A Literature Review Of Family
Introduction:
Schizophrenia is regarded as one of the major psychiatric disorder which leads the individuals unable to act properly in society. The caregivers play an essential role in managing schizophrenia patients so that their symptoms do not escalate and through effective care, their mental health can be controlled to make the individuals lead a normal life (Sekar et al. 2016). However, it is found that caring of schizophrenia patient is not easy as it requires extensive participation of caregivers throughout the day which makes them exhausted resulting in the development of errors in care (Chan and Ho, 2016). Thus, to ensure continuous and effective care it is seen that psychiatrist is referring the use of the family intervention in assisting recovery of schizophrenia patients in the community. This is because it leads the family members to understand the way they can meet the needs of the schizophrenia, in turn, acting to avoid relapse of the illness (van Os, 2016). Further, the family intervention is effective to make the family members understand the way they can manage their emotions and stress to participate in caring for the schizophrenic individual to improve the family environment and deliver proper care for their family member affected by schizophrenia (Ribé et al. 2018).
Definitions and Relevant policy
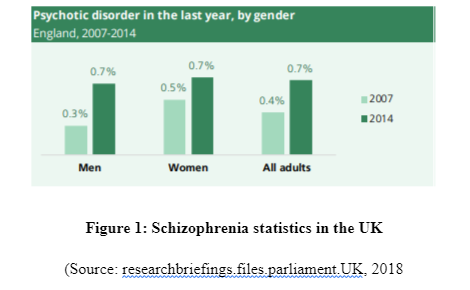
Schizophrenia is referred to as the chronic and extensive psychiatric disorder which impacts regarding the way a person feels, thinks and behaves with others in the society. The person suffering from the disorder is often seen to have lost contact with reality and is living in their make-belief world (Campellone et al. 2016). The family intervention in schizophrenia is referred to the condition in which the mental health professionals informs and educates the family members regarding the person suffering from schizophrenia in the family to let them understand the cause of the person’s actions and the way they can personally act to resolve it (Burbach, 2018). The psychiatrist is trying to include family therapy in assisting recovery for schizophrenia patients as they are finding it useful to ensure the stable mental health of the patients (psychiatry.cam.ac.uk, 2014). In the UK, the prevalence of schizophrenia shows that 14.5 people out of 1000 individuals are suffering from the illness (psychiatry.cam.ac.uk, 2014). In 2014, it is reported that nearly 22,000 people in England are treated by the NHS for schizophrenia (livingwithschizophreniauk, 2019; NICE, 2015). The statistics regarding schizophrenia published by the UK government mentions there has been an increase in the incidence of the mental illness by 0.7% from 2007 to 2014. It is also mentioned that women are more affected by schizophrenia compared to men in England, UK (researchbriefings.files.parliament.uk, 2018). Thus, the topic of family intervention is being focused for recovery of schizophrenia patients in this study so that the prevalence of the mental disorder can be resolved and better mental conditions for the patients can be built.
Critical Literature Review
Schizophrenia is a mental illness in which people shows unusual behaviour, speak strangely and expresses reduced ability to differentiate between reality and illusion. The individuals with schizophrenia often are expresses positive and negative symptoms (Ardizzi et al. 2016). The positive symptoms experienced by schizophrenic individuals are the signs which normal people do not experience and is exclusively found only among the people affected by the illness. As asserted by Eichner and Berna (2016), the positive symptoms of schizophrenia involve disordered thoughts and speech, delusion, auditory, visual and gustatory hallucinations and others. The patients who show positive symptoms are often seen to show proper response to medications provided helping the person to lead a normal life. As criticised by Marder and Galderisi (2017), the negative symptoms are the emotional responses which are seen among other people as well as people affected schizophrenia such as lack of speech, less emotion, low motivation, inability to feel pleasure and others. The negative symptoms in schizophrenic patients are seen to show less response to be resolved through medication and treatment which results the individuals to experience poor quality life, improper functional ability and being burden of care on others (Cella et al. 2017). The people affected by schizophrenia are also seen to show improper cognitive ability. The
presence of degree of cognitive inability among the schizophrenic patients mentions the extent of their functionality rather than the presentation of positive or negative symptoms (Remington et al. 2016). The presence of schizophrenic patient in the family is seen to create emotional pressure on the family members to manage the patient. This is because it is reported that schizophrenic patients often shout, yell, become hostile and fight unnecessarily with family members due to their low cognitive ability to differentiate between reality and illusion. The further progress of the illness makes the patient show greater psychotic episodes which emotionally drain the family members as they are unable to tolerate the situations created by the patient (Ardizzi et al. 2016). As mentioned by Von Kardorff et al. (2016), the presence of schizophrenia patient in the family also leads the family members to bear financial burden. This is because long-term care and clinical intervention are required to be provided to the patient to help the individuals cope with their mental illness. As argued by Bishop and Greeff (2015), schizophrenia patients increase stress among family members. This is because the patient reacts improperly at all situations which make the family member develop tension of experiencing shame due to the