Obesity Prevention in Children (5-14 years) in the London Borough of Hackney
Introduction
Health Need assessment [HNA] can be considered as the systematic approach in which the health issues of a particular population are identified and then effective resource allocation is conducted to ensure that all the healthcare resources are used to meet all these determined health needs thereby prompting positive health and wellbeing of the population [NHS, 2019]. PHE (2019) mentioned that in the UK, people have several health needs that needed to be identified and met for not only reducing the health inequalities in the society but also promote the positive mental and physical health of the people [PHE, 2019]. This assignment will present a Health Need Assessment (HNA) in which it will prioritise a particular health need, the obesity prevention of 5-14 years of children in the London borough of Hackney. This assignment will set three important HNA approaches out of which it will use one approach to meet the identified health needs of the target population. Then this assignment will discuss the stages that are involved in that HNA thereby discussing how systematically the process and tool will be implemented to meet the selected health needs. This assignment will discuss the local and local healthcare policies that are developed and implemented in relation to meet the selected heath needs of target population. Finally, this assignment will a make a summary of the entire discussion in highly which the main aspects of the discussion will be concluded. If you need assistance with healthcare dissertation help, we are there to support you at every level.

Hackney is highly populated borough of inner London with more than 236,000 residents and 44600 children ad relatively young population. Majority of the population of Hackney is 5-14 years that reside in the North east region of this borough (hackneyjsna.org.uk, 2019). The major community in hackney is Charedi community (orthodox Jewish). Evidence suggests that majority of the population in Hackney are young people and children in Hackney and this proportion is predicted to be raised by more than 7% in 2025. Hackney has different ethnic group out of which 16% children and young people of 10-13 years belong to the black ethnic minority community, 27% belong to whitish community. Evidence suggests that the ethnic diversity in Hackney is strongly associated to the heath inequalities and the lack of health care to the minority ethnic community (hackneyjsna.org.uk, 2019). The evidence suggests that the life expectancy is relatively lower in Hackney because of poor healthcare facilities to the resident, lack of systematic and health lifestyle, lack of unemployment and lack of financial stability that interfere with overall quality of daily living of residents in Hackney (Chi et al. 2017).
Here the assignment has selected obesity prevention as the major health need in Borough of Hackney (PHE, 2019). The selection of this health need is highly relevant to the current health care context of Hackney, in which 1 out on 4 children in London live with obesity and overweight. The PHE (2019) report shows that, prevalence of obesity in children and young people belong to the age group 5-14 year as compared to the other age group (PHE, 2019). From the recent World Health Organisation (2018) report it has been shown that more than 23% of Year 6 children (10-11years) in London borough of Hackney suffers from obesity and overweight as compared to 20% of that in England [WHO, 2018]. Over the last five years prevalence of childhood obesity had increases by more than 1.9% in London. PHE (2018) mention that childhood obesity is associated with many chronic and acute illness such as cardio vascular disease, pulmonary disease, lung infection, coronary arterial disease and cancer. In this context, the selection of this health need is highly suitable and realistic to the current health care context in Hackney. Through developing this heath need assessment (HNA), this study will raise public awareness on childhood obesity and will recommend the care strategies to the health and social care staffs in Hackney to prevalent damage obesity in children and young people.
Selected health need: Obesity prevention
Target population: children of 5-14 years
Location: London borough of Hackney
Health need assessment (HNA) approaches:
Three HNA approaches that are selected for preventing childhood obesity in 5-13 years population in the Hackney are as follows:
Eliminate the risk factors and the improving the health determinants of childhood obesity
Effective implementation of person-centred care (PCC) approach for carrying out effective prevention and management of the childhood obesity
Development of healthy lifestyle behaviour and healthy habits in the target population for preventing obesity in them
All these three HNA approaches have both the health benefits and limitations that needed to be considered to promote holistic wellbeing in the target group in Hackney.
