The Impact of a Certificate Merit System on Classroom Behavioural Incidence
Abstract
The dissertation report had discussed the impact of the certificate-based merit systems on the behavioural incidences of the students in primary and secondary schools. The report had given special relevance to the primary and secondary school students in the Middle East; however the education systems in other countries had been drawn into discussion on a number of occasions in order to comprehend the differences in the merit systems. The dissertation report had also presented a number of behavioural and motivational theories that had been practiced in the education systems across the world in order to motivate the primary and secondary school students to perform better in the class and that had been monitored through the behavioural changes that had been noticed among the students. The different behavioural impact had been assessed using different tools and the approaches though had been different, but the motive had been the same. The different journals have been analyzed for the purpose to obtain the required outcomes, and the methods have been discussed along with the results as obtained. The standard of academic inquiry is very high. the support offered by Masters Dissertation Help becomes a source that provides students with the necessary assistance to navigate the complexities of their research journey with precision and proficiency.

Glossary
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Introduction
The research looks into the impact of the certificate merit systems on the classroom behavioural incidents of the primary and the secondary students by assessing how they respond to the instructions of the teachers and how diligently they perform the tasks assigned to them. It is the belief of many educators and psychologists that it is much easier to motivate the students by awarding them with rewards based on their performance in the class (MacCoyet al., 2019). They also believe that the concept of corporal punishment generally has a negative impact on the behaviour of the students in the primary as well as in secondary school. The research dissertation is going to look into these claims and see how the certificate merit system in the form of external rewards can be a motivation for the learners in the primary as well as in the secondary school students.
1.2 Background of the Research
Classroom behavior is considered one of the fundamentals of developing a good and cordial relationship between the students and the teachers. According to Yeager, (2016), classroom behavior is considered to be a key in motivating the students towards making accomplishments in the field of academics. The demand to develop and adopt new strategies and techniques to improve the behavior as well as the academics of the students continues to be there in different schools.
Take a deeper dive into general impact of experience with our additional resources.
The conduct of a student in a class has been often used by the educators in schools in order to evaluate the potential of a student and train them to be more resourceful in the academic as well as the non-academic fields (Dalton, 2020). The teachers in a school utilize different sets of strategies in order to train the good students who pay attention in the class and follow the instructions of the teachers as well as the bad students who do not pay attention in the class and are less obedient. However, the teachers should not make any demarcation while imparting education to them.
1.3 Rationale of the Research
Take a deeper dive into Tech and Secondary Education with our additional resources.
The teachers in the primary, as well as secondary schools, are constantly motivating the students in order to excel in every field whether it is academics or extracurricular activities. In order to encourage them and to acknowledge their accomplishment and efforts, the merit system was introduced in primary and secondary schools. However, the question remains whether the use of certificate merit systems as a form of external reward system always produces positive results or whether it also has a negative outcome, as it is seen in many cases that extrinsic rewards diminishes the intrinsic motivation to perform (Fang, Gerhart & Ledford, 2013). The research dissertation is also going to look into this aspect of the use of certificate merit systems in primary as well as secondary schools as a form of external reward systems.
1.4 Problem Statement
The research dissertation looks into the impact of the certificate-based merit system on the classroom behavioral incidences of the primary as well as the secondary school students in the Middle East. The positive impact of it is seen in motivating the students to perform their tasks diligently in the class by the educators and it has been positively accepted by many as in most occasions it is giving positive outcomes which are evident from the good performances of many students (Downes, 2020). But it is not accepted uniformly everywhere as in many cases it failed to get the minimum amount of response from the students, and there lies the main problem in the adaptability of these systems in all the schools in the Middle East.
1.5 Research Aim
The research dissertation aims to investigate how certificate-based merit systems have an influence on the classroom behaviour of the primary and the secondary school students in the Middle East in comparison to the classroom behaviour school students in other countries.
1.6 Research Objectives
- To analyze the practice of certificate-based merit systems in primary and secondary schools in different countries.
- To identify the impact of certificate-based merit systems on the behavioural incidences of the primary and secondary school students in various nations.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of the certificate-based merit systems on the behavioural changes among the primary and secondary school students in the Middle East.
1.7 Research Questions
- What is the primary impact of the certificate merit system on the classroom behavioural incidences of the primary as well as the secondary school students?
- How is the certificate merit system being utilized by the educators and the schools for the students belonging to the primary as well as the secondary schools in the Middle East?
- What are the impacts of the certificate merit system that has been noticed in the behavioural tendencies of the primary as well as the secondary schools?
- What are the common problems faced in order to establish a relationship between the certificate-based merit system and the realization of the behavioural changes among the primary and secondary school students in the Middle East?
1.8 Significance of the Research
The significance of the research dissertation is to find out the best and the most effective form of merit-based systems that can be implemented in the primary as well as in the secondary schools in the Middle East in order to enhance the classroom behavioral incidences among the students and help them to be motivated in order to excel in every field in their life (Burroughs et al., 2019). A significant number of studies revealed that schools were much more focussed on developing a positive path towards behaviour management, and in most cases that happened to be their topmost priority.
The sign that was seen in the studies that the reward systems were tailored made according to the schools and the students, and this was done in order to ensure that the offered rewards were something that the students aspired to achieve or receive (Assets.publishing.service.gov.uk, 2020). The findings of such studies have been quite encouraging in order to explore more about this aspect of the dissertation. The gap in the literature that the dissertation wishes to fill in is about finding the effective and optimal certificate-based merit system that can be uniformly be implemented in the education systems across the world, that can have an institutional impact on the behaviour of the students.
The primary significance of the research dissertation is to highlight both the positive as well as the negative aspects of the certificate-based merit systems, on the behavioural incidences of the primary and the secondary school students in the Middle East.
1.9 Dissertation Structure

Chapter 1: Introduction: This is the first chapter of the research dissertation which gives an elaborative view of the overall work of research. The reason for choosing the topic of the research is also mentioned in this chapter. The aims and objectives of the research dissertation are also stated in this chapter.
Chapter 2: Literature Review: This is the second chapter of the research dissertation which mainly concentrates on the previous literature that has been conceptualized by earlier researchers based on the same research topic. This chapter helps to gain a number of useful information related to the topic of research.
Chapter 3: Research Methodology: This is the third chapter of the research dissertation which is considered as one of the important chapters in the whole work of the research dissertation. This chapter helps to determine the effective methods which are going to regulate the course of the research work. The research philosophy and approach elaborated in this chapter is going to depict how the researcher has gone about to collect the relevant data and information on how the merit-based system has been affecting the behavioural incidences of the students in different schools across the world.
Chapter 4: Data Analysis: This is the fourth chapter of the research dissertation which primarily concentrates on analyzing the data that has been collected from various sources during the work of research.
Chapter 5: Conclusion and Recommendation: This is the fifth and the last chapter of the research dissertation where the researcher finally arrives at a conclusion based on the findings and the analysis of the data collected. This chapter also gives recommendations that can help the future works of research on the same topic.
1.10 Summary
The first chapter of the research dissertation is the introductory chapter which happens to be one of the most crucial parts of the research dissertation. It is in this chapter that the significance of choosing the research topic is highlighted. In other words, it can be put down simply that this chapter speaks about the importance of choosing the topic for the research dissertation and gives an overall overview of the research dissertation. Besides, the research rationale gives a detailed insight into the identified issues in the research dissertation in order to have a better understanding. The aims and objectives associated with the research dissertation are also mentioned in this chapter in order to have a clear idea about how the work of research is going to proceed in order to get the answers to the research questions. The next chapter is going to review the literature of the dissertation.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
The literature review for the research paper is concerned with the merit rewarding system of primary and secondary students. For this paper, the research is on the impact of certificates merit system on the behaviour of students of primary and secondary school students (Raharjanto, 2019). This chapter has focused on the pattern of changes and what regulatory concerns the merit system has and the impact it has on the students of primary and secondary school. Along with all the research, the gap in the literature is also analyzed, and the chapter will provide all the vital theories to understand the impact of the merit system on students' behavioural incidents of primary and secondary school..
2.2 Factors affecting the certificate of the merit system in primary schools and Secondary Schools
There have been various factors responsible for enhancing learning systems as well as its merit system. Kim et al (2018), stated that students on the basis of merit may have positive behavioral incidences. It had been critiqued by many other scholars from various points of view. As influenced by Ullah, Xiaoduan &Bhuttah (2019), it has been recognized that educational policies and rewarding systems play an important role in mitigating the social distinctions on the mental state of learners in schools as well. For example, a child's self-image and self-confidence are vital elements for academics; they help in the development and determination of the child's understanding and their inclination towards education.
2.2.1 Motivation
According to Rautakivi, Siriprasertchok &Korng (2019), human psychology has a unique aspect, which had helped to accomplish their goals, with motivation. It determines the fact that learners' psychological aspects play a significant role in the motivational outcome. For example, motivation from a deeper association with parents and teachers involved in life. This mainly happens with the primary students in terms of mental satisfaction, love, and affection.
On the other hand, as influenced by SAKILA (2018), parents’ availability forms the primary and the most important support, which acts as motivation in a learners’ ability to perform well. Considering present-day situations, parents' long-term involvement at work, as to fulfill their aspirations and the needs, which leave them drained by the end of the day that leaves children, feel lonely. In certain situations, parents were found to be busy at work and ignore the evaluation of their kids. For secondary students, along with parent’s support, financial conditions also form an element of motivation (Kim, Joo& Lee, 2018). Considering the situation of two different sections of the society where on belong to the wealthy section whereas the other hails from a middle-class family. In order to do both the task successfully, the student needs to be motivated, and as opined by Rozalia (2019) parents are the best motivators under all circumstances and that would help the students to achieve their desired goals regarding academics.
