Challenges, Adaptations, and Recovery Efforts
- 13 Pages
- Published On: 15-12-2023
Introduction
The emergence of COVID-19 brought about significant uncertainties making forecasting in business environment beyond the bounds of possibilities. But then industries thought they could try their luck in the midst of the pandemic, specifically the event industry. According to analysis conducted by Parnell et al. (2020), among four hundred events professionals based in Europe planned their strategic recovery plan on reopening about five thousand events specifically the sports events; English Premier League between the months of March and May the year 2020, but some had to close down immediately. The event sector is known for its consistent adjustment, and it might be the one of the many sectors that have encountered the most radical alterations in the manner it percolates. For instance, in this era of digitalization, social media, online equipment, big data have affected the industry modifying it, but cannot replace the human resource involved that need to interact at close range is rather the opposite. In an industry that bases it business model on people interaction and social gathering, the restriction means profound impact if not complete shutdown. The business dissertation help available can provide valuable insights into navigating such unprecedented challenges.
Further, the study estimated that the event industry will take a dip of thirty per cent of the global event arrivals as well as a loss of at least fifty million jobs throughout its sector with more devastating denouements on events such as the cancellation of Metropolitan Opera in New York- US Cannes Film Festival, the Summer Olympics in Tokyo- Japan as well as the Wimbledon In the United Kingdom due to the impact of Coronavirus pandemic was all-embracing with all-rounded socio-economic and geopolitical connotations (Ozili and Arun, 2020).

The sports ecosystem of the United Kingdom is no different from the financial, educational, as well as commercial organization that were affected by the effects of COVID-19 that progressively spreads across the country as studied by Ratten (2020) in an on ‘Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and sport entrepreneurship’. All matches as well as competitions were postponed or cancelled, altering government institutions, organizers, teams and athletes, not leaving out the live sports content that was expected according to a report compiled by Keshkar et al. (2021). The owners of clubs, the sponsors and the sports broadcasters came up with methods to navigate the effects and implications of the events cancellations and modifications.
In this research proposal, the focus is to investigate the COVID-19 pandemic has had on the event industry, taking a case in study of Clearwater Events. As such, it will explore the performance of the company measuring such metrics as number of events held, financial returns, workforce, and general perception held within during this pandemic period. The investigation will be grounded following systematically outlined method that include philosophy, research approach and strategy that focuses on quantitative research such as online surveys in attempt to collect reliable and problem-driven data.
Literature Review
According to studies by the World Health Organization (2020), Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease, an illness caused by a novel coronavirus currently depicted as Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2; previously depicted as nCoV), where it was originally noticed amid an outbreak of respiratory illness cases in the City of Wuhan, the Province of Hubei- China. It was first reported to the World Health Organization on the last date of the month of December 2019, and was declared the COVID-19 epidemic on the first date of January 2020 a global health emergency.
In a study conducted by Mohanty et al. (2020), it discovers that the event industry is one of the fasted-developing industries contributing significantly to the global economies that accounts for 10 per cent, that is, almost 90 trillion US dollars of the world gross Domestic Production (GDP), over three hundred million jobs, a one in ten jobs, also making up one point seven trillion US dollars (six point eight per cent) of the total world exports and a nine hundred and forty billion US dollars; four point three per cent of the total investments by the end of the year 2019. The event sector makes up a vital segment of the tourism and hospitality framework as they operate as a significant factor both as the original points as the event promote the travel, and hospitality, and normally it is the destination point, that is event is a pull factor in the marketing. The industry depicts a broad spectrum of kinds based on its nature, size, professionalism as well as volume. In recent times, the event industry was identified to provide tourism service providers, where first were specializing in offering events such as sports, local festivals, community fairs, thence drawing attention first the local communities and visitors while offering economic and social gains to the local communities involved. In another study by the United Nations Word Trade Organization (UNWTO, 2020), the event industry has experienced massive disorder in the face of a never before health emergence; COVID-19 pandemic across the world.
The pandemic in Event Industry
In a study meant to measure the economic effect of COVID-19 on the sport sector n the UK that was commissioned by the European Commission’s Directorate General for Education, Youth, Sports and Culture (DG EAC) and undertaken by Ecorys (2021), it was estimated that the UK alone experiences the second largest fall after Germany in sport income, where out of the twenty-eight countries in the European Union countries UK accounted for 9.5 billion Euros, that is, 8.6 billion Pounds, which is 17% of the total downturn across Europe. Germany recorded the biggest drop in the sport-connected GDP in the year 2020 that lost 23 billion Euros which is 405 if the Europe’s total loss. This is after analysis of the cost of compulsory closure of sports clubs, gyms, stores and the events, leading to these negative effects for sport services like sport media, tourism, transport and accommodations.