Limitation and benefits of the three approaches
The first HNA approach is highly realistic which will assist the health and social care professionals to identify the risk factors, causative factors and the determinants of childhood obesity. Epidemiological study shows that, many determinants or risk factors are associated with increasing the prevalence of obesity in children and young people in Hackney (Bel-Serrat et al. 2018). The major determinants of childhood obesity are irregular and lack of systematic lifestyle, unhealthy habits (alcohol, smoking and drug abuse), unhealthy eating lack of regular exercise, lack of activeness and consumption of high amount of junk foods (Bell et al. 2018). This HNA approach is highly effective in the current health care context which will provide the information to health and social care professionals regarding the risk factors that needed to be considered while developing effective care plan for three children suffering from obesity. One of the limitations of this approach is that, this HNA approach prioritises mainly that risk factors and determinants of childhood obesity but fails to consider other important factors such as dietary intake, lifestyle changes and socio-cultural changes that are also strongly associated with childhood obesity.
The second HNA approach is highly realistic and widely used approach in the modern healthcare context, which enables the healthcare professionals to use PCC for promoting holistic wellbeing of children suffering from obesity (Breheny et al. 2018). This HNA is highly useful in assisting nurses and healthcare staffs to determine the holistic needs of children who suffer from obesity rather than focusing only on their physical health needs. The limitation of this HNA is that while implementing this approach the healthcare professional and nurses inn Hackney can face some challenges such as lack on cooperation and support from children and their parents in terms if implementing innovative care plan, lack of support and poor healthcare infrastructure.
The third HNA is one of the most important approach that will enable nursing professionals to provide valuable healthcare advise to the children (5-14 years) regarding bringing about the positive transformation in the lifestyle behaviour and dietary intake in children. The drawback or limitation of this HNA can be the lack of skilled and well-trained nurses and health care staffs in providing health advise to children and parent, lack of highly experienced dieticians and poor cooperation from parents of children.
Selection of one HNA approach:
Among all of these three HNA approaches, this study has selected the third HNA approach:
HNA approach 3:
“Developing healthily lifestyle behaviour and healthy habits in the target population for preventing obesity in them”.
Reason behind choosing the HNA approach:
The third HNA approach is chosen by this study to develop healthy diet and improve the entire lifestyle of the target population in Hackney. As compared to the other two approaches this approach is best suited in case of children in Hackney who suffer from Obesity because it will not only guide and train the target children regarding heathy eating habits, sleeping pattern (Chi et al. 2017). Exercise process and dietary intake, but also develop the self-management skill in them. Under this approach, different training will be conducted for target children such as weight management training, dietary advise and stress management training which will empower the children to develop heathy and positive thoughts and good physical and psychological wellbeing, the self-management skill will enable obese children in Hackney to learn how make good control on their glucose level by eating the healthy foods and performing regular exercise (Enö et al. 2018). In this context, the selection of the HNA approach is highly appropriate and realistic to the current context of childhood obesity in Hackney, which will empowers the target children by improving their knowledge and understanding on effective prevention as well as management of obesity.
Stages of health assessment
This HNA is going to be accomplished in following stages:
Setting clear aim and objectives for this HNA:
Objectives:
The objectives of the HNA are as follows
To make positives transformation oof lifestyle behaviour in target children
To provide the effective healthcare information to the target children in the Hackney regarding the dietary intake and the nutritional needs
To educate target children and parents regarding maintaining a systematic and healthy lifestyle to reduce the prevalence of obesity.
To provide weight management training t the target children for maintain the heaty weight and BMI.
To develop strong self-management skill in target children thereby empowering them to have good control on their glucose level.
Aim:
This HNA aims to educate the target children and the parents regarding maintaining heathy habits, healthy lifestyle and positive behavioural transformation in them to reduce their vulnerability to obesity. Moreover, this HNA also aims to empower children by developing the self-management skill in them that will enhance their self-confidence in managing their health and wellbeing.

2. Resources management and capacity building:
This is stage is about to check whether all the needed resources are available to the organisers of this HNA in terms of ensuring that the HNA will be accomplished successfully and all the pre-set objectives under the HNA approach would be met. Under this HNA approach, effective analysis of all the needed resources had been done which organisers of this HNA to utilise all these resources systematically thereby meeting all the set goals.