individual’s improper act in front of the society. In addition, the family members of the schizophrenic patients feel stressed as they ate tensed regarding the future of the individual and the way they are to manage the individual so that the person is able to manage their own emotions at progressing age (Amagai et al. 2016). In the study Hernandez-Yánez et al. (2015) it is mentioned that people with mental illness often depends on the family for arranging and considering their care as they lack cognitive ability to make proper judgements or provide opinions to select the nature of care services. This informs that including the family members in recovering schizophrenic patient would be effective to help the individual access proper treatment as on their behalf the family members can make trusted care decision to ensure their well-being. Thus, the study by Burbach (2018) mentions that to execute effective family intervention for the recovery of schizophrenia patients the mental health professionals have the role of initiating effective and detailed communication with the family members of the adults suffering from schizophrenia. This is because through communication the health professionals inform them about the responsibilities family members are to take to ensure reduction of symptoms of the disorder among the adult suffering from schizophrenia. In addition, they inform about the way family members can act to resolve their stress due to the presence of the diseased person in the family. In contrast, the study by Fiorillo et al. (2016) mentions that in family intervention for

In the study Hernandez-Yánez et al. (2015) it is mentioned that people with mental illness often depends on the family for arranging and considering their care as they lack cognitive ability to make proper judgements or provide opinions to select the nature of care services. This informs that including the family members in recovering schizophrenic patient would be effective to help the individual access proper treatment as on their behalf the family members can make trusted care decision to ensure their well-being. Thus, the study by Burbach (2018) mentions that to execute effective family intervention for the recovery of schizophrenia patients the mental health professionals have the role of initiating effective and detailed communication with the family members of the adults suffering from schizophrenia. This is because through communication the health professionals inform them about the responsibilities family members are to take to ensure reduction of symptoms of the disorder among the adult suffering from schizophrenia. In addition, they inform about the way family members can act to resolve their stress due to the presence of the diseased person in the family. In contrast, the study by Fiorillo et al. (2016) mentions that in family intervention for schizophrenia patient’s service providers has the role to deliver proper training to the family members to make the family members develop effective competence in offering care to the patients. The health commissioners in the NHS, UK are seen to play the role of guiding proper referral pathways for family members of adults with schizophrenia so that they are able to access the services of family intervention in ensuring improved well-being of the adult (livingwithschizophreniauk, 2019).
The family intervention in schizophrenia is referred to the process in which family members of the patients are involved in the care for the individuals by forming an alliance with them by the healthcare professionals so that needs and demands of the patients are properly fulfilled (Okpokoro and Sampson, 2014). The goal of the family intervention in schizophrenia is to let the family members understand the way they can control their stressor to show love and affection through proper care to the patients in their family who feels at threat due to the mental health issue. The family intervention acts as effective way to improve the life of the schizophrenia patients as they feel valued and dignified under the care and affection of their family members (Lasebikan and Ayinde, 2013). The family intervention in schizophrenia is to be coordinated by trained professionals so that the patients, as well as family members, are made to comply with one another in the process (Tas et al. 2012). The family intervention in schizophrenia care is regarded as valuable experience for all members in the family as it creates opportunity for the members to understand emotions and thoughts of each other (Foster et al. 2016). This is because in this intervention the family members are seen to work as a group to evaluate each other’s need and provide effective support to the schizophrenic individuals to ensure their improved well-being. The understanding makes the family members accordingly interact with one another to ensure the bond of the family remains and improved mental condition of the individual in the family suffering from schizophrenia can be attained through collaborative approach (Wang et al. 2017). In contrast to the study, the article by Bademli and Duman (2016) mentions that lack the family which shows controlled emotions towards managing schizophrenic adults in their family led to avoid relapse of symptoms of the disorder. However, families which show elevated emotions in controlling schizophrenic patients in the family fails to ensure proper care and in them, the family intervention does not act fruitfully to ensure better well-being of the patient. This is because uncontrolled emotions make the family members unable to play their role properly required in family intervention to ensure effective support to the patient. Thus, the evidence gathered from various instances mentions that family intervention is effective for adults with schizophrenia to control the relapse of their symptoms and ensure effective care.
