HR Operations and Learning Interventions
Introduction
From the definitive perspective of a graduate trainee Human Resource Officer employed at the Human Resources Department of a specific organisation, the objective of the entire corresponding study undertaking could be determined, to be, the development of the reservoir of knowledge and information, regarding the formulation of better understanding of the cross organisational operational undertakings in human resource management processes, at the organisational operational levels. The purpose of the entire study assignment would be the formulation of an effective and extensive awareness concerning the context of learning intervention for the objective of obtaining the most effective mechanisms to fulfil the organisational developmental necessities which are critical in supporting the strategic operations of any business organisation, from a human resource based perspective.
P1: Analysis of employee knowledge, skills and behaviours required by HR professionals
The utilisation of the Continue Personal Development (CPD) map for the development of Human resources utilisation could be considered to be a practical and standard instrument in the analysis of the skills and knowledge of employees as well as the methods of improvement of their professional behaviours, by the Human Resource Management officials of any specific business organisation. According to Woodcock (2017), the efficacy of this could be realised from the perspective of the ability of such a framework in delivering all of the stages of successful employee knowledge and professional behaviour management and improvement. The CPD map is primarily focused on the behavioural aspects, knowledge and activities which any employee of the business organisations such as the one under consideration in this study could demonstrate. Thus, a proper benchmark could be effectively set regarding the excellence of the Human Resource Management processes regarding the evaluation of the knowledge and skill measures possessed by the individual employees. Further, Raes et al (2015) opine that the objective in this regard is to add the most sustained value to the employer organisation, both in the current perspective as well as concerning the future responsibilities.
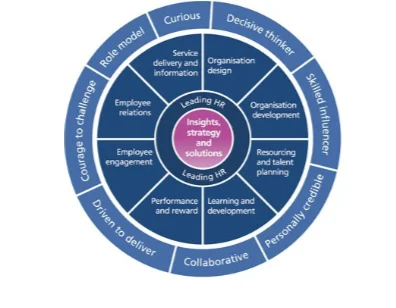
As could be determined from the research observation of Armstrong and Taylor (2014), the CPD map is primarily formulated upon a multiplicity of sections. At the peripheral regions of the hypothetical circular map, there could be situated eight different behavioural aspects which could be observed within the employees and the working personnel of any business organisation. According to Bratton and Gold (2017), these could be identified in the manner of decisive thinking capability, ability of influencing others with skill sets, credibility of personality, the ability of undertaking collaborative work, impetus of delivering the results, the courage of confronting work related challenges, the acumen of becoming a role model for others and ultimately, the urge of learning through consistent curiosity. The entirety of this developmental framework is primarily oriented towards the assessment of the behavioural preferences, activities as well as knowledge base of the employees through underpinning the benchmark criteria which could be useful regarding the development of the services through which the professional and individual developments could be undertaken regarding the business objective achievement in the concurrent market scenario.
The eight aspects thus listed are indicative of the information on which the Human Resource professionals could base their assessments. Furthermore, the accompanying bands of professional competencies have been indicative of the various requirements and transitional challenges which could be encountered by the Human Resource management operatives as well as the working personnel of the business organisations.
Continue your exploration of Learning Interventions with our related content.
According to Albrecht et al (2015), the map as well highlights the different areas of professional responsibilities which are also reflective of the necessities and implications of the development of different skill sets and professional competence based activity proficiency. The professional responsibility management areas, ten in number, could be outlined from the research of Meijerink, Bondarouk and Lepak (2016), as development of the organisational operations, streamlining the organisational design, planning the talent management as well as resource acquisition and placement, concentrating on rewarding outstanding performance, engagement with the employees to the necessary extent, management of the employee relations so that their grievances and requirements could be addressed, delivery of services as well as maintaining the most adequate sharing mechanism of critical information, the core responsibility of evolving the management based insights and strategic solutions of different challenges and finally the overall implications of the Human Resource operational conduct. Furthermore, the most expected skills and capabilities from an HR officer could be variegated and multifarious. These could be identified as fostering close cooperation with the existing organisational departments in the role of a consultant and assisting the line managers with different issues, co-ordinating with the policy stakeholders and staff performance management, promotion of diversity management and equality encouragement as the organisational culture, execution of the multiplicity of responsibilities of staff recruitment and management, providing advisory services in the form of remuneration related activities and assisting the employer organisation to develop and implement effective policies on a range of aspects such as conditions of work, management of opportunity provisioning, formulation of procedures of imposition of discipline and even on management of attendance on part of the employees.
