outward or inward imbalances incorporated within it (Leigh, 2018).
4.3 The Mental Body
The brain makes portrayals of the vital and physical encounters, which eventually brings about conduct decision. Decision will be influenced by the individual's past encounters, associations, and social environment. As because our brain is associated with all parts of the body through the system of nerves the psychological body can influence physical capacities through nervousness, dread, or other negative encounters. The feelings of ego can influence both conduct and ensuing decision of potential choices, which thus is transmitted to the cerebrum in input circles or also known as “feedback loop”. Numerous subjective mental investigations have uncovered the impact of the brain and its influence both by psychosomatic manifestations and conduct potential for both delight and torment (Leigh, 2018).
4.4 Supramental Body
The quantum scientist Amit Goswami composes that the supramental body is the genuine spot where quantum recuperating can be powerful. It is the place individual experience reaches out to perceive the interrelationships which give the setting to mental meaning (Goswami, 2011). It is the space of awareness which contains the laws and prototype settings of physical, mental and energy developments. The supramental body is thought to be the degree of instinct (Leigh, 2018). The predominant force for the supramental body is the chakra framework. This level is likewise called the “level of archetypes”, a term initially credited to Plato and now more broadly perceived through crafted by Carl Jung (Goswami, 2011).
Archetypes are likewise achieved by joint examples of vitality discharged through the chakras. Another author clarifies that
“Each chakra holds within it a negative or dysfunctional archetype as well as a functional one. Its level of vitality, well-being and awareness is associated with the archetype it embraces”.
A negative block with regard to vitality can likewise be expelled if the client encounters a picture, shading, or the representative appearance of a cherished individual; by perceiving the imagery and discharging the negative feeling from the body. Through this approach, the client regularly encounters a vigorous delicacy and a feeling of opportunity (Leigh, 2018).
4.5 Bliss body
The bliss body is the place the recuperation of completeness through profound spiritual healing is accomplished. Scientist Amit Goswami composes that it is this disclosure of completeness which recuperates the brain of the issue of personality separation or from the feeling of ego. The feeling of ego refers that it has no compelling reason to attempt to help itself out of dread, since it is encircled by adoration. This recuperating of the personality rebalances the psychological energies which influence the physical organ systems of the body. The individuals who had experienced the bliss body discovered that their memory stays clear for a broad timeframe, anyway concise the experience. The ecstasy body is adroitly expelled from the other subconscious bodies. It is accessed through the crown chakra, which is the seventh or most noteworthy vitality centre. Some spiritualists report experiences and dreams, depicting an otherworldly reality not of their own creation (Leigh, 2018). A model from current times is that of Thomas Merton, who encountered an unbidden brightness in 1958 in Louisville, Kentucky. He later stated that –
“I was suddenly overwhelmed with the realization that I loved all those people, that they were mine and I theirs, that we could not be alien to one another even though we were total strangers”.
The chakras are considered to be the vitality places of body. They gave methods for getting and deciphering the vitality from the all inclusive stream of the Universe. With the removal of negative vitality, every point turns out to be progressively prepared to get new recuperating vitality. American composer Ruth White recognized that mental and social issues which can be tended to by operating with chakra amalgamation. She proposed such zones as augmenting family connections (associating the heart, root and crown chakras), settling issues of the heart" (heart and root chakra), self as a person on the globe (sacral, sun oriented plexus and throat chakras), inward intelligence (heart, crown and throat chakras), and "spiritual manifestations" (throat, crown and forehead chakras) (Leigh, 2018).
A considerable lot of the extraordinary healers, particularly from India, 128 have composed of the need to relinquish the sense of self or “ego”, remembering it as the wellspring of partition from the general progression of vitality. It is by relinquishing the sense of self that the subconscious bodies have more opportunity to investigate the pictures which are introduced to them. With the help of this technique, people figure out how to decipher the pictures, and let go of old ones, which are keeping them down. Moreover, the process of releasing them brings about an encounter of opportunity, and an extension of vitality (Leigh, 2018).
Quantum science proposes personality capacity to be a dream. In this respect, Ken Wilber composed that the bliss body speaks to the otherworldly eye of examination, a spot where the spiritualist encounters correspondence with the extraordinary. The Christian spiritualists also composed that it's anything but a position of consistent steadfastness, while simultaneously living inside the materialistic world (Leigh, 2018).
5. The application of quantum medicine for the treatment of depression
According to the definition of National Center for Alternative and Complementary Medicine (NCCAM), the complementary and alternative medicine approach comprises of varied clinical and healthcare frameworks, formulations and practices which are not a part of the conventional or allopathic medicines. The practitioner of CAM may be physicians practicing the conventional medicine or may be physicians prescribing naturopathic medicines, herbalists, nutritionist etc. The NCCAM categorised the treatment of CAM into 7 divisions and among them one is bio electromagnetic therapies and the other consists of nutritional and the life style modifications, manual healing strategies, mind body therapeutics, the healing approaches involving the utilization of energies such as hypnosis, acupuncture, manipulation of spine. Studies have been reviewed for the application of CAM therapies for the treatment of depression (Ravindran, et al. 2009). From a survey, it was evident that 32% of both genders were undertaking CAM therapies for any kind of persistent problems and 40% of the people were utilizing both the CAM and conventional therapies without reporting it to their physicians. Moreover, it was also evident from several studies that the aptitude of taking up CAM as therapeutic regime is depended on several factors such as the type of population, the physiological and psychological status of the individuals, the particular clinical consideration and also upon the geographical location (Nahas and Sheikh, 2011). A survey conducted with a population size of 7485 individuals residing at Canberra, Australia revealed that only 2.28% of the population used CAM therapies for depression whereas 0.59% individuals utilized combined approach of CAM and conventional therapies for depression. Therefore, literatures as a backing to alternative therapies for the mild or moderate forms of depression are conflicting. The CAM therapies are supported because of its potentiality to offer more good for more number of individuals in comparison to potential harm. Therefore, the treatment approach is considered to be safe for the individuals suffering from depression but more research is required to elucidate the mechanism. The CAM approach uses the detailed thought process for conducting treatment of the individual for instance the fundamental causes such as nutritional deficiency, exposure to any forms of chemicals which is neuro toxic in nature, requirement of nutritional healing due to the lost neurochemical balance because of excessive utilization of sugar. This form of treatment is also known as curative treatment (Sardá, et al. 2009).
Similar another study conducted by a group of researchers in Taiwan on the exploration of efficacy for CAM and application of antidepressants among outpatients in the phase of remission following 1 month after the discharge from hospitalization of psychiatric unit. The study conducted a telephonic survey with a population size of 201 members. The study findings highlighted that 50.2% have undertaken the treatment of CAM following one month after the hospital discharge whereas 41% have applied both CAM and antidepressant treatment after getting discharge from the hospital. The most notable features for this part of the study are the strategies utilized within CAM therapy for instance the techniques for relaxation, spiritual healing process and herbal medicines. Therefore, it is very much beneficial for nurses to identify the strategies that patients are using for alleviating the symptoms of depression and their possible side effects. Moreover, it has been also suggested that combined approach of CAM and conventional medicines can help to manage the symptoms of depression and associated psychological stress (Hsu, et al. 2009).
Among the other approaches used under CAM, another one is mind body techniques. It is evident that this particular approach can be utilised for the treatment of variety of persistent health disorders that includes depression. Several individuals suffering from depression do not receive proper mental health treatment, therefore, the mind body approach is considered to be a potential alternative treatment for those individuals. However, the rate of up taking of this approach is found to be lower among racial or ethnic minorities, whereas they are evident to utilize prayers or spiritual healing along with herbal remedies for depression (Rajagopal, et al. 2018).
The mind body approaches rehearses concentrating on the connections among the psyche, body, mind, and conduct that are not considered within the branch of frontline medication. The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health records the accompanying within the rehearsing of mind and body: needle therapy, massage, the approach of meditation such as mindfulness meditation, treatments related to movement, techniques used for relaxation such as breathing activities, guided symbolism, and relaxation of progressive muscles, t'ai chi or qigong, spinal control, yoga, contact of healing and hypnotherapy. As per evidence, the traditional healers and supplication are likewise usually referred with the mind body complementary health approaches (CHA). Moreover, in excess of 33% of grown-ups and over half of those with depression or nervousness is said to report utilizing some sort of complementary health approaches. Mind–body CHAs are considered to be the basic segments of care based mediations, for example, mindfulness based cognitive therapy and mindfulness based stress reductions (MBSR) which are likewise broadly used to treat depression (Edenfield and Saeed, 2012). Most of the individuals who access the treatment for depression at a primary care setting usually comprises of antidepressants which are the most widely recognized type of treatment. Be that as it may, it was observed that strict adherence to antidepressants was poor (40%–75%), and numerous people do not consider antidepressants to be safe and adequate treatments for depression and moreover, want to be treated without medication. However, individuals who were disappointed with the accessibility of conventional mode of treatment, express dissatisfaction about the treatment process, or could not get treatment were observed to opt for mind body CHA. It was observed that herbal medicines, relaxation techniques and yoga are the most used complementary health approaches within CAM (Rajagopal, et al. 2018).
The energy healing is also considered to be a part of the quantum medicine approach to treat depression. As depression is a significant cause that can affect the quality of life of (QOL) people, a study was conducted by a group of researchers within India to investigate the efficacy of Pranic Healing (PH) which is considered to be a form of energy healing for the mild to moderate forms of depression as an adjuvant therapy. The study used the randomised control trial study design using 52 blinded participants of mean age around 34.4 years. The seriousness of depression was studied using the Hamilton Depression Rating (HAM-D) scale for the total period of five weeks. The study comprised of two groups namely: medicine + Pranic Healing (PH) and medicine + placebo or mock PH. The study findings highlighted that the average decrease in HAM-D score among medicine + PH group was of median 11 and it was comparatively higher in comparison to the other group which had a median value of 6.5. Following the study the evaluation report highlighted that there was a progress within the depression category among 69.2% of the participants in the placebo or mock treatment group and 100% within the medicine + PH group. Therefore, this study provided a basis for the efficacy of energy healing for the individuals suffering from depression. Other vitality recuperating methods demonstrated comparative changes when applied in cases for depression (Rajagopal, et al. 2018). A RCT led in South Korea with 94 grown up participants on impacts of Qi-treatment on mental manifestations in the older had indicated a useful impact upon mental health. Practices of energy healing influence the body through the meridian. Similar to previous mentioned evidences RCT investigations utilizing acupressure have demonstrated help from overcoming the pangs of depression. According to the concept of the practice, people who have exhausted mentally possess reduced enacted fundamental chakras (Lee, et al. 2003). According to practice of energy healing in China, the fundamental chakra relates to the needle therapy point DU (GV). Prior investigations have demonstrated that some profoundly based recuperating rehearses, while conjuring for higher energies, were seen as helpful in the decrease of burdensome side effects of depression and promotes health and wellbeing of individuals. In the practice of pranic healing (PH) appealing to higher energies is a significant step. The steps include the following: vitality rebalancing, which have a potent impact upon the body and brain. At the time of PH meeting, the healers initially appeals to the god, during and after the process, which encourages the nearness of celestial vitality in recuperating procedures. Therefore all the above evidences have revealed that energy healing is a potential process when combined with medication for treating the mild to moderate cases of depression (D'Silva, et al. 2012).
Another important aspect within the quantum medicine approach is the aspect of nutritional healing. The awareness of the people regarding the association between depressive mental disorder and nutrition is still not clear enough. The concept that surrounds the mental disorder depression is all the more normally thought of as biochemical-based or has a deep rooted connection with emotions of psychological disturbances (Jacka, 2017). However, it has been observed that the concept of nutrition can assume a key job in the initial phase, with regard to the seriousness of the disease and length of disorder. A considerable amount of propensity for the items of the food which was evidently to be associated in the preceding phase of depression are equivalent to those that happen during the time of suffering from the disorder. These may incorporate the patterns for instance, poor craving, skipping dinners, and a prevailing want for sweet foods. The branch of nutritional neuroscience is a developing field that reveals insight into the mechanism that healthful variables or parameters are interwoven with human comprehension, conduct, and feelings (Jacka, 2017).
The pattern of dietary intake among the common populace in numerous American and Asian nations mirrors that they are regularly lacking in numerous supplements, particularly fundamental nutrients, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids (Amen, 2015). Interestingly, a striking element regarding the diet plans of patients experiencing the symptoms of mental disorders proved that the seriousness of the disorder enhances with regard to the insufficiency among these nutrients (Amen, 2015). Past investigations have shown that day to day enhancements of indispensable supplements are frequently compelling in lessening the symptoms of patient. It is evident those dietary supplements rich in the content of amino acids have likewise been found to decrease manifestations of depression and other related mental disorders, as they get converted to neurotransmitters which thus ease the problems associated with the disease (Lewis, et al. 2013). Therefore scientific evidences are developing the platform for nutritional healing as therapeutic intervention for mental health disorders. Evidence have proved that this intervention is effective in controlling the disorders such as depression, bipolar disorder, eating disorder, anxiety and other attention deficit disorder (ADD/ ADHD), learning disability, autism and schizophrenia. It should be noted that those patients who were showing non compliance with the psychiatrist regarding the administration of antidepressants due to its immense associated side effects are at more risk to commit suicide and being admitted to institution. Therefore, as an alternative approach, nutritional healing can be considered for these individuals. The psychiatrists recommend the food supplements based on the past scientific evidences with regard to their efficacy and then modifications are done by them based on the report of evaluation or observation (Lewis, et al. 2013).
At the point when researchers investigated about the dietary routine of individuals suffering from depression, a fascinating perception have been observed that their nutritional propensity is a long way from satisfactory. It is evident because those individuals settle on pitiable food decisions and choosing nourishments that may really add to their suffering. Scientific evidences had recommended a connection between reduced content of serotonin and suicide. It is embroiled that reduced concentration of neurotransmitter can lead to a general cold-heartedness toward future outcomes to some degree, activating hazardous, rash and forceful practices which may eventually result in self destruction, a definitive demonstration of deep down coordinated imprudent aggression. As evident that neurotransmitter deficiencies, for instance in the content of dopamine, serotonin, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and noradrenaline are frequently connected with depression (Jacka, 2017). As detailed in a few examinations, the amino acids tyrosine, tryptophan, methionine and phenylalanine are regularly useful in treating several psychological disorders including depression. When expended alone on an unfilled stomach, tryptophan, an antecedent of serotonin, is typically changed over to serotonin. Subsequently, tryptophan can prompt rest and serenity. This suggests re establishing that serotonin levels lead to reduced degree of depression, which get accelerated by serotonin deficiencies (Lewis, et al. 2013). Tyrosine and its antecedent phenylalanine are changed over into dopamine and norepinephrine and dietary enhancements containing phenyl alanine and additionally tyrosine plays the functions for trigger and arousal. The two omega-3 unsaturated fats, namely the eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) which changes over into docosahexanoic acid (DHA) within the body, found in fish oil, have been found to show the impact of antidepressants. Preliminaries based on RCT which included vitamin B12 and folate highlighted that patients treated with 0.8 mg of folic acid/day or 0.4 mg of nutrient B12/day were demonstrating diminished symptoms for depression. Moreover, the findings of a few contextual case study analyses where patients were supplemented with 125-300 mg of magnesium (as taurinate or glycinate) along with every meal and at time of sleep prompted fast recuperation from significant symptoms of depression within seven days for the majority of the patients (Bender, Hagan, and Kingston, 2017).