Stakeholders’ analysis:
Following are the stakeholders of this HNA:
General practitioners in Hackney
Hospital doctors
Nurses and healthcare staffs of the local NHS hospitals
Commissioning managers
Health administrative board
Community health council
Trust managers
Health and social care officials of voluntary and statutory organisation
Parents of the target children
Stakeholders’ analysis Table:



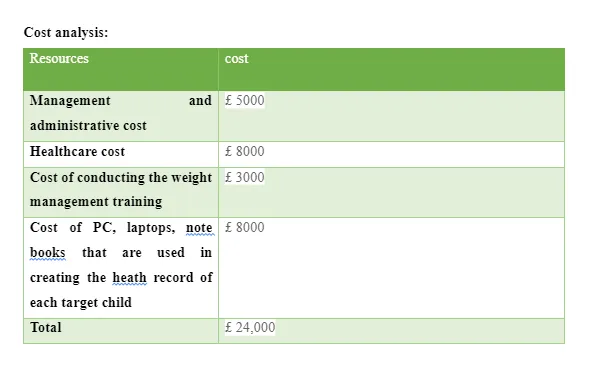
3. Developing effective action plan
Under this action plan of HNA, following strategies or actions are going to be implement for meeting the HNS objectives:
Promote healthy and positive lifestyle behaviour in target children
Under this strategy, the nurses and health care professionals will provide valuable advice to the target children in Hackney regarding how to make positive transformation of their lifestyle behaviours [PHE, 2019]. Obesity in children is strongly linked to the poor lifestyle behaviour which impacts on the metabolic function of body (Levy and Redstone, 2017). Under this HNA approach, the health and social care staffs provide advice to target chidden regarding healthy sleeping patter, sufficient sleep, healthy food habit, per day calorie intake, sufficient water intake and regular exercise. Highly experienced dieticians of this HNA will provide advice to the parents of the target children about what types of food need to be served to their children and which foods need to be strongly avoided.
Developing healthy habits in target children:
The health professionals who are involved in this HNA will provide advise to the children in Hackey in terms of developing heathy habits such as early rising, early sleep, no skipping of meals, say no to junk foods, regular exercise, maintain hygiene and consume heathy as well as homemade foods (Lidgate et al. 2018). Nurses who are involved in this HNA also provide the health education to parent about how to encourage and supporting children regarding developing healthy habits.
Conduct weight management training for target children
In this weight management training program, target children in Hackney will get the available assistance from the experienced dieticians, trainers and physiotherapist who will train them regarding reduction of their excessive weight and maintain a healthy BMI (Matvienko‐Sikar et al. 2019). Weight management is crucial in in case of children for reducing the prevalence of obesity in them. Here the physiotherapists and trainers will train children regarding performing different types of free hand exercise that are associated with not only reduce the body weight of children but also improve the digestives system and the metabolism thereby maintain healthy weight (Nittari et al. 2019). Dieticians why are involved in this weight management program will provide advice to the target children regarding what types foods and drinks need to be eaten before and after the exercise., how much gap can be taken between two meals and what types of meals needed to be consumed to maintain healthy weight.
Current strategies:
All service providers of this HNA need to address the following national and local strategies in reducing the prevalence of obesity in children.
Childhood obesity: A plan for action:
This is the national obesity prevention policy set by the UK government (Department of Health and Social Care) (Pérez‐Escamilla et al. 2017).
This policy is set to prevent obesity in children belonging to the age group 5-14 years. NICE (2019) sets the guidelines as well as strategies that need to be implemented and followed by all the healthcare providers in the UK.
The organisers and the health and social care professionals of this HNA will address and follow all the following guidelines and strategies:
National Service framework (NSF): prevent and mange overweight and obesity:
Under this policy, all the healthcare providers of this HNA will work closely with target children in the Hackney to prevent and manage the obesity in them. Under NSF, the health and social care staffs, the healthcare professionals and voluntary and the statutory healthcare organisations of this HNA will work collaboratively with one another to determine the health needs of target children in Hackney (Robinson, 2017). Healthcare providers of this HNA will also complying with the statuary guidelines of NICE (2019), to bring about effective changes in the lifestyle and dietary habits of the children of Hackney. NICE (2019) recommend that, while working with children for improving their lifestyle and dietary intake for weight management and reduction of the risk of obesity in children, healthcare providers must ensure that throughout the health promotion, the autonomy, right to confidentiality and preferences of children will be respected.
