Impact of Social Distancing and Lockdown Measures on Self-reported
Abstract
The study looks into the correlation between social distancing and lockdown measures play in capping upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs), specifically the rate of common cold (CC) referred commonly to as cold flue during the pandemic period. The research took place through the use of a questionnaire where participants provided insights into their social lives as individuals susceptible to a wide range of respiratory infections and the impact that social distancing and lockdown measures have had in capping the spread. The research allows the public to be aware of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPI’s) such as social distancing and lockdown measures that have helped to reduce the incidence rate of the common cold in England and consider the long-term implications that these compliance methods may have for future emergency pandemics. It indicates how the rates of infections reduce due to precautionary measures put in place to ensure success of capping the spread of cold flu among individuals. Mask wearing, hand washing and two metre distance have contributed heavily to the decrease of susceptibility in upper respiratory infections, highlighting the importance of public health measures not only against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) but also the common cold in the United Kingdom (UK). Therefore, the social distancing and lockdown measures play an important role in capping the spread of cold flues amongst the population. Most acute self-reported studies are limited as they focus on using scientific instruments to measure infection, rather than simply relying on self-reported measures alone. Through the focus on patient report outcome the research will establish whether the factors indicted reduce the risks factor of cold Flu. If you need assistance with your healthcare dissertation, then join us for expert guidance with healthcare dissertation help at every stage of the process.
Introduction
Social distancing and lockdown measures were put in place since the outbreak of Covid19. The measures have helped the public health sector throughout the world in capping the spread of the viruses. However, there are also some diseases that have reduced due to the measures. Cold Flues are some of those that have significantly reduced especially the United Kingdom. Through this, it can be deducted that social distancing can play an important role of ensuring that the country continually reduce cases of common colds among the population. The Covid19 management and capping measures can be used in indicating how various cold flues can be contained to avoid spending a lot of resources. The pandemic resulted in causing a worldwide disruption with many countries globally enforcing an emergency lockdown. In 1918-19, influenza A virus (H1N1) was the first time in history an emergency pandemic was declared. United States (US) was the first to issue a series of NPI’s put into place, with the help of the precedent of SARS and MERS that has been there for while other countries followed the same procedure for SARS-CoV-2. In the United Kingdom (UK) the Public Health England (PHE) set out various compliance social distancing and lockdown methods in order to help control the spread of the virus, resulting in significant disruption to the economy, businesses, education, healthcare, employment, housing and relationships (NHS, 2021).

Common colds (flues) have an impact on the economy. A lot of resources are spent by both the government and individual in treating and capping the spread. Due to the severe nature that some of the common colds ca have that need to be taken seriously and ensure they are controlled. For example corona virus and the adverse effects it has on the economy and public health, it was declared a pandemic. Pandemic can be defined in terms of endemic, epidemic, pandemic do not indicate severity of a particular disease, and instead it informs the extent of its spread, WHO declared COVID-19 a pandemic (Ahn et al., 2020). A pandemic is defined as a worldwide occurrence of a disease in a community, region or other population at risk which is above levels of normality. The outbreak had caused severe impact all over the world which prompted the World Health Organization to declare it a pandemic. The same way the approach of fighting common colds should be taken seriously to ensure they are controlled.
Cold flues have reduced since the control measures for the Covid19 started being put in place. There are a number of coronaviruses that have been reported a while. The etiological agent of corona virus disease, is known as a SARs caused by SARS-CoV which first emerged in 2002-2003 in China, Guangdong province (Ahn et al., 2020). A second outbreak in Saudi Arabia, known as the Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) coronavirus causes by MERS-CoV appeared in 2012 (Ahn et al., 2020) followed by a third epidemic coronavirus (SARS-Cov-2) introducing a pathogenic virus into the human population, resulting in a continuous rise of the people who have been infected by the virus and the number of deaths. SARS-CoV-2 belongs to a group of single stranded RNA viruses. There are four main sub-groupings of the coronaviruses these include, alpha, beta, gamma and delta. Though only two types of viruses are capable of infecting humans there are a number of viruses that exist in this family (Ahn et al., 2020). Geneticists have been able to identify that SARS-CoV-2 belongs to a family of bat coronavirus (Ahn et al., 2020) which is also a bat corona virus that has a closest identity by phylogenetic analysis possibly being accounted as the third zoonotic disease.
Cold flues like SARS-CoV-2 mainly spreads by coughing, droplet inhalation and sneezing. However, due to the fact that there are few clinically approved vaccines and drugs that can deal with Covid19 effectively, there is need for control measures. A characteristics that is almost similar to that of the common colds. Countries came up with spreading control measures of different kind where some had long-term and short-term measures to ensure the rete of virus spread is capped and delay the epidemic. In particular the United Kingdom (UK) government released strategies of social distancing, wearing of masks, hand washing, and lockdown measures in order to slow down the pathogen exposure before a vaccine becomes widely available. Non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPI’s) are measures put into place for communities to help slow down seasonal and pandemic influenza viruses (Qualls et al., 2017) by reducing contact rates within general population (Ferguson et al., 2020). The government have come up with number of guidelines in order to slow the incidence rate (Ahn et al., 2020). NPI’s can be phased in depending on the severity of local transmission patterns.
