Von Neumann Computer Architecture
Task One
Internal and External Components of Computer System
The Von Neumann computer is named after its inventor John Von Neumann, who was an established mathematician and physicist in 1945. Notably, the computer was the first one that had a stored program because the earlier versions had to be rewired after completing one task so that they can work on another task. As a general computer, the Von Neumann computer could be built in a way that it could run different programs.
As the image shows, the computer consists of a, a memory unit, central processors and input, and output devices. The memory is used to store information, the central processors are used to process the information, and input devices play the role of getting the information into the computer while the output devices play the role of getting the data out of the computer.
A diagram of a Personal Computer and its parts


Purposes of Internal Components of a computer
Some of the interior mechanisms of a computer include a motherboard, power cable, disk, CD/DVD drives, cooling fan, a central processing unit, hard disk drive, random access memory, and power supply as explained by Owan (2013). The motherboard is the body of the computer which holds all other components. Its complex electronic system is used to provide electrical connections which are paramount for the communications of other components of the system. The central processing unit is used to execute the computer programs and for this, it is commonly known as the main computer because it controls all functions and without it there is no computer. The central processing unit is used to fetch, decrypt, implement and write back data. The first step involves getting information from the program memory, the decrypt step breaks the instructions into many components. The implementation step connects various components of the CPU so that they can carry out the given command. The last step which is the decoding step gives the results of the process to a memory.


The Random Access Memory is stuck to the motherboard and used to accumulate the data running on the computer. As a fast-access memory, it is usually cleared when the computer is shut off. Notably, it has several integrated circuits that ensure that the data stored can be retrieved in any order. Firmware is also an internal component of the computer which is loaded from the Read Only Memory. The firmware contains both software and hardware. As a software, it is a computer program which is executed by a microcontroller. Given that it is attached to the read-only memory, it is also considered to be a hardware (Owan 2013). The power supply is also a part of the internal components of the computer. It is a device that supplies power to various components of a computer. Through a case, it holds a voltage control, a transformer and sometimes a cooling fan. They are designed in a way they can turn off and off through instructions from the motherboard. Removable media devices also contain of internal devices and they include CD and DVD drives.
External Parts of the Computer and Their Purpose
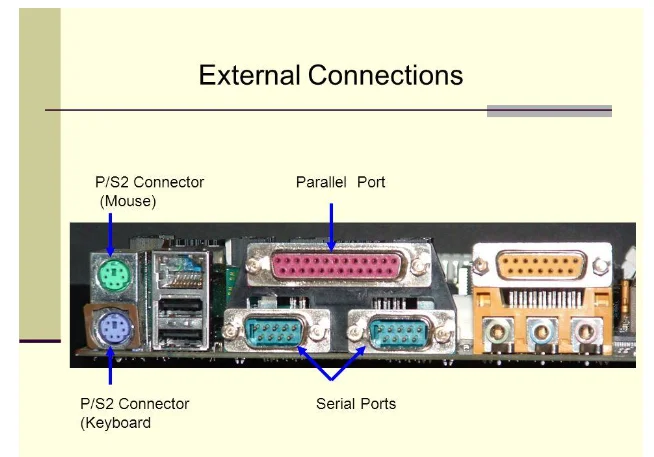
The tower is one of the biggest external parts of the computer. It can be considered to be the brain or the center of activities because it holds all internal components needed by the computer to function well. Notably, there are several designs of the tower and this includes one in which it sits flats and another one in which it is upright. Almost all ports needed for plugging in other devices such as printers, cameras and speakers are located in the tower. The monitor is also an external part of the computer and it shows what is happening to the computer through its visual display. A mouse is another external component of a computer and it is used to navigate the cursor on the screen. As a result, it is possible to select icons and links with more ease than using the keyboard. The mouse is also used to make commands to the computer. The keyboard, which is also an external component of the computer, it is used to feed information to the computer. It has numbers, symbols, alphabets and special function keys that are important in typing out a command to the computer. The images shows how the motherboard is connected to the external components.