In another report by Mastromartino et al. (2020), the fan engagement in sports events in the UK where in the past they were expected in various stadia, was altered shifting the experiences from actual attendances to stadia, to virtual one-on-one connections. Stadia have been left for sport men and women to train and compete, leading to questions on how can these venues be better used, or what would happen if these events progress without crowds according to Colucci et al. (2020) in a report on ‘Coronavirus and Impact on Football; A Sport Law and Policy Centre and Law in Sport Joint Survey’. As a result, there has emerged huge investment in the digital platform, technology as well as cyber services to promote the sport industry in the UK.
While Exploring the sports economic impact of the pandemic on professional soccer, Drewes et al. (2021) identify that the sport industry were identified mainly from the loss of revenue from licensing, membership, tickets, broadcasting, sponsorship, subscriptions, participation or event sales. The cash flow was hard hit entailing paying rent, contracts and wages. The employment security as well as income led to jo cuts as well as loss of skills among employees, athletes, coaches, and freelance workers. Volunteering was not exempted as their staff were unpaid and not able to participate in events due to progressive restriction of movements.
The operating models of organizations were pushed to transition to contemporary functioning models, while others forced to adapt whether they have been planning or not. Commercial relationships such as the broadcasters, sponsors as well as partners faced a hard legal and financial implications of an abrupt shutdown of the sports events.
Dig deeper into Organizational Change in the Modern Business Environment with our selection of articles.
Event Industry operations models
Within the event industry, there exist a management model that also entails stages that help the management in organizing events. These stages according to studies conducted by Tum et al. (2006) entail analysis, detailed planning, implications and delivery as well as performance evaluation. Within the analysis stage it is basically pointed at the internal and external surrounding of which the events administrators are operating. In addition to the external factors of the analysis stage of the model, there are other factors such as stakeholders and competitors. In detail planning, the themes of the events are aligned with the objectives that are required to be attained. Further, they have to aligned with the venue, budget as well as timelines that will be finalized. Implication of the event management are coordinated is where logistics, manpower as well as other suppliers’ needs are finalized. In this stage, communication, cooperation, and coordination to amplify the stages are applied to achieve the objectives as affirmed by Leveson (2011) researches. Finally, performance evaluation is conducted via surveys as well as post-events evaluations are part of this last stage. There is comparison of the input against the output, taking into account the gaps between them. Here the expectations of the clients are put against the objectives that were to be met.
In another research conducted by Ravichandran et al. (2010), identify that the event management model in the event industry is best expounded by use of the SERVQUAL approach. This concept depicts that the quality of service in the event management is defined by first considering clients’ expectations, experiences and ultimately satisfactions. In other words, it is the concentration made on the tangible aspects of services, since that are simple to measure and put in the right way.
Methodology
Provided the oddity of the unusual nature of Coronavirus, there is a scarcity of research articles extent the effect of Coronavirus on the events industry. This ontological assumption about the realities of the COVID-19 effects on the sport events industry will determine the choice of the research methodologies to employ in development of knowledge on the impact of COVID-19 on the sport event industry as depicted by Saunders et al. (2018). Thence, this research focuses on the exploring the effects of Coronavirus on the events industry, focusing primarily on the Clearwater Events. Therefore, the method applied is the quantitative and qualitative research methods together with focus groups that specifically applied online surveys and questionnaires as a data collection method, and data analysis meant to assess various performance indicators as depicted by the company.
Quantitative research method, as pointed out by Sue and Ritter (2012), identify that online survey and questionnaire method in conjunction with focus group, a popular data collection method was used with some set of questions formulated and sent to various event organizations that plan mega-events, the various employees, investors, and sports fans to provide target samples. On the other hand, for the qualitative research method, de Casterlé et al. (2012) identifies that data analysis, specifically the content analysis is meant to analyze text data, meant to interpret meaning from the common text data, thus considered to adhere to the naturalistic paradigm. Its ability to determine the presence of certain context, themes or even approaches with some given text and provide more insight by analyzing its presence, meaning as well as relationship of some context such as newspaper, television interviews, headlines, speeches, media historical documents and several other sources. Hence, in this research, a mixed method will be used.
The survey is sent to potential participants where they can fill and send feedback online. Via the online surveys, adequate and precise information from the affected organization, Clearwater Events, of the event industry would be collected for analysis (Easterby-Smith et al., 2011). Unlike other primary data collection such as focused group and interviews, as argued by Veal (2011), online survey is easy to follow and monitor in addition to adhere to government restriction of movement. The data from online survey will be analyzed using thematic analysis tool.