6. Recent Approach towards health
The significant way of the approach of biomedicine has been to concentrate on material reasons for contamination, ailment, and worsening or weakening of physical capacity in any or the entirety of the frameworks of the physical body. In the course of the most recent hundred years, point by point information has been progressed on every single organ functioning and their reasons for dysfunctioning from birth throughout life till the very end. Such information has been significant regarding the best outcome for health, numerous reasons for disease or infection have been erradicated, and physical arrangements have been found in medical procedure and restoration to enhance the greater part of the incapacitating conditions of the body which result from the day to day lives of mankind (Jacka, Mykletun, and Berk, 2012).
These ways have additionally assisted with expanding life span. Notwithstanding, numerous people have additionally been trapped amidst complex recuperation programs which also incorporate pharmacological intercessions which help the issue, yet demonstrates manifestations of contradictions at different parts of the body. It is often noticed that people grumble that they have not been heard by their own wellbeing point of view, while others get themselves reliant on a wide scope of pharmaceuticals, which they should take for the remaining of their lives, often with severe outcomes in the event that they overlook or in any case neglect to do as such (Colbert, 2007).
Basically the primary five pillars of health and wellbeing can be separated conventionally into the accompanying zones such as physical, psychological, mental, spiritual and social. Addressing lopsided characteristics in the accompanying five arenas is the beginning stage and will not just augment the general wellbeing of the individuals yet more critically can be considered as protection medication and a measure for the management process of the disease (Zafar, Sikander, Haq, Hill, Lingam, Skordis‐Worrall, and Rahman, 2014).
Another approach to address the wellbeing and health of individuals based on the essential vitality concept of the quantum field, and in accordance with the investigations obtained from the Quantum University, numerous experts are extending their teaching process. Few individuals may perceive that people are in actuality consistently washed with the flow of this energy (Jacka, Mykletun, and Berk, 2012). Accurate results necessitate that both the specialist and the patient should know about this procedure, and that they should figure out how to co-work with its ramifications to help the two gatherings.
Quantum Scientist, Amit Goswami has composed in his book “The Quantum Doctor” how the hypothesis of quantum material science can be comprehended as coordinating admirably with basic hypotheses of vitality medication, especially in the acknowledgment of "downward causation" (Goswami, 2013). New ideas additionally necessitate that a specialist healer assess the entire individual in growing new medications in the field of healthcare practice. This is on the grounds that, every individual is personally associated with each of the decision undertaken. The choice happens preceding the occasion, in awareness to them. In this regard, the statements of the pioneer in the field of mind medicine body, Deepak Chopra should be highlighted –
“…mind and the body are inseparably one. The unity that is “me” separates into two streams of experience. I experience the subjective stream as thoughts, feelings and desires. I experience the objective stream as my body. At a deeper level, however, the two streams meet at a single creative source. It is from this source that we are meant to live” (Zafar, Sikander, Haq, Hill, Lingam, Skordis‐Worrall, and Rahman, 2014).
6.1 The biomedical approach
The biomedical way to offer treatment has been considered as the essential methods for the conveyance of human services since the start of the twentieth century and is regularly alluded to in the West as the "orthodox medicine". According to the National Cancer Institute, expansive meaning of the above mentioned term, which is - a framework where clinical specialists and other healthcare experts, that incorporates the medical caretakers, drug specialists, and advisors to treat indications and maladies utilizing medications, radiation, or other associated medical procedures. This practice is additionally referred as biomedicine, allopathic medication, conventional approach of medication, frontline medication and Western medication (Brody, and UNESCO1993).
Clinical schools in the principal half of the 20th century used to address more of the perceived problems of body parts and treating all way of those physical issues than the individual who was being dealt with. The assortment of information for instance the age, gender, profession, nationality, and the detailed life histories turned out to be substantially more significant for those patients attending the community wellbeing organisations, chambers of physicians, and emergency clinic wards in the afterwards. Moreover, disappointment with biomedicine approach of treatment, has urged more people to assume liability for their own wellbeing by up taking alternative modes of treatment. Therefore, it is additionally time to perceive the significance of having equal frameworks of biomedicine and elective medicine for the wellbeing of people. It is smarter choice to decide how each can support each other, as opposed to contend with one another (Hollenberg, 2006).
6.2 The alternative medication approach
The accentuation on the symptomatic indications is significant for the treatment and management of any malady and infection control, and different medicines which require prompt consideration after mishaps such as broken bones, and heart or brain malfunctioning. Be that as it may, the board utilization of a similar approach to deal with all illnesses restricts the potential outcomes of recuperation by disregarding the multidimensional part of the individual being dealt with throughout the world. The integrated deficiency for treating entire individual issues or patient focused treatment started to be addressed by people, who got option of alternative or complementary medications in the second part of the twentieth century (Coulter, and Willis, 2007). Therefore, form that time onwards, these advocates have gotten perpetually vocal. However still, the conventional concept of biomedical practices remain too biased to even consider allowing something besides seeing these vitality based practices as "counter culture" (Jacka, Pasco, Mykletun, Williams, Hodge, O'Reilly, and Berk, 2010).
Few alternative approaches for the treatment of depressive disorder have been discussed below:
7. Traditional chinese medication for depressive disorder
The recent monoaminergic frameworks based medication for the treatment of depressive disorder is considered to be a long way from being perfect. In the course of recent decades, tremendous endeavours have been stressed on the improvement of novel medications toward new potential focuses past the monoamine theory. However, none of these endeavours can be considered to be successful in the advancement of any basic level novel prescriptions for the depressive disorder (Berton and Nestler, 2006).
According to the latest information based on scientific research, ketamine, which is an antagonist of NMDA receptor, produces quick progress towards alleviating the symptoms during the time of depression. Various investigations had been carried on ketamine that had prompted the exploration of a few fast acting chemical agents that focus on the receptor NMDA, along with the particular antagonist GluN2B, Ro-25-6891 (Preskorn et al., 2008) and traxoprodil (Li et al., 2011), and also a positively acting allosteric modulator of NMDA receptor for instance rapastinel (Burgdorf et al., 2013). However, these medications demonstrate addiction and potential toxicity to nervous system. Specialists administer these medications because of guaranteed quick action as antidepressants and clinical examinations are as of now in progress (Gerhard and Duman, 2018). Moreover, there are numerous reasons behind looking for new antidepressants is considered to be difficult among them the first one is, the strong objective proteins are extensively produced or synthesized all through the cerebrum and the peripheral tissues which demonstrates various physiological impacts in various cerebrum locales. It expands the worry of the toxic reactions within nervous system due to any operator coordinated against these objectives. The second significant reason is that depression can be considered as a multi factorial and multi genetic disorder, in which manifestations can widely differ among patients. Therefore, it definitely cannot be considered as a single condition (Preskorn et al., 2008).
In this way, advanced methodologies for viable treatment of depression should jointly target the improper regulation of certain genetic arrangements responsible for the pathophysiology of disorder. In case of patients with gentle and moderate types of manifestations, the best mending approach should be the understanding of the chief reason that is one of a kind to every individual patient and afterward to apply with a proper psychotherapy or clinical treatment to address the homeostatic irregularity. A framework involving the physiology orientated mending way to deal with this issue is thought to be available within Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) (Jacka, Pasco, Mykletun, Williams, Hodge, O'Reilly, and Berk, 2010).
TCM is a medication developed based on varied encounters that has been created in China more than a huge number of years ago, and stresses on the reliability of the human physiological system including the physical or passionate impacts of the outer condition on inside balance. The fundamental guideline is the maintenance of active homeostasis (Jacka, Pasco, Mykletun, Williams, Hodge, O'Reilly, and Berk, 2010).
7.1 Mechanism of TCM working
According to the concept of TCM, varied diseases originate from a homeostatic lopsidedness, which can happen as a result of an assortment of ecological or social components. Thusly medications work to re establish interior parity. In light of its mechanistic perspective, a commonplace treatment approach in TCM addresses the body as all in all element and fixes any sickness by lightening its side effects, yet in addition re establishing inward parity. In addition to the above conditions, in TCM, a mix of different medications is regularly used to guarantee the powerful activity on different targets (Refer Figure 1). As indicated by TCM, the condition of depression is brought about by a lopsidedness inside organ frameworks that in the end brings about dysregulation of the capacity of brain, and therefore considered as a multi factorial disease with an assortment of symptomatic manifestations among various patients. Depression might be brought about by blockage of "Qi" (imperative vitality), improper functioning of flow of blood, "Re" (means inflammation), wetness and mucus within the physiological system (Burgdorf et al., 2013).

According to the concept, TCM specialist commonly distinguishes the chief reason for the condition of depression that is one of a kind to every patient and eventually administers needle therapy (acupuncture) or clinical treatment as per the requirement. The discharge of deteriorated blocked vitality is the usual remedial guideline for depressive disorder (Feng et al., 2016). It might demonstrate remedial action by actuating blood dissemination, inhibiting inflammatory process or with the removal of mucus and clamminess.
The framework involving the multi-tranquilizer, multi-target approach within TCM consummately addresses the multi factorial manifestations of despondency. Currently there are varied TCM experimental stimulant recipes, which are broadly applied for the treatment of patients with depression in Eastern part of Asia today. Depending on the evidence of clinical research these formulations for antidepressants are powerful (Yeung et al., 2015). Then again, though incredible endeavours have been made to deductively clarify these formulations, the comprehension of several researchers with respect to their mechanistic approach, secondary active metabolites, and pharmacology involved behind the principle of synergy and the compatibility of the metabolites, is still at basic level (Zarate et al., 2006; Preskorn et al., 2008).
7.2 Hope surrounding TCM with regard to treatment of Depression
Experience based on clinical encounters and physiological framework based TCM medications gives a brilliant worldview to assist the progress of novel prescriptions for the successful pharmacotherapy of depressive disorder. Thus, the investigation carried out concerning treatment of depression with TCM likewise gives a chance to logically decipher the advantages and dangers of TCM stimulant formulations. Investigation on TCM will stand out and support remarkable researchers sooner rather than later, for a few reasons for instance the reactions and prospective for misuse of medications are thought to be basic issues. These focused glutamate transmission fast acting chemicals demonstrating toxicity, despite the fact that, it has been guaranteed that a few chemicals have less psychotomimetic manifestations in comparison to ketamine (Zarate et al., 2006; Preskorn et al., 2008). These adverse reactions are hindering the persistent use of allopathic medications.
7.3 Rationale for opting for TCM
Moreover, updated compounds that can be utilized on a day to day continued premise are required urgently. Despite the fact that these compounds can quickly mitigate adverse manifestations of depression, new agents that can continue both the synaptic just as the healing activities of the fast acting compounds are in urgent demand. Another significant reason is that usually patients with depression likewise show different side effects, for example, ceaseless weakness, interminable torment, indigestion, lupus, persistent constipation, etc. Medications that can act as adjuvant coordinated toward those side effects are needed.
7.4 TCM investigated for treatment of depressive disorder
It has been evident based on recognizable proof concerning bioactive constituents fundamentally augmenting the comprehension of researchers concerning the activity for instance the advantages or dangers of a TCM energizer formulations even at the sub-atomic level (Drevets et al., 2013).
It tends to be illustrated with the investigation on Ibogaine, a psychedelic alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga, and Yuanzhi-1, a triterpenoid saponin isolated from Polygala tenuifolia. Based on evidence, the two herbs are experimentally utilized for the cure of despondency. With regard to mechanistic approach, Ibogaine has been appeared to restrain both transporters of dopamine and serotonin, however is special among the transporter ligands in which it hinders without competition and evidently ties to the surface receptor outside the cells of a cytoplasmic-confronting transporter adaptation (Jacobs et al., 2007; Bulling et al., 2012). Then again, Yuanzhi-1 was accounted for to repress each of the three monoamine transporters with a high power at a range of low nanomolar concentration (Jin et al., 2014, 2015).
Another model pertinent to TCM is scopolamine, which is a characteristic compound extracted from the group of plants belonging to family Solanaceae and which has been utilized for sedation before surgical procedures. Scopolamine is a non-specific antagonist mAChR and has been accounted for fast stimulant impacts inside few days, with the mechanistic hindrance of mAChR1 on interneurons GABA (Drevets et al., 2013; Voleti et al., 2013; Wohleb et al., 2016).
These investigations give scientific evidence that treatment with scopolamine brings about a quick explosion of glutamate in the prefrontal medial cortex and expands the quantity of spine synapses. Even though fast acting compounds produces quick reactions against depressions, the impacts keep going for only around a week, within which patients normally show backslide (Duman, 2018). Within the practice of TCM, a patient suffering from depression is generally given a combined formulation to use on a day to day basis continued for half a month, so as to reduce burdensome side effects. The composite formulation is certainly not a single target agent, but a fairly formed combination which acts based on indications of inside organ frameworks, endorsed to fit every individual patient and work with an objective to actuate blood flow, wipe out mucus and clamminess, restores stomach related and gastrointestinal malfunctions, and augments the immune capacity of every concerned individual and so on. In this unique circumstance, TCM could apply its qualities as an adjuvant to the quick acting antidepressants through various hidden pathways (Drevets et al., 2013; Wohleb et al., 2016).
Another recommended medication for the recuperation of gastrointestinal (GI) sicknesses is "Dai-Kenchu-To" (DKT in Japanese), for instance to additionally show that TCM could act as perfect adjuvant. It is a notable fact that the bidirectional correspondence between microbiota inhabiting at GI and the cerebrum connects the central nervous system with fringe intestinal capacities by methods for endocrine, neural, humoral and immune communications (Rhee et al., 2009; Diaz Heijtz et al., 2011). “Dai-Kenchu-To” is prepared decoction blend of three herbs which can be utilized for the treatment of varied types of gastrointestinal issues (Hasebe et al., 2016).Therefore, it has been recommended that the GI tract and microbiota are engaged with the pathophysiology and etiology concerning depressive disorder (Schroeder et al., 2007; Desbonnet et al., 2008; Bravo et al., 2011; Arseneault-Breard et al., 2012).