USB drives and CD/DVD drives are also external parts of a computer and are used to provide extra storage and also to input programs into the computer. Notably, the USB drivers are more preferred lately because of their ease of use and reliability. Lastly, printers are also considered to be external components of computers also they do not necessarily contribute to the overall function of a computer. They, however, help in document management such as by loading a text into the CPU.
Task Two
Characteristics of the Various Types of Internal Memory of the Computer
Internal memory explains those parts of the computer which stores a small amount of data when the computer is running. In exemption of the ROM, they store data temporarily as the data is usually wiped off when the computer stops running. Notably, there are many types of of internal memory of a computer and they include ROM, Cache, and RAM. Notably, they have different characteristics and this has been essential in the way they carry out their functions. ROM, which is an abbreviation of the read-only memory is not volatile. A person using the computer cannot alter or introduce new data to ROM without special access. Notably, the internal memory is located on the motherboard as a chip and it is used to store the bios of the computer and also other important information that is needed by the computer to function well. It has been characteristically designed in a way that it can be accessed by the computer without the help of other hardware's. Cache, on the other hand, is volatile and used to store tiny bits of data that is frequently accessed by the RAM. This depicts that the processor will not have to wait for the RAM to respond every time it wants the same information. Cache is very small but very fast and found in various components of a computer. Unlike ROM, the cache is volatile and it wipes all data once the computer is turned off. RAM is another type of memory which as earlier stated is volatile in nature. It serves a very critical purpose as it is the middleman between the CPU and the storage devices. When a user accesses a piece of information, it is usually moved from the hard drive into the RAM. After that, the CPU reads the information from the RAM instead of from the hard drive in a much easier way. This explains why for a computer to be fast, it has to have a large RAM so that information can be easily retrieved. Sizes of RAM Include 1 megabyte to 8 megabytes per stick. One of the most common forms of RAM is DDR3 which comprises small sticks that are plugged into the motherboard. Notably, a motherboard can support up to four sticks. This means that it is possible to adjust the speed of one's computer.
Purpose and Functions of the System Busses of a Computer
A system bus can be considered to be the tracks that connect the Central Processing Unit (CPU) with the computer memory and the devices such as keyboards, audio system, and screen. Most of the buses are in the form of gold plated traces that are located on the motherboard. If the buses are not working, it is impossible to use the computer as everything happening is communicated through the system busses (Berisha-Shaqiri 2014). The system bus can be considered to be a set of three tracks and each track is obligated to carry address, data, and control. The data are the digital pieces of information usually output or input that needs to get somewhere or needed to do to something. The address shows where the data is located and where it should go in order to carry out a given function. The control part, on the other hand, is considered to be data that manages the flow of data and address. This includes the direction in which the transfer of the information should take place and how the information should be transported through the computer system.
Bus Width and the Effect It Has On the Bus Performance
Bus width is the number of bits that can be taken to the computer at the same time. The bus speed elucidates the speed at which a group of bits of data can be sent per second. Notably, the width of the data bus determines the maximum amount of information that can be processed and delivered at one time. These are different widths ranging from 8 bits to 64 bits (Owan 2013). The address bus carries the location of data in the memory and internal hardware components receive the address and then receives or rejects the data. It then communicates its response to the designated location through the address bus still. There are other communication buses that have been essential in the performance of the computer, they include Universal Serial Bus and Controller Area Network. Notably, it is usually possible for external peripherals to be set up in a way that they can use the internal bus. It is possible to extend a system bus in a way that it can communicate with other computers through a backplane. Notably, several computers can be connected through a single backplane and this will lead to fast communication between computers.
Role and Characteristics of the North and South Bridge of a Motherboard
A motherboard chipset comprises of electronic components that manage the flow of data in the processor, the peripherals and minority. The Northbridge is one of the chipsets on the motherboard and if the system is that of Intel, it is named memory controller hub (MCH) and if the system is that of a VGA it is named integrated memory controller (IMCH). The role of the Northbridge is to handle communication that occurs in the RAM, ROM, and the CPU. Some of the north bridges also have graphics and memory controller hubs which are used as video controllers (Whitworth and Ryu 2009). It is important to note that different processors and RAM have different signaling and because of this the functions of a Northbridge are usually limited to one or two classes of CPU. On the other hand, the Southbridge is also located on the motherboard but iced to implement the slower functions of the motherboard. In an Intel system, the Southbridge is referred to as the Input/output Controller Hub (ICH) (Casey 2015). It can be differentiated from the Northbridge by the fact that it is not directly connected to the CPU. Another difference between the two is that the Southbridge chip looks smaller than the Northbridge.