One of the rules that has been adopted is the 2 metre distance rule. It reduces the transmission route of the virus (distance, exposure, relationship). Through this the rate of transmission of the virus will be reduced. Studies indicate that droplets travel 1.5 – 2m shows us virus particles are capable of travelling distance (NHS, 2021). Therefore, when the distance is maintained the spread of the virus reduces. Some of the distance factors considers include whether the person generated them – are they infectious? Do the particles contain active viruses? Is the active virus sufficient to cause infection? Lastly, if the particles land on surfaces and humans. The same way the common flues can be spread from one person to the other, but the distance reduced the probability of spread reducing the cases.
Common colds have some effects on the immunity but they cannot compromise it to the levels that corona virus has turned out to become a threat to humanity. Persons who have compromised immunity are susceptible to severe impacts both physically and emotionally to common colds. These group of people in the society required protection and care to ensure that they could not adversely be affected by the virus (Ahn et al., 2020). Due to this there were different measures that were recommended to protect this vulnerable groups and the population at large. The social distance measures can play an important role of reducing the impact that humanity could experience due to common colds.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) alongside other global public health bodies/government issued advice on regular handwashing and hygiene guidelines, social distancing measures. In areas that were adversely affected like some parts of UK, the Prime Minister (PM) placed lockdown protocols to prevent the spread of the virus. The guidelines have not only helped the spread of corona virus but also the cold flues. By restricting social interaction between individuals outside households, it results in adverse effects on health, emotion and socio-economically for many individuals. These factors affect our ability to make healthy choices and shape our lives (NHS, 2021). Employment provides income that helps with housing, education, medical care and food. In contrast, adults of lower
socioeconomic status or unemployment limit these choices and cause mental health issues that lead to stress an innate immune response thus decreasing host resistance to infection. Social isolation/quarantine has been one of the most effective and oldest tools used back in 1918 in Italy when ships at Venice port from plague infected ports, anchor wait 40 days (Ahn et al., 2020) and no effective treatment has been established. There are treatments that are more effective against the dominant variants, it has been documented of high effectiveness against numerous severe diseases, infection and transmission. This is supported by Hall et al, 2021 who studied the effectiveness of BNT162b2 vaccine against infection on health care workers (asymptomatic vs symptomatic) results showed at week 3 72% effective at 1st dose and 86% effective at the 2nd dose, through this they are able to know which way treatment can be more effective. Although they are not perfect in eliminating the virus, they help to lower the incidence rate within a community, it is important that we continue to abide by public health interventions.
Common Cold
The common cold (CC) are an acute viral infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract mainly affecting the nasal dorsum and pharynx (Ferguson et al., 2020). The CC circulates annually, although more cases are frequent throughout Autumn and Winter, adults typically having from 2 to 5 infectious and children from 6 to 12 episodes annually (Rondanelli et al., 2018), resulting in 5.9 hours of work/school a day lost, causing absenteeism and financial burden. The CC is transmitted by aerosol droplets of rhinoviruses; fluid from someone who is sick, spreading into the air and hoarding onto surfaces for a prolonged period of time, thus the same principle applies to Sars-Cov-2. Places of education institutions like schools, colleges and universities contain a number of pupils who are more susceptible to viruses, especially infants who have lower immunity systems making them a susceptible target as well as the perfect opportunity for viruses to further spread (Rondanelli et al., 2018). To our current knowledge from previous research studies, frequent hand washing and regular use of hand sanitizer helps to destroy he viruses.
Despite cases of the upper respiratory illnesses peaking during the months of Autumn and Winter, due to social distancing and lockdown measures incidence rates of the common cold have drastically declined, this has relived substantial pressure on the national health service (NHS) as resources have primarily been dedicated to corona virus patients. Ina situation where there is no pandemic a non-pandemic year resources would be dedicated to upper respiratory illnesses meaning a strain on supplies and overburden on the NHS. Although this does not possess a long-term solution for reoccurring seasonal influenza, the current flu jabs remain the best option in order to suppress local and global transmission (Qualls et al., 2017). Still incorporating emphasis on regular increased personal hygiene in order to limit the spread of respiratory particles and implementing movement restrictions when needed.
There is fear amongst many people that if easing of lockdown and social distancing measures will lead towards the increased incidents of upper respiratory infections and also Sars-Cov-2 in the community. Even if 10% of social distancing compliance was continued throughout the year, at least that would result to 10% less transmission of viruses. Even though, the global impact of Covid-19 has been profound, community mitigating measures show a role in preventing the common cold, it possesses both advantages and disadvantages for many individuals, but there may be the benefit of reduction in respiratory illnesses (Ferguson et al., 2020).
The need for public health education is crucial as it helps the community understand how to deal with different health issues. Public health can be defined as ‘the art and science of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts of society’ (Qualls et al., 2017) not only did Sars-Cov-2 cause severe effects and disruption, it evidently showed us individuals vary with compliance to social distancing and lockdown measures. It is important to educate the public and implement future public health policies to help reduce the risk of mass community spread of common colds as it has far much more economic and social consequences (Ahn et al., 2020). For example, months with the highest incidence of common cold rates in the UK, compulsory regulations of face coverings when in open public spaces may be implemented to help limit the spread of viral transmission.