To determine the barriers that are associated with implementing effective lifestyle changes as well as dietary changes in the target children. These barriers are the personal taste of children, cultural trend, social perspectives, lack of cooperation, lack of assertiveness and lack of knowledges on developing healthy food habits and healthy eating.
Under this NSF policy, all the doctors and nurses of this HNA will prioritise the holistic needs of the children in Hackney rather than focusing only on their physical wellbeing. Here regular physical abasement will be carried out to check the BMI, weight, ketones body level and cholesterol, and BP of each child (Rudolf et al. 2019).
Under NICE (2018), all the health and social care providers will ensure that each child will be treated fairly without any chances of force or discrimination on them. The autonomy of each child will be respected throughout the HNA.
Person centred care approach (PCC)
All healthcare providers of this HNA will use PCC approach in terms of determining and meeting the personalised health needs of each child (Sonntag, 2017). Under NICE (2018), healthcare providers must determine the physical, psychological and emotional needs of children which are crucial for promoting healthy habits and lifestyle changes in them. In this HNA approach, all the healthcare providers will maintain clear and effective communication with all the children and their parents to get the valuable information regarding the dietary intake and regular lifestyle of children. Based on the monthly health assessment report of this HNA the health professional will develop an effective care regimen for each child that will contain the medication regimen, the diet plan, exercise routines and the guidance for the lifestyle habits.
Recommendations:
The officials of the health care authority should work in collaboration with the health and social care workers of local statutory and voluntary healthcare organisation in conducting effective need assessment for target children in Hackney. Under this Need assessment the holistic needs of each child should be determined thereby effective strategies would be developed to meet all these neds. The health and social care workers will work with children to support their health needs thereby meeting all the health need according to reduces the risk of obesity in them. The officials of healthcare organisations must provide the effective healthcare information to children on the risk factors and determinants of obesity, the prevention and management of obesity, heath check-up facility and weight management advise.
Heath Service Executives must administer whether all children in Hackney follow healthy lifestyle and diet which are important for receding the prevalence of obesity in them
Local healthcare authority should arrange an online obesity prevention campaign against childhood obesity under which all the target children and their parents will be invited and provided with the clear information regarding what is obesity, how it develops in children, its adverse impact of physical, mental and social health of children and the effectives managements of obesity. Health care providers must educate parents of the target children regarding what types of food nd drinks they can serve children on regular wise to manage their weight within the recommended limit and improve the overall dictatory intake and food habits of these children.
Health care officials should conduct a weight management program in Hackney, in which all the target children would be encouraged to attend the program. This program should improve the lifestyle changes and dietary intake of the target children by providing the information on regular exercise. Here the weight management trainers must provide the training to each child regarding which exercise he or she can do regularly to manage weight and reduce the risk of obesity.
Health and social care staffs must provide the health education to children and young people regarding healthy eating and healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion:
From the overall discussion it can be summarised that obesity is most common in the London borough of Hackney. The unhealthy lifestyle and poor dietary intake are associated with developing obesity in children in Hackney. Health needs assessment (HNA) is crucial for determining all the heath needs of the target population and then arrange all the resources and meet the gaols of HNA. Though developing effective and realistic approach this HNA would be able to reduces the prevalence of obesity in children.
Reference list:
- Anderson, S.E., Sacker, A., Whitaker, R.C. and Kelly, Y., 2017. Self-regulation and household routines at age three and obesity at age eleven: longitudinal analysis of the UK Millennium Cohort Study. International Journal of Obesity, 41(10), pp.1459-1466.
- Bell, L.K., Perry, R.A. and Prichard, I., 2018. Exploring grandparents' roles in young children's lifestyle behaviors and the prevention of childhood obesity: An Australian perspective. Journal of nutrition education and behavior, 50(5), pp.516-521.
- Bel-Serrat, S., Heinen, M.M., Mehegan, J., O’Brien, S., Eldin, N., Murrin, C.M. and Kelleher, C.C., 2018. School sociodemographic characteristics and obesity in schoolchildren: does the obesity definition matter?. BMC public health, 18(1), pp.1-12.