2.2.2 Teaching and learning resources
According to Jones (2020), lack of resources, that includes study materials and the teaching faculty impact students of both primary and secondary school. Apart from that Aina&Ayodele (2018), at the primary school lack of passionate teachers leads to a lack of interest in students that affects the merit rewarding for the concerned students. Teachers have been known to shape the pathways for students especially the ones weaker in their academics, and lack of such enthusiasm leads to deterioration merit rewarding for students. In this respect, as argued by (Kim, Joo& Lee, 2018), not always teachers are responsible for the deteriorating academics of students. Students should have the will to perform and excel,
2.2.3 Social factor
The students are affected by social factors such as relationships, student followings, club membership, and sports. According to Daniel, Bornstein & Kane, (2018), there is a bit of agreement in which elements can be focused more on all the social elements. It has been observed that students from low social backgrounds are not able to achieve the merits to their full potential. On the other hand, truancy factors in students also lead to poor performance. Truancy for primary students can be a reason for negligence from their parents and for secondary students can be a casual approach towards education, which had led to poor merits for the students of the primary as well as the secondary sections. As opined by Crul et al (2017), truancy can be a cause of lack of attention from parents, or the social difference between pupils that make them feel insecure among their classmates.
Besides, Al-Ansari et al (2016), argued that the social difference can have a great impact on the student's mind and thinking process as a society forms the base of civilizations. It determines that social factors can lead to stress in students and the lack of interest in education and achieving merit. For example, it had been analyzed on a secondary based pieces of evidence that often students from primary compared to secondary had their involvement on social media that turn down their emotional efficacies and stresses upon their merit system as well (Darnon et al. (2018). Hence, this has been a mere area that has been highlighted.
2.2.4 Cultural
There have been theories that students' merits are dependent on the culture of the individual and the cultural differences for students who relocate. According to Bendermacher et al (2017), the teacher's learning is intervened by the environment and culture if the school directly or indirectly, For example, American schools have a culture of social gatherings like homecoming and prom, which is not a recognized event in the European school culture. So, if students move from America to Europe will face the cultural difference that will lead to a loss of interest and lead to the sinking of their merit achievement. Therefore, as opined by Lara, Mogorrón-Guerrero & Ribeiro-Navarrete (2020), for merits and better achievement, the relationship between learning and culture should be viewed well.
2.3 Impact of the merit system on behavioral incidences on secondary students compared to primary students
According to Gavin & McGrath‐Champ (2017), in order to encourage positive behavior and reduce negativity on students, schools should have merit systems for different sections of the school. For the primary section, schools should allocate teachers to implement age-appropriate classes; the students should be educated about cultural diversity and tolerance. Parents have played a significant role in promoting diversity and equality as they have the best knowledge about their child’s behaviour and abilities regarding the concerned situation.
However, Affandi, Saputra&Husniati, (2020), argued that the strategies employed by teachers for classroom management, primarily focussed on the physical aspects rather than concentrating on the social and emotional aspects of the class. It had been seen that while dealing with the behavior issues of the class, the teachers preferred the behaviouristic approach to deal with the problem. As for the secondary section, schools required to allocate the management to teach students to discipline themselves that had been helping students to have a productive life that had helped them in accomplishing the goals they had set regarding their academics and the extra circular activities.
2.3.1 Merit Rewarding
In Western countries, in order to satisfy the needs and requirements in order to be selected to the desired universities students have to work hard to meet the set criteria by those institutions. As stated by Mountford-Zimdars& Moore (2020), the criteria may be set regarding the academic accomplishments, along with the extra circular being an add on to the requirement list. So, the merit system in school works in rewarding the students as per their performance in the categories.
On the other hand, as opined by Sabic-El-Rayess(2016), add on for the extracurricular activities, the students are rewarded with chances to perform at the deserving platforms that can provide them the recognition required for achieving their target. For example, if one is interested in dance, but cannot afford professional training, the merit system will encourage the student to work on the dance as they will be given the stage to showcase their talent. Froese et al (2019) opined that dealing with academic scholastic works, it has been hard to accomplish the goals and achieve rewards. In all respects, the merit rewards have shown positive changes in students towards their academics and life plans.
On the other hand, Glater (2017), have further commented that the merit system has planned to support its reward systems and policies for its teachers, as they form the pillars for students. Teachers play a primary role in shaping student’s direction by understanding their potentials and encouraging them to work on those areas. In the opinion, Ogada&Mwalw’ (2020) stated that teachers have always encouraged and rewarded along with a contribution to building the future of the nation. It has mainly indicated on the students with the right direction that had helped in improving a society leading to the betterment of the nation.
2.3.2 Merit Pay
The merit system helped in the recognition of better performance in individuals. According to Munroe (2017), in education, the student's performance was the priority and education depends on numerous factors, most important being teachers. In order to improve the quality of teachers the policy used is of merit pay. As per research, it has been noticed that students who get sufficient and good guidance from teachers are able to perform well in their academics than gears with the less effective teacher (Rumbaugh, 2019). This had encouraged teachers to persuade the students, and make the necessary changes in their attitude, helping improve their achievements and motivate them towards innovations. As teachers are underpaid in comparison to other professions, merit pay would be an effective solution towards providing them with justices.
On the other hand, Froese et al (2019), argued that merit pay programs helped in accumulating talented students, as confident people would like to develop opportunities that would help them in professional life later. It had also helped to recruit and maintain the bright minds of the nation as for higher-income many times teachers consider changing their profession in order to have a sustainable life.
Moreover, while implementing the merit pay the requirements should be prepared ahead, as reward would be based on characterizing, behaviour, or student achievement under the teacher. No single requirement will be sufficient in order for ideal merit pay; the list should be created with a proper understanding of the situations.
2.4 Effective implementation of behavioral changes on students of Primary and Secondary Schools using different theories
2.4.1 Behaviorist Theory of Learning
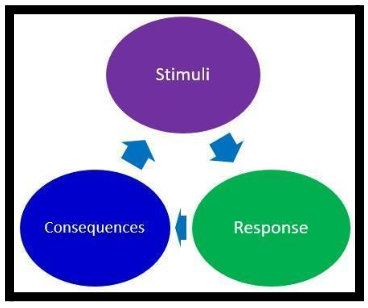
According to Syafei&Ulfah (2020), the process of learning happens through a sequence of rewards and punishments. This theory happens to be one of the commonly used tools today in the classrooms for behavior management of the students in the primary as well as secondary schools. The two practices of role-playing and repetition which are linked with the behaviorist theory are still practiced by educators. The theory believes that the rewards generally increase the probability of the repetition of a particular behavior of a student, while punishments generally decrease the probability of repetition.
In simple words, the theory means to say that if anything is given or added to the environment, the interaction is positive, while when something is removed or taken away, then the interaction is negative. Chao (2019) argued that the behavioristtheory ignores the mental processes that are involved in the learning process, unlike the cognitive learning approach. In this theory, the spontaneous behaviour of the students is often overlooked which is quite crucial towards the learning process and gaining knowledge. This theory also disregards the possible involvement of the biological factors in the students that are necessary for the learning process and generally any change in them has a different response towards a particular learning concept and as a result have different consequences or outcomes under different scenarios.
2.4.2 Cognitive Theory of Learning
According to Lefrancois (2019), the notion that learners are passive and respond only to changes in the external environment was rejected.The cognitive theory considers the minds of the students as computers that take in information from an external environment which are normally the instructions of the teachers, then that information is processed in their minds, and then the processed information helps the students in their learning process by giving meaningful outcomes. One of the main importances of the cognitive theory of learning is that it teaches the students the skills that promote their growth in the field of academics. Barbier et al.(2019), stated that the Achievement Orientation Model (AOM) has been instrumental in order to figure out the various pathways for accomplishments in academics for academically talented students under education settings, especially in secondary education. The cognitive theory of learning aids in the development of a student in a modular manner rather than a linear manner.
2.4.3 Maslow’s Theory of Motivation
According to Suleiman Abdulrahman (2018), Maslow's theory of motivation seeks to fulfill the low-level needs before it tries to fulfill the high-level needs of the students in the secondary and primary schools towards motivating them to perform in their classes. The educators are identified as the motivators whose main task is to provide adequate motivation to the students in order to make them perform their necessary tasks and help them grow academically. This theory looks into the needs of the students, where psychological and safety are the low-level needs and esteem and self-actualization are the high-level needs, where the low-level needs required to be satisfied before the high-levels can be realized.
Korpershoek et al. (2019), argued that Maslow's theory of motivation presumes that all the students experience the needs in the same order as mentioned in the theory, thus failing to identify the behavioural and cultural differences between the students of primary and secondary schools. The theory also does not explain quite accurately how self-actualized students actually feel and behave in the class.

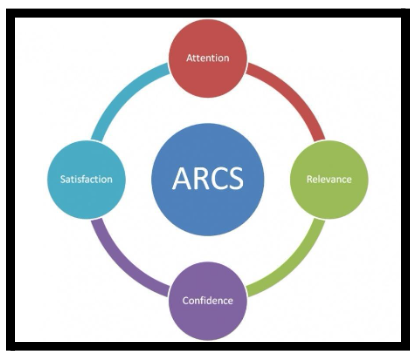
2.4.4 ARCS Model of Motivation
According to Jamil et al.(2019), the ARCS model is an approach towards a pedagogical arrangement that mainly concentrates on the motivational facets of the learning environment by addressing the four constituents of motivation: inciting interest, conceiving applicability, establishing assurance of success, and enhancing contentment through internal and external rewards. ARCS model of motivation plays a key role in identifying how tenacity is connected to the student's anticipation of accomplishment and how optimistic feelings about the learning process generally leads to greater contentment from the gain of knowledge.
According to Lumbantobing (2019), attention, Relevance, Confidence, and Satisfaction are the four key aspects of this theory which have helped the students to be more independent in order to solve problems and find their solutions by themselves without the assistance of others. The theory has been fundamental towards the motivation of the primary and the secondary students so that they can perform to deliver their best in academics as well as in co-curricular activities.