Intermittent social distancing measures could be implemented and reintroduced when cases begin to rebound, not only will this help to reduce transmission rates but will also help those within the general population who could not comply with the rules. The use of face masks will reduce risk of infection in close proximity, some protection may be imbued from mask wearing in community settings like in Public transport, SD better evidence than mask wearing, mask wearing in justifiable settings where SD not possible, reduce likelihood of developing symptoms. Some research on mask wearing were only undertaken only when masks worn during duration of study, mask type not specified.
The general population vary within their normal patterns of social contact which determines the level of susceptibility to upper respiratory tract infections will differ amongst many individuals. Due to their nature of work, essential workers and other individuals in the community found it difficult to navigate through the community in a safer way. NPI’s will help in ensuring people observe the laid down procedures that assist in the navigation and keeping the community safe. Research from Ahn et al., 2020 has shown effectiveness of only one intervention is not enough, multiple NPI’s combined together has ‘proven to have a substantial impact on suppressing COVID-19’ (Ahn et al., 2020). This method can effectively help to mitigate Covid19 during the seasonal months of Autumn & Winter but not suppress it. However, the actions were beneficial as they helped with the control of common cold in the process.
The evolution of the respiratory disease causing of viruses has been constant making difficult to cap its spread. Interferons are a group of signalling proteins produced via host cells in response to a virion. Immunologically this is seen as a first line defence mechanism. Research has shown us Sars-Cov blocks this defence mechanism because of co-evolution. There has been constant change of the kind of viruses being discovered that keep on changing the approach of combating the spread. Thus, showing us for future severe cases of respiratory diseases like COVID-19 taking turns to come out of lockdown(s) will help maintain ‘R’ value (Jarvis, 2020).
It is also important to mention those who did not want to comply believed social distancing and lockdown measures would lead to economic impacts and lead to increase of domestic violence. Others indicate that due to lack of exercises, they are likely to have reduced immunity system. Although immunologists confirm this to be false. The term ‘Hygiene Hypothesis’ is used to describe individuals have been and continue to be exposed to a variety of unharmful -microbes, they have acquired immunity since childhood and will continue to do so. Unlike Sars-Cov-2 which is a relatively new virus many of us have not yet developed immunity showing the need for compliance procedures to be put into place.
Methodology
For the study, the participants were recruited through response to an advertisement on Instagram, which then provided potential participants with a web link straight to the questionnaire. There was no any form bias when selecting the participants, it was a voluntary exercise that allowed all those who were willing to have their input captured. Instagram was used to advertise the questionnaire, as it is the sixth most commonly used social media platform. Participants were asked to fill the questionnaires using their Instagram accounts and send the feedback. The sampling method that was used in the recruitment of the participants was a mix of convenience sampling (asking my Instagram contacts) and snowball sampling (asking them to pass on the request to their friends). All the participants were allowed to reject or agree to participate in the study.
Before the participants were allowed to take on the survey, a brief description of the inclusion criteria required in order to participate was presented first. Those who agreed and fit within these criteria guidelines to take part in the research study were then able to complete online informed consent and the online questionnaire. Participants who did not agree to informed consent and did not fit these criteria guidelines were not able to proceed to the questionnaire. The approach was undertaken to ensure the kind results obtained will assist in forming a general opinion that is better. On the other had the inclusion criteria was that participants were required to be aged 18 and over, without any existing medical condition(s), residents within the United Kingdom (UK) and a healthy adult who occasionally catches the common cold (excluding Sars-Cov-2). All these was to ensure the right people who could provide viable information were involved in the study for the study to be viable and reliable.
The data was collected between February 5th 2020 and March 5th 2021. The study included 42 healthy individuals, N=women and N=men aged between 18 to 65 years old whom were all UK residents. The average age for those who participated is estimated at 35 years. Participants were voluntary, and were able to terminate the questionnaire at any time desired. The questionnaire was anonymous, information confidentiality was reassured. Investigator, supervisor and head of department contact details were provided if any concerns arose about the individual’s participation within the research study. The study used ethical approaches that were generally regulated by my supervisor. The fact that there was no person who was forced to take part of the survey was an ethical requirement. Further, the participants being informed on the various aspects of the survey before starting the questionnaire took place as a form ethical observation.
Measures
Common cold is one of the infectious diseases that can be transmitted through the contacting of susceptible and infectious individuals in either the household, workplace, school or randomly in the community. When individuals are close to one another, they pass the infections to one another due to lack of social distance. It is due to these that the social distance and lockdown measures have played an important role of ensuring that the rate of common colds among the UK residents has reduced. The online questionnaire was designed to assess susceptibility of upper respiratory tract infections like the common cold by investigating contacts of social interactions and individual compliance with social distancing and lockdown measures having an impact on the common cold. The fact that social distancing and lockdown measures were put in place during the Covid19 will act as a basis through which the impact could be measured among residents of UK.