However, chemicals that demonstrate action against inflammation could be utilized to forestall depression before insusceptible dysregulation triggers neurobiological changes within the cerebrum. In this regard, an aggregate of 54 herbs were concentrated by looking at their consequences for six primary systems that underlie inflammation. The results highlighted that 93% of the herbs applied action against inflammation by means of one hidden mechanistic pathways and 68% through at least two pathways. TCM recipes that tries to lighten inflammation actuated depressive indications by and large contain at least one herb within the classification. In this manner, the researchers inquired as to whether "Qing-Re-Yao"- containing upper mentioned formulations could be utilized to forestall inflammation actuated burdensome manifestations. A few investigations have been by and large acknowledged in this respect. First, TCM herbs can be utilized consistently, as most off-counter day to day supplements from local drug store. Second, most TCM herbs apply their activity by means of numerous components in a combined approach contrasted with single-target medications. Multi-focused medications can possibly treat a sickness with different side effects such as depression. Third, TCM is considered to be a customized medication. Overall "Qing-Re-Yao" can be considered to be a potential medication or formulation acting via the anti inflammatory pathway and eventually results in irreversible prevention of inflammation associated depressive symptoms.
7.5 TCM for women suffering from depression and postpartum depression
Scientific evidences announced that females are twice as liable to experience the ill effects of depression (Kuehner, 2017) and that antidepressants have differential mechanism and efficacy related success among males in comparison to females. Sex explicit pathophysiology of depression is restricted and currently no antidepressants, particularly for ladies are accessible in the commercially. Studies have uncovered that ladies are bound to encounter episodes of depression during the times of hormonal action after giving birth to baby and prior to menopausal periods (Ahokas et al., 2001; Parker and Brotchie, 2004).However, there are a few TCM formulations which are considered to be appropriate for ladies which can be adjusted based on singular manifestations and extra factors. A delegate recipe for treatment of post birth depression is "Xiaoyao-san" (XYS), which is accomplished by blending of eight herbs. It must be stressed that within this recipe, Angelica sinensis is usually used to enhance blood composition, augments the flow of blood throughout the body and to treat blood insufficiency and menstrual issue, for example, dysmenorrhea and unpredictable cycles of menstruation (Wu and Hsieh, 2011). Several clinical model investigations have shown that XYS applies an antidepressant activity among stress-stimulated laboratory models through different fundamental mechanistic pathways, which incorporates the enhanced level of 5-HT within both the hippocampus and the cerebral cortex, by the controlling of the HPA pivot, by the enhancement of BDNF production within the hippocampus region, and with the decrease of levels of certain cytokines in blood serum (Jing et al., 2015).
8. Approach of energy healing or meditation for depressive disorder
As of late, the utilization of meditation based practices for the healing of depressive disorder has been considered with expanding logical and medical enthusiasm, because of reduced associated adverse effects, prospective decrease of multiple medication therapy, and also because of hypothetical contemplations that such intercessions may focus on the basics of the intellectual underlying foundations of depression. The preliminaries carried out at the beginning on the present efficacy and accessibility of psychotherapeutic and pharmacological medications for the remission of the disorder were found to be fifty percent successful after conducting numerous trials and by and large have restrained impact proportion. Moreover among patients with associated chronic or severe comorbidites, medication therapy with regard to depression conveys the hazard for “polypharmacy”, contradictions due to multiple medications, and eventually associated expanded adverse reactions. Therefore, the requirement for new medicines or any other form of therapy with an increasingly ideal advantage for risk management profile along with various pathways of activity from existing medications are in urgent need. Enthusiasm and curiosity for the usage of mind body treatments for varied mental issues and specifically for MDD is rising among the focus group populations 8 and also expanding among professionals, for instance, "mindfulness" is most noteworthy among the remedial intercessions appraised, destined to increment in use within the upcoming few years by the experts in the field of psychotherapy (Akbaraly, Brunner, Ferrie, Marmot, Kivimaki, and Singh-Manoux, 2009).
8.1 Defining the term meditation
The word meditation alludes to a vast type of practices which are psychosomatic in nature and within this process it includes preparing and directing consideration towards exteroceptive or interoceptive foci, or deliberately developing pictures within brain, while watching or re establishing the consideration from diverting thoughts. Instances of interoceptive foci are thought to be the feelings related to inhalation and exhalation of the body or the different body parts, or "mindfulness itself" whereas the exteroceptive foci may incorporate varied things such as a fire illuminating substances or sculpture along with intellectually produced imaginable portrayals or optical representations which may incorporate “verbal mantras” (tedious words or assortments of syllables) (Ahokas et al., 2001). Those contemplation procedures includes supported thoughtfulness regarding a particular concentrating subject or restricted scope of inward or external encounters have regularly been alluded to as thoughtful or cantered consideration rehearses. While those practices that fuse a more extensive concentrative focus to a variety of changing upgrades have been called mindfulness, open-consciousness, or open monitoring rehearses. The rehearsing involves open checking, non accentuates the outline of an illustrative concentration for non-receptive yet clear and distinctive perception of second to second experiences (Estruch, 2013).
However, there prevails a difference about which therapies depend on reflection and are similar with respect to the action mechanism. In endeavouring to address this controversial discussion, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) suggested a definition depending on contemplation using an altered Delphi process. According to this recent definition recommended there are 3 standards fundamental to the practice of meditation: a characterized strategy, unwinding rationale, and a self-initiated state or mode. Characterized strategy or “defined technique” indicates a describable arrangement of guidelines; unwinding rationale or “logic relaxation” alludes to an absence of "plan" to examine, judge, or make assumptions about the training; and self-incited state or the “self-induced state” recognizes contemplation from mesmerizing or guided symbolism rehearses. Among couple of instances of practices recognized as contemplation based included the process of mindfulness, Tai Chi, numerous sorts of yoga, qigong and Transcendental Meditation. Notwithstanding, this definition was crossed with some analytical comments because of comparatively improper specification. Therefore, a later emphasis from the AHRQ was to separate "absolutely reflective" methods, completed while keeping up a fixed stance, from those that used a thoughtful mindfulness during the process of mobility. In any case, neither extensive reasons for barring the development rehearses nor for holding fixed contemplation groupings was provided (Akbaraly, Brunner, Ferrie, Marmot, Kivimaki, and Singh-Manoux, 2009).
At the time of meta-examination of the clinical writing on contemplation procedures used as therapeutics for mental manifestations, numerous researchers have crumpled across various reflection treatments utilizing a similar kind of contemplation for example Mindfulness Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) and Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) or general classifications of contemplation or care methods, for example, centred consideration and open checking practices, or may or may not incorporate mobility and attempted to make inferences about the size impact of reflection or care strategies within a group. The conducted meta-investigations have commonly inferred that procedures of meditation give little to considerable amount of direct healthy advantages with regard to the adverse reactions of depression for patients who are also associated with co-morbid clinical ailments, for example, rheumatoid joint pain, malignancies, coronary illness and fibromyalgia. Among these meta-examinations, 2 preliminaries additionally dissected contemplation treatments based on strategies, however while doing so the gathered subjects with varied symptomatic manifestations for instance seriousness, anxiety and mood fluctuations possibly confused the screened outcomes (Akbaraly, Brunner, Ferrie, Marmot, Kivimaki, and Singh-Manoux, 2009).
8.2 The therapy of meditation for the depressive disorder
The therapeutic stages for clinical depression happens depending on 3 different periods of the ailment such as intense, continuation, and maintenance stages, along with backslide anticipation in the intense or continuation phase. It is also evident that introductory medications for the disorder bring about relief just around 33% of the cases, with the frequent presence of additionally a sub acute stage where the individuals who have encountered halfway advantage by an underlying introductory treatment further progresses with either pharmacological or psychotherapy (Estruch, 2013).
Many researchers conducted evaluation and exploration of the usefulness of these methods of meditation for the alleviation of adverse effects of depression have assembled patients with the disorder over the downturn life cycle, but not segregated them on the basis of various periods within the burdensome illnesses. In this regard it must be noted that this methodology may considerate little or overvalue the size impact for relying upon contemplation strategies with regard to stages of the disorder. For instance, patients in the midst of an intense significant depressive scene may fall short on the focus requirement expected to meditate as successfully as during the stage of partial remission, and eventually the impact of contemplation might be considered over the true value during halfway abatement stage. On the contrary, the impact of meditation practice may be more vulnerable for those patients who are within the sub acute stage of the disease in partial reduction because of the overall impact for progressiveness (Estruch, 2013). It is along these lines considered to be significant that surveys on efficacy of contemplation practices for depression should take period of the disorder into thought within the study design (Sánchez-Villegas, Delgado-Rodríguez, Alonso, Schlatter, Lahortiga, Majem, and Martínez-González, 2009).
Consideration of the stages of the depressive disorder has been thoughtfully practiced distinctly only with MBCT. A few preliminaries have explored to make a decision if MBCT may diminish the backslide rate for patients with significant depressive disorder but at the phase of remission, and most of these study findings have exhibited a decrease in backslide rate comparative with therapeutic procedure carried out commonly or against placebo treatment. Meta-examination carried out systematically showed that MBCT is a viable treatment for the burdensome backslide among patients suffering from MDD who in their past have gone through more than 3 (not lesser than 2) intense episodes of depression. On the other hand, the particular job of contemplation practice in these outcomes stays muddled up in light of the fact that a unorganised study neglected to separate MBCT consequences for backslide counteraction from an intellectual based treatment intended to imitate the strategies of MBCT yet without experiential care components. The only exception is within an optional investigation that demonstrated expanded viability of MBCT among subjects with elevated degrees of trauma from childhood stage. Moreover systematic audit has never been attempted to explain the clinical proof base for the treatment of medical relevance depressive disorder over the range of thoughtful treatments (Sánchez-Villegas, Delgado-Rodríguez, Alonso, Schlatter, Lahortiga, Majem, and Martínez-González, 2009).
Several randomised control trials were investigated and within the study the parts of contemplation worked on concentrating on the praxis itself, were inferred using elucidating standards drawn from Patañjali's Yoga Sutras, 16 mental symbolism theory and the Satipatthana Sutta. The screened investigation incorporated the significance of mobility, otherworldliness, mental symbolism for instance the inside portrayals of visual, physical, or verbal or sound-related areas, the other objects of consideration such as somatosensory, psychological, outside, intellectual, the quantity of investigations on involving the mediation, the scope of an all encompassing philosophical perspective, and some other related restorative components. The study conducted data analyses based on size impact measures (Hedge's g) were determined utilizing the accompanying equation: (ū1 − ū2)/Sp, where ū1 is the mean of the group allocated for treatment (for correlations within group) or baseline (for inside examinations of the gathering), ū2 is the mean of the control or benchmark group (for correlations within group) or endpoint (for inside examinations of the gathering), and Sp is the pooled difference. Several studies adjusted the impact sizes were for small focus group population (Sánchez-Villegas, Delgado-Rodríguez, Alonso, Schlatter, Lahortiga, Majem, and Martínez-González, 2009).
Strategies used within meditation
The most every now and again examined procedures included MBCT within eight investigations, three of the preliminaries included Tai Chi , two investigations incorporated Sudarshan Kriya Yoga (SKY) and another two studies included Patanjali Yoga (Jacka, Mykletun, Berk, Bjelland, and Tell, 2011).
Among all the intercessions none used a solely one-oriented central summit of consideration all through the mediation, on the other hand for the most part comprised of numerous distinctive oriented attentional foci and procedures. Apart for Sahaj Yoga, the practices contained a lot of thoughtful mindfulness during non-oxygenic consuming building work out, along with fixed stances, while just Tai Chi concentrated only on reflective commitment at the time of mobility. It was evident that within 7, about 4 treatments used the process of mental symbolism to alter the state of feelings at the time of certain practices such as Patañjali Yoga, Inner Resources Meditation, Sahaj Yoga and MBCT during body filter practice. It was also observed that 4 out of 7 unequivocally incorporated a comprehensive philosophical outline for the training such as Patañjali Yoga, MBCT, Sahaj Yoga and qigong. Out of 7 procedures 2 of them which includes Inner Resources Meditation and MBCT gave extra restorative components drawn from psychological conduct treatment, while every one of them with the conceivable elimination of case Sahaj Yoga, for which this was uncertain incorporated a component of gathering support (Sánchez-Villegas, Delgado-Rodríguez, Alonso, Schlatter, Lahortiga, Majem, and Martínez-González, 2009; (Jacka, Mykletun, Berk, Bjelland, and Tell, 2011).
Capability of meditation treatments in the intense period of major depressive disorder
Nearly 11 preliminaries included members with a recent episode of major depressive disorder or a blend of patients with significant MDD, dysthymia, and those with indications at the phase of remission. Among these investigations 5 preliminaries involved patients suffering from significant episodes of depression and demonstrated enormous gathering impact sizes within range of 0.93 to 3.33. While the remainder of the examinations included blended populaces and exhibited impact sizes extending from 0.33 to 1.47. In case of the five examinations for MDD, three incorporated a blend of patients who were offered with mediation as of essential therapy or augmentation treatment, whereas another 2 of the investigations were completed with patients who were not receiving medications in an inpatient setting (Jacka, Mykletun, Berk, Bjelland, and Tell, 2011). The huge sample of the 11 examinations incorporated subjects in the phase of major depressive episodes (MDE) of around 219 subjects demonstrated that the adequacy of MBCT didn't show any variation with respect to patients experiencing a MDE or had remaining indications of sub acute phase (Jacka, Mykletun, Berk, Bjelland, and Tell, 2011).
Capability of meditation treatments in the sub acute phase of disorder
Only 3 examinations were discussed where just patients with lingering side effects of depression after intense stage treatment and these exhibited impact sizes within the range of 0.65 to 1.02 (Jacka, Mykletun, Berk, Bjelland, and Tell, 2011; Sánchez-Villegas, Delgado-Rodríguez, Alonso, Schlatter, Lahortiga, Majem, and Martínez-González, 2009).
Capability of meditation treatments in comparison to control gatherings
Comparative with studies of wait list or treatment as regular the control examines exhibited considerate to enormous impact sizes 0.47 - 2.12, except for the study conducted by Yeung et al. (2012) where, the wait list control gathering displayed a strangely massive decrease in signs of depressive disorder demonstrating gathering impact size inside 1.54 in comparison to the benchmark groups of different examinations (in between gathering impact sizes ranging 0.60 - 0.35). Those investigations that utilized pseudotherapy or psychoeducation control bunch arms, the between bunch sizes that supported practice of meditation and were considerate to enormous (0.39 - 1.54). The inside subject impacts among psychoeducation bunches were within the range of 0.02 - 0.59 (Jacka, Mykletun, Berk, Bjelland, and Tell, 2011).