Shehzadi et al.(2020), argued that this theory is difficult to implement in primary and secondary school education as the teachers and educators may have to completely rethink and bring about a change in their mode of instruction. This theory is difficult to apply when students in primary and secondary schools have different levels of motivation.
2.5 Ethical Regulatory Concerns and Standardization on the Merit System in Education
2.5.1 Ethical Regulatory Concerns in the Education System
According to Hernandez (2019), one of the ethical concerns towards the standardization of the merit systems is ensuring fairness in the assessment systems which happen to be one of the important criteria for the education system in any country. Fairness is considered as one of the important factors for the interpretation of valid test scores of the students in the primary as well as in the secondary schools.
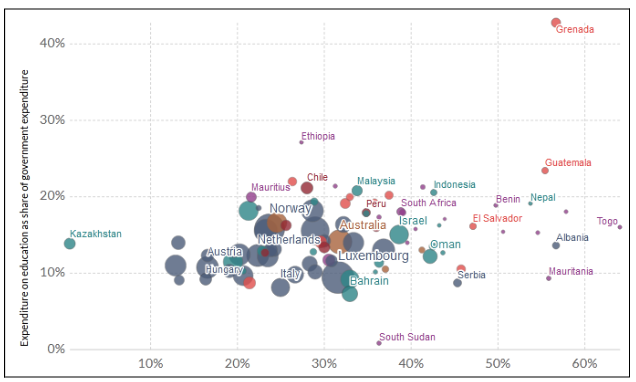
The graph highlights how the Government had contributed overtime on education on priority levels in various countries. It had forecast specifically in many nations that the degree of contribution was less that had its impact today. Fairness in the evaluation of test scores remains one of the ethical challenges for the education system towards integrating the ethical regulations required for standardizing the merit-based system in primary and secondary schools in most nations across the world.
The education system has been changing across the world and the method of evaluation has been constantly evolving in order to make the assessment systems more transparent and standardized and with that, the ethical regulatory concerns concerning the merit-based systems have increased manifold (Badran et al. 2019). Maintaining parity between the strong and the weak students in terms of academics in the primary and the secondary schools remains an ethical concern for the teachers and the schools. Sonnleitner& Kovacs (2020), argued that assessment is not always the favorite tool of the teachers in the primary and secondary schools for figuring out the competencies and the deficiencies among the students. Though assessment remains one of the crucial methods of evaluating the students it is seen that the teachers and educators are insufficiently prepared through the various teacher training programs and vocational courses, and this happens to be another ethical regulatory concern in the education system.
2.5.2 Standardization of the Merit System in the field of Education
According to Wikström&Wikström (2020), there are quite a lot of advantages in the standardized level, course, and pace of learning in the primary and secondary schools. The advantages being that facilitates the implementation of new courses and learning objectives at scale and helps to meet the expectations of the teachers and the educators according to the planned objectives and reduces the significant risks that are associated with the change by making it more acceptable for all. Standardizing assessments can be an efficient tool in highlighting the issues concerning equity, which facilitates in comparing the performance of a large group of students irrespective of their socioeconomic status. Standardizing assessments also help to provide feedback based on the performance of primary as well as secondary school students and helps to identify their areas of strengths and weaknesses.
Haasler et al.(2019), highlighted the disadvantage of this approach being incompetent for any student’s learning process and generally commits to the disconnection among the students. The most distinct and concrete problem towards the standardized level, course, and pace of learning in the primary and secondary schools is that it does not serve the purpose of the students who are far away from the category of average in the field of academics. Standardizing assessments can be quite costly when it is done on a large scale maintaining top-notch quality especially in the case of multiple-choice assessments which have a very limited and defined utility in measuring the accomplishments of individual students.
2.5.3 Ethical Regulatory Concerns and Standardization on the Merit System in the Australian Education System
According to Schirmer (2019), professional codes of ethics are generally designed keeping a number of aspects that help to provide means of protection through means of accountability and generally offer a point of reference in order to guide different practices. Ethical codes do contain certain unavoidable restrictions, the most important being they are able to communicate the minimum requisites for professional practices, but they are not satisfactory to guide the moral to fulfill the ethical perspectives of the codes. This is no different in the field of education where the teachers have dual responsibilities as moral agents as well as values educators in order to preserve the integrity of the profession.
The ethical codes and conduct for the educators in the Australian education system represent shared values that aim to guide the students both at the primary as well as secondary schools and helps them to perform their roles and responsibilities. The educational system in Australia does highlight certain ethical dilemmas and tensions in the works of teachers in the primary and secondary schools which generally arises due to some relational issues arising due to limited interactions between the teachers and the students. The code of ethics for teachers can create different types of hopes from the teachers as moral role models in society and can create different sets of outcomes for the students.
2.5.4 Ethical Regulatory Concerns and Standardization on the Merit System in Middle East Education System
According to Badran et al. (2019), one of the biggest ethical regulatory concerns and standardization on the merit system in the Middle East primary as well as secondary schools has been the poor socioeconomic conditions of many Arab countries as compared to many of the developing Asian countries which were once at par in terms of development. There has been a continuous failure in terms of industrialization and creating successful businesses has been the biggest setback for the economy of many countries in the Middle East. The gender bias has been another contributing factor towards inefficient education systems in the Middle East which is one of the ethical regulatory concerns and towards standardization of the merit-based system in the primary and secondary schools in the Middle East. Pfeffer (2015), stated that the multifaceted type of standardization had deluded a prognosis of the link between standardization and the educational quality. The standardized education systems had considerably reduced the local discrepancies in terms of content and aspect of education. The government has taken several measures including giving scholarships based on merit in order to promote the primary and secondary education standards in the Middle East.
2.6 Literature Gap
The researcher has gone through a number of scholarly articles and publications some of which are noteworthy of mentioning in the literature of the research dissertation and all of them were a rich source of gathering information on the impact of the merit-based system on the behavioral incidences of the primary as well as the secondary school students (Shehzadi et al. 2020). It is seen that this topic has been a topic of interest for many researchers and a number of notable works of research have been done on this topic in many countries across the world. On analyzing the literature as obtained from several journals and publications it is seen that maximum works of research highlight the positive impacts of merit-based systems as external rewards on the behavioral incidences of the primary school as well as secondary school students, but only a small number have discussed its negative impact (Rumbaugh, 2019). The concept of merit pay in motivating the students to perform well in their classes has not been discussed so much in detail in the previous literature.
The theories of learning and motivation in the education system have found prominence in many of the works of literature but most of the works of the literature failed to explore that such theories cannot be applied uniformly on all the students as the educational framework and the learning capacity and the rate of learning of all the students are not the same. This research dissertation seeks to work on those gaps in the literature and provide some concrete support to them.
2.7 Conceptual Framework
2.8 Summary
This chapter has provided a detailed understanding of the impact of the certificate-based merit system of the behavioural incidences of primary as well as secondary school students. The idea of motivating the primary and the secondary school students by implementing merit-based systems as an external based system also finds its presence in this chapter. Other than that, an elaborative discussion on the socio-economic and cultural perspectives affecting the merit-based systems in the primary and secondary schools has made this chapter more acceptable and significant in this work of research.
The discussion has included the opinion of several scholars and some notable works are also mentioned in this chapter which gives the research dissertation a true momentum and noteworthy value. This chapter has highlighted the merit-based system which is one of the debatable topics in the education system in many countries across the world. The researcher has explained how uniformity in the merit-based system can bring about a radical change in the classroom behavioural incidences of the primary as well as the secondary students. The next chapter is going to focus on the methodology of the dissertation.
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.1 Research Paradigm
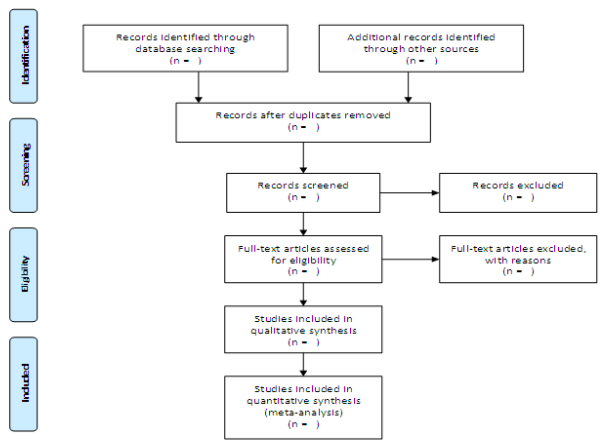
Based on the flow chart, the research paradigm that is used in the work of research is interpretive, where related philosophical ideologies have been utilized to promote the notion that the concept of merit system has an impact on the classroom behavioural incidence of primary and secondary school students. In other words, it has been based on thematic analysis. The interpretive research paradigm allows us to understand that there can be numerous interpretations of the impact of the merit system on the behavioural incidence of students from different perspectives (Nordstrum & Brombacher, 2016. p.1). Hence, such interpretations need to be analyzed through the eyes of the participants rather than the researcher. The theoretical framework that has guided the research work is that motivation has been key in altering the process of teaching and learning. Motivated students have been found to put extra effort into the process of learning, and motivated teachers have been found to put extra effort into the teaching process. The motivation can be provided through incentives or rewards, which has proved to bring about significant change in behaviours, and this has been the theory based on the research work that has been executed.