Take a deeper dive into ANA Testing: Diagnostic Advances with our additional resources.

P3: Analyse differences between organisational and individual learning, training and development.
At the onset of such considerations, according to Cohen (2015), it is necessary to ascertain the different dimensions and the overall meaning of the necessity to drive sustainable business operations individual learning, training and development within any operational perspective. This could be understood to be the financial, environmental as well as personnel based resource contribution of any such business organisation over a specific period of time to contribute the development of the employees through constituting proper training and learning processes. The aspects of sustainability is also closely associated with the executive reward and performance management mechanism which could as well be influenced through proper Human Resource operations and various fluctuations, which could be of both long and short term based incidents, of the economic perspective such as share prices which could influence the differential employee training and learning practices observed within specific organisations. It is thus necessary for the managerial personnel of any business entity to look into the future to understand the necessities of the employees regarding which segments require through and particular training and which segment of employees could benefit from supervision based learning processes. This could only be possible from the perspective of sustainable human resource and material based performances. The performance agility infusion is the core difference regarding the previously mentioned three processes holistic development, learning and training necessities of organisational entities, within the operational structure of any business organisation is the cornerstone on which the entire aspect of sustainability based change as well as adaptation to altered business climate could be based. Within the specific business organisation under which the designated HR officer could be employed, the continuous professional development process could be effectively utilised by any HR officer to obtain competencies regarding the concerned profession. Safeguarding the career of such a professional is key objective in this regard. Continuous Professional Learning is different from personal learning and training on multiple perspectives. Within any specific organisation, Continuous Professional Learning could ensure the capabilities of the existing standards of professional qualities. Apart from this, Continuous Professional Learning also assists the HR officers to enhance and maintain the knowledge and skills which could be effective in enabling the HR officials to adapt to differential operational scenarios and to organisational policy changes. Making of meaningful and beneficial contribution to the organisational working processes within the specific organisation under consideration could as well be made through utilisation of Continuous Professional Learning. Thus, Stone et al (2015) has stated that alignment of organisation design is also to be understood as an insight which recurs consistently so that the ensuring of the proper co-ordination of the different parts of any business entity as well as provisioning of the necessary support mechanism to the concerned employees within the real time based exigencies. In terms of the responsibilities of the HR department to ensure sustainability in alignment of designs and operations with goals and objectives, one critical factor emerges from the research of Wilton (2016). This could be comprehended in the manner of bringing together the organisational values and the business methods and strategic as well as tactical considerations regarding the utilisation of the individual working personnel behaviour within the entire system of the company under consideration. Ultimately, this factor is completely oriented towards the achievement of organisational survival perspectives while the implementation of changes could be underway within any transitional or transformation sequence of any specific market condition. Here lies the actualities of the factors which differentiate the training and learning necessities of different employees and human resources of various business organisations.