For this a web-based questionnaire was adopted. The questionnaire was developed using Smart Survey software. Participants answered 15 questions relating to social interactions, mask wearing, social activities, hand washing, two metre rule and essential activities (grocery shopping, healthcare, school and work). The first set of questions were a series of descriptive statistics including age, sex, social isolation they experienced, changes at work (face to face contact).These were recorded in order to understand the individual’s background a little better. Furthermore, participants provided information on their everyday lifestyle and social activities, and how they have now changed due to COVID-19 restrictions have been put into place.
Finally, the last set of questions were statements designed in order to understand whether participants understood and complied with various COVID-19 measures issued by the government, to do this participant had to pick an answer from the following options available (‘’Yes - strictly’’, ‘’Yes – mostly’’ and ‘’No – not really’’) this was then used to measure compliance. Compliance was measured against two main COVID-19 mitigation measures ‘’social distancing and ‘’lockdown’’ measures. The compliance is linked to the cases of common colds that were recorded during this period to understand the impact they have on the spread of infectious diseases.
Statistical Analysis
All analysis was conducted using the SPSS software to be determined. The analysis used the raw data that was obtained from the survey and put together for use. Dependent variable was used to calculate the common cold rates that caught people during the period in question. The mean or median was calculated to understand the level of transmission. The independent variable was compliance with social distancing and lockdown measures. From a different perception independent variable are the colds per non-pandemic vs pandemic year (pre-post comparison) how will this relate to compliance? An acute is represented by self-reported study to measure short term frequency of infectious illnesses. The change in normal behaviour is what that was investigated in the research. Further, the research looks into the social networks that people can meet like schools/education institutions, supermarkets, and gyms, where they can spread the infectious diseases. If the number of common colds (independent) caught during lockdown correlates to the stringency of lockdown measures adopted (dependent). The survey takes into account occupational epidemiology which is associated with job related exposures plus illnesses that helps us to understand and ensure adequate in work physical protection is in place. All the above undertaking will allow the correct results that form proper findings and conclusion.
Findings and Analysis
Crosstabs

Case Processing Summary
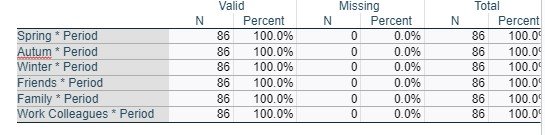


Autum * Period

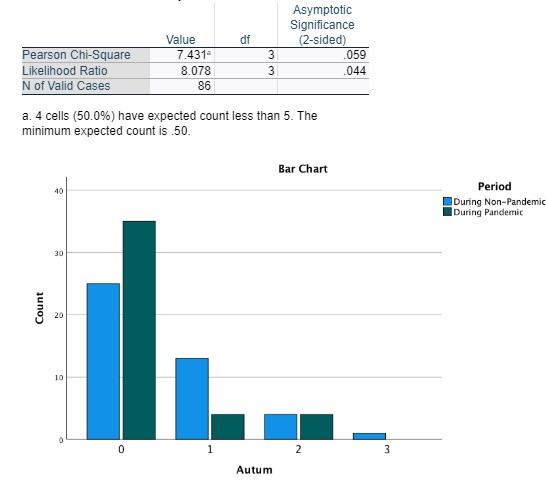
Winter * Period
Crosstab

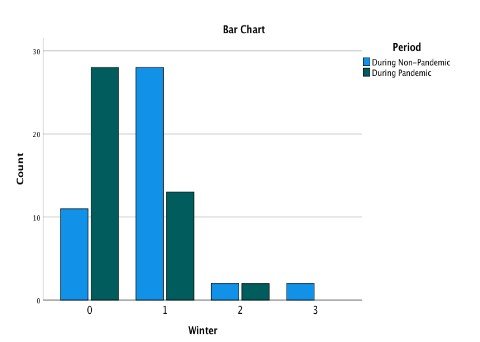
Friends * Period
Crosstab
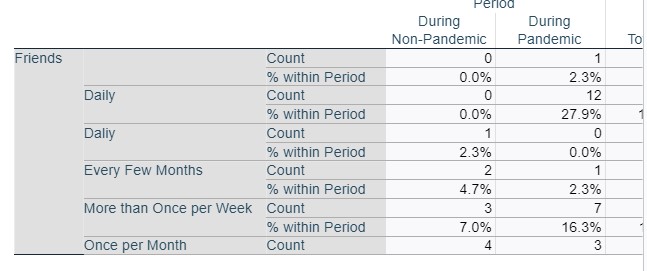
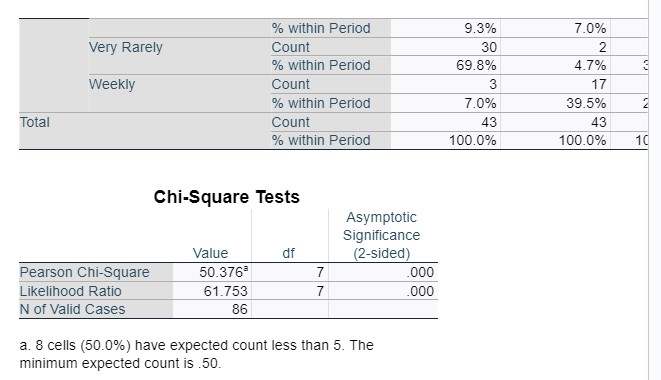

Family * Period
Crosstab
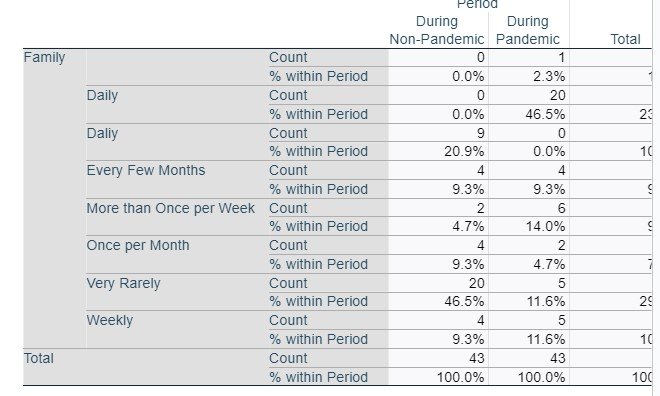
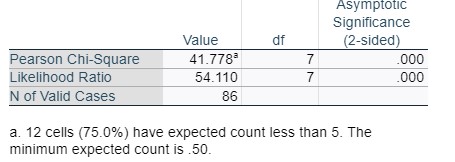
Chi-Square Tests