3.2 Research Strategy
The research strategy used in the work of research is based on a case study that focuses on the in-depth investigation of different techniques and research strategies that support educational goals. The case study has been developed for the Bureau for Economic Growth, Education, and Environment (E3) under the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), and the data that has been used in the research work has been collected from the report based on this case study. According to Harrison et al. (2017), a case study research strategy has been used in a work of research to have a comprehensive understanding of the disparate range of issues that has changed the perspectives, preferences, and interpretations of a research problem. Accordingly, the selected case study is going to guide the research work in identifying the changing patterns and perspectives of merit systems and how it has been affecting the behavioral incidences of the students. The study primarily focuses on the impact of incentives to motivate the teachers to teach and the students to read in schools in Jordan (Nordstrum, L. &Brombacher, A., 2016, p.1). Moreover, the case study is going to present the findings of an incentive pilot program that has been conducted on a short-term basis that has been organized in one of the governorates in Jordan. The pilot program involved giving away non-financial incentives to the students studying at treatment schools based on the condition that they have to read a minimum of 24 books over a time period of 8 weeks which has been considered as the implementation period for the program. On the other hand, the teachers were also granted non-financial incentives, based on the condition that they have to receive high scores in most (minimum of 50%) of the classes conducted by them from the mentors of the program. The case study has been chosen in accordance with the aim of the research work which is finding out how merit systems have an influence on the classroom behavior of students in primary and secondary schools.
3.3 Rationale
The interpretive research paradigm has been used in the work of research to relate the different philosophical theories pertaining to the impact of the merit system on the behavioral incidence of primary and secondary school students in order to actively construct a perception how such systems have been influencing the students and the education system. The case study research approach has been utilized in the research work in order to have an in-depth understanding of how the merit system has an impact on the behavioral incidence of primary and secondary school students by focussing on a specific educational organization. Moreover, the case study research strategy facilitates a composite and varied investigation of the research problem.
3.3Techniques used as per the case study for the research work
The pilot incentive program involving the students and the teachers from a treatment school in Jordan had been designed and implemented in accordance with the Reading and Math Program (RAMP) and had been funded by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). The program had targeted the students and teachers of the early grades in Jordan, under this 5-year long program. According to Mosleh&Alshaboul (2020), the incentives that had been designed for the teachers and the students under this program were mainly to motivate them and improve their performance. The pilot program instead of offering rewards in the form of cash or token to either the students or the teachers went ahead of offering symbolic incentives primarily in the form of certificates and giving public recognition to the individuals who had successfully participated in the program at a local awards ceremony. The incentive programs under this case study focused on how it had motivated the students and had an influence on the behavior of the students which is the main aim of the research work. The case study had been extended to include more students as well as teachers with the belief of encouraging the students to read more at home, which had been one of the primary objectives of RAMP. The motive of giving incentives to the teachers in order to put into practice what the teachers had been trained to do which also happens to be another objective of RAMP.
3.4Methods followed in the case study as a part of research work
3.4.1 Students
The case study involved tracking the reading activities at the home of the students from 47 different schools in Jordan. The reading activities of the students belonging to grade 2 outside the school had been the primary focus for the incentive program designed for the students under the pilot study. The grade 2 students were instructed to read books on a regular basis, at least thrice a week at home and maintain a log of the records of the books that they had completed reading with their parents/guardians, and then returned the same log to the schools (Nordstrum, &Brombacher, 2016, p.11). Based on the logs the students were to be evaluated and, and would be receiving recognition and certificate at an award ceremony after the completion of the term. The details of the program were briefed to the students and the parents by the principals of the schools, who were in turn briefed by the mentors of RAMP. The reading logs were handed over to the students and them along with their families received specific instruction about how to fill up the reading logs.
The objective of the program was to figure out whether the provision of incentives to the students was instrumental in improving their reading habits and enhancing the frequency of reading books at home (Kaimal& Jordan, 2016). The information was gathered by the RAMP mentors during their visits all through the 8-week implementation period of the program and handed over to the RAMP data collection group at the end of the term.

3.4.2 Teachers
The case study also focussed on the teachers from the same 47 schools in Jordan whose students were a part of the pilot program in order to realize the implementation of RAMP. The teachers were acquainted that if they presented the competent discharge of the classroom teaching practices they were qualified to use, and at the end of the term for that, they would be given special recognition in a ceremony organized by the school. The program made it clear that the teachers would be receiving the recognition in the form of a certificate if they are able to get an implementation score of 4 or more on a scale of 5-point for the bulk of their attended lessons. The data based on the classroom investigation were being collected twice a month by the RAMP mentors as a part of evaluating the performance of the teachers in the classrooms (Alkhawaldeh, 2017). The observational process in order to gather relevant data focussed on the teaching materials utilized by the teachers, the different assessment and characteristic tools implemented by the teachers, and the adequate teaching practices, and all this composed of the protocol that was going to be followed under the pilot program. The next task involved aggregating the observations in order to figure out the composite implementation score for each teacher every visit by the RAMP mentors. The aim of the program was to arbitrate whether the practical implementation of RAMP could be inspired by the academic appreciation of the high-quality work that had been initiated by the teachers.
During a semester, the teachers were observed from two to six times, however, all the teachers under this program did not receive the same number of visits from the mentors, and hence there was a difference in the number of observations made for each teacher. The number of visits made by the mentors was not under the restriction of the pilot program, rather it depended on the discretion of the RAMP mentors. The RAMP mentors made the most out of every visit to collect the relevant data based on the observations which primarily focussed on the teaching practices. Later on, these data were passed on to the RAMP mentoring database by the RAMP mentors.
3.4.3 Control Schools
A total of 42 control schools did not engage in either of the teacher or student incentive programs and that was evident from the fact that these schools were not told whether they would be eligible for any awards if they somehow met with the objectives of the program. Certainly, they were not informed about the incentive program at all, but however, they were provided with some information which otherwise very similar to the ones provided to their analogs in the treatment schools. The students from the control schools were also motivated to read books at their home, and then to fill out the reading logs, and submit the same to their respective schools. The relevant data were gathered by the RAMP mentors during the time of their classroom visits. The classroom performance scores were also computed for the individual teachers at the control schools during the mentoring observations.
3.5 Plan of Communication
The treatment and control segments of the program were corresponded by various printed posters that were distributed by the RAMP mentors. Besides that, the RAMP mentors propagated the information about the program under the case study to the principals, followed by the teachers and students of grade 2, and then subsequently to the parents and guardians of the students in the form of a cascading model.
The various components that were distributed by the RAMP mentors to the participating schools under the pilot program are as follows:
- Fliers: The details of the incentive programs for the students and the teachers were mentioned in the form of printed materials.
- Reading logs: The students maintained the records of the books they finished reading at home every week.
- Recording logs: The teachers maintained the records of every student on a weekly basis in order to keep a track of the books they have read every week.
3.6 Sampling Methodology and selection of schools
The selection of the schools for the case study had been carried out through a deliberative and continued process. The endeavors were made in order to randomize certain facets of the selection procedure in order to achieve overall randomization but some that were not viable for this particular case study.
The Jerash governorate was chosen on account of its geographical location for this particular case study, and moreover, it was comparatively firm and the number of schools (about 100) was very much convenient for a study with various treatment conditions. It was found that out of 110 schools under the Jerash governorate, only 21 were handled by the mentors under the Education Ministry and the rest were managed by the mentors under RAMP, and hence were not selected for this particular case study. The randomization technique was considered for categorizing the remaining 89 schools into two groups of control and treatment, but there was a concern that the schools might be located at close adjacency to one another, which might have led to exchange or leakage of information between the control and the treatment schools. In order to avoid such a dilemma, the schools were grouped together in the form of geographical clusters, the clusters were chosen arbitrarily into 47 schools under the treatment group and 42 schools under the control group.
The students and teachers from grade 2 from these chosen schools took part in the incentive program under this case study. The students were however not compelled to take part in this particular. During the communicating the program, it was made clear that the participation in this program was purely intentional and in no way or the other, non-participation in this program was going to hamper the school grades of the students.
The incentive program under this particular case study relied on the participants of the focus groups that were primarily the teachers and the students from whom the relevant information was directly gathered. A relatively limited number of students of grade 2, comprising 11 participants, out of which 6 were female students and 5 were males students, and also a small number of teachers, comprising 13 participants, all of which were female teachers, were chosen from three treatment schools in order to participate in this case study. The participants from focus groups were not chosen at random. There were three focus groups that consisted of the teachers and there were another three focus groups that consisted of the students.
3.7 Collection of Data
The data relevant to the reading activities of the student was first recorded by the students in their individual reading logs as provided by their respective schools, and then subsequently that was computed by the teachers at the classroom level. The responsibility of the students was to return their reading logs to the schools every week, and then the teachers were to take a note of how many books the students who participated in the study read each week, as a part of the 8 weeks implementation period. The control data on the reading activities of the students were not gathered prior to any form of mediation. The activities mentioned henceforth formed a part of the data collection techniques ascertained for the student incentive program.
The mentors played a pivotal role in observing the instructional practices of the teachers practiced in the classrooms, especially to figure out the extent to which the teachers were enforcing RAMP. The mentors gathered the relevant data which pertained to the teaching practices, which primarily consisted of the teaching materials utilized by the teachers, the various diagnostic and assessment tools used by the teachers, and the competent and appropriate teaching practices (Klein et al., 2019). The relevant data were enrolled electronically into an observation-based software on computer tablets and uploaded on the databases that were specifically maintained for RAMP.
The focus groups were instructed in Arabic by the RAMP staff with the teachers and students that were participating from the chosen three schools. The conversations were recorded during the focus groups, and later on, the audio clips were interpreted in Arabic and that was translated into English.
3.7 How the Data Analysis has been conducted
The data collected is analyzed in order to get the required outcome in the case study. The conversations recorded the library submissions were analyzed for students as well as teachers across treatment and control schools in Jordan. The analysis of the student's incentive program regarding reading books, (Turner, 2017), showed that the students of treatment schools met the criteria better than the students of the control schools. The tests provided the differences between the students regarding the inventive criteria and book reading. The difference between female students and control school were significant, as well as for the male students from both the schools.
Considering the focus groups, created for the research procedure, it was observed that the difference between the motivation of males and females was not much, and the teachers agreed about the generalization of the program.