The 3 investigations conducted with MDD along with 1 study where the sample population was depressed individuals with psychoneurosis, both the studies explored the efficacy of front line therapy for depression such as MBCT in comparison with CBT, Patañjali Yoga against amitryptiline and SKY in comparison with imipramine. However the study demonstrated no such significant variations among the experimental and the control focus gatherings. The investigation which utilized SKY also utilized the optional therapy for depression such as Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) which can be considered as the next controlled parameter but it demonstrated the reduced efficacy of the intervention of SKY revealing the size effect of 0.94 in comparison to ECT (Akbaraly, Brunner, Ferrie, Marmot, Kivimaki, and Singh-Manoux, 2009).
Critical Discussion
The information that had been gathered from several RCTs proposed that thoughtful mediations or practice of meditations might effectively affect symptomatic indications among patients with clinically analyzed depressive disorder, including those who were encountering intense significant episodes of depression and those lying with halfway phase of remission. Within the screened preliminaries, the top limit of impact sizes was found to be bigger for subjects experiencing an intense significant scene than those with lingering side effects, which can be attributed to the overall blend of progressiveness for subjects with leftover side effects. Nonetheless, the distinction within the parts or the inside components of the distinctive contemplation treatments brought about our reasoning that the treatments were not comparative enough to consider induction of a typical impact size (Akbaraly, Brunner, Ferrie, Marmot, Kivimaki, and Singh-Manoux, 2009).
It was evident that within the investigations there were a few factors over the preliminaries that, while expanding the dissemination of the findings across clinical condition type and disease stage, restricted their shared trait. Understanding populaces contained a blend of patients with various types of depressive disorder within a few of the selected preliminaries, that incorporated significant MDD, dysthymia, and numerous "psychoneurotic disorders" (Sánchez-Villegas, A., Delgado-Rodríguez, M., Alonso, A., Schlatter, J., Lahortiga, F., Majem, L. S., & Martínez-González, M. A. (2009)

Limitations of the studies screened
There are troubles faced for recognizing the useful segments of meditation treatments due to few reasons such as a thorough correlation of the praxis components of individual thoughtful treatments has not been attempted among various studies, and in this way the degree of shared trait was not known. As because there is lack of proof to propose that wide types of thoughtful practices include distinctive neuronal substrates, overall considered contemplation therapies that consolidate various practices influencing the physiological substrates of targeted mental signs in an unexpected way (Jacka, Mykletun, Berk, Bjelland, and Tell, 2011). Moreover, it was also indistinct that all contemplation treatments dependent on a specific type of reflection, for example, "mindfulness treatments", also reveals a typical neural action mechanism. For instance, it might be that the intellectual segment to MBCT connects with neural components not lying within the less subjectively directed MBSR intervention. By gathering various types of practices of meditation, the researchers might be clouding singular contrasts among reflection treatments that may bring about varied impact sizes (Akbaraly, Brunner, Ferrie, Marmot, Kivimaki, and Singh-Manoux, 2009).
In spite of the fact that the studies were screened based on the AHRQ definition for meditation practice to incorporate important examinations, the researchers themselves revealed significant heterogeneity within praxis as part of the assessment with regard to reflection treatments that they themselves recommended. These varieties included components of mobility, otherworldliness, consideration coordinated towards various foci, mental symbolism, and whether the practices occurred inside the arrangement of a bigger philosophical structure. The researchers also revealed that they arranged to some degree with regard to the foundations formulated by Shear, which incorporated the kinds of intellectual capacities used for example consideration, visual symbolism, how the resources were utilized for example dynamic, aloof, the foci for these resources for example considerations, real sensations, soul/God. On the other hand, divisions dependent on components other than praxis are conceivable, for example, by focusing attention on the expressed objective of the contemplation practice, the logical and authentic foundation of the training, or the thoughtful state experienced because of the practice. The mixed blending within praxis, along with the probability of various mechanism of neural system, blocked ascribing the impacts of the reflection treatments to a typical action mechanism (Jacka, Mykletun, Berk, Bjelland, and Tell, 2011).
To conclude another significant question of research concerning the clarification of the idea of the cooperation among contemplation and other medicines for depression, that includes the following psychotherapy, stimulant drugs, and other way of life changes. This is fundamentally significant for deciding how thoughtful meditation methods appropriately sit within the built up restorative armamentarium for depressive disorder. It is a matter of research that such cooperation might be in part or completely additive, beneficial, or inhibitory. Similarly as the combined result of psychotherapy and stimulant medicine can eventually result into progressive findings, the equivalent might be valid for consolidating contemplation with pharmacotherapy. In fact, interviews among the focus group opting for meditations along with antidepressants offer similar response that demonstrates that might be the real story. Those investigations that contrasted various types of contemplations, within which the equivalent neurophysiological measures and psychometric are applied, may demonstrate the degree to which the advantages of various reflection treatments are interceded by basic action of mechanism (Jacka, Mykletun, Berk, Bjelland, and Tell, 2011).
9. The approach of nutritional healing for depressive disorder
The conceivable helpful effect of changes within the dietary regime on the present category of psychological maladies is not known properly. However, the current scope of observational proof of wide number of nations among varied gatherings of age had provided backing to the conflict that quality of diet is considered to be a potential defensive or hazard factor for depressive disorder. Despite the fact that there are numerous variants of a “healthy eating routine” across various nations depending on the culture of the populace inhabiting, the accessible proof from observational investigations or randomized control preliminaries proposed that eating regimen with high plant products nourishments, for example, fruits, organic products, green vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, including fish, are related with a decreased hazard for depression, whereas dietary formulations that incorporate foods which are processed and especially sweet items are related with an expanded danger for the disorder. Although cognisant of the impediments with regard to information available from observational data, these confirmations are typically seen to be autonomous of financial status, training and other possibly confusing factors and not really clarified by turn around causality. Moreover, based on another report of meta-investigation which announced that raised obedience to a Mediterranean eating regimen was related with a decrease of 30% hazard factors for the depressive disorder although there is no proof for distribution predisposition (Psaltopoulou, Sergentanis, Panagiotakos, Sergentanis, Kosti, and Scarmeas, 2013). Moreover, it has been also observed that the Mediterranean eating routine is perceived as an invigorating dietary example and is broadly connected with decrease of persistent illness hazard factors. In accordance to current information, a systematised review affirmed the connections within worsening regimes of diet, portrayed by higher admissions of nourishments with saturated forms of fat and refined sugars, and processed items of food, and worse condition of psychological wellness among kids and teenagers. A few cohort concentrates additionally detailed relationship between the nature of weight control plans among ladies at the time of pregnancy and the developing hazard factor for malfunctioning within the psychological system among the youngsters, along with new bits of knowledge into potential action mechanism that incorporate plasticity of brain, the microbiological inhabitants within the gut and pathways related to oxidative stress and inflammation.
In spite of the fact that there are information recommending that some of the nutritional enhancements might be of considerable importance as adjunctive treatments with regard to mental disorders, yet the research arena concentrating on the connections between a whole quality of diet and mental issues is an emerging one. Moreover, it has been linked up to a great extent with the constrained consideration depending on animal model study and observational examinations among individuals. Along these lines, although the current observational information bolster a causal connection between diet quality and depressive disorder based on the Bradford Hill measures along with supporting large data information with animal model studies, randomized controlled preliminaries are in necessity to examine the causal connections and to distinguish whether changes in the dietary regime can improve psychological well-being among individuals suffering with such conditions (Akbaraly, Brunner, Ferrie, Marmot, Kivimaki, and Singh-Manoux, 2009).
Based on the evidences most of these investigations announced enhancements with regard to proportions suffering from depressive disorder with adherence to the mediation, but at the hour of the survey it was observed that no examinations satisfied the standards for quality for the inclusion and exclusion of mental health populaces or carried out with the intention to test the speculation that dietary improvement may bring about upgrades in status of mental health. Therefore from that point, only a single investigation was communicated assessing the conceivable effect of a way of life changes, which includes both eating regimen and physical activity routine, on the symptomatic manifestations of mental health among patients suffering from depressive disorder. However, the particular investigation failed to depict any distinctions within the indication levels among the sample group of intercession in comparison to the consideration control gathering. Then again, a post hoc examination of an enormous scope intercession based examination offered an initiating help for the improvement of diet regime as a methodology for the essential counteraction of depression. Though these investigations fuelled to survey the viability of the mediation for forestalling the depressive disorder, there were proofs (which are not powered based on statistical tool analysis) with regard to the decreased occurrence of hazard parameters for clinical depression that were randomized to a Mediterranean eating routine containing nuts (Pina-Camacho, Jensen, Gaysina, and Barker, 2015).
A study was conducted by a group of researchers with the application of a RCT plan, was meant to research the adequacy of a formulated diet regimen for the treatment of significant depressive scenes. Within the preliminary, the researcher structured the Supporting the Modification of Lifestyle In Lowered Emotional States (SMILES), they estimated that organized dietary help, concentrating on improving eating regimen quality utilizing an adjusted Mediterranean eating regimen model, would be better than a social help control condition in decreasing the seriousness of symptomatology of depression. According to the study it was a three months, equal gathering, RCT blinded singly with respect to a dietary mediation for the effective therapy of moderate to extreme cases of depression. The members for the study were enrolled from two locales namely Barwon Health in Geelong and St. Vincent's Health in Melbourne (Victoria, Australia) for the total time frame of 3-years. Study members were randomized to get either help in the form of social or diet. In accordance with the guidelines the members within the two gatherings finished evaluating the primary and secondary outcomes preceding to the initiation of the study (standard), with the essential and optional results estimated after the fulfilment of the program (3 months, essential endpoint). According to the study ethical guidelines written educated assent was accomplished from all members following a total portrayal of the examination offered to them. The researcher prepared the conventions for conducting the investigation as per the Standard Protocol Items - Recommendations for Interventional Trials (SPIRIT) rules. Announcement of the data outcomes relating to essential and auxiliary results was done as per the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) 2010 rules with regard to their expansion to non-pharmacologic therapeutic regimes (Jacka, F. N., Mykletun, A., Berk, M., Bjelland, I., & Tell, G. S. (2011).
The intercession approached within the study comprised of individual seven diet counselling meetings conveyed by a clinical dietician. The investigation was carried on within a controlled condition that also involved a social help convention during the similar visit timetable and length. The researchers studied the essential endpoint symptomatic manifestations of depression utilizing the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) on the third month of the study. Auxiliary results included the phase of remission and change of feelings or temperament and state of mind. Examinations of the data were done depending on a probability based blended impacts model such as Mixed-Effects Model Repeated Measures (MMRM) approach. The power of evaluations was researched through affectability examinations.
The findings of the investigation highlighted that 166 members for qualification, among them 67 were enlisted (diet intercession, N = 33 and control gathering N = 34). Within the populace N = 55 were undergoing particular form of treatment such as N = 21 were jointly utilizing pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy; N = 9 were under solely psychotherapy; and N =25 were under just pharmacotherapy. There were N = 31 within the eating routine care group and N = 25 within the social help control gathering from whom the total information were gathered at the end of 3 months. The dietary regimen group exhibited fundamentally more prominent improvement from the baseline to the end of 3 months by the MADRS in comparison to social help control gathering, t (60.7) = 4.38, p 0.001, Cohen's d = –1.16. As characterized on MADRS score 10, the remission was accomplished for N = 10 (32.3%) and N = 2 (8.0%) within the mediation and control gatherings, individually χ 2 (1) = 4.84, p = 0.028). the Number Needed To Treat (NNT) in light of the scores of remission was 4.1 (95% Confidence Interval of NNT 2.3 to 27.8). The analysis of sensitivity for the investigation, examining the left members from the category of missing indiscriminately (MAR) supposition, demonstrated that the effect of the mediation was strong in comparison to the infringement of MAR presumptions (Psaltopoulou, Sergentanis, Panagiotakos, Sergentanis, Kosti, and Scarmeas, 2013).

Therefore, these outcomes give fundamental RCT proof to dietary improvement as a strong methodology of therapeutic regime for significant scenes of depression. The researchers of the investigation eventually reported critical decreases among the indications of depressive disorder because of this intercession, with a general size impact of 1.16 values. The group of researchers also stated that these impacts have been found to be autonomous with regard to any adjustments in parameters of self-viability, BMI, smoking rates as well as exercises. At the conclusion of this preliminary the researchers proposed that with the improvement of eating regimen of an individual as indicated by recent proposals focusing on depression might be a helpful and available methodology for the tending to despondency populace within both common and in medical settings. However, numerous information are available which recommends that eating a more healthier regimen is comparatively costlier than a less invigorating eating routine (Psaltopoulou, Sergentanis, Panagiotakos, Sergentanis, Kosti, and Scarmeas, 2013), but definite displaying of the expenses for 20 of SMILES members as stated by the research group eating less carbohydrate diet in contrast with the expenses of the eating regimen they demonstrated that their system could be reasonable. Moreover, the broad scope of observational findings connecting quality of diet to psychological well-being has over and again demonstrated that connections observed depends on autonomously of different proportions of the composition of body. However, according to other evidences as stated above there are numerous other physiological pathways via which improvement in the dietary regime might impact depressive disorder. The past investigations have demonstrated on the basis of oxidative strain and inflammatory (Pina-Camacho, Jensen, Gaysina, and Barker, 2015) pathways, plasticity of brain and also on the basis of new proof concentrated on the microbiological inhabitants of gut. Every one of these pathways is proposed to assume a job within the depressive disorder along with additionally affected by quality of eating regimen. Additionally, changes within the conduct of an individual is related with food are a normal result of a nourishment mediation, and these adjustments during the strategy may likewise have a remedial advantage (Pina-Camacho, Jensen, Gaysina, and Barker, 2015).
Another systematic review examination intended to decide the adequacy of dietary intercessions for the alleviation of manifestations of depression and also anxiety by directing a meta-investigation of all randomized controlled preliminaries (RCTs) within the electronic database to till date. The researchers additionally utilized subgroup investigations to look at impacts of dietary mediations on depression (taken into consideration for this study) among both clinical and nonclinical populaces and to investigate which parts of these are related with any potential more noteworthy viability. This meta-examination was based on the PRISMA articulation for straightforward, complete detailing of procedure undertaken along with their outcomes. To rule out the analyst inclination, the inquiry procedure, measures for incorporation and extraction of information, the in total and prior described investigations of subgroups utilized in this meta-examination were tentatively enrolled with PROSPERO (Estruch, 2013).