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to An In Depth Review of Hotel Room Pricing Models.
Summarisation of key issues and justification of the topic
The summarization of the findings presented in the critical literature review mentions that various gaps are present in the existing studies. This is evident as studies lacked the depth to inform regarding the exact role and responsibility family members have to take for assisting the effective recovery of schizophrenia patients. In addition, the evidence gathered lacked information in details regarding what extent the family intervention is being affective to let the schizophrenic patients get recovered from their deteriorated mental health situation. There is lack of data regarding the steps taken in family intervention for assisting recovery of schizophrenic patients. There is also lack of information regarding the challenges to overcome in making the family intervention successful for the recovery of schizophrenia patients. Thus, this study is to be executed to develop in-depth information regarding the impact, role and benefits of family intervention in assisting recovery of schizophrenia patients.
Relevance of the topic
The topic of the study is relevant to the context of practice because being a nurse in the mental health ward it is seen that even after effective care is provided to the schizophrenic individuals yet the patients take longer to recover. Moreover, often family members of the schizophrenic individuals are found to be stressed with the conditions of the patients and provide informs that avoid taking them home as they cannot control the individual’s demands and needs (Okpokoro and Sampson, 2014). Thus, the study is relevant to the practice as it is going to inform regarding the way family intervention can be used to assist the effective recovery of schizophrenic patients in the environment through family care. Moreover, the study would inform regarding the way family members of the patients can be made less stressed and have better competence in controlling the patients after discharge from the hospitals to ensure avoiding relapse of the symptoms, in turn, helping the individuals lead a normal life.
Research Questions
What is the role and impact of family intervention in assisting recovery of schizophrenia patients in the community?
Aims and Objectives of the study
The aim of the study is to develop a literature review to explain the impact of family intervention in assisting patients to help them recover from schizophrenia in the community.
- To identify the way of providing family intervention for schizophrenia patients
- To analyse the impact of family intervention for assisting recovery of schizophrenia patients in the community
- To evaluate the challenges faced in providing family intervention to assist recovery of schizophrenia patients in the community
Research Method
The research methods include the use of different process to analyse a certain topic of concern to develop proper findings. In this chapter, the research method to be used for formulating the research question related to the study topic is to be discussed. The way electronic searches are to be executed and the keywords to be used for executing search to retrieve existing articles and journals regarding the topic are to be mentioned. The research method to be used for the examination of articles and their quality appraisal to ensure they are suitable for the study is to be explained.
PICO Questions and Keywords
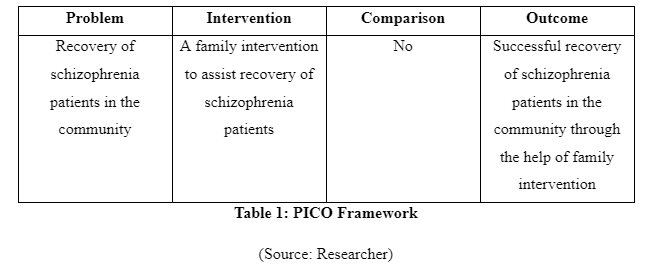
The PICO framework is a tool used in evidence-based studies for formulating the research question related to the clinical topic of interest discussed in the study (Leonardo, 2018). As asserted by Chrastina (2016), the clinical research question required to be formulated in such a way so that it directly relates to develop a proper inquiry regarding the raised research problem. This is because such a question would lead the researcher to understand the area of focus for initiating the study and develop proper findings for resolving the raised problems in the study. In this study, the PICO framework is to be used because it helps in building a research question that is directly related to the identified problem in the study. The PICO stands for problem, intervention, comparison and outcome (Scells et al. 2017). The problem is mentioned as a key clinical issue, intervention is the measures to be used in resolving the issue, the comparison is to understand the effect of intervention with control group and outcome is mentioned as the finding of the research (Köpke et al. 2019). In this study, the problem to be focussed is the recovery of schizophrenia patients in the community. The intervention in this research is family intervention to assist recovery of schizophrenia patients. There is no comparison made in the study and the outcome of the study is to attain successful recovery of schizophrenia patients in the community through the help of family intervention.