The teacher quality was also observed to be varying related to book reading and a very low percentage of teachers were recognized to meet the incentive criteria. Moreover, the teacher quality resulted in their behaviour in the class with the students. Teachers with better observations were able to provide help and time to students and encouraged them to read in school.
The focus groups also reflected the perception of students as well as teachers regarding the program, especially student incentives. As for the students, they enjoyed reading and therefore the pilot program was interesting for them, along with the competitive nature of the program was an added experience. All the students liked to be informed about their classmates reading books, and they wanted to read as much as others (Guryan, Kim & Park, 2016).
As for the teachers' focus groups, they acknowledged that the pilot program was working as motivation, as the students were enjoying reading books along with competing with their friends. The program stimulated not only strong readers but also the other students who were not recognized as frequent readers.
3.8 Validity and Reliability of the Research
For the research, the data was collected and analyzed across the control and treatment schools of Jordan as per the case study. Therefore, the data collection for this research paper is secondary, which has been conducted by means of descriptive statistics as retrieved. The validity of the research outcomes is reliable as the case study used for the research process has been published for the office of education and reviewed by the agencies for international development. As opined by Mohajan, (2017), the sources of data collection are valid, the information and the outcomes of the research are reliable.
3.9 Limitations of the Study
The research being conducted by scholars, the information sources were limited. The data gathered was general, and the size of the data collected was huge. For the paper, the time provided was limited, and the research was based on the merit system of primary and secondary schools, all the schools were to be recognized. Moreover, owing to the pandemic, COVID-19, the schools were shut, thus primary research could not be followed. Therefore, the procedure was conducted by secondary means, by gathering information from journals, case studies, and publications.
Chapter 4: Data Analysis
Systematic Review
Out of the 5 short listed articles, the majority of them has been found to have adopted predominantly the qualitative methodologies of data collection, in order to understand the impact of the certificate based merit systems on the behavioural incidence of the primary and secondary school students. Out of the predominant articles employing qualitative methodologies of data collection, some were exclusively qualitative in nature and there has been no triangulation with quantitative methodologies. Swanson et al. (2014), for example, used the experimental or quasi-experimental methods of empirical analysis in order to examine the primary studies on the Promise Programs. The article focussed on the published articles, dissertation papers, working papers and conference papers on similar topics in order to gather quality and reliable data for the study. The sources without quantitative treatment like case studies, journalist accounts, program descriptors and programmes has been found to be excluded in this particular article. The article has focussed on programs that has been limited within the US and the studies that has been written in English. The preference of such programmes over other international has been found to be due to the unique structure of the post-secondary education funding in the US.
Chapter 4: Data Analysis
4.1 Systematic Review
Out of the 8 short listed articles, the majority of them had been found to have adopted predominantly the qualitative methodologies of data collection, in order to understand the impact of the certificate based merit systems on the behavioral incidence of the primary and secondary school students. Out of the predominant articles employing qualitative methodologies of data collection, some were exclusively qualitative in nature and there had been no triangulation with quantitative methodologies. For instance, Swanson et al. (2016), used the experimental or quasi-experimental methods of empirical analysis in order to examine the primary studies on the Promise Programs. The article focused on the published articles, dissertation papers, working papers and conference papers on similar topics in order to gather quality and reliable data for the study. The sources without quantitative treatment like case studies, journalist accounts, program descriptors and programmes have been found to be excluded in this particular article. The article has focused on programs that have been limited within the US and the studies that have been written in English. The preference of such programmes over other international ones has been found to be due to the unique structure of post-secondary education funding in the US. Nordstrum & Brombacher (2016), used the data that had been recorded on record logs by students and tabulated by the teachers at the schools which reflected about the number of books that were read by the students in a week. However, the baseline data pertaining to the student reading had not been collected prior to the intervention. The article also shows that the data had been gathered on the teaching practices and the various assessment tools utilized by the teachers in order to evaluate the efficiency of the teachers in guiding the students in the class. However, in this case the baseline data based on the classroom teaching had been gathered prior to the intervention. The article had also reflected that complete randomization of data had not been achieved due feasibility issues arising in the study, and hence it had been not utilized in the sampling process. Kirsten (2018), in the article had utilized the PRISMA technique or better known as the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis for collection and extraction of data. The PRISMA technique in the article had reported about the information sources that had been used in the search process, the individuals who participated in the search process and the date thereof which had been crucial with the process of data collection. One of the advantages of the tool had been that it had been applied across non-randomized controlled trial reviews, which had made it unique in terms of data collection techniques, as compared to other data collection techniques. The article also mentioned the use of NOTARI as the data extraction tool for the qualitative methodologies utilized in the aforementioned article. The data extraction tool had been developed as a control instrument in order to present the data in a format that had eased the process of analysis and synthesis.
4.2 In-depth Review of Results
For a detailed inspection of the research made all over, most applicable eight articles were incorporated for the in-depth review. This in-depth review disclosed basic dissimilarities between learning methodology researches based on their concepts of strategic learning. Learning strategy research that involved self-management assumptions as central to the research outline. Learning strategy research that made use of conventional language acquiring strategy processes while accepting the contributions of self-management. Learning strategy in a research that has developed in the field having unusual but new zones i.e. by exploring new means like structures, instruments and also inspecting correlation between strategic learning and other theories.
At least two members from the research team gave detailed analysis of each of the articles with the prime inspector to form such in-depth reviews. An in-depth documented assessment is created and its addition is very important for this paper. Among all the reviews a few of them are discussed here in a condensed form for a better picture. A few of the articles were brought in as examples to give clear illustrations of the divisions made by the reviewers about the research.
As per the analysis and research of Nordstrom & Brombacher (2016) an experimental encouragement program was run collaterally with RAMP (Reading and Math Program).These student encouragements were recorded every week by the teachers by calculating the journals read and submitted by the students. There were coaches made as observers for the teachers to keep a record of their execution of RAMP on students by invigilating their classroom guidance practices. The coaches updated themselves with the instruments, constructive ideologies and the equipment for assessing the children used by the teachers. These data were fed by computerized methods in observation software on tablets and thus into the RAMP tutorial database. The standard data on classroom teaching got collected before the coaches stepped into the observation. The RAMP staff then comforted the group by translating data into Arabic as they required it primarily along with the teachers and the students of the three selected schools. These oral communications between them were then recorded and noted in Arabic and English for further use.
In another research type done by Liebowitz & Porter (2019), sample spotting was done to testify the qualitative ranking of the study of the new subjects whose characteristics are known as its members are already subjects of a larger trial of research. Basically it is the descendant of a larger research and its subjects in detail. Identifiers were created based on the initial broadcasting of the studies of the researchers as three researchers groups, one data resource and all remaining were designated as “unique”. The tutorial was then grouped into two categories of temporary and opinionative. It was specified that the temporary tutorials must include imaginable but externally originating ideologies that focused on designated method of study by randomly selecting a member into an observation slot, opinion differences calculation, or variable implementation of instruments procedures. In lack of the externally originating differences, any studies employing matching or structural equation modelling (SEM) were not specified. No specific quality of study was determined other than the target evaluation to know if the result depends upon the externally originating differences in the process to avoid any addition of any coating of hazy outcome to Meta Analytic process. By the calculations of the direct estimations of SEM, when the author's final and exact model had covariates, each predictor and result pair were regulated. But in some cases the selected model was missing due to which the authors were contacted for detailed information. But it stood unobtainable so the coefficient from the final model was drawn out.
Based on the Meta Analytical model calculations, different researches contribute different outcomes both for expected and quantitative. On the contrary in this case it was evaluated that multiple outcomes contribute less to the actual and entire session of research.
On the other hand Kristen (2018), had used the PRISMA method for the elaboration of the data collection system for the respective research. The PRISMA constituted of the following items: details of the resources of the data, details of the person or the team conducting and collecting the data, a complete plan of the search detail that was followed and the various databases used for the search with the terminologies and compound. As the system is only depending on the proofs out of the researches to be mentioned in the chronological reporting, the PRISMA can be used for the studies not including randomized control trial system. The data removal equipment was used as a standard tool of extraction in the present data in the same process for elaboration and analysis.
Swanson et al. (2016) in the research has provided a different method of quasi –experimental methods of empirical analysis. This method fundamentally included the opinion difference calculation system but differed in its outcome as is based only to the point answer of the exact questions. But the same opinion differential method is used in the higher education system between qualified and non- qualified candidates in the earlier and present time of execution. This system identifies location based scholarship on at least any of the following-K12 academic results featuring degree issuance rates, standard test marks, high school grading system with the points added individually, post-secondary results clarified itself as increased number of attendance ,evaluated by ACT scoring in college scores, grades, attendance and college continuity and community enhancement results explains as experimental researches that are conducted were in a hope to regenerate the socio-economic condition of the localities under the rural zone. This system is interlinked with the K12 system.
Yet another instance can be set by the eliminative research of Aslam et al. (2016), where it is stated that a primary tool was designed in the beginning to resource the investigators for extraction of their data analysis of the research. Forms were created and filled up by each and every students which made the screening phase of the research through. Though primarily these forms were introduced only for investigation of data but later it clarified the queries that were targeted to be clarified for each of the studies dealt on the research. Many forms of questions had floated, among which those that had no limited answer were sorted into smaller groups and supported with subsequent tables of data. These forms brought forward many existing questions on the process of research, study plan, the answered questions of the research, factors depending upon context of the study, and various other questions. With the continuation of this rigorous study process it took the entire research study to a final set of featured results that put forth some powerful findings which either had gone through or opposed or focused it's neutrality for the different suggested associations between the inclusions and results from the research study. The convention clarified that depending upon the type of studies researchers claimed and the data thus accepted by them could be further put into a Meta analytic process for a detailed numerical calculation of the subject study which however was not applicable. The final results from the subjective study of the research highlighted that the researching teacher effectiveness reforms, at par couldn't permit the exact calculation of the exact size or meta-analysis. The outcome is so produced in a subjective form in detail and no calculation could be progressed identifying the critical points of data that clarified the note of questions framed during the research study.