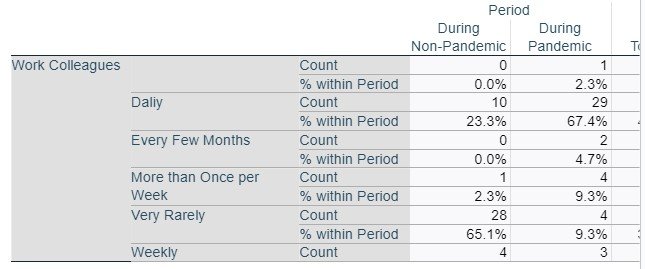
Work Colleagues * Period
Crosstab

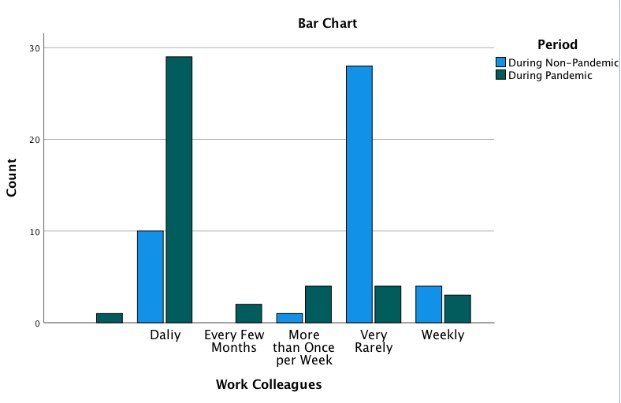
Results Analysis
There was a negative correlation between social distancing measures and the number of cases of common colds that were reported. The study included a total of 100 participants, among them 50 were men and 50 were women. Mean age of the participant subjects was 40.38 years. All the participants indicates that there was a general decreases of common colds among them. The attribute that they indicate can be associated to the measures of social distancing that were announced by the government. The seriousness that they took about the virus helped in a great way in fighting the virus.
Some of the new cases that are reported are associated with lack of strict control measures. New influenza cases and common cold stringency on social distancing likelihood will get common cold (Graph linear regression). For essential workers such as doctors and nurses their work did not stop. Coughing into a supermarket or a grocery store spreads the droplets and since these are indoor places, people might walk into other respiratory clouds. Participants self-reported high rates of compliance. Compliance with COVID-19 mitigation measures caused negative financial and social impacts. Many people lost their jobs and lots of businesses were closed. Correlation between compliance measures and the confounding variables were taken into consideration. Correlation between independent and dependent variable were also considered. Therefore, all factors associated with different control measures on how to ensure spread of infectious disease is capped should be treated with seriousness to avoid reoccurring of cases that otherwise one could avoid.
Depending on how different people take the measures, there will be a varied spread rates across communities. People who have more practical capacity to comply are less likely to violate rules. People older refrained from non-essential outings and they were more likely to comply with the regulations because of better knowledge (obligation to obey the law). A day after lockdown movement of Londoners dropped by 15% because they still had phobia for the virus. Compliance is dependent on an individual’s own ability. Where people do not see the importance of the control measures there is likelihood of continuous reoccurring.
There is a great contribution of hygiene habits on the number of cases that will be reported. Hygiene habits like hand washing and sanitising emphasis work in limiting spread and killing of respiratory virus particles for example 32% men and 64% of women wash their hands after using toilet in contrast people now wash their hands more regularly (unclear about 20 seconds limitation). The move to close schools was because kids are susceptible to infections due to lower immunity, opportunity for transmission to rise. Social distancing was set as droplets can spread from 1.8 metres coughing sneezing and talking, people working from home, no/limit mass gatherings. Masks act as barriers to protect against any infectious disease. However, regardless of all these, it is the individual seriousness that will determine the level of spreading of common colds in the community.