As per the research of Dong et al (2017), the second of such factors could be underlined as, the distribution of the leadership in the most effective manner as the thematic construct for the engagement of the working personnel and human resources of any business entity such as the hypothetical one under concern in this study. This engagement could be considered to be a deliberate attempt to foster the human resource personnel to expose their particular inclinations and shortcomings regarding their respective professional practices and work designations. Such outcomes could then be put into effect, academically, to outline the differences amongst the necessities and outcomes of organisational learning and individual training initiatives. Other than these, the peripheral aspects are to be identified, as Runhaar and Sanders (2016) has outlined, as the sharing of information and knowledge based expertise and communication of the visions and values which could be associated with the organisational mission statement. These processes could only be observed at organisational learning, training and development processes where a top down and often regimented approach is involved other than the individual learning initiatives of particular learners and personalised training measures which individuals could cater to for the purpose of career and capability development.
P4:Analyse the need for continuous learning and professional development to drive sustainable business performance
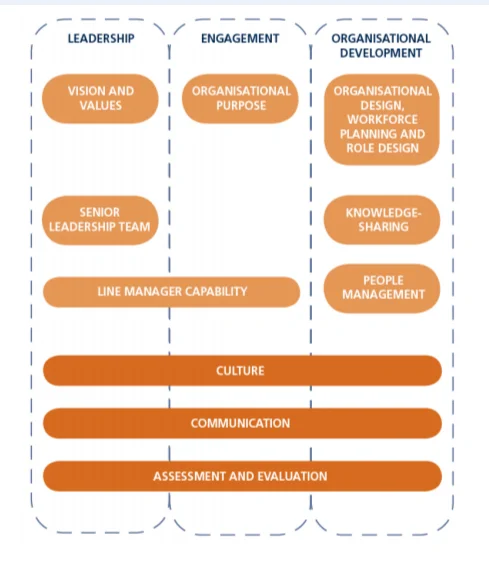
The key aspect of all of the issues which the Human Resource Management department of any business organisation including that of the hypothetical one under consideration could encounter, could be understood from the research perspective of Nankervis et al (2016), as that of Sustainability in business performance. According to Hollenbeck and Jamieson (2015), there are several factors which could be studied as deliberate insights which drive the sustainable performance of any business organisation concerning the enablers related with the particularities of operations and responsibility management in terms of employee training and learning necessities and differences of development processes which could be imperative for the organisation to undertake, both from the Human Resource as well as from the administrative and planning perspectives. These factorial insights generally extend across the key thematic constructs which determine the progression process of any business operation and organisational learning based development and training processes assist in such procedures to a great extent. As an instance, the initial enabler or factor in this context is related closely with the alignment of the organisational design concerning the planning of the workforce and role of working conditionalities under which the human resources could be put to operations. This is the core aspect of any organisational, methodical human resource development process. Individual learning and training, on the other hand, is primarily subjective in nature since this generally occurs on the perspectives of short term based goals which are more or less influenced by the immediacy of necessities which the learner may experience. Al-Haddad and Kotnour (2015) opines that this leadership based operational perspective is related to the entirety of the levels of leadership which could be observed within the company under consideration in this specific study. The distributable or delegation based leadership has to be inclusive of the process through which all of the senior leadership elements of the concerned business organisation of McDonalds could set their organisational strategy and then undertake the empowerment of the subordinate managerial personnel for the purpose of providing the impetus to the existing and newly recruited employees to think about and develop innovative operational practices within the hypothetical business organisation under consideration. Again, this form of leadership based approach is also another difference between organisational and personal learning and training based development since the involvement of such methodical approach is generally non-existent even in cases where personal learning and self-regulated training could be observed to have been implemented. The process is completely oriented towards enabling the mid and lower level managerial personnel of the specific business organisation under which I have also opted to become an HR manager, to drive the organisational performance which could be sustainable to a great extent. Brulin and Svensson (2016) suggests that this approach is perfectly suited towards enabling the an HR managerial aspirant such as me, to accept the leadership roles either on the temporary or permanent basis as per the appropriateness of the nature of work. Katzenbach and Smith (2015) outlines three important aspects which are included in the entire process of delegation of responsibilities from the perspective of human resource management responsibilities which I could have to perform within the particular concerned organisation of McDonalds and these could be understood in the manner of instituting required measure of governance and encourage the innovation opportunities as well as the creativity management within the selected organisational human resources. The emphasis is always on the cultivation of the approach of distribution of the work initiatives which could be better suited to draw the technical as well as professional skills and expertise and the capabilities which could better enable the entire working process to progress further in the most qualitative manner. This process is also augmented by the sharing of information and solving of problems throughout the entire spectrum of business engagement structure of the business organisations under consideration under the philosophy of continuous as well as effective improvement.