The study conducted by Harry (2019), had been about the implementation of an advanced proficiency examination in the school curriculum which had been primarily a qualitative study in nature. The analysis of data had been done simultaneously with the collection of data in the study in order to maintain uniformity. The verbatim transcription of the audio recordings of semi-structured interviews and observations had been carried out in the study. The transcribed data had been cross checked with the audio clips in order to test the reliability and validity of the two. The analysis of the data in the study had been done initially on a manual basis. The data analysis began initially with the repeated reading of the transcriptions in order to have an overall idea of the whole interview, which in turn facilitated a deeper meaning about the perspectives of the teachers with regard to the implementation of the advanced proficiency examination in the school curriculum. The responses of the teachers had been linked with the notions the teachers had about the new curriculum and the way they had been implementing the same in a class. The factors that aided and deferred also been linked with the responses in order to have a better understanding of the barriers that came in the path of implementation of the new curriculum. Segments of transcripts were coded along with the research questions. The codes had been classified into two types, essentially as the implicit codes and the vivo codes based on the interview transcripts of the teachers. The codes which shared some common characteristics based on comparison had been used to generate themes, and this had been done in order to identify the similarities and patterns in the coded data. In order to infuse the themes, the constant comparative method had been used to identify any form of inconsistencies or anomalies in the data. The study refined the contents of each category which led to several themes and sub-themes, and all these contributed towards understanding the perspectives of the teachers about the barriers that had been there towards the implementation of the advanced proficiency examination in the school curriculum, and as such has been categorized under a theme as “school-contextual factors”. Another theme “external contextual factors” had been about the different approaches taken towards innovation in the curriculum, financial and resources constraints, ineffective professional development and training and other allied factors.
The four major themes that came up in the study conducted by Harry (2019), were the notions that the teachers had about the new curriculum which included the CAPE Communication Studies, the gaps in the implementation of CAPE Communication Studies, the barriers that had been perceived with regard to the implementation of CAPE Communication Studies and the factors that facilitate the implementation of the CAPE Communication Studies. Most of the teachers expressed positive views regarding different aspects of CAPE Communication Studies and to some extent supported its implementation in the new curriculum, as they felt the concept was quite unique and novel.
Korpershoek et al. (2019), revealed in the study that the quantitative methods had been used exclusively, and a sample size of 30 students had been chosen in order to carry out the correlational analysis, The analysis had been based on seven parameters which are motivational outcomes, behavioral engagement, absence/dropout rates, academic accomplishment, self-perceptions, perceived learning environment, and educational aspirations/attitudes, which had been found to be fundamental parameters in connection to a student. In order to have a differentiation in the results, different geographical regions, different grades and different socio-economic backgrounds had been the differentiating parameters among the students on whom the study had been conducted. The results of the study based on the correlation analysis showed the correlation coefficients to be positive for most of the student outcomes, only the parameter of absence/dropout rates showed negative correlation coefficients. Again the correlation coefficients between the school belongings as compared to that with academic accomplishment and that with absence/dropout rates showed small values (r=0.18 and r=0.16 respectively ). On the other hand, the results revealed that the correlation coefficients on the basis of the other parameters like motivational outcomes, behavioral engagement and socio-emotional outcomes showed medium to moderately high values which (varied between r=0.30 to r-0.39), which showed that the students sense of belonging in the schools are largely governed by these parameters as compared to the other parameters used in the correlation analysis. The academic accomplishments of the students in terms of school grades, the motivational outcome in terms of a desire to achieve a goal, the social-emotional outcomes as self-efficacy and self-outcome and behavioral outcomes in terms of cognitive involvements were some of the outcomes based on which the students sense of belonging in the schools had been analyzed closely monitored during the study.
The study conducted by Korpershoek et al. (2019), further showed that the school belonging of the students was positively associated with the measure of school grades (r=0.18). Standardized tests were also seen to have a positive impact on the school belonging to the students, though it was not as strong as measured against the school grades. Student's sense of school belonging was also seen to be positively attached to the perceived learning environment, for instance perceived classroom environment (r=0.40) and also was positively influenced by the factor of career-oriented goal structure (r=0.44), which reflected that the students with high levels of school belonging were more positively influenced by the perceived learning environment and career-oriented goal structure as these parameters motivated them more as compared to other parameters. The study further revealed that there were significant differences in the correlation values to express the student's outcomes in terms of school belonging as the instruments for measurements differed. The values of measurement differ mostly based on the parameters of academic accomplishments, behavioral engagements, self-perceptions and motivational outcomes. The correlation values differed to some extent with respect to the different regions especially in the domains of perceived learning environment and behavioral obligation.
Considering the study of Lambert (2020), it was recognized that the qualitative systematic review was conducted by the process of synthesis of studies from diverse sources which provided more detailed data regarding the research. As a total, about 176 reports and articles are analyzed and evaluated to meet the criteria of research which included journal articles, national studies, and conference papers. In order to have an unbiased judgment, a second researcher was included and with the help of their opinions only forty-six studies were selected to perform the research. The research was conducted in two phases, and all the information was collected from website sources. Considering the first phase, the analysis of the quantified statistics was adopted which included various factors related to the research, such as, country of origin, the technology used there, number of students participating in the program, and the research procedure along with the aims and the results obtained. For the second phase was qualitative analysis, which included various methods to analyze the information and make a conclusion depending on the similarities and differences based on the aim, principle, and results of the research. The analysis was based on four questions, which were addressed as global distribution and characteristics, aims and aspirations, the different types of learners and the policies to benefit all.
Considering the global distribution of the Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs), it was recognized that North America, Canada, and the UK are directed towards open and distance learning. There was a spike recognized in the publication related to education, which was later on slowed. This revealed that the interest in MOOCs slowed down after the introduction and the funding was also limited.
For the aims of the MOOC, a great percentage was recognized to be enrolling and transitioning in order to improve the student equity which was around 47.8 percent. It was observed that around 36.9 percent if the process aimed to improve the student's resources whereas around 15 percent aimed towards social inclusion.
Analyzing the different types of learners, the recognized categories were learners with fewer skills or confidence, bilingual or non-English learners, disabled learners, and learners from vulnerable or weak communities. The results were based on the mentioned categories and the programs were designed to help the learners address the issues.
On the other hand, nearly half of the studies were based on the policies and practices for the staff and the learners in order to design programs to encourage the development of the MOOC towards students and staff benefits for the future.
Moreover, technical specifications were aimed yi made to make innovation in the learning procedure in order to make it more efficient and decrease the deterioration for all the MOOC learners especially the disabled learners
4.3 Discussion
In order to achieve the results, the various analysis was performed in the journals, and the outcomes of those have been discussed in the section.
For the research conducted by Aslam et al (2016), eight studies we're recognized, of which two were considered to be of high quality and the rest as moderate. The research covered various countries which included India, Kenya, Nigeria, Pakistan, Togo, and Mali. The results revealed that contract teachers were as efficient as the regular teachers and even better sometimes. The contract teachers are recognized to put in extra effort comatose to the regular. The contract helped to improve accountability for the teachers, as they are recruited from the local community. The union worked and implemented the reforms in a centralized manner and recognized the barriers that affected the reforms.
Considering the research performed by Harry, the analysis revealed that the teacher's beliefs regarding innovations were not transferred in the classroom as expected and the implementation was affected and the challenges arose. There are numerous obstacles as recognized, namely school contextual, external contextual, and the innovation-related which altogether involve the implementation process. The implementation was also successful owing to the norms of the education initiatives and the curriculum planners did not recognize the effects of the various contexts in the classroom.
In association with the research conducted by Kirsten, Y. (2018), the articles were focused on the behavioral model with respect to emotional aspects such as support and ability to supervise. Considering the individual level, the teachers were considered for the WIL and mentoring to help the students and was focused to bring in positive feedback from the teacher-student relationship. The teachers as mentors see positive and motivated, so the program should focus on the development by providing counseling, information, and challenging assignments to help build self-esteem. The schools should support the teachers, especially in rural areas to help get positive outcomes.
Considering the study as performed by Korpershoek et al (2019), the outcomes revealed the student's perception of being accepted, respected, and supported in the school environment. The students who were accepted and included were recognized ti perform better and showed motivational and confident behavior. The optimistic behavior indicated the student’s goal orientation and they were more related to the school environment. The positive relationship between the student and the school demonstrated efficiency and the emotional connection. The negative association of students with the school was recognized leading to more dropouts and absence from the students.
On the other hand, for the survey performed by Lambert (2020), the first phase was recognized to be preferred and consisted of a well-educated audience, open to a variety of education programs. The learners' support was considered to be significant in the success of the process. The second phase helps to add on the understanding of the different types of learners and the results enabled to plan the education programs. The research helped to design the approaches for the MOOC for all the types of learners.
In relation to the survey conducted by Nordstrum, L., & Brombacher, A., (2016), it was recognized that the students from treatment schools were more interested in reading in controlled schools. Moreover, the girls were recognized as more frequent. The teachers of the treatment school were recognized to be better in meeting the incentive criteria when compared to the controlled schools. The outcomes revealed that even with the limitations, the incentive program was found effective and cost-efficient in motivating the students as well as the teachers.
For the research performed by Swanson et al (2016), it was observed that the promise program showed positive outcomes in the development of the school environment. The program was implemented with the help of private contributors that wanted the education to be directed towards development. The program was recognized to provide good benefits for the middle class and low-income category students. The survey revealed that the program applied only to a few schools or local community schools, and the development was mainly concentrated on the application of promise programs.