The findings of the investigation as highlighted by the researchers that 16 qualified RCT analyses had been considered for the study analysis. Arbitrary impacts meta-examinations were directed to decide impact estimates (Hedges' g with 95% of confidence interim [CI]) for dietary intercessions in contrast to the control conditions. The strong origin pertaining to heterogeneity was investigated utilizing subgroups and statistical meta-regression examinations. The qualified RCT analyses with result information for 45,826 members were incorporated among them most of the inspected tests are on depression (N = 15 examinations). It was observed that in any case, dietary mediations altogether diminished the manifestations of depressive disorder (g = 0.275, p = .002, 95% CI = 0.10 - 0.45). Comparative impacts were seen among excellent preliminaries (g = 0.321, p = .002, 95% CI = 0.12 - 0.53) and when contrasted and both latent (g = 0.308, p = .038, 95% CI = 0.02 - 0.60) and dynamic controls (g = 0.174, p = .035, 95% CI = 0.01 - 0.34). It was also mentioned by the group of researchers within the investigation that studies with female members were found to gather prominent advantages by up taking the dietary intercessions, for the alleviation of adverse effects of depression (Estruch, 2013; Pina-Camacho, Jensen, Gaysina and Barker, 2015).
Dietary supplements playing the role of antidepressants
Omega-3's–supplementation is potentially suggested by a developing number of specialists as a fundamental piece of treatment for depression. Dr. Neil Nedley, MD and Stephen S. Ilardi, scientist guarantees that nourishment regime which is high in omega-3's may aid the treatment of both significant form of depression and bipolar issues. Since the western nourishment pattern will in general need nourishments containing omega-3's, it might be valuable to think of a supplemental source, for example, fish oil or flax seed. A few researchers may hold guarantee that the alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) found in flax is not a bio-accessible origin of Omega-3 unsaturated fats. Fish oil might be another practical choice. Pecans likewise contain a generally elevated level of Omega-3's. Notwithstanding source, omega-3 supplementation has reliably shown a decrease in symptomatic manifestations of depression in the past confirmations (Riediger, 2009).
Folate and Vitamin B-12 – Depressed patients will in general exhibit higher inadequacy levels of nutrient B-12. Folate levels ordinarily are lower among patients suffering from depressive disorder (Bodner, 2005). It has been elucidated that an insufficiency in both of these nutrients may disable the process of methylation within the central nervous system that is important to create monoamine neurotransmitters (Penninx, 2000). This physiological phenomenon may thusly prompt the hindered mind-set side effects which can be vividly observed among depressed patients.
It is also evident that level of Vitamin D or serum 25-hydoxyvitamin D levels in general is considerably diminished among people suffering from depressions. A few researchers contend that there might be a causal connection among depression and absence of Vitamin D micronutrient (Jorde, 2008), while others keep up that the proof is not that sufficient till now. Considerably all the more befuddling is the absence of a set up measurement or dosage value to treat different disarranges which also incorporates depression. A few investigations propose a portion of 2000 IUs per day for general admission (Vieth, 1999). For the therapy of depressive disorder, a few investigations have utilized doses as extreme as 20,000 – 40,000 IUs/day (Jorde, et. al 2008) which is not dependent on the fact whether there is any presence of any causal relation among the two factors; it creates the impression that a few examinations are yielding positive outcomes in decreasing burdensome manifestations.
Hypericum perforatum L. (St. John's Wort) is right now considered as a hot topic for the research study. It is generally well known in Europe, and utilized within the front line therapy for mellow to moderate level of depression. The United States is somewhat more unenthusiastic to embrace this herb into the domain of psychotherapy, as it accompanies a few contraindications with other prescribed medication. Numerous precise audits present befuddling and opposing outcomes. A meta-examination by conducted by author Linde, et al. had seen Hypericum as compelling as standard antidepressants to diminish burdensome manifestations in gentle to reasonably serious form of depression (Linde, 1996). Almost certainly, more examination should be finished before St. John's Wort turns into an acknowledged treatment for the depressive disorder in the United States. However, these intercessions are not intended within the clinical prescription of pharmacotherapy. Supplements, and even nourishments, may cause contraindications with the present drugs as stated by the researchers (Popa, and Ladea, 2012). Late exploration has concentrated on the job of nourishment in the controlling of depressive disorder. The authors highlighted that for the production of neuro chemicals needs satisfactory measures of nutritional supplements. Among these supplements, the researchers focused on the amino acids (tyrosine, tryptophan and glutamine), minerals (copper, zinc, magnesium, iron), and B nutrients (folic acid, B12, B6). These are available within the entire grains (zinc, magnesium, copper), cheddar, eggs, yogurt (zinc, glutamine, magnesium, tyrosine), vegetables, beans, particularly green leaf ones, cabbage, broccoli, corn, spinach, poultry, fish, etc. Most of the foods referenced above are considered to be the part of Mediterranean eating routine, known for the wholesome formulation it provides. Furthermore, a sound eating regimen just like the Mediterranean kind (wealthy in organic products, fish, vegetables and oats, yet low in meat and dairy items) has been related with a lower danger of acquiring depression. Then again, an eating regimen that is high in refined starches and sugars is a typical factor in burdensome ailment. Liquor can likewise have a serious depressant impact (Popa, and Ladea, 2012).
In the most recent decades, according to the recent evidences lacking of neuro chemicals, for example, serotonin, dopamine, noradrenalin, and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) were related with major depressive disorder. A few investigations showed that amino acids, for example, tyrosine, tryptophan and phenylalanine could be useful for the therapy of depression (Firk, and Markus, 2007). Based on these scientific evidences, it may be very well suggested that re establishing serotonin levels may diminish the side effects of despondency which was hastened by serotonin insufficiencies. The drug aside, this objective can be accomplished through adherence to a sound eating regimen that is high in tryptophan. Also, the amino acid tyrosine and some of the time it’s antecedent phenylalanines are changed over into dopamine and norepinephrine (Popa, and Ladea, 2012).
In this regard, a recent investigation which in (McLean, Rubinsztein, Robbins, and Sahakian, 2004), the final stage incorporated 3,486 grown-up participants somewhere in the age range of 33 to 55 years old must be mentioned. The researchers classified the participants as having either an "entire or wholesome food" (which is high in content with food items such as fish, leafy foods and fruits) or "handled or processed food " (containing high content of prepared meat, sugary food items such as sweet pastries, pies, chocolates, toppings, oil fry food, refined oats and high fat containing dairy items) as their nourishment pattern. Thereafter for the analysis of the findings the parameters of age, vitality admission, conjugal status, drug, other ailments and so on., were adjusted and the findings highlighted that members with the most elevated admission of 'wholesome or entire food' category were to the least extent liable to be depressed in contrast to with those of the other category, the most minimal adherence to this dietary intervention, in light of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies-Depression Scale (CES-D scale) (McLean, Rubinsztein, Robbins, and Sahakian, 2004). Accordingly, an eating regimen containing high content of prepared food may build up the danger of developing depressive disorder. It is also evident from few investigations that there is a additional likelihood that those as of now at more serious danger of depression may will in general devour increasing amount of prepared or processed food high in carbohydrate and lipid content. In spite of the fact that the researchers had presumed that with the poor quality of eating routine, the danger for depression gets enhanced, however, circumstances and logical results could not yet define the association between the two factors. To establish the causal relationship between the two factors the role of every individual food items with regard to enhancing danger for depression would be surveyed for a causality relationship to be illustrated (Akbaraly, Brunner, Ferrie, Marmot, Kivimaki, and Singh-Manoux, 2009).
However, it must be mentioned that the connection between processed food and depression has as of late been affirmed with the help of research studies. The enormous examination conducted in Europe followed and investigated the way of life and eating routine of higher than 12,000 volunteers who are not suffering from depression within time frame of 6 years (Sánchez-Villegas, Toledo, De Irala, Ruiz-Canela, Pla-Vidal, and Martínez-González, 2012). It was observed that those members who are consuming higher quantity of trans-fats (available within the high sugar food items like pastries and inexpensive food) demonstrated about 48 percent expansion in the hazard of developing depression when contrasted with those members who did not follow such dietary routine. With further studies on the role of polyunsaturated fats (that incorporated an enhanced amount of fish and vegetable oils) and olive oil in the advancement of MDD, these items were seen as related with a lower danger of acquiring of despondency (Akbaraly, Brunner, Ferrie, Marmot, Kivimaki, and Singh-Manoux, 2009).
The researchers had stated that the worldwide ascent with regard to the number of cases for MDD victims as of late could be inferable to the essential alterations within the wellsprings of fats devoured in Western eating regimens, where the researchers had subbed particular kinds of healthy fats for instance polyunsaturated and monounsaturated available in vegetable oils, nuts and fish for the trans and saturated fats available within meats, spread and different items, for example, mass-delivered baked goods and cheap food items. Therefore, as a consistent pattern with reference to the discoveries referenced above, the alleged "Western" dietary example (which is found to be high in saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fats along with trans-unsaturated fats which are very much common in Northern Europe and USA) has been embroiled as a pertinent hazard factor for the advancement of depressive disorder (Akbaraly, Brunner, Ferrie, Marmot, Kivimaki, and Singh-Manoux, 2009; Sánchez-Villegas, Toledo, De Irala, Ruiz-Canela, Pla-Vidal, and Martínez-González, 2012).
However the dietary examples taken all in all, the role played by various dietary supplements with regard to the danger of creating despondency has been concentrated extensively as of late. The cerebrum or brain is considered to be among of the organs with the most elevated content of lipids. The lipids present within the cerebrum are made out of unsaturated fats, are structural components of the membrane covering. Moreover, it is evident that the grey matter of brain incorporates about half content of polyunsaturated fatty acids and of which about 33% have a place within the omega-3 family. As these are primary or essential fatty acids which imply that they cannot be manufactured or synthesised within the physiological system, they should be provided through eating routine. According to one of the principal cognizant investigations on the impact of dietary substances on the structure and function of the brain, analysts considered the functioning of omega-3 fatty acids (McLean, Rubinsztein, Robbins, and Sahakian, 2004). Laboratory investigations were first done on x-vivo refined cerebrum, and then further studied point on within the in vivo cells of the cerebrum, lastly on biochemical, physicochemical, neurosensory, physiological, and factors related to conduct. However, research studies that had been directed uniquely on unsaturated fats present in the formulation of milks for newborn children, the outcomes showed that the idea of polyunsaturated fatty acids (specifically omega–3 fatty acids) could decide the cerebral, visual, and scholarly capacities (Parker, Gibson, Brotchie, Heruc, Rees, and Hadzi-Pavlovic, 2006).
The examples of two omega-3 unsaturated fats, for instance docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), found in fish oil, have been found to have alleviating impacts from depression. DHA can be considered more important within this subject, since our body transforms EPA into DHA, however there are restricted clinical investigations on unadulterated DHA. In this regard, an EPA bioconversion pathway additionally includes the synthesis of thromboxanes, prostaglandins and leukotrienes. A significant number of the proposed components of this change include the involvement of neurotransmitters. For example, the alleviating impact from depression might be because of bio transformation of EPA to prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and different synthetic compounds required by the cerebrum and ensnared for the safety reactions within our physiological system. Whichever might be the situation, proof assembled during the time has demonstrated that omega-3 unsaturated fats can help treat the depressive disorder. In adequacies in the content of omega-3 unsaturated fats have been recognized as a contributing variable to temperament issues and offer a potential objective treatment approach. Case-control examines have demonstrated that those patients going through the phases of depression have altogether lower levels of omega-3 nutrient (Ross, Seguin, and Sieswerda, 2007) and clinical preliminaries have shown that the adequacy of omega-3 as an adjunctive approach of treatment for significant form of depression. Amassing proof from segment concentrates based on demographic examinations additionally demonstrated a connection between consumption of high amount of fishes and diminished occurrences of mental issues; this lower rate being the immediate after effect of omega-3 unsaturated fat administration (Parker, Gibson, Brotchie, Heruc, Rees, and Hadzi-Pavlovic, 2006). Moreover, exploratory examinations have uncovered that diets with diminished content of omega-3 polyunsaturated unsaturated fats (PUFAs) lead to impressive unsettling influence on the neural capacity of the brain (Sinclair, Begg, Mathai, and Weisinger, 2007).There is naturally conceivable proof to propose that omega-3 PUFAs may assume a job as adjunctive treatment for the depressive disorder, however much examination is required to decide the best omega-3 PUFA (DHA, EPA or a blend of both) and the best effective portion.
Besides, as per another examination (Levenson, 2006), supplementation with nine vitamins, at about multiple times in overabundance of normal suggested dietary stipend (Recommended Dietary Allowance) for 1 year might result in the augmentation of mood fluctuations. It should be mentioned in regard to this study reference that these adjustments in mind-set following a year happened despite the fact that the blood status of nine nutrients arrived at a standard level or plateau following three months. Numerous neurochemicals additionally rely upon the accessibility of amino acids. It is already a known fact that eight out of twenty amino acids must be provided through our eating routine, for they cannot be manufactured within the human body. Therefore, these are referred as “essential amino acids”. A top quality diet based on protein content incorporates all the fundamental amino acids. Food which are highly proteinaceous in nature incorporates the following especially milk, meat and other dairy items, and eggs. Therefore, protein consumption by an individual and thus the respective amino acids can influence the working capacity of brain and the status of mental health. Low blood levels of tyrosine were also evident among few MDD patients (Parker, Gibson, Brotchie, Heruc, Rees, and Hadzi-Pavlovic, 2006).Mineral inadequacies have likewise been connected to development of MDD, albeit quite a bit of this relationship anticipates increasingly broadened research. Zinc and selenium are two of the minerals that stirred logical intrigue. An audit recognized five examinations which demonstrate that low selenium administration is related with brought down mind-set status.Other contemplates have indicated that zinc levels are in reduced amount among people with significant clinical depressive disorder. Besides, research showed that the admission of oral zinc can upgrade the viability of the treatment of depression. At present varied flow research in the field of psychoneuroimmunology is focusing on the interactions of varied interconnected pathways that can establish the reason for a more clear comprehension of the connection between wholesome nourishment regime, central nervous system, and the immunological capacity of an individual which cumulatively impacts the emotional well-being status of a person. A few late investigations have ensnared the physiological phenomenon of inflammation during the physiopathology of depressive disorder (McLean, Rubinsztein, Robbins, and Sahakian, 2004). It is also evident based on the research that those nourishment formulations which are high in content of refined sugar, starches, and saturated or trans-fats, with reduced or diminished contents of naturally available antioxidative agents and fiber from organic products, vegetables, fruits and entire grains, and with diminished level of omega-3 unsaturated fats may cause an initiation of the pathways related to inflammation [42]. The above mentioned facts could imply that the physiological phenomenon associated with inflammation could advance the stages of depression and its burdensome side effects. In this way, diets have a strong correlation with inflammation and which in turn can transform the process of inflammation into depression (Parker, Gibson, Brotchie, Heruc, Rees, and Hadzi-Pavlovic, 2006).