Task Four
Components and the Structure of CPU and How CPU Works
A CPU, which is an abbreviation of central processing unit controls the functions of the computer. As the control center, it has a lot of electronic circuits that execute the instructions from the stored programs.

As shown in the diagram, the two components of the CPU includes the control unit and the arithmetic/logic unit (Casey 2015). The control unit is that part of the CPU that has circuit which uses electrical signals to guide the computer system on what to do (Casey 2015). Notably, it does not execute the instructions itself but it guides the other parts of the computer to communicate. The arithmetic/ logic unit, on the other hand, on the other hand, contains the electronic circuit that carries out all logical and arithmetic operations. The arithmetic/logic unit (ALU) has an electronic circuit responsible for carrying out all the arithmetic and logical operations (Young 2002). This includes mathematical calculations such as multiplication, addition decision, and subtraction. Additionally, it performs logical operations which mainly involve comparison (Whitworth and Ryu 2009). For instance, there can be a comparison between special characters and number. The computer can then act depending on the verdict of the comparison. Several conditions that are tested by the logical operations include equivalence condition where the arithmetic/logical unit does a comparison of two pieces of data and determines if they are equivalent. For instance, in a movie, the number of tickets sold out is equivalent to the number of seat in the theater and if all tickets are sold, the movie is declared to be sold out. Another logical condition that is tested is the less than the condition. The computer usually compares some given value to determine which is lesser than the other and act from the verdict. Lastly. Logical operations test for the greater condition where the computer determines the greater of two values and uses the information to make a verdict.

The Fetch Execute Cycle of CPU in Reference To Its Components and RAM
The fetch-execute cycle is a procedure through which the central processing unit fetches data, from the memory, regulates the command and then carries out the command. The cycle is usually repeated until the computer is shut down. The cycle is commenced by the program counter (PC) which keeps track of the memory address where the instruction is supposed to be carried out (Young 2002). The memory address register (MAR) then address the key program that is being worked on either as an Input or output (Young 2002). After that, the memory buffer register (MBR) offers a two-way record that is used to grasp the information that is drawn from the memory as it awaits being stored in the memory. From there the current instruction register (CIR), holds the directions from the memory briefly. The control unit (CU) than decodes the command in the CIT and then selects machine resources that coordinated the activations of the data or the information. The arithmetic logical unity (ALU) on the other hand performs all mathematical a logical operations needed. It is important to note that the failure of either of the components of the cycle will lead to the failure of the whole process. This usually is fixed by creating different commands that make the system works as expected, Additionally, depending on the type of command, an instruction that is sent to either of the components might not be executed. For instance, if the data being fetched is locked through a password and the user is not aware of the password, it will be impossible to execute any further action. Understanding the components is essential as one will be able to address any problem that might arise from the malfunctioning of the components.
References List
Berisha-Shaqiri, A., 2014. Management Information System and Decision-Making. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 3(2), p.19.
Casey, J., 2015. Computer Hardware: Hardware Components and Internal PC Connections.
Owan, V., 2013. The Role of Operating System to the Computer/System Communication.
Vokorokos, L., Madoš ,B., Ádám, N. and Baláž, A., 2013. Innovative Operating Memory Architecture for Computers using the Data Driven computation model. Acta Polytechnica Hungarica, 10(5), pp.63-79.
Whitworth, B. and Ryu, H., 2009. A comparison of human and computer information processing. In Encyclopedia of Multimedia Technology and Networking, Second Edition (pp. 230-239). IGI Global.
Young, R., 2002. How Computers Work: Processor and Main Memory. How Computers Work.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