4.4 Analysis
The analysis of the gathered information for the concerned research different programs was selected which were implemented in order to help the development and benefit the students. The different strategies were observed and the process was analyzed to reach the required outcomes. The different procedures related to the education and school environment along with building the student-teacher relationship were analyzed and evaluated in order to obtain the effects it has on the behavior of the students and their academics.
Chapter 5: Conclusion and Recommendations
5.1 Conclusion
After the culmination of the overall dissertation, the responsibility of the researcher lies in drawing an inference from the dissertation. Thus, in this final chapter of the dissertation, the inference is going to be presented. On analyzing the data that has been collected and reviewed, it can be realized that a number of initiatives have been taken across the world in schools in order to motivate the students in primary and secondary schools by presenting them with non-monetary rewards in the form of incentives or scholarships. The approaches seen in the different works of research may have been different, but the motive of each of them has been the same, that is to motivate the students by rewarding them and in turn comprehending the impact of such rewards on their behavior. The initiative has been found to be beneficial in many occasions as it helped the students to take more interest in their studies. The level of motivation has been found to be different in case of different students and so the impact on their behavior has also been found to be varying in each case. Overall, the impact of certificate-based merit systems on the behavioral incidence of the primary and secondary schools students has been found to be quite encouraging as in most occasions they have shown increased interests in their studies. Therefore, it is anticipated that such certificate-based merit systems would also have a positive impact on the classroom behavioral incidences of the primary and secondary school students in the Middle-East.
The overall dissertation has been segmented into five chapters and each of the chapters bear a significance of their own in order to make the dissertation impeccable. In the introductory chapter the research has elaborated in details about the entire dissertation. The second part of the dissertation has been relevant to the discussion based on the different pieces of literature on the impact of the certificate-based merit systems on the behavioral incidences of the primary and secondary school students. The different motivational and behavioral theories along with the concept of merit based pay has found relevance in the discussion made in this chapter. The third chapter of the dissertation has been about the methodological part of the work of research. The researcher has outlined the research philosophy, strategy and the data collection techniques. The limitations in terms of collection of data has also been outlined in this chapter.
5.2 Linking with Objectives
It has been found to be quite evident that a researcher frames the research questionnaires based on the objectives of the research work. The researcher is also responsible for linking the individual chapters of the dissertation to each other in order to present the significance of the dissertation and convey its usefulness as a part of the overall research work. The objectives of the work of research signifies the context based on which the whole dissertation has been developed. However, these objectives need to be linked to the literature review as well as the data analysis parts stated in the dissertation. The three objectives as stated in the dissertation has been mentioned below:
Objective 1:
-
To analyze the practice of certificate-based merit systems in primary and secondary schools in different countries
In connection to this objective, the researcher has tried to evaluate the practices of certificate-based merit systems that have been followed in the primary and secondary schools in the different countries. This objective has been realized in the literature review through the point which discussed the factors that has affected the certificate-based merit systems in primary and secondary schools
Objective 2:
-
To identify the impact of certificate-based merit systems on the behavioral incidences of the primary and secondary school students in various nations
The researcher with the help of this objective has tried to identify the impact that certificate-based merit systems had on the behavioral incidences of the primary and secondary school students in different nations. This objective can be linked to the point in the literature review where the impact of the merit system on behavioral incidences of the secondary school students has been compared to that of the primary school students.
Objective 3:
-
To evaluate the effectiveness of the certificate-based merit systems on the behavioral changes among the primary and secondary school students in the Middle East
The objective mentioned here as narrowed down the search and helped the researcher in order to focus only on the effectiveness of the certificate-based merits systems on the behavioral changes among the primary and secondary school students in the Middle East. The relevant points that have been linked to this objective in the literature review which has discussed the effective implementation of behavioral changes on the primary and secondary school students using the different behavioral and motivational theories. Moreover the points in the literature review discussing the ethical regulatory concerns and standardization of the merit systems with special relevance to the education system in the Middle East also links to this objective.
5.3 Limitation of the Research
The researcher has put in all the efforts to conduct the research by following all the appropriate steps and gathering the data by maintaining its reliability and authenticity. In spite of so much adequacy, there has been some limitations in the work of research. The first and foremost limitation has been the unpredictable and unprecedented situation due to the recent global pandemic situation arising out of the COVID-19 outbreak which has restricted the research methodology to a secondary qualitative research. The researcher has been forced to rely on the secondary sources like journals and articles in order to gather the relevant and necessary data in order to complete the research work. Moreover, the analysis of data has to be done as a systematic review of the data found in relevant journals which has somehow restricted the universality and astuteness of the research work.
Other than that time has been one of the factors that has been a restricting aspect in the work of research. The time boundness of the research work has not allowed the researcher to explore further and looked into the in-depth underlying factors that could have contributed more essence and depth to the research work.
5.4 Future Scope of the Research
On evaluation of the limitations that have been found in connection to the research work, it can be said that the research has a scope to be carried on further by any engrossed researcher may be utilizing some other approach. The work of research in future may be carried out utilizing primary qualitative and quantitative methodologies in order to generate more intuitiveness and astuteness in the findings and further analysis of the collected data. In this way, more new findings would come up relevant to the topic of the dissertation which may have been missing in this dissertation. Again, the future researchers may select another location and this may produce a differentiation in the result. However, the future researchers should try to allocate more time in order to complete the work of research in-depth unlike the present researcher who faced a constraint in time to complete the work.
The results may vary here also if the same research in the future is extended beyond the school level to include the colleges and universities, and figure how the merit systems have an impact on the behavioral incidences of those students keeping in mind the level of maturity they have attained with age. These factors can be chalked out by the future researchers before they start with the dissertation work, so that they can effectively plan out the course of action to be taken during the work.
5.5 Recommendations
After evaluating all the relevant data and information, the researcher has figured out some problems that need to be resolved on an immediate basis. The researcher has prepared some recommendations based on the problems that have been identified, besides that the researcher adds a justification for each recommendation in order to have a better understanding.
Recommendation 1:
- The education department under the government's needs to play an active role in facilitating certificate based merit-based systems in schools.
Justification for the recommendation
The researcher has identified that the education department under the government has not taken so many initiatives in implementing the appropriate certificate based merit-based systems in schools and this has been quite a discouraging approach shown by them. So the education department under the government needs to take a proactive role in implementing the certificate based merit-based systems in the primary and secondary schools.
Recommendation 2:
The proper coordination among the school administration and the teachers in order implement the certificate based merit-based systems in schools.
Justification for the recommendation
The researcher had found out that on several occasions the coordination among the school administration and the teachers has not been there which made it difficult in implementing the certificate based merit-based systems in schools. The teachers in several cases have been seen to have no idea about the system and how to utilize it. So a proper coordination needs to be built among the school administration and the teachers about the system and the ambiguity about the system among the teachers needs to be cleared.
References
- Affandi, L. H., Saputra, H. H., &Husniati, H. (2020, August). Classroom Management at Primary Schools in Mataram: Challenges and Strategies. In 1st Annual Conference on Education and Social Sciences (ACCESS 2019) (pp. 263-266). Atlantis Press.
- Aina, J. K., &Ayodele, M. O. (2018). The Decline in Science Students' Enrolment in Nigerian Colleges of Education: Causes and Remedies. International Journal of Education and Practice, 6(4), 167-178.
- Al-Ansari, A., Al-Harbi, F., AbdelAziz, W., AbdelSalam, M., El Tantawi, M. M., &ElRefae, I. (2016). Factors affecting student participation in extra-curricular activities: A comparison between two Middle Eastern dental schools. The Saudi dental journal, 28(1), 36-43.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. (2017). School-based teacher training in Jordan: Towards on-school sustainable professional development. Journal of Teacher Education for Sustainability, 19(2), 51-68.
- Aslam, M., Rawal, S., Kingdon, G., Moon, B., Banerji, R., Das, S., & Sharma, S. K. (2016). Reforms to Increase Teacher Effectiveness in Developing Countries: Systematic Review, September 2016.
- Badran, A., Baydoun, E., & Hillman, J. R. (Eds.). (2019). Major challenges facing higher education in the Arab world: Quality assurance and relevance. Springer.
- Barbier, K., Donche, V., &Verschueren, K. (2019). Academic (under) achievement of intellectually gifted students in the transition between primary and secondary education: An individual learner perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 2533
- Batruch, A., Autin, F., Bataillard, F., &Butera, F. (2019). School selection and the social class divide: How tracking contributes to the reproduction of inequalities. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 45(3), 477-490.
- Bendermacher, G. W. G., oudeEgbrink, M. G., Wolfhagen, I. H. A. P., & Dolmans, D. H. (2017). Unraveling quality culture in higher education: a realist review. Higher education, 73(1), 39-60.
- Burroughs, N., Gardner, J., Lee, Y., Guo, S., Touitou, I., Jansen, K., & Schmidt, W. (2019). Teaching for Excellence and Equity: Analyzing Teacher Characteristics, Behaviors, and Student Outcomes with TIMSS. IEA Research for Education. Volume 6. International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement.
- Chao, C. M. (2019). Factors determining the behavioral intention to use mobile learning: An application and extension of the UTAUT model. Frontiers in psychology, 10, 1652.
- Crul, M., Schneider, J., Keskiner, E., &Lelie, F. (2017). The multiplier effect: How the accumulation of cultural and social capital explains the steep upward social mobility of children of low-educated immigrants. Ethnic and Racial Studies, 40(2), 321-338.
- Dalton, M. R. (2020). Level Systems in EBD Classrooms: Are They Effective in Changing Behavior, and How are They Perceived by Teachers and Students? (Doctoral dissertation, UCLA).
- Daniel, H., Bornstein, S. S., & Kane, G. C. (2018). Addressing social determinants to improve patient care and promote health equity: an American College of Physicians position paper. Annals of internal medicine, 168(8), 577-578.