Limitation of results
There are cases that may not be formally be reported and some may not be symptomatic. Some people may have the flu but avoid going doctors/hospitals with the fear as to catching Covid19 (evidence may not reflect true reality as to why this study is important). The scenario is similar to common colds that people may not be getting to hospitals for the correct statistics be obtained. Therefore, the results obtained may not reflect the true picture of what happens on the environment.

Discussion
General background
The cold flues have been affecting people all over the world for a while now. They have been causing effects that require different public health organizations to come up with solutions the can address different problems for a while now. Different approaches have been used in controlling the spread of the infectious diseases and common colds in general. There are challenges associated with the spread of infectious diseases among different people. During the pandemic, there was a positive impact seen because of the social distancing and lockdown measures. Like cold flues, COVID-19 is an infectious disease that is growing concern and interest of many expertise worldwide. This pandemic has not only caused uncertainty but impacted other respiratory diseases, in particular the common cold. The rates have reduced a sign that with social distancing measures common colds can be controlled. The outcome of the common cold has always been unpredictable however, NPI’s set out have not only impacted beneficial effects for COVID-19 but also for the common cold.
The findings of the study indicate that there was a correlation of social distancing and lockdown measures and the decrease of the number of cases associated with common colds. The results indicate that individuals who complied with social distancing and lockdown measures were less likely to catch the common cold. The findings is a confirmation of the correlation that exist between the two variables of social lockdown and the number of cases being reported. Similar findings have been also presented by other Ferguson et al., 2020 showing if compliance is adhered to there is a reduction in the number of COVID-19 cases, the same principle applies in regard to the common cold. Ferguson et al., 2020 indicate that the association between the social lockdown measures and the reduction of the number of cases of common cold is an indication that they fall within the category of diseases spread through close contacts. Further, they indicate that Covid19 pandemic may have had negative impacts to the economy, but it has helped in reducing the number of resources being spent on other infectious diseases allowing healthcare professionals concentrate on important activities.
There has been different activities taking place to ensure that the pandemic is brought to an end. One of the NPI’s goal is to delay influenza in order to buy time to develop vaccine. The NPI does this by decreasing the burden or stress on NHS, daily reduction of influenza cases/R rate, and protect infrastructure. Their target is being achieved through having social distancing and lockdown measures that control the spread of other infectious disease. The demand for the influenza cases reduced in a great deal presenting an ideal measure that could be used in allowing the existing infrastructures towards the development of vaccines and drugs that can control the occurrence of Covid19. Qualls et al., 2017 discusses the impact of having the rate of influenza under control and its positive impact in the fight against common colds. The rate of spread can only be controlled through having effective vaccines that could make the cold flues not be a threat because of their infectious nature. Also, majority of the common flues are spread through air.
Epidemiologically is a condition where a patient has contact with one or more persons, who already have the disease or were contact with a person exposed to an infectious disease. It play a great role in the spread or control of common colds because their spread happens when the close contacts pass them from one person to the other. In this situation, we can implement the best restrictions in the world against any respiratory disease. The restrictions include, closing the borders to avoid an entry to exit of an infectious person, contact tracing to lower the infectious rate, use of masks and sanitizers and social distancing. But if people are not going to compliance with these restrictions, they’re not going to have the desired effect in bringing infection rates down. They are crucial factors that can be used in the control of spreading of different common colds because how effective they have been during the pandemic period. The role of measures have generally reduced the number of cases of cold flue in the UK something that has allowed healthcare professionals to handle emergency cases that arise due to Covid19.
The finding indicate that the response of people towards various measures will determine how effective the control of spread take place. It is important to note that the current pandemic period, people have been serious in following the restrictions put in place because of the serious impacts that Covid19 has had on people. Though in the past various methods have been implemented to cap the spread of common colds, sometimes it has not been efficient because of lack of seriousness. Those people with compromised immunity have been the main reason why some of the restriction have been successfully implemented. Common colds have serious effects on people with compromised immunity. It crucial to study how people behave and respond to restrictions as it will help to discover the kind of knowledge that will address about whether restrictions are/aren’t enough to bring cases down, or whether they could be enough if compliance was higher. Further, the research acts as an important avenue through which various measures can be interrogated and find the most appropriate for different common colds and have them under control. The results show that when individuals do comply there are lots of beneficial effects. One of the main benefits the reduction of the number of cases associated with common colds since the social distancing and lockdown measures were put in place. Since the start of the pandemic, around 70,000 people across the UK have been participating in UCL's COVID-19 Social Study every week. Through the study, it was deducted that there was a positive improvement of different measures that generally lead to reduction of the rate of other infectious diseases. Though there were mostly negative impacts associated with the lockdown and social distancing measures, the impact on the spread of diseases was evident and it was positive. Also, the study considered the effects of compliance with the restrictions and indicates that there was a generally positive impact on the public health sector as most of the infectious diseases reduced. It has allowed the healthcare professionals to direct the resources to other areas that need emergency addressing. Generally during the pandemic period, there was a high percentage of people who observed the measures and restrictions. The research found that compliance has been