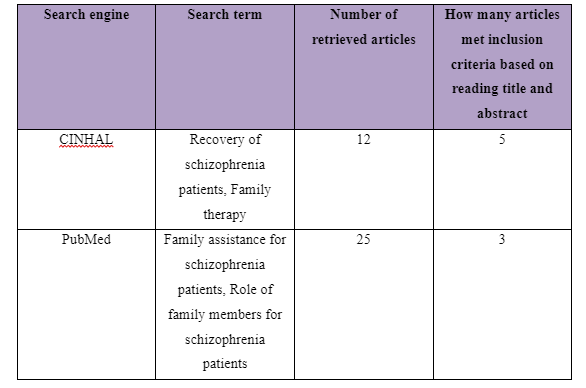
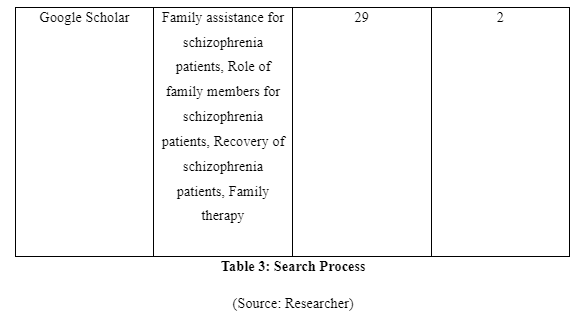
The search terms or the keywords to be used to execute searching of information regarding the research question is essential so that updated and well-informative, as well as relevant journals and articles, can be found from leading electronic search platforms to develop a comprehensive study. The keywords to be used in executing the search as considered from the PICO questions are: “Family intervention”, “recovery of schizophrenia patients”, “family therapy”, “family assistance for schizophrenia patients” and “role of family members for schizophrenia patients”. The customisations of the keywords are to be made as per search requirements in different search platforms to gather relevant data. The manual search is also to be executed so that relevant articles and information regarding the raised clinical question can be properly identified.
Electronic Search
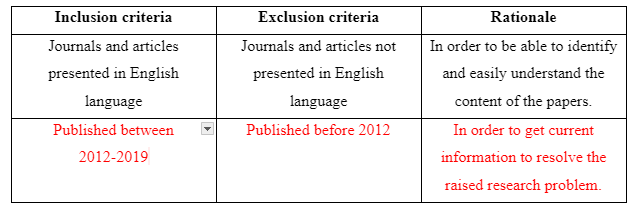
The electronic search is executed through online database and search engines to gather updated data and information in accomplishing the study. It is also required because electronic search allows the researcher to gather data from variety of sources in simple manner without facing difficulty of going through each page of the books and journals to ensure its relevance as seen in manual searches (McGowan et al. 2016). The search platform which is to be used in the study is CINHAL, PubMed, Google Scholar and others. The CINHAL mainly to be used as it contains various full-text journals regarding updated clinical and nursing topics (health.ebsco.com, 2019). In executing the search, the Boolean operators such as “AND” and “OR” is to be used for relating different keywords as suggested in 2.2.1 to gather data regarding the study. The limits in the searches are no journals or articles published before 2013 would be not be considered, non-English journals would be avoided, journals relating information of recovery for schizophrenia patients other than family intervention would also avoided being considered.
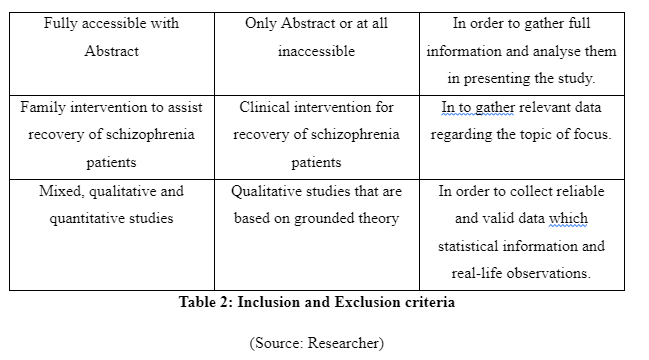
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria of the study are the characteristics or factors that are required to be present in the research and exclusion criteria are the factors which are disqualified to be involved in the study as they create study errors (Atkinson et al. 2015). In this study, the inclusion criteria are journals that are written in English, articles published from 2012-2019, journals related to the role of family intervention to assist recovery of schizophrenia patients and the mixed, qualitative and quantitative studies. The exclusion criteria are journals published before 2012, qualitative studies that are based on grounded theory, non-English journals and papers related to clinical intervention for recovery of schizophrenia patients. The articles published from 2012-2019 is considered and journals published before 2012 is not considered so that the researcher can retrieve and gather the most updated information avoiding inclusion of backdated data regarding the topic of study. The qualitative studies which are focussed on ground theory are not considered for the study as it leads to create difficulty in availing reliable and valid data (Koivunen and Saranto, 2018). The mixed studies, as well as systematic, meta-analysis qualitative and quantitative studies, are to be used as it helps to gather statistical as well as real-life data regarding the study topic (Rouleau et al. 2017). The non-English papers are not to be considered for the topic as the researcher does not know other languages except English. The papers which show family intervention to recover schizophrenia patients are to be included in the study and papers which include other intervention are not to be considered so that relevant data regarding the topic of focus can be gathered.