According to Epstein (2018), the sharing of the purpose could be understood to be the next factor regarding the sustainable business process management which could involve the prospects of both the employee engagement as well as the leadership elements with whom I could have to operate as the responsible HR management officer. The emphasis is again upon the purpose of brand identity management. Zhong, Wayne and Liden (2016) has opined it as the raison d’être to which the working processes have be aligned through sensitisation of the employees to undertake a proper development of a strong and often emotional bond with the core objectives of the organisation under consideration. This could be comprehended as my ultimate objective as the HR manager within the selected McDonalds organisation. This important from the perspective that such individuals who could thus be sensitised, could be motivated to a certain extent to infuse the necessary effort which could enable them to put in better performance perspectives.

P5: Application of knowledge and understanding of the ways in which high-performance working (HPW) contributes to employee engagement and competitive advantage
Marchington (2016) has asserted that the modern business organisational functioning is always oriented towards the achievement of competitive advantage over the market based rivals. One critical aspect in this regard, in the specific business conditionalities of the current global scenario, could be understood in the manner of the utilisation of the roles of organisational employees to achieve the competitive leverage which could be utilised in the market based operations by the employer organisation. In terms of the concept of High Performance Work Practices (HPWP), Shen and Benson (2016) has observed that this conceptual construct is primarily an instrument in the management of the shifting of priorities within the greater perspective of the Human Resource Management (HRM) operational purposes. From the perspective of the particular hypothetical organisation under which the HR officer could have to operate as a specific employees, the emphasis is always on the change management concerning the shift from the mostly workplace practices which could signify the control elements exerted by the hierarchy of the organisational administration of McDonalds under the auspices of the systems of participative management processes. Thus, Huang et al (2016) has observed that the framework of High Performance Work Practices (HPWP) consists of the knowledge and information as well as skills for the promotion of the better performance of the business organisations. The outcomes concerning the organisational level work processes could be understood, concerning the utilisation of specific HPWP frameworks, as the reduction in employee turnover, profitability and productivity of the employees. Guan and Frenkel (2018) has noted that the process of Human Resource Management bundling could constitute the core of the application of HPWP framework. This process is further enhanced by the two additional ideas such as the horizontal fit and internal coherence of practices of Human Resource Management mechanisms. These ideas of horizontal fit and cohesive operational capabilities could be further acknowledged to be instrumental in instituting changes within the overall organisational perspective of the selected organisation of McDonalds. Formulation of the most effective overall work environment is the key outcome of the utilisation of such HPWP framework within the organisational working architecture of McDonalds. The other outcomes of implementation of the HPWP structure could as well be understood to be the organisational culture which could be friendly and accommodative towards the employees, fostering meaningfulness of work, management of resources through the most optimised business perspective and progressive practices of human resources. All of these frameworks generally have properties which are mutually supportive of each other. The analysis of the work performances under the HPWP framework is thus necessary to involve the manner of coherent bundle based performance outcome evaluation. Isolative work analysis process is not encouraged under such perspectives. The objective is to obtain the gains which could add better value to the larger organisational initiatives. Nankervis et al (2016) highlights the fact that the individual practices of the Human Resource Management are mostly performed through the utilisation of the commonality of work philosophies and approaches so as to ensure that the outcomes could be synergistic as well as positive in nature. According to Hollenbeck and Jamieson (2015), the integration of the individual practices of the Human Resource Management into differential yet coherent groups or bundles of High Performance Work Practices (HPWP) frameworks, the activation of the complementary properties could be achieved so that the performance optimisation could be achieved on the organisational human resource levels. Cohen (2015) states that considerable disagreement between various scholars could exist, regarding the components which, could constitute effective High Performance Work Practices (HPWP) frameworks.