increasing since September, especially as stricter measures have been brought in & since the new variant was first reported in December. Despite, the number of Covid19 cases being on the rise, they have generally lead to reduced number of cold flues being reported. People also reported feeling that the new lockdown rules were stricter and easier to understand. The economic impact was somehow negative but on the public health perception, it was necessary for the virus to be contained. Almost 3 in 4 said they broadly understood the rules. Meaning that many understood better how various activities and measures would impact them and the positive impact it would have in the long term. The rules that people report breaking most often is meeting up with more than the recommended number of people outdoors. Through such actions of breaking the laid down procedures there were increased number of cases of Covid19 cases reported. However, due to the serious impact that the pandemic has on people’s lives majority (76%) still reported following this rule. They follow the strictly laid down measures to ensure various aspects on spreading of the infectious diseases are taken and brought under control to allow normalization of operations in the economy. Less than 1% of people reported never maintaining the recommended distance from others. The people who failed to observe the laid down measures were reported to indicate a general increase in the number of cases that were being reported. 49% say that they always follow this rule. Less than 1% of people said they never wear a face mask or other covering where recommended, and 93% reported that they always do. The deduction from the findings is that majority of the people observe the measures due to fear of contracting Covid19. However, it further helps in capping the rate of spread in the society. In the consideration of Covid19, there has been the rise of cases reported instead of reducing. However, the case is different based on the fact the cases have reduced drastically. The fact the disease had already been spread and people had not known how to deal with it, there was spread that occurred before the control measures took place. Falling of the number of reported cases can only be achieved ones those who were already affected have been isolated from the rest of the population. Therefore, even for the case of common colds, the incubation stage can be an important part of the controlling the spread amongst people in the community.
At the beginning of the pandemic despite the governments putting control measures in place, they might not been effective to ensure the virus is completely stopped from spreading. The virus is more transmissible and current rules aren't tight enough to contain it. Lockdown rules this time are looser than they were in spring, so whilst more people might not be breaking rules, the virus still has more opportunities to spread. Therefore, there was still gaps that could allow the spread of the virus. Relating to common colds, there is need for control measure put in place to be tough enough to ensure that there are no gaps. People should be serious enough to address the kind of problems they might be facing. Common colds are very rampant in the community and the cost is not seriously considered. The pandemic period made us understand the control measure to cap infectious diseases requires a serious approach that otherwise can result to cases of improvement. In the case that people are in laxity, then the impacts can be severe and they can result to even worse situation. The measures put in place can punitive and have far reaching consequences but still help in capping more losses that could have been experienced into later times. Whilst this is an improvement on findings from August (that suggested that less than 1 in 5 people isolated when required to), it is still likely to have considerable effect on onwards transmission. Importantly the study found that this differed by income suggesting that those who can afford to isolate are more likely to do so. The Government scheme introduced in September has seen an increase in compliance but these findings suggest that it's not yet accessible enough. However, there is a general agreement that social distancing and lockdown measures played a significant role of suppressing the street of infectious diseases. Common colds also have reduced significantly during this period of the pandemic, an indication that social distancing and lockdown measures have played a great role of ensuring that they are controlled.
Limitations
Limitations of this study include the questionnaire did not explore questions relating to duration of each contact(s) for example, some participants did not comply with social distancing and still allowed friends/family to visit their direct households, this could potentially impact the transmission of the common cold. For example, person A visits person B household, however person A still maintains a 2-metre distance and wears a face mask Vs Person A who visits person B household without maintaining a distance nor wearing a face mask. Both scenarios can impact the likelihood of transmission and contracting the common cold. Therefore, there can be results that are not regulated in a manner that is better.
This particular research study fails to address this a number of issues. First, it did not explore timing of each social intervention to help ‘flatten the curve’. Next it did not explore transmission within household contacts = "secondary attack rate" - this is what we consider within household transmission. The SAR represents the probability that an infected individual (our index case) will transmit the disease to another susceptible individual (our secondary case) within a specified time period. We can calculate the SAR for various settings & see how this compare. Findings suggest that the risk of COVID-19 transmission within households is high, occurs quickly & can originate from children & adults. Quick adoption of control measures if someone falls sick could reduce opportunity for intra-household transmission. And finally, remembering that physical distancing, good hand & respiratory hygiene, & keeping rooms well-ventilated.
Social isolation helps in reducing transmission rates, but also has negative effect on mental health, if not taken into consideration. Failure to consider the negative impacts it may not articulately address the positive effects that social distancing and lockdown measures could have to the general public health. Further, the study fails to address how negative results that arise due to control measures. Therefore, it may look a positive path to take but at the end of the day, they may end up having more harm to the general public.
Limitations to this research analysis, which includes biases in peoples reporting, lack of detail on recall (questionnaire) (recall bias) or twist the truth to make their answers reflect better on them (social desirability bias). There is also a question that arises whether the small sample used was a convenient sample. Therefore, there could be answers that may not be giving an informed opinion. Since the findings and analysis is based on the data from the questionnaires the conclusion is going to be biased.