Assessment of Retrieved Articles
The articles found in the electronic search are assessed to understand which of them are to be included in the study for presenting informative results.
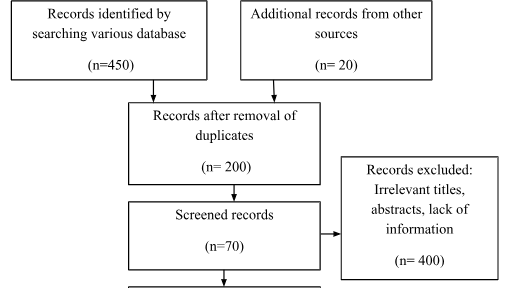
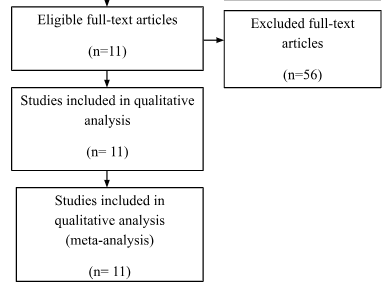
Quality Appraisal and Data Extraction
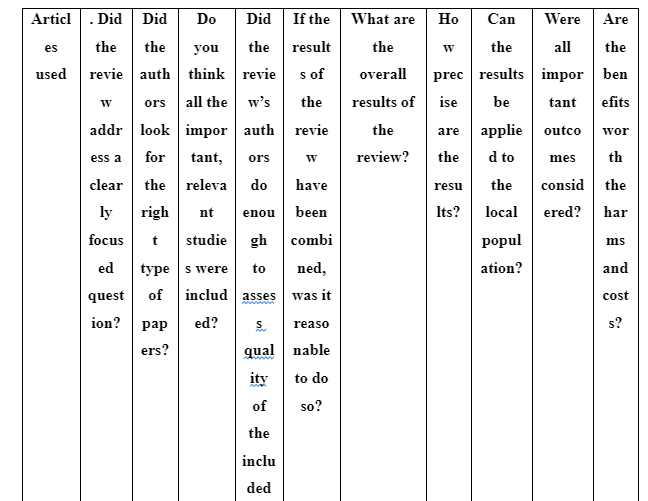
The CASP tool has the main focus for assisting individuals to adopt skills for determining and making sense of information in the study for implementing the gathered information in practice (Carvalho et al. 2017). Thus, the CASP Tool is to be used for quality appraisal of the selected articles in the study. (Refer to Appendix 2)
Ethical Consideration
The four key ethics to be considered in the nursing study are justice, beneficence and nonmaleficence (Kangasniemi et al. 2015). The justice in the research is to be maintained by presenting all the information in true manner as mentioned by the previous researchers. The beneficence is to be maintained in the study by highlighting proper information such as role and benefits of family intervention in recovering schizophrenia patients so that the significance of the intervention can be made understood to required patients suffering from schizophrenia. The nonmaleficence is to be maintained within the study by revealing no personal information of patients if found from studies to prevent them from harm due to disclosure of personal details. The confidentiality of the information gathered in the study is to be maintained by protecting the data through passwords. The data to be presented are to be properly referred to the original authors so that proper credit to the owner of the information is provided. In order to gather consent for the studies of other authors, the authors are to be directly contacted to share details and no information is to be presented in the study without their due permission.
Results and Findings
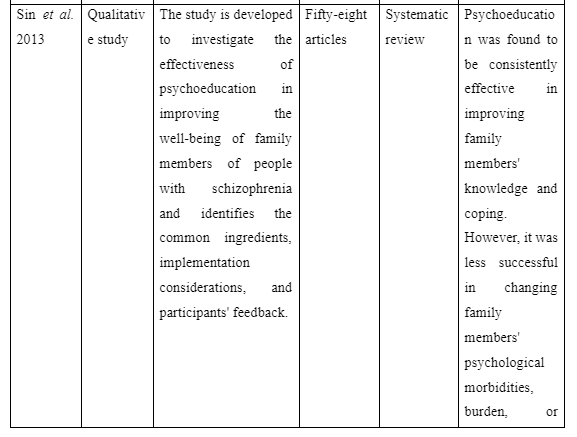