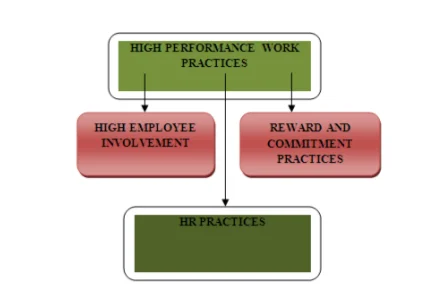
High Performance Work Practices (HPWP) could be understood to be an entire framework constituted by several processes and practices of human resource management which could be aimed at development of the knowledge and abilities of a range of employees so that McDonalds could have a qualitative resource of work process personnel at its disposal to be utilised to outperform the competing organisations. The objective is always competitive advantage and this could generally be considered to be incumbent upon implementation of the transformational vision of the business leaders. In this context, the High Performance Work Practices (HPWP) communicates the intention of the organisation to the employees so that these human resource elements could transcend their personal limitations. Runhaar and Sanders (2016) had considered the fact that misapplication of the processes of transformational leadership and High Performance Work Practices (HPWP) is a definite perspective. In this respect, one perspective could be highlighted in the hypothetical instance of overzealous nature of the transformational leadership elements in terms of the achievement of the organisational performance which could lead, however inadvertently, to the exposition of the employees to excessive pressure of work and increased demand of the associated stress concerning such workload. It is thus, from the perspective of Wilton (2016) to utilise the High Performance Work Practices (HPWP) frameworks in conjunction with the knowledge and information which could be only privy to the transformational leadership elements, it is always necessary to be on guard and considerate about the counter productiveness of such efforts and the outcomes which are undesirable from the organisational perspective. The accentuation of the effects of High Performance Work Practices (HPWP) application and attenuation of the implications regarding the improvement of the employees are prime considerations in this regard.

P6: Evaluation of the ways in which performance management, collaborative working and effective communication can support high-performance culture and commitment performance management and accountability
Administrative execution of performance management could be considered to be both a means as well as a method for considering the organisational working personnel regarding their responsibility to induce effective and coveted results. Accountability as well as the sense of responsibility comes from clarification of the necessary initiatives, observing and monitoring the process advancements, generating feedback and critical appreciation and management of the consequences of both the negative as well as the positive outcomes and following through such results with maximum integrity. While these components increase the measure responsibility and accountability from a definitive point of view, the most significant aspect regarding the utilisation of knowledge based HPWP, is the process of following through the outcomes of the endeavours and the associated effort investment regarding the employee performance enhancement mechanism. According to Dong et al (2017), three different elements are to be considered in this respect while application of HPWP could be undertaken regarding the performance management, collaborative working and effective communication institution within any organisational structure. These could be understood as the criticality of the roles and the assignments which could be accorded to individual employees as well as the working teams, the measure of performance of each of the work activity based individual efforts and finally, the standardisation of the performances through which the activity execution could be properly conducted so that the organisational goals could be achieved. One instance could be comprehended in this regard. Furthermore, Al-Haddad and Kotnour (2015), has observed that customer service, maintenance, manufacturing and sales based operations could require management of work responsibilities within McDonalds which could span across the entire spectrum of the jobs and employee engagement scenario. Regarding such instances, the requirements of performance could be identified to endure over a considerably longer period within McDonalds which have enabled the organisation better competitive advantage and resource management proficiency enhancement in comparison with such task requirements which could be at best internal and secondary in nature. These could form the basis on which the expectations of the performance based objectives could be established, thus making such knowledge based HPWP application to be greater effective. For improvement of organisational learning and encouragement of the working personnel to engage in continuous personal development, the process at various organisations such as, in terms of study perspective, at the McDonalds Restaurants Limited, is primarily based on maintenance of highest of quality. Through the initial phases of welcoming the new recruits, the visions and standards of expectations are clarified to the new employees at this organisation. The crew training officers closely co-operate with those of the new trainees to teach them the skills of operations at each of the 11 workstations of operations at every restaurant outlets of McDonalds. Utilisation of the instruments of Observation Checklists to provide the on-going training to the new recruits is a commonplace practice at this organisation. This involves the on the job training which is mostly floor based to make the employees learn to operate the state of the art equipment for management of food services and to make such employees gain sufficient knowledge regarding the procedures of operations practiced at McDonalds. Furthermore, the utilisation of two distinct management processes, in the forms of shift and systems management, to encourage the trainee managers and employees to engage in skill and technique improvement initiatives as well as increasing their knowledge of various systems of operations, could be mentioned in this regard.