Another limitation of the study is that it looks at one epidemiological metric from one angle, but still hopes to give useful insight into reductions in peoples contact and behaviour with compliance measures and how this has impacted not only COVID-19 but the common cold, and the need to place emphasis on public health measures in order to not only curb the epidemic but also other respiratory diseases. It could have looked at other control measures that have been adopted under other pandemics and the impact they have had on the cases of common colds being reported. However, it failed completely to consider the impact they had during their time.
Various countries have demonstrated several studies that combine multiple interventions (NPI’s) and benefit from that. However, this study did not explore combined interventions. It could have been of great importance if they could have identified the areas that combined intervention play role and determine the impact they have on the control of infectious diseases. Combined interventions may be the best approaches to ensure that common colds are controlled by the study failed to consider their impact.
With the fact that study specifically deals with social distancing and lockdown measures, it may not be effectively addressing the general impact of different combinations that may have led to the results obtained. There is still small evidence that face masks still possess a small possibility in catching respiratory infections for example one may still get a mild dose of COVID-19 but not as severe (same principle applies for the common cold). Complex issues should be discussed to have a general approach in the way different approaches and impacts that the whole system will have.
Future
Avoid rebound in transmission ongoing surveillance of intensive testing, contact tracing and quarantine should continue. Artificial intelligence is also helping to discover mobile phone apps/devices to track and diagnose infectious diseases. Ultimately, this virus spreads as a result of human behaviour and interaction. If we can better understand this, we can tailor our restrictions (including our messaging around these & how we support these) so that they work for all of us.
Effectiveness of health interventions not only relies upon clinical efficacy but also behaviours and attitudes of the community implementing them. Behaviours and attitudes towards interventions are often shaped by social and cultural factors. The first solution is for the government to set a local lockdown and provide stronger signal to public of threat of infection which may encourage better compliance. The next solution is by used of contact tracing, testing, health supplies can be prioritised to higher risk regions for example supported by china 1/3 fewer cases in early lockdown, Wuhan and Italy reduced transmission to outside world by local lockdowns may see short term increase in local numbers/transmission within households. Countries differ in population, structure, deprivation, healthcare and other parameters an emphasise should be placed on understanding the local context of transmission as it is crucial to communication, ensuring adherence and reducing transmission whilst minimising negative socio-economic consequences of lockdown
Conclusion
Social distancing and lockdown measures play an important role in controlling the spread of common colds. There is a strong correlation between the common colds in people and the kind of social distance that maintain amongst themselves. People will always have increased level of cold flues if they do not observe any form of social distancing. Engaging in such activities plays a key role in capping the spread of common flues. It is important to note that social distancing is one of the factors that determines the level of infection that will be seen in the society. Though Covid19 measures were not aimed at controlling cold flues. They were important as they helped address the problem of the cold flues and reduced the resources spent.
The population that has compromised immunity is more susceptible to cold flues and they require higher level of protection. Therefore, it can be observed that the level of measures undertaken to ensure protection during the Covid19 pandemic should continually be observed for the other common flues to be controlled. It is important for the society to ensure that social distancing and other activities that allow control of people coming cross to one another. Such activities like online shopping, online studies and others, play an important role of ensuring control of spread of infectious diseases.
Control measures to ensure common colds do not spread in the community depend on the attitude of the community. Therefore, it is important for the community to educate its members on the importance of having control measures. Like in the case of Covid19, the community may go through punitive measures with far reaching consequences but at the end their will be a positive gain for all the sacrifices. Considering the cost that common colds have in the society it’s important to start engaging on measures that can reduce the spread in the community.
We found that those who did not comply with social distancing and lockdown measures showed significantly higher incidence of upper respiratory tract infections, in particular the common cold compared to those who did comply with social distancing and lockdown measures. Even though those who were unable to comply due to being considered essential workers were at higher risk of developing upper respiratory tract infections, due to social distancing measures that were put into place (hospitals, supermarkets, schools) showed substantial evidence to help limit the spread of viral transmission. Further studies are needed to indicate long-term results.
References
- WHO, 2021. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) advice for the public
- NHS, 2021. NHS England and NHS Improvement coronavirus
- Ahn, Shin, Kim, Lee, Kim, Myoung, Kim, & Kim, 2020. Current Status of Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Therapeutics, and Vaccines for Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). J Microbiol Biotechnol. 30(3):313-324.
- Qualls, Levitt, Kanade, Wright-Jegede, Dopson, Biggerstaff, Reed, and Uzicanin, 2017.Community Mitigation Guidelines to Prevent Pandemic Influenza - United States. MMWR Recomm Rep 66(1):1-34.
- Ferguson et al., 2020. Report 9: Impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) to reduce COVID-19 mortality and healthcare demand. Imperial College COVID-19 Response Team.
- Michael C. Jarvis, 2020. Aerosol Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Physical Principles and Implications. Front. Public Health.
- Rondanelli et al., 2018. Self-Care for Common Colds: The Pivotal Role of Vitamin D, Vitamin C, Zinc, and Echinacea in Three Main Immune Interactive Clusters (Physical Barriers, Innate and Adaptive Immunity) Involved during an Episode of Common Colds—Practical Advice on Dosages and on the Time to Take These Nutrients/Botanicals in order to Prevent or Treat Common Colds. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
Dig deeper into The Impact of Fasting on Heart Health with our selection of articles.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