- Breheny, K., Adab, P., Passmore, S., Martin, J., Lancashire, E., Hemming, K. and Frew, E., 2018. A cluster randomised controlled trial evaluating the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the daily mile on childhood obesity and wellbeing; the Birmingham daily mile protocol. BMC Public Health, 18(1), pp.1-7.
- Chi, D.L., Luu, M. and Chu, F., 2017. A scoping review of epidemiologic risk factors for pediatric obesity: implications for future childhood obesity and dental caries prevention research. Journal of Public Health Dentistry, 77, pp.S8-S31.
- Enö Persson, J., Bohman, B., Tynelius, P., Rasmussen, F. and Ghaderi, A., 2018. Prevention of childhood obesity in child health services: follow-up of the PRIMROSE trial. Childhood Obesity, 14(2), pp.99-105.
- Felső, R., Lohner, S., Hollódy, K., Erhardt, É. and Molnár, D., 2017. Relationship between sleep duration and childhood obesity: Systematic review including the potential underlying mechanisms. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases, 27(9), pp.751-761.
- Gregg, R., Patel, A., Patel, S. and O’Connor, L., 2017. Public reaction to the UK government strategy on childhood obesity in England: A qualitative and quantitative summary of online reaction to media reports. Health Policy, 121(4), pp.450-457.
- Hennessy, M., Byrne, M., Laws, R., Mc Sharry, J., O’Malley, G. and Heary, C., 2019. Childhood obesity prevention: priority areas for future research and barriers and facilitators to knowledge translation, coproduced using the nominal group technique. Translational behavioral medicine, 9(4), pp.759-767.
- Lanigan, J., Tee, L. and Brandreth, R., 2019. Childhood obesity. Medicine, 47(3), pp.190-194.
- Levy, L. and Tedstone, A., 2017, March. UK dietary policy for the prevention of cardiovascular disease. In Healthcare (Vol. 5, No. 1, p. 9). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute.
- Lidgate, E.D., Li, B. and Lindenmeyer, A., 2018. A qualitative insight into informal childcare and childhood obesity in children aged 0–5 years in the UK. BMC public health, 18(1), pp.1-13.
- Matvienko‐Sikar, K., Griffin, C., McGrath, N., Toomey, E., Byrne, M., Kelly, C., Heary, C., Devane, D. and Kearney, P.M., 2019. Developing a core outcome set for childhood obesity prevention: A systematic review. Maternal & child nutrition, 15(1), p.e12680.
- Nittari, G., Scuri, S., Petrelli, F., Pirillo, I., Di Luca, N.M. and Grappasonni, I., 2019. Fighting obesity in children from European World Health Organization member states. Epidemiological data, medical-social aspects, and prevention programs. Clin Ter, 170(3), pp.e223-e230.
- Pérez‐Escamilla, R., Lutter, C.K., Rabadan‐Diehl, C., Rubinstein, A., Calvillo, A., Corvalán, C., Batis, C., Jacoby, E., Vorkoper, S., Kline, L. and Ewart‐Pierce, E., 2017. Prevention of childhood obesity and food policies in Latin America: from research to practice. Obesity Reviews, 18, pp.28-38.
- Robinson, S.M., 2017. Preventing childhood obesity: Early‐life messages from epidemiology. Nutrition Bulletin, 42(3), pp.219-225.
- Rudolf, M., Perera, R., Swanston, D., Burberry, J., Roberts, K. and Jebb, S., 2019. Observational analysis of disparities in obesity in children in the UK: Has Leeds bucked the trend?. Pediatric obesity, 14(9), p.e12529.
- Sonntag, D., 2017. Why early prevention of childhood obesity is more than a medical concern: a health economic approach. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism, 70(3), pp.175-178.
- Tyson, N. and Frank, M., 2018. Childhood and adolescent obesity definitions as related to BMI, evaluation and management options. Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 48, pp.158-164.
- Ziauddeen, N., Roderick, P.J., Macklon, N.S. and Alwan, N.A., 2018. Predicting childhood overweight and obesity using maternal and early life risk factors: a systematic review. Obesity Reviews, 19(3), pp.302-312.
Continue your exploration of Nursing Professionals in Mental Health with our related content.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