9.1 Discussions
The pathways with the help of which these changes within the dietary regime can offer profit to the populace suffering from psychological disorder presently cannot seem to be completely settled. In any case, diet may act upon varied mechanisms that are ensnared in by the mental health disorders also. Dietary intercessions hold guarantee as a new mediation for diminishing indications of depression over the populace. Further research is demanded in the near future to decide the particular segments of dietary intercessions that improve emotional wellness, investigate basic components, and set up compelling plans for conveying these mediations in clinical and general wellbeing settings (Pina-Camacho, Jensen, Gaysina, and Barker, 2015).
9.2 Limitations
The researchers stated several limitations or constrains within the study that there might be bias in the form of expectation as the study further needed to be more illustrative in terms of showcase about the type of intervention along with the incapability to blind the members of the study towards the intercessions. The researchers also declared that they were not able to carry out the investigation with the required number of members so their study could not be considered as a representative and the findings cannot be generalised. Moreover, due to this issue the size impact might be elevated than the true estimation. Another important feature mentioned by the researchers that most of the members within the study were recruited based on the worse diet regimen they used to follow so this may also hinder to generalise the data to a wider context. Over analysis of all the scientific evidences have revealed the existence of publication bias within the meta analysis. The inclusion criteria set for the RCT studies were not stringent and this led to the over mixed population of the data with many confounding factors that might reduce the impact of the study (Estruch, 2013).
Most of the studies included comprised of small number of focus group participants. Therefore, the researchers of most of the studies suggested conducting further investigations with higher number of participants to explore the efficacy of the therapeutic intervention. Moreover, maximum of the studies considered for the meta analysis were based on a particular form or severity of depressive disorder participants, however, severe forms of depression along with individual focused consideration should be conducted to assess the expanding nature of intervention. Several authors also suggested that higher sample size along with stratified analysis and regression analysis will be required to establish the efficacy of the emerging therapeutic approach. Among the other weakness observed among the investigations many studies with small sample group did not include any active control group for their studies. Studies conducted upon the mind body intervention were very scarce and moreover did not include any particular type of mind body techniques or strategies for a specified group of populations for instance for the population who are at higher risk but could not avail the therapeutic regime for mental health. However, the findings of the studies highlighted about the positive aspects such as feasibility, efficacy and acceptability of the intervention and therefore, the researchers also highlighted that the upcoming studies should include active control for comparatively larger sample size and must ensure longitudinal data on the efficacy of the interventions among the high risk population who are at disadvantaging position with regard to access of treatment.
10. Overall Conclusion
Clinical depression is considered among the most common disorders with enhancing prevalence. At a worldwide level, more than 300 million individuals are evaluated to experience the ill effects of depressive disorder. The incidence of depression is increasing among females (5.1%) than in comparison to the male counterparts (3.6%). Depression hinders any individual from accomplishing their maximum capacity, hinders human capital, and is related with untimely mortality from self destruction and different associated sicknesses. Treatment for the depressive disorder can include a blend of way of life changes, talking treatments for instance cognitive behavioural intervention and medication mostly antidepressants. However, the strict adherence to antidepressants was found to be poor and numerous people do not consider antidepressants to be safe and adequate treatments for depression due to its immense side effects and moreover, want to be treated without medication. The concept of quantum medicine is considered to be an emerging one in the field of medicine to several persistent conditions and this is considered under the practice of complementary or alternative medicine. The concept of quantum medicine is based on the fact that the body of living organisms is composed of electromagnetic waves or radiations that demonstrate changes along with the mental, physical or chemical alterations within the body. Bio electromagnetic therapies, nutritional healing, energy healing, relaxation techniques, herbal medications, behavioural interventions and mind body therapeutics are the most utilized strategies under the quantum medicine approach. However, past studies on the following arena is comparatively scarce. Moreover, it was also evident from several studies that the aptitude of taking up CAM as therapeutic regime is depended on several factors such as the type of population, the physiological and psychological status of the individuals, the particular clinical consideration and also upon the geographical location. The CAM approach uses the detailed thought process for conducting treatment of the individual and therefore, it is also known as curative treatment. Several individuals suffering from depression do not receive proper mental health treatment, therefore, the mind body approach such as t'ai chi or qigong, muscle relaxation, spinal control, yoga, contact of healing and hypnotherapy, nutritional healing with specific nutrient supplements within the diet regime of patients such as omega 3 fatty acids, energy healing such as pranic healing, Qi treatment and techniques for relaxation are considered to be a potential alternative treatment for those individuals in terms of safety and effectiveness in comparison to the front line allopathic medication and hospitalization to psychiatric wards for alleviating the symptoms of clinical depression. The detailed etiological factors of depression had been discussed within the write up. The pathways are interrelated with several components of hereditary vulnerabilities, structure and function of the brain, neuroendocrine and neurotransmitter involved procedures and the pathways involved in relation to the immunological mechanism. Moreover, the quantum based views regarding depressive disorder had been clearly outlined. According to the concept of quantum thinking the unconscious state of mind is an origin of parallel or quantum thinking and the state of cognitive depression is related to the total misarranged state of quantum thinking. Along these lines, the five bodies within the quantum medicine approach had been discussed in details.
The significant way of the approach of biomedicine has been able to concentrate on material reasons for contamination, ailment, and worsening or weakening of physical capacity in any or the entirety of the frameworks of the physical body. These ways have additionally assisted with expanding life span. Notwithstanding, numerous people have additionally been trapped amidst complex recuperation programs which also incorporate pharmacological intercessions which help the issue, yet demonstrates manifestations of contradictions at different parts of the body. Basically the primary five pillars of health and wellbeing can be separated conventionally into the accompanying zones such as physical, psychological, mental, spiritual and social. The biomedical way to offer treatment has been considered as the essential methods for the conveyance of human services. This practice is additionally referred as biomedicine, allopathic medication, conventional approach of medication, frontline medication and Western medication. Moreover, disappointment with biomedicine approach of treatment, has urged more people to assume liability for their own wellbeing by up taking alternative modes of treatment. The integrated deficiency for treating entire individual issues or patient focused treatment started to be addressed by people, who got option of alternative or complementary medications in the second part of the twentieth century.
From the details above, contemporary and classical sense both impact our mental health and possible adjustable features that can harness therapeutical interventions. Current robust interventional proof shows available shady support for various applications of these elements through heat and sauna therapy, green exercise, nature and horticultural activity, breathing exercises, and balneotherapy. We ought to understand that these interventions never had a definitive study to treat psychiatric illness, and therefore, it is early to contemplate that they are standard therapies (Dubois et al., 2010). Nevertheless, the evidence confirms several positive mental health benefits. For example, known effects of like morning sunlight raises cortisol and serotine production, modulate temperature that improves immunity and blood circulation.
Many of the inventions from the above do not adhere to strict reductive analysis of some methods recommended for psychiatric disorders but they aim to provide various ways of thinking putting consideration in working with conventional of interventional treatment to develop mental health. Many of these interventions do not possess strong evidentiary support and needs more research using controlled and randomised design. There is need for more study on these elements most especially hydrotherapy, nature-exposure therapy and sauna and heat therapy on mental health and depression.
Potential benefits of harnessing these elements exist for the purpose of our health being. The approach is part of the upcoming “lifestyle medicine” field. Besides providing the basics of supporting life, and possible mental health aids, there are other ancillary benefits. These kinds of approaches may improve physical health, enhance social life, increase self-mastery or “self-efficacy” and promote cognition and brain health (Streeter et al, 2010). The approaches are mostly low cost but choices might be limited in developing countries and countries with polluted and overindustrialized surroundings. Recent data from the UK suggest that there still exist barriers hindering this lifestyle medicine from implementation. Primary aspects on why lifestyle modification is not implemented in most clinical practice is because there is no support from the organisation, lack of knowledge and roles on this practice, lack of time to engage in the practice and a low perception on the benefits of these practices (Kardakis et al., 2018). Overpowering these obstacles within mental health organisations presents more challenges, possible motivational problems, low socio-economic status for mental illness patients, increased comorbidity and shortage of medical staff equipped with lifestyle medicine skills and training. Currently, there is no fast resolution, but there is increased emphasis to bring awareness on the new lifestyle and more interface greatly on clinical bodies and policy makers. There are other aspects linked to mental health issues like open spaces but warrant more investigation, especially for open who do not go to space.
There is encouragement from psychiatric field and the larger medical field to venture into the fundamentals in ways of understanding the benefits and possible use of these elements in mental health. A point to note is that we are not ignoring the roles played by the psychological and pharmacotherapy methods in treating psychiatric disorders but we also need to acknowledge that nature also has a key to solving many problems that are affecting the current society. Society is increasingly becoming more hyper stimulated and socially isolated and relating more to the biosphere and other human will have mental health nourishment.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) assesses, challenges, and adjusts useless considerations that continue during the phase of depression. Interventions related to behavioural therapies are likewise used to increment charming exercises to treat anhedonia. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is viable as a single therapy in despondency in youth. Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) has demonstrated successful in paediatric despondency; concentrating on helping people showing declination in relational clashes by showing them relational critical thinking abilities and helping them change correspondence designs. Antidepressant medication determination ought to be individualized dependent on clinical components, including side effect profile, co morbidity, bearableness profile, past reaction, potential medication sedate collaborations, persistent inclination, and cost. No antidepressant medication has been plainly demonstrated to be better than another; all FDA-endorsed antidepressant drugs ought to be considered conceivably suitable for first-line treatment.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), mirtazapine, bupropion, and a few more up to date specialists are commonly utilized as first-line prescriptions in light of the fact that their security and bearableness might be desirable over patients and clinicians contrasted with those of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs).
The recent monoaminergic frameworks based medication for the treatment of depressive disorder is considered to be a long way from being perfect. Tremendous endeavours have been stressed on the improvement of novel medications toward new potential focuses past the monoamine theory. However, none of these endeavours can be considered to be successful in the advancement of any basic level novel prescriptions for the depressive disorder. Advanced methodologies for viable treatment of depression should jointly target the improper regulation of certain genetic arrangements responsible for the pathophysiology of disorder. A framework involving the physiology orientated mending way to deal with this issue is thought to be available within Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that has been created in China more than a huge number of years ago. medications work to re establish interior parity. In light of its mechanistic perspective, a commonplace treatment approach in TCM addresses the body as all in all element and fixes any sickness by lightening its side effects, yet in addition re establishing inward parity. Ibogaine, a psychedelic and Yuanzhi-1, a triterpenoid saponin the two herbs are experimentally utilized for the cure of despodency. Another model pertinent to TCM is scopolamine has been accounted for fast stimulant impacts inside few days. Within the practice of TCM, a patient suffering from depression is generally given a combined formulation to use on a day to day basis continued for half a month, so as to reduce burdensome side effects. Another recommended medication is "Dai-Kenchu-To". It is a prepared decoction blend of three herbs which can be utilized for the treatment of varied types of gastrointestinal issues. Therefore, it has been recommended that the GI tract and microbiota are engaged with the pathophysiology and aetiology concerning depressive disorder. Another medication named "Qing-Re-Yao" can be considered to be a potential medication or formulation acting via the anti inflammatory pathway and eventually results in irreversible prevention of inflammation associated depressive symptoms.
Enthusiasm and curiosity for the usage of mind body treatments for varied mental issues and specifically for MDD is rising among the focus group populations and also expanding among professionals. The word meditation alludes to a vast type of practices which are psychosomatic in nature and within this process it includes preparing and directing consideration towards exteroceptive or interoceptive foci, or deliberately developing pictures within brain, while watching or re establishing the consideration from diverting thoughts. However, there prevails a difference about which therapies depend on reflection and are similar with respect to the action mechanism. Several randomised control trials were investigated and within the study the parts of contemplation worked on concentrating on the praxis itself, were inferred using elucidating standards drawn from Patañjali's Yoga Sutras, 16 mental symbolism theory and the Satipatthana Sutta. Only 3 examinations were discussed where just patients with lingering side effects of depression after intense stage treatment, and these exhibited impact sizes within the range of 0.65 to 1.02. Nearly 11 preliminaries included members with a recent episode of major depressive disorder or a blend of patients with significant MDD, dysthymia, and those with indications at the phase of remission. The huge sample of the 11 examinations incorporated subjects in the phase of major depressive episodes (MDE) of around 219 subjects demonstrated that the adequacy of MBCT didn't show any variation with respect to patients experiencing a MDE or had remaining indications of sub acute phase.
The conceivable helpful effect of changes within the dietary regime on the present category of psychological maladies is not known properly. Omega-3's–supplementation is potentially suggested by a developing number of specialists as a fundamental piece of treatment for depression. The examples of two omega-3 unsaturated fats, for instance docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), found in fish oil, have been found to have alleviating impacts from depression. It is also evident that level of Vitamin D or serum 25-hydoxyvitamin D levels in general is considerably diminished among people suffering from depressions. A few researchers contend that there might be a causal connection among depression and absence of Vitamin D micronutrient (Jorde, et. al 2008), while others keep up that the proof is not that sufficient till now. Randomized control preliminaries proposed that eating regimen with high plant products nourishments, for example, fruits, organic products, green vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, including fish, are related with a decreased hazard for depression, whereas dietary formulations that incorporate foods which are processed and especially sweet items are related with an expanded danger for the disorder. Study outcomes give fundamental RCT proof to dietary improvement as a strong methodology of therapeutic regime for significant scenes of depression. The researchers of the investigation eventually reported critical decreases among the indications of depressive disorder because of this intercession, with a general size impact of 1.16 values. It was also mentioned by the group of researchers within the investigation that studies with female members were found to gather prominent advantages by up taking the dietary intercessions, for the alleviation of adverse effects of depression.
Take a deeper dive into Journey Mapping Tool on Lidtka Model with our additional resources.
Reference List
- Amen, D. G. (2015). Change Your Brain, Change Your Life (Revised and Expanded): The Breakthrough Program for Conquering Anxiety, Depression, Obsessiveness, Lack of Focus, Anger, and Memory Problems. Harmony.
- Bender, A., Hagan, K. E., & Kingston, N. (2017). The association of folate and depression: A meta-analysis. Journal of psychiatric research, 95, 9-18.
- Chopra, D. (2015). Quantum healing: Exploring the frontiers of mind/body medicine. Bantam.
- D'Silva, S., Poscablo, C., Habousha, R., Kogan, M., & Kligler, B. (2012). Mind-body medicine therapies for a range of depression severity: a systematic review. Psychosomatics, 53(5), 407-423.
- Edenfield, T. M., & Saeed, S. A. (2012). An update on mindfulness meditation as a self-help treatment for and depression. Psychology research and behavior management, 5, 131.
- Essau, C. A., & Chang, W. C. (2009). Epidemiology, comorbidity, and course of adolescent depression.