- Darnon, C., Wiederkehr, V., Dompnier, B., &Martinot, D. (2018). ‘Where there is a will, there is a way’: Belief in school meritocracy and the social‐class achievement gap. British Journal of Social Psychology, 57(1), 250-262.
- Downes, P. (2020). The benefits of a positive behavioral management strategy, influenced by student's voices, on private-sector students.
- Fang, M., Gerhart, B., & Ledford Jr, G. E. (2013). Negative effects of extrinsic rewards on intrinsic motivation: More smoke than fire. World at Work Quarterly, 16(2), 17-29.
- Froese, F. J., Peltokorpi, V., Varma, A., &Hitotsuyanagi‐Hansel, A. (2019). Merit‐based rewards, job satisfaction, and voluntary turnover: moderating effects of employee demographic characteristics. British Journal of Management, 30(3), 610-623.
- Gavin, M., & McGrath‐Champ, S. (2017). Devolving authority: The impact of giving public schools the power to hire staff. Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources, 55(2), 255-274.
- Glater, J. D. (2017). To the rich go the spoils: Merit, money, and access to higher education. JC & UL, 43, 195.
- Guryan, J., Kim, J. S., & Park, K. H. (2016). Motivation and incentives in education: Evidence from a summer reading experiment. Economics of Education Review, 55, 1-20.
- Harry, S. N. (2019). The implementation of the Caribbean Advanced Proficiency Examination (CAPE) Communication Studies curriculum innovation in secondary schools in Trinidad and Tobago: teachers' perspectives (Doctoral dissertation, University of Leicester)
- Haasler, S., Müller, N., Nonnenmacher, A., & Wicht, A. (2019). The interplay between education, skills, and job quality. Social Inclusion, 7(3), 254-269.
- Harrison, H., Birks, M., Franklin, R., & Mills, J. (2017, January). Case study research: Foundations and methodological orientations. In Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung/Forum: Qualitative Social Research (Vol. 18, No. 1).
- Hart, C. (2018). Doing a literature review: Releasing the research imagination. Sage.
- Hernandez, J. (2019). IN FAIRNESS TO OUR SCHOOLS.
- Jamil, M. M., Ningrum, E., &Yani, A. (2019, June). Level of Learning Motivation Student Based on ARCS Model on Geographic Subject. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 286, No. 1, p. 012010). IOP Publishing.
- Kaimal, G., & Jordan, W. J. (2016). Do Incentive-Based Programs Improve Teacher Quality and Student Achievement? An Analysis of Implementation in 12 Urban Charter Schools. Teachers College Record, 118(7), n7.
- Kim, Y., Joo, H. J., & Lee, S. (2018). School factors related to high school dropout. KEDI Journal of Educational Policy, 15(1).
- Kirsten, Y. (2018). Conducive organisational behaviour of work integrated learning and mentorship training for secondary schools: a systematic review (Doctoral dissertation, North-West University).
- Klein, C., Lester, J., Rangwala, H., &Johri, A. (2019). Technological barriers and incentives to learning analytics adoption in higher education: insights from users. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 31(3), 604-625.
- Korpershoek, H., Canrinus, E. T., Fokkens-Bruinsma, M., & de Boer, H. (2019). The relationships between school belonging and students’ motivational, social-emotional, behavioral, and academic outcomes in secondary education: A meta-analytic review. Research papers in education, 1-40.
- Lambert, S. R. (2020). Do MOOCs contribute to student equity and social inclusion? A systematic review 2014–18. Computers & Education, 145, 103693.
- Lara, F. J., Mogorrón-Guerrero, H., & Ribeiro-Navarrete, S. (2020). Knowledge of managerial competencies: cross-cultural analysis between American and European students. Economic Research-EkonomskaIstraživanja, 33(1), 2059-2074.
- Lefrancois, G. R. (2019). Theories of human learning. Cambridge University Press.
- Liebowitz, D. D., & Porter, L. (2019). The effect of principal behaviors on student, teacher, and school outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the empirical literature. Review of Educational Research, 89(5), 785-827.
- Lumbantobing, W. L. (2019, June). Effect of ARCS Model on Learning Independence of 21st Elementary School. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1233, No. 1, p. 012105). IOP Publishing.
- McCoy, S., Byrne, D., O’Sullivan, J., & Smyth, E. (2019). THE EARLY IMPACT OF THE REVISED LEAVING CERTIFICATE GRADING SCHEME ON STUDENT PERCEPTIONS AND BEHAVIOUR. ESRI RESEARCH SERIES NUMBER 85 JANUARY 2019.
- Mohajan, H. K. (2017). Two criteria for good measurements in research: Validity and reliability. Annals of SpiruHaret University. Economic Series, 17(4), 59-82.
- Mosleh, M. A., &Alshaboul, A. K. (2020). The Degree of Application of Teachers in the First Basic Seminar in Jordan for Teaching Strategies to Teach Reading Comprehension in Arabic in the Light of RAMP Program. Journal of Educational and Psychological Studies [JEPS], 14(1), 108-127.
- Mountford-Zimdars, A., & Moore, J. (2020). Identifying merit and potential beyond grades: opportunities and challenges in using contextual data in undergraduate admissions at nine highly selective English universities. Oxford Review of Education, 1-18.
- Munroe, A. (2017). Measuring Student Growth within a Merit-Pay Evaluation System: Perceived Effects on Music Teacher Motivation Career Commitment. Contributions to Music Education, 42, 89-106.
- Nordstrum, L., & Brombacher, A., (2016). Retrieved 21 September 2020, from http://ierc-publicfiles.s3.amazonaws.com/public/resources/Jordan%20Incentive%20Pilot%20report_21Sep2016_Final_0.pdf
- Ogada, E. O., &Mwalw’a, S. (2020). Contribution of Reward Systems towards Teachers’ Job Satisfaction among Public Secondary Schools in Kikuyu Sub-County, Kiambu County, Kenya. Journal of Education, 3(2), 54-67.
- Pfeffer, F. (2015). Equality and quality in education. A comparative study of 19 countries. Social Science Research, 51, 350-368
- Raharjanto, T. (2019). SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEWS: SISTEM MERIT DALAM MANAJEMEN SUMBER DAYA MANUSIA SEKTOR PUBLIK. JurnalPemerintahan Dan KeamananPublik (JP dan KP), 103-116.
- Rautakivi, T., Siriprasertchok, R., &Korng, V. (2019). Extrinsic work motivation of urban secondary school teachers: a case study of public secondary schools and a model secondary school in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. International Journal of Management in Education, 13(2), 156-169.
- Roser, M., & Ortiz-Ospina, E. (2020). Financing Education. Retrieved 7 September 2020, from
- Rozalia, R., 2019. AN ANALYSIS OF ENGLISH TEACHER-PARENTS’COOPERATION AND STUDENTS’ACHIEVEMENT IN ENGLISH SUBJECT (A Correlation Study on the Second Grade Students at SMPN 17 Mukomuko in Academic Year 2018/2019) (Doctoral dissertation, IAIN Bengkulu).
- Rumbaugh, R. (2019). Teacher Merit Pay in a Rural Western North Carolina County: A Quantitative Analysis of the Effects of Student Characteristics on a Teacher's Likelihood of Receiving a Monetary Bonus in Math Or Reading in Grades Three-eight (Doctoral dissertation, Appalachian State University).
- Sabic-El-Rayess, A. (2016). Merit matters: Student perceptions of faculty quality and reward. International Journal of Educational Development, 47, 1-19.
- SAKILA, F. (2018). THE CORRELATION BETWEEN PARENTAL SUPPORT AND STUDENTS’ENGLISH ACHIEVEMENT AT MTsN 7 TULUNGAGUNG.
- Schirmer, J. (2019). From ethics to ethos: An expanded agenda for counselor training and development. Psychotherapy and Counselling Journal of Australia, 7.
- Shehzadi, K., Afridi, T., &Kaleem, A. (2020). MOTIVATIONAL STRATEGIES USED BY BEGINNING TEACHERS AT SECONDARY LEVEL. Al-Qalam, 25(1), 320-330.
- Shirin, A. (2020). Determining the relationship between academic achievement and the prosocial behavior of secondary school students in Dhaka City.
- Siburian, J., Corebima, A. D., & SAPTASARI, M. (2019). The correlation between critical and creative thinking skills in cognitive learning results. Eurasian Journal of Educational Research, 19(81), 99-114.
- Sonnleitner, P., & Kovacs, C. (2020). Differences Between Students’ and Teachers’ Fairness Perceptions: Exploring the Potential of a Self-Administered Questionnaire to Improve Teachers’ Assessment Practices. Frontiers In Education, 5.
- Suleiman Abdulrahman, A. (2018). The implication of Motivation Theories on Teachers Performance in the Context of Education System in Tanzania. International Journal Of Secondary Education, 6(3), 46.
- Swanson, E., Watson, A., Ritter, G. W., & Nichols, M. (2016). Promises Fulfilled? A Systematic Review of the Impacts of Promise Programs. Education Reform Faculty and Graduate Students Publications.
- Syafei, I., &Ulfah, A. F. (2020). Implementation of Behaviorism Learning Theories in Arabic Learning Planning. Al Mi'yar: JurnalIlmiahPembelajaran Bahasa Arab danKebahasaaraban, 3(2), 197-214.
- Turner, D. S. (2017). Reading motivation: Using extrinsic incentives as a motivational tool. Unpublished Dissertation). Jefferson City: Carson-Newman University.
- Ullah, H., Xiaoduan, C., &Bhuttah, T. M. (2019). Comparative Study of the Factors Affecting Initial Teacher Education in Pakistan and Zimbabwe. European Journal of Social Sciences, 57(4), 383-392.
- Yeager, R. B. (2016). School-wide positive behavior support: Effects on academics and behavior. Northcentral University.
Looking for further insights on School Of Business Law Profesional Policing? Click here.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