Data Requirement Table

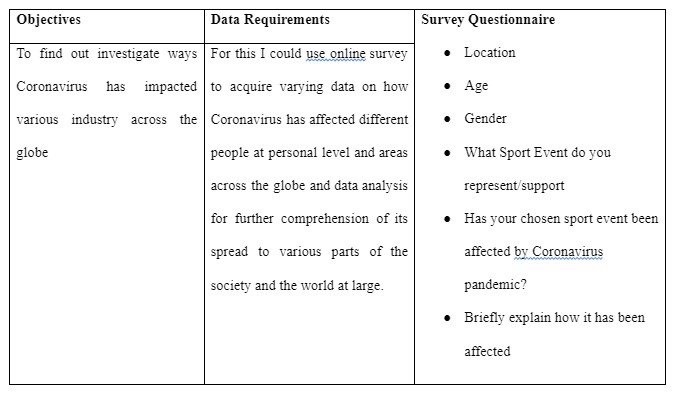


Conclusion
The report proposal on the impact of COVID-19 on the event industry provide the insight on further studies to be conducted despite the coronavirus still ravishing through the industry, and various other aspect of the society and economies. The primary objective is to identify the impacts COVID-19 has had on the event industry, focusing in particular on the Clearwater Events performance during this period. However, studies conducted on the effect of the Coronavirus on the event industry are little since the pandemic has just been in existence for just over a year now and there has been minimal efforts conducted on the study of the same. Therefore, the research proposal could be applied as one of the many that will take place to explore further on the study.
References
de Casterlé, B.D., Gastmans, C., Bryon, E. and Denier, Y., 2012. QUAGOL: A guide for qualitative data analysis. International journal of nursing studies, 49(3), pp.360-371.
Drewes, M., Daumann, F. and Follert, F., 2021. Exploring the sports economic impact of COVID-19 on professional soccer. Soccer & Society, 22(1-2), pp.125-137.
Easterby-Smith, M., Thorpe, R. & P. Jackson (2011). Management Research. London, Sage.
Ecorys. 2021. Revealed: economic impact of COVID-19 on UK sport industry: four nations may shoulder second highest fall in sport-related GDP across
Europe.https://www.ecorys.com/united-kingdom/latest-news/revealed-economic-impact-covid-19-uk-sport-industry-four-nations-may
Keshkar, S., Dickson, G., Ahonen, A., Swart, K., Adeasa, F., Epstein, A., Dodds, M., Schwarz, E.C., Spittle, S., Wright, R. and Seyfried, M., 2021. The effects of Coronavirus pandemic on the sports industry: An update. Annals of Applied Sport Science, pp.0-0.
Leveson, N.G., 2011. Applying systems thinking to analyze and learn from events. Safety science, 49(1), pp.55-64.
Madray, J.S., 2020. The Impact of COVID-19 on Event Management Industry. International Journal of Engineering Applied Sciences and Technology, 5(3), pp.2455-2143.
Mastromartino, B., Ross, W.J., Wear, H. and Naraine, M.L., 2020. Thinking outside the ‘box’: a discussion of sports fans, teams, and the environment in the context of COVID-19. Sport in Society, 23(11), pp.1707-1723.
McIntosh, K., Hirsch, M.S. and Bloom, A., 2020. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). UpToDate Hirsch MS Bloom, 5, pp.1-1.
Ozili, P.K. and Arun, T., 2020. Spillover of COVID-19: impact on the Global Economy. Available at SSRN 3562570.
Parnell, D., Widdop, P., Bond, A. and Wilson, R., 2020. COVID-19, networks and sport. Managing Sport and Leisure, pp.1-7.
Ratten, V., 2020. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and sport entrepreneurship. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research.
Ravichandran, K., Mani, B.T., Kumar, S.A. and Prabhakaran, S., 2010. Influence of service quality on customer satisfaction application of servqual model. International Journal of Business and Management, 5(4), p.117.
Saunders, M., Thornhill, A., & P. Lewis (2018). Research Methods for Business Students. Harlow, Pearson.
Sohrabi, C., Alsafi, Z., O'Neill, N., Khan, M., Kerwan, A., Al-Jabir, A., Iosifidis, C. and Agha, R., 2020. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). International journal of surgery, 76, pp.71-76.
Sue, V.M. and Ritter, L.A., 2012. Conducting online surveys. Sage.
Tum, J. and Norton, P., 2006. Management of event operations. Routledge.
UNWTO. (2020). Impact Assessment of the Covid-19 Outbreak on International Tourism.
World Health Organization, 2020. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): situation report, 82.
Veal, A. J. (2011) Research Methods for Leisure and Tourism. Harlow, Pearson
Take a deeper dive into Case Reflections in Social Work Practice with our additional resources.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