- Gupta, S., & Sharma, M. (2016). Lean services: a systematic review. International Journal of productivity and performance management.
- Hill, C. E., Knox, S., & Hess, S. A. (2012). Qualitative meta-analyses of consensual qualitative research studies.
- Hsu, M. C., Moyle, W., Creedy, D., Venturato, L., Ouyang, W. C., & Tsay, S. L. (2009). Use of antidepressants and complementary and alternative medicine among outpatients with depression in Taiwan. Archives of psychiatric nursing, 23(1), 75-85.
- Jacka, F. N. (2017). Nutritional psychiatry: where to next?. EBioMedicine, 17, 24-29.
- Lee, M. S., Jang, J. W., Jang, H. S., & Moon, S. R. (2003). Effects of Qi-therapy on blood pressure, pain and psychological symptoms in the elderly: a randomized controlled pilot trial. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 11(3), 159-164.
- Lewis, J. E., Tiozzo, E., Melillo, A. B., Leonard, S., Chen, L., Mendez, A., ... & Konefal, J. (2013). The effect of methylated vitamin B complex on depressive and anxiety symptoms and quality of life in adults with depression. ISRN psychiatry, 2013.
- Marshall, A. G. (2012). The Great Global Debt Depression: It’s All Greek To Me. AndrewGavinMarshall. com, 15.
- Merikangas, K. R., Cui, L., Kattan, G., Carlson, G. A., Youngstrom, E. A., & Angst, J. (2012). Mania with and without depression in a community sample of US adolescents. Archives of general psychiatry, 69(9), 943-951.
- Nahas, R., & Sheikh, O. (2011). Complementary and alternative medicine for the treatment of major depressive disorder. Canadian Family Physician, 57(6), 659-663.
- NHS Digital, (2019). Psychological Therapies: reports on the use of IAPT services, England July 2019 Final including reports on the IAPT pilots. https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/psychological-therapies-report-on-the-use-of-iapt-services/july-2019-final-including-reports-on-the-iapt-pilots (Accessed on 1st May, 2020).
- Office for National Statistics, ONS (2018). www.gov.uk (Accessed on 1st May, 2020).
- Otte, C., Gold, S. M., Penninx, B. W., Pariante, C. M., Etkin, A., Fava, M., ... & Schatzberg, A. F. (2016). Major depressive disorder. Nature reviews Disease primers, 2(1), 1-20.
- Pandarakalam, J. P. (2018). Certain Bio-Cognitive and Quantum Views of Depression. American Journal of Psychiatry and Neuroscience, 6(2), 33.
- Patel, V., Saxena, S., Lund, C., Thornicroft, G., Baingana, F., Bolton, P., ... & Herrman, H. (2018). The Lancet Commission on global mental health and sustainable development. The Lancet, 392(10157), 1553-1598.
- Rajagopal, R., Jois, S. N., Mallikarjuna Majgi, S., Anil Kumar, M. N., & Shashidhar, H. B. (2018). Amelioration of mild and moderate depression through Pranic Healing as adjuvant therapy: randomised double-blind controlled trial. Australasian Psychiatry, 26(1), 82-87.
- Ravindran, A. V., Lam, R. W., Filteau, M. J., Lespérance, F., Kennedy, S. H., Parikh, S. V., & Patten, S. B. (2009). Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) Clinical guidelines for the management of major depressive disorder in adults.: V. Complementary and alternative medicine treatments. Journal of Affective Disorders, 117, S54-S64.
- Sardá Jr, J., Nicholas, M. K., Asghari, A., & Pimenta, C. A. (2009). The contribution of self-efficacy and depression to disability and work status in chronic pain patients: a comparison between Australian and Brazilian samples. European Journal of Pain, 13(2), 189-195.
- World Health Organization. (2017). Depression and other common mental disorders.(WHO reference number: WHO/MSD/MER/2017.2). Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.
- Yanick, P. (2002). Quantum medicine: A guide to the new medicine of the 21st century. Basic Health Publications, Inc..
- Saveanu, R. V., & Nemeroff, C. B. (2012). Etiology of depression: genetic and environmental factors. Psychiatric Clinics, 35(1), 51-71.
- Brummelte, S., & Galea, L. A. (2016). Postpartum depression: Etiology, treatment and consequences for maternal care. Hormones and behavior, 77, 153-166.
- Lohoff, F. W. (2010). Overview of the genetics of major depressive disorder. Current psychiatry reports, 12(6), 539-546.
- Stuart-Parrigon, K., & Stuart, S. (2014). Perinatal depression: an update and overview. Current psychiatry reports, 16(9), 468.
- Penninx, B. W., Milaneschi, Y., Lamers, F., & Vogelzangs, N. (2013). Understanding the somatic consequences of depression: biological mechanisms and the role of depression symptom profile. BMC medicine, 11(1), 129.
- Slavich, G. M., & Irwin, M. R. (2014). From stress to inflammation and major depressive disorder: a social signal transduction theory of depression. Psychological bulletin, 140(3), 774.
- Vesga-Lopez, O., Blanco, C., Keyes, K., Olfson, M., Grant, B. F., & Hasin, D. S. (2008). Psychiatric disorders in pregnant and postpartum women in the United States. Archives of general psychiatry, 65(7), 805-815.
- Burke, H. M., Davis, M. C., Otte, C., & Mohr, D. C. (2005). Depression and cortisol responses to psychological stress: a meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 30(9), 846-856.
- Paulson, J. F., Dauber, S., & Leiferman, J. A. (2006). Individual and combined effects of postpartum depression in mothers and fathers on parenting behavior. Pediatrics, 118(2), 659-668.
- van Rossum, E. F., Binder, E. B., Majer, M., Koper, J. W., Ising, M., Modell, S., ... & Holsboer, F. (2006). Polymorphisms of the glucocorticoid receptor gene and major depression. Biological psychiatry, 59(8), 681-688.
- Howren, M. B., Lamkin, D. M., & Suls, J. (2009). Associations of depression with C-reactive protein, IL-1, and IL-6: a meta-analysis. Psychosomatic medicine, 71(2), 171-186.
- Malik, M. A., & Lindesay, J. (2009). Quantum physics: Relevance to psychiatry. NeuroQuantology, 7(2).
- Goswami, A. (2011). The Quantum Doctor: A Quantum Physicist Explains the Healing Power of Integrative Medicine. Hampton Roads Publishing.
- Tarlacı, S., & Pregnolato, M. (2016). Quantum neurophysics: From non-living matter to quantum neurobiology and psychopathology. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 103, 161-173.
- Ab Latif, W. A. N. I., & Ggha, S. (2019). Understanding neurobehavioural dynamics: a close-up view on psychiatry and quantum mechanics. The Malaysian journal of medical sciences: MJMS, 26(1), 147.
- Leigh, G. M. (2018). Reconceptualising health: a conversation between quantum science, energy medicine and mystical theology.
- Jacka, F. N., Mykletun, A., & Berk, M. (2012). Moving towards a population health approach to the primary prevention of common mental disorders. BMC medicine, 10(1), 149.
- Colbert, D. (2007). The seven pillars of health. Charisma Media.
- Zafar, S., Sikander, S., Haq, Z., Hill, Z., Lingam, R., Skordis‐Worrall, J., ... & Rahman, A. (2014). Integrating maternal psychosocial well‐being into a child‐development intervention: the five‐pillars approach. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1308(1), 107-117.
- Goswami, A. (2013). Physics of the soul: The quantum book of living, dying, reincarnation, and immortality. Hampton Roads Publishing.
- Goswami, A. (2003). A quantum explanation of Sheldrake's morphic resonance. Online bulletin of science within consciousness. Brody, E. B., & UNESCO. (1993). Biomedical technology and human rights (p. 36). Dartmouth.
- Hollenberg, D. (2006). Uncharted ground: patterns of professional interaction among complementary/alternative and biomedical practitioners in integrative health care settings. Social science & medicine, 62(3), 731-744.
- Coulter, I., & Willis, E. (2007). Explaining the growth of complementary and alternative medicine. Health Sociology Review, 16(3-4), 214-225.
- Jacka, F. N., Pasco, J. A., Mykletun, A., Williams, L. J., Hodge, A. M., O'Reilly, S. L., ... & Berk, M. (2010). Association of Western and traditional diets with depression and anxiety in women. American Journal of Psychiatry, 167(3), 305-311.
- Jacka, F. N., Mykletun, A., Berk, M., Bjelland, I., & Tell, G. S. (2011). The association between habitual diet quality and the common mental disorders in community-dwelling adults: the Hordaland Health study. Psychosomatic medicine, 73(6), 483-490.
- Akbaraly, T. N., Brunner, E. J., Ferrie, J. E., Marmot, M. G., Kivimaki, M., & Singh-Manoux, A. (2009). Dietary pattern and depressive symptoms in middle age. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 195(5), 408-413.
- Jacka, F. N., Cherbuin, N., Anstey, K. J., & Butterworth, P. (2015). Does reverse causality explain the relationship between diet and depression?. Journal of affective disorders, 175, 248-250.
- Jacka, F. N., Kremer, P. J., Berk, M., de Silva-Sanigorski, A. M., Moodie, M., Leslie, E. R., ... & Swinburn, B. A. (2011). A prospective study of diet quality and mental health in adolescents. PloS one, 6(9), e24805.
- Sánchez-Villegas, A., Delgado-Rodríguez, M., Alonso, A., Schlatter, J., Lahortiga, F., Majem, L. S., & Martínez-González, M. A. (2009). Association of the Mediterranean dietary pattern with the incidence of depression: the Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra/University of Navarra follow-up (SUN) cohort. Archives of general psychiatry, 66(10), 1090-1098.
- Psaltopoulou, T., Sergentanis, T. N., Panagiotakos, D. B., Sergentanis, I. N., Kosti, R., & Scarmeas, N. (2013). Mediterranean diet, stroke, cognitive impairment, and depression: a meta‐analysis. Annals of neurology, 74(4), 580-591.
- Estruch, R. i in.(2013), Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a Mediterranean diet,“. The New England Journal of Medicine, 368(14).
- Jacka, F. N., Ystrom, E., Brantsaeter, A. L., Karevold, E., Roth, C., Haugen, M., ... & Berk, M. (2013). Maternal and early postnatal nutrition and mental health of offspring by age 5 years: a prospective cohort study. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 52(10), 1038-1047.
- Pina-Camacho, L., Jensen, S. K., Gaysina, D., & Barker, E. D. (2015). Maternal depression symptoms, unhealthy diet and child emotional–behavioural dysregulation. Psychological Medicine, 45(9), 1851-1860.
- Steenweg-de Graaff, J., Tiemeier, H., Steegers-Theunissen, R. P., Hofman, A., Jaddoe, V. W., Verhulst, F. C., & Roza, S. J. (2014). Maternal dietary patterns during pregnancy and child internalising and externalising problems. The Generation R Study. Clinical nutrition, 33(1), 115-121.
- Jacka, F. N., Cherbuin, N., Anstey, K. J., Sachdev, P., & Butterworth, P. (2015). Western diet is associated with a smaller hippocampus: a longitudinal investigation. BMC medicine, 13(1), 215.
- Dash, S., Clarke, G., Berk, M., & Jacka, F. N. (2015). The gut microbiome and diet in psychiatry: focus on depression. Current opinion in psychiatry, 28(1), 1-6.
- Berk, M., Williams, L. J., Jacka, F. N., O’Neil, A., Pasco, J. A., Moylan, S., ... & Maes, M. (2013). So depression is an inflammatory disease, but where does the inflammation come from?. BMC medicine, 11(1), 200.
- Moylan, S., Berk, M., Dean, O. M., Samuni, Y., Williams, L. J., O’Neil, A., ... & Maes, M. (2014). Oxidative & nitrosative stress in depression: why so much stress?. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 45, 46-62.
- Sarris, J., Murphy, J., Mischoulon, D., Papakostas, G. I., Fava, M., Berk, M., & Ng, C. H. (2016). Adjunctive nutraceuticals for depression: a systematic review and meta-analyses. American Journal of Psychiatry, 173(6), 575-587.
- Zainuddin, M. S. A., & Thuret, S. (2012). Nutrition, adult hippocampal neurogenesis and mental health. British medical bulletin, 103(1), 89-114.
- Levinger, P., Wee, E., Margelis, S., Menz, H. B., Bartlett, J. R., Bergman, N. R., ... & Hill, K. D. (2017). Pre-operative predictors of post-operative falls in people undergoing total hip and knee replacement surgery: a prospective study. Archives of orthopaedic and trauma surgery, 137(8), 1025-1033.
- Forsyth, A., Deane, F. P., & Williams, P. (2015). A lifestyle intervention for primary care patients with depression and anxiety: a randomised controlled trial. Psychiatry research, 230(2), 537-544.
- Abdallah, C. G., Sanacora, G., Duman, R. S., and Krystal, J. H. (2015). Ketamine and rapid-acting antidepressants: a window into a new neurobiology for mood disorder therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Med. 66, 509–523. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-053013-062946
- Ahokas, A., Kaukoranta, J., Wahlbeck, K., and Aito, M. (2001). Estrogen deficiency in severe postpartum depression: successful treatment with sublingual physiologic 17 beta-estradiol: a preliminary study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 62, 332–336. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v62n0504
- Arseneault-Breard, J., Rondeau, I., Gilbert, K., Girard, S. A., Tompkins, T. A., Godbout, R., et al. (2012). Combination of Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175 reduces post-myocardial infarction depression symptoms restores intestinal permeability in a rat model. Br. J. Nutr. 107, 1793–1799. doi: 10.1017/S0007114511005137
- Bangasser, D. A., and Valentino, R. J. (2014). Sex differences in stress-related psychiatric disorders: neurobiological perspectives. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 35:303–319. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2014.03.008
- Berman, R. M., Cappiello, A., Anand, A., Da, O., Heninger, G. R., Charney, D. S., et al. (2000). Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Soc. Biol. Psychiatry 47, 351–354. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00230-9
- Berton, O., and Nestler, E. J. (2006). New approaches to antidepressant drug discovery: beyond monoamines. Nat. Rev. 7, 137–151. doi: 10.1038/nrn1846
- Bravo, J. A., Forsythe, P., Chew, M. V., Escaravage, E., Savignac, H. M., Dinan, T. G., et al. (2011). Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 16050–16055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102999108
- Bulling, S., Schicker, K., Zhang, Y. W., Steinkellner, T., Stockner, T., Gruber, C. W., et al. (2012). The mechanistic basis for noncompetitive ibogaine inhibition of serotonin and dopamine transporters. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 18524–18534. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.343681
- Burgdorf, J., Zhang, X., Nicholson, K. L., Balster, R. L., Leander, J. D., Stanton, P. K., et al. (2013). GLYX-13, a NMDA receptor glycine-site functional partial agonist, induces antidepressant-like effects without ketamine-like side effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 38, 729–742. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.246
- Butcher, E. C. (2005). Can cell systems biology rescue drug discovery? Nat. Rev. 4, 461–467.