Conclusion
The ultimate objective of the preceding academic endeavour could be understood to be the utilisation of proper and accurate information and knowledge in comprehending the methods through which the High Performance Working mechanisms. The emphasis has been on the application of performance management models so that high performance working cultures could be supported within the organisational perspectives. Such major purposes have been augmented with additional considerations such as formulation of a professional development outline, in the format of a clarified plan where developmental objectives including new skills as well as knowledge acquisition, management of learning resources and the standards to which such learning and skill acquisition measures could be observed through preferences of specific disciplines.
Reference List
- Albrecht, S.L., Bakker, A.B., Gruman, J.A., Macey, W.H. and Saks, A.M., 2015. Employee engagement, human resource management practices and competitive advantage: An integrated approach. Journal of Organizational Effectiveness: People and Performance, 2(1), pp.7-35.
- Al-Haddad, S. and Kotnour, T., 2015. Integrating the organizational change literature: a model for successful change. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 28(2), pp.234-262.
- Dong, Y., Bartol, K.M., Zhang, Z.X. and Li, C., 2017. Enhancing employee creativity via individual skill development and team knowledge sharing: Influences of dual‐focused transformational leadership. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 38(3), pp.439-458.
- Brulin, G. and Svensson, L., 2016. Managing sustainable development programmes: A learning approach to change. Routledge.
- Guan, X. and Frenkel, S., 2018. How HR practice, work engagement and job crafting influence employee performance. Chinese Management Studies.
- Hollenbeck, J.R. and Jamieson, B.B., 2015. Human capital, social capital, and social network analysis: Implications for strategic human resource management. Academy of management perspectives, 29(3), pp.370-385.
- Jiang, J.Y. and Liu, C.W., 2015. High performance work systems and organizational effectiveness: The mediating role of social capital. Human Resource Management Review, 25(1), pp.126-137.
- Meijerink, J.G., Bondarouk, T. and Lepak, D.P., 2016. Employees as active consumers of HRM: Linking employees’ HRM competences with their perceptions of HRM service value. Human resource management, 55(2), pp.219-240.
- Raes, E., Kyndt, E., Decuyper, S., Van den Bossche, P. and Dochy, F., 2015. An exploratory study of group development and team learning. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 26(1), pp.5-30.
- Runhaar, P. and Sanders, K., 2016. Promoting teachers’ knowledge sharing. The fostering roles of occupational self-efficacy and Human Resources Management. Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 44(5), pp.794-813.
- Stone, D.L., Deadrick, D.L., Lukaszewski, K.M. and Johnson, R., 2015. The influence of technology on the future of human resource management. Human Resource Management Review, 25(2), pp.216-231.
- Zhong, L., Wayne, S.J. and Liden, R.C., 2016. Job engagement, perceived organizational support, high‐performance human resource practices, and cultural value orientations: A cross‐level investigation. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 37(6), pp.823-844.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