- Charney, D. S. (2004). Psychobiological mechanisms of resilience and vulnerability: implications for successful adaptation to extreme stress. Am. J. Psychiatry 161, 195–216. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.161.2.195
- Desbonnet, L., Garrett, L., Clarke, G., Bienenstock, J., and Dinan, T. G. (2008). The probiotic Bifidobacteria infantis: an assessment of potential antidepressant properties in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 43, 164–174. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2008.03.009
- Diaz Heijtz, R., Wang, S., Anuar, F., Qian, Y., Björkholm, B., Samuelsson, A., et al. (2011). Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 3047–3052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010529108
- Drevets, W. C., Zarate, C. A., and Furey, M. L. (2013). Antidepressant effects of the muscarinic cholinergic receptor antagonist scopolamine: a review. Biol. Psychiatry 73, 1156–1163. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.09.031
- Duman, R. S. (2017). Sex-specific disease-associated modules for depression. Nat. Med. 23, 1015–1017. doi: 10.1038/nm.4391
- Duman, R. S. (2018). Ketamine and rapid-acting antidepressants: a new era in the battle against depression and suicide. F1000Res 7:F1000 Faculty Rev-659. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.14344.1
- Duman, R. S., Aghajanian, G. K., Sanacora, G., and Krystal, J. H. (2016). Synaptic plasticity and depression: new insights from stress and rapid-acting antidepressants. Nat. Med. 22, 238–249. doi: 10.1038/nm.4050
- Feng, D. D., Tang, T., Lin, X. P., Yang, Z. Y., Yang, S., Xia, Z. A., et al. (2016). Nine traditional Chinese herbal formulas for the treatment of depression: an ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacology review. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 12, 2387–2402. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S114560
- Gerhard, D. M., and Duman, R. S. (2018). Rapid-acting antidepressants: mechanistic insights and future directions. Curr. Behav. Neurosci. Rep. 5, 36–47. doi: 10.1007/s40473-018-0139-8
- Guan, F., Lam, W., Hu, R., Kim, Y. K., Han, H., and Cheng, Y. C. (2018). Majority of Chinese medicine herb category “Qing Re Yao” have multiple mechanisms of anti-inflammatory activity. Sci. Rep. 8:7416. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25813-x
- Hasebe, T., Ueno, N., Musch, M. W., Nadimpalli, A., Kaneko, A., Kaifuchi, N., et al. (2016). Daikenchuto (TU-100) shapes gut microbiota architecture and increases the production of ginsenoside metabolite compound K. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 4:e00215. doi: 10.1002/prp2.215
- Jacobs, M., Zhang, Y. W., Campbell, S. D., and Rudnick, G. (2007). Ibogaine, a noncompetitive inhibitor of serotonin transport, acts by stabilizing the cytoplasmic-facing form of the transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 29441–29447. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704456200
- Jin, X. L., Shibata, C., Naito, H., Ueno, T., Funayama, Y., Fukushima, K., et al. (2001). Intraduodenal and intrajejunal administration of the herbal medicine, dai-kenchu-tou, stimulates small intestinal motility via cholinergic receptors in conscious dogs. Dig. Dis. Sci. 46, 1171–1176. doi: 10.1023/A:1010690624187
- Jin, Z. L., Gao, N., Li, X. R., Tang, Y., Xiong, J., Chen, H. X., et al. (2015). The antidepressant-like pharmacological profile of Yuanzhi-1, a novel serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitor. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 25, 544–556. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.01.005
- Jin, Z. L., Gao, N., Zhang, J. R., Li, X. R., Chen, H. X., Xiong, J., et al. (2014). The discovery of Yuanzhi-1, a triterpenoid saponin derived from the traditional Chinese medicine, has antidepressant-like activity. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 53, 9–14. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.02.013
- Jing, L. L., Zhu, X. X., Lv, Z. P., and Sun, X. G. (2015). Effect of Xiaoyaosan on major depressive disorder. Chin. Med. 10:18. doi: 10.1186/s13020-015-0050-0
- Kuehner, C. (2017). Why is depression more common among women than among men? Lancet Psychiatry 4, 146–158. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(16)30263-2
- Labonté, B., Engmann, O., Purushothaman, I., Menard, C., Wang, J., Tan, C., et al. (2017). Sex-specific transcriptional signatures in human depression. Nat. Med. 23, 1102–1111. doi: 10.1038/nm.4386
- Lepack, A. E., Fuchikami, M., Dwyer, J. M., Banasr, M., and Duman, R. S. (2015). BDNF release is required for the behavioral actions of ketamine. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 18:pyu033. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyu033
- Li, N., Liu, R. J., Dwyer, J. M., Banasr, M., Lee, B., Son, H., et al. (2011). Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists rapidly reverse behavioral and synaptic deficits caused by chronic stress exposure. Biol. Psychiatry 69, 754–761. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.12.015
- Li, Y., Chen, Z., Yu, N., Yao, K., Che, Y., Xi, Y., et al. (2016). Chinese herbal medicine for postpartum depression: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016:5284234. doi: 10.1155/2016/5284234
- Maeng, S., Zarate, C. A., Du, J., Schloesser, R. J., McCammon, J., Chen, G., et al. (2008). Cellular mechanisms underlying the antidepressant effects of ketamine: role of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors. Biol. Psychiatry 63, 349–352. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.05.028
- Manji, H. K., Drevets, W. C., and Charney, D. S. (2001). The cellular neurobiology of depression. Nat. Med. 7, 541–547. doi: 10.1038/87865
- Mazure, C. M., and Jones, D. P. (2015). Twenty years and still counting: including women as participants and studying sex and gender in biomedical research. BMC Womens Health 15:94. doi: 10.1186/s12905-015-0251-9
- Murata, P., Kase, Y., Ishige, A., Sasaki, H., Kurosawa, S., and Nakamura, T. (2002). The herbal medicine Dai-kenchu-to and one of its active components [6]-shogaol increase intestinal blood flow in rats. Life Sci. 70, 2061–2070. doi: 10.1016/S0024-3205(01)01552-1
- Nestler, E. J., Barrot, M., DiLeone, R. J., Eisch, A. J., Gold, S. J., and Monteggia, L. M. (2000). Neurobiology of depression. Neuron 34, 13–25. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00653-0
- Parker, G. B., and Brotchie, H. L. (2004). From diathesis to dimorphism: the biology of gender differences in depression. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 192, 210–216. doi: 10.1097/01.nmd.0000116464.60500.63
- Preskorn, S. H., Baker, B., Kolluri, S., Menniti, F. S., Krams, M., and Landen, J. W. (2008). An innovative design to establish proof of concept of the antidepressant effects of the NR2B subunit selective N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist, CP-101,606, in patients with treatment-refractory major depressive disorder. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 28, 631–637. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e31818a6cea
- Rhee, S., Pothoulakis, C., and Mayer, E. A. (2009). Principles and clinical implications of the brain-gut-enteric microbiota axis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6, 306–314. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2009.35
- Schroeder, F. A., Lin, C. L., Crusio, W. E., and Akbarian, S. (2007). Antidepressant-like effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor, sodium butyrate, in the mouse. Biol. Psychiatry 62, 55–64. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.06.036
- Soldin, O. P., and Mattison, D. R. (2009). Sex differences in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 48, 143–157. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200948030-00001
- Tokita, Y., Satoh, K., Sakaguchi, M., Endoh, Y., Mori, I., Yuzurihara, M., et al. (2007). The preventive effect of Daikenchuto on postoperative adhesion-induced intestinal obstruction in rats. Inflammopharmacology 15, 65–66. doi: 10.1007/s10787-006-1552-2
- Ung, C. Y., Li, H., Cao, Z. W., Li, Y. X., and Chen, Y. Z. (2007). Are herb-pairs of traditional Chinese medicine distinguishable from others? Pattern analysis and artificial intelligence classification study of traditionally defined herbal properties. J. Ethnopharmacol. 111, 371–377. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.11.037
- Voleti, B., Navarria, A., Liu, R. J., Banasr, M., Li, N., Terwilliger, R., et al. (2013). Scopolamine rapidly increases mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling, synaptogenesis, and antidepressant behavioral responses. Biol. Psychiatry 74, 742–749. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.04.025
- Wohleb, E. S., Franklin, T., Iwata, M., and Duman, R. S. (2016a). Integrating neuroimmune systems in the neurobiology of depression. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 497–511. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.69
- Wohleb, E. S., Wu, M., Gerhard, D. M., Taylor, S. R., Picciotto, M. R., Alreja, M., et al. (2016b). GABA interneurons mediate the rapid antidepressant-like effects of scopolamine. J. Clin. Invest. 126, 2482–2494. doi: 10.1172/JCI85033
- Wu, Y. C., and Hsieh, C. L. (2011). Pharmacological effects of Radix Angelica Sinensis (Danggui) on cerebral infarction. Chin. Med. 6:32. doi: 10.1186/1749-8546-6-32
- Yang, L., Di, Y. M., Shergis, J. L., Li, Y., Zhang, A. L., Lu, C., et al. (2018). A systematic review of acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine for postpartum depression. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 33, 85–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2018.08.006
- Yeung, W. F., Chung, K. F., Ng, K. Y., Yu, Y. M., Zhang, S. P., Ng, B. F., et al. (2015). Prescription of Chinese herbal medicine in pattern-based traditional chinese medicine treatment for depression: a systematic review. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015:160189. doi: 10.1155/2015/160189
- Yoshikawa, K., Shimada, M., Kuwahara, T., Hirakawa, H., Kurita, N., Sato, H., et al. (2013). Effect of Kampo medicine “Dai-kenchu-to” on microbiome in the intestine of the rats with fast stress. J. Med. Invest. 60, 221–227. doi: 10.2152/jmi.60.221
- Zarate, C. A., Singh, J. B., Carlson, P. J., Brutsche, N. E., Ameli, R., Luckenbaugh, D. A., et al. (2006). A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 63, 856–864. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.8.856
- Zhou, W., Wang, N., Yang, C., Li, X. M., Zhou, Z. Q., and Yang, J. J. (2014). Ketamine-induced antidepressant effects are associated with AMPA receptors-mediated upregulation of mTOR and BDNF in rat hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Eur. Psychiatry 29, 419–423. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2013.10.005
- Mitchell, A. J., Vaze, A., & Rao, S. (2009). Clinical diagnosis of depression in primary care: a meta-analysis. The Lancet, 374(9690), 609-619.
- Gotlib, I. H., Lewinsohn, P. M., & Seeley, J. R. (1995). Symptoms versus a diagnosis of depression: differences in psychosocial functioning. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 63(1), 90.
- Carter, J. D., McIntosh, V. V., Jordan, J., Porter, R. J., Frampton, C. M., & Joyce, P. R. (2013). Psychotherapy for depression: a randomized clinical trial comparing schema therapy and cognitive behavior therapy. Journal of affective disorders, 151(2), 500-505.
- Luty, S. E., Carter, J. D., McKenzie, J. M., Rae, A. M., Frampton, C. M., Mulder, R. T., & Joyce, P. R. (2007). Randomised controlled trial of interpersonal psychotherapy and cognitive–behavioural therapy for depression. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 190(6), 496-502.
- Sewitch, M. J., Bexton, B., Rahme, E., Galarneau, S., & Blais, R. (2009). Cross‐generational comparison of dispensed pharmacotherapy for depression. International Journal of Health Care Quality Assurance.
- Alexopoulos, G. S. (2011). Pharmacotherapy for late-life depression. The Journal of clinical psychiatry, 72(1), e04.
- Flint, A. J., & Rifat, S. L. (2001). Nonresponse to first‐line pharmacotherapy may predict relapse and recurrence of remitted geriatric depression. Depression and Anxiety, 13(3), 125-131.
- Veale, D., Le Fevre, K., Pantelis, C., De Souza, V., Mann, A., & Sargeant, A. (1992). Aerobic exercise in the adjunctive treatment of depression: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 85(9), 541.
- Kemmeren, L. L., van Schaik, A., Smit, J. H., Ruwaard, J., Rocha, A., Henriques, M., ... & Zukowska, K. (2019). Unraveling the black box: exploring usage patterns of a blended treatment for depression in a multicenter study. JMIR mental health, 6(7), e12707.
- Freeman, M. P., Fava, M., Lake, J., Trivedi, M. H., Wisner, K. L., & Mischoulon, D. (2010). Complementary and alternative medicine in major depressive disorder: the American Psychiatric Association Task Force report. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 71(6), 669.
- Latendresse, G., Elmore, C., & Deneris, A. (2017). Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors as First‐Line Antidepressant Therapy for Perinatal Depression. Journal of Midwifery & Women's Health, 62(3), 317-328.
- Popa, T.A. and Ladea, M., 2012. Nutrition and depression at the forefront of progress. Journal of medicine and life, 5(4), p.414.
- Firk, C., & Markus, C. R. (2007). Serotonin by stress interaction: a susceptibility factor for the development of depression?. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 21(5), 538-544.
- McLean, A., Rubinsztein, J. S., Robbins, T. W., & Sahakian, B. J. (2004). The effects of tyrosine depletion in normal healthy volunteers: implications for unipolar depression. Psychopharmacology, 171(3), 286-297.
- Akbaraly, T. N., Brunner, E. J., Ferrie, J. E., Marmot, M. G., Kivimaki, M., & Singh-Manoux, A. (2009). Dietary pattern and depressive symptoms in middle age. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 195(5), 408-413.
- Sánchez-Villegas, A., Toledo, E., De Irala, J., Ruiz-Canela, M., Pla-Vidal, J., & Martínez-González, M. A. (2012). Fast-food and commercial baked goods consumption and the risk of depression. Public health nutrition, 15(3), 424-432.
- Parker, G., Gibson, N. A., Brotchie, H., Heruc, G., Rees, A. M., & Hadzi-Pavlovic, D. (2006). Omega-3 fatty acids and mood disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry, 163(6), 969-978.
- Ross, B. M., Seguin, J., & Sieswerda, L. E. (2007). Omega-3 fatty acids as treatments for mental illness: which disorder and which fatty acid?. Lipids in health and disease, 6(1), 1-19.
- Sinclair, A., Begg, D., Mathai, M., & Weisinger, R. (2007). Omega 3 fatty acids and the brain: review of studies in depression. Asia Pacific journal of clinical nutrition, 16(S1), S391-S397.
- Levenson, C. W. (2006). Zinc: the new antidepressant?. Nutrition reviews, 64(1), 39-42.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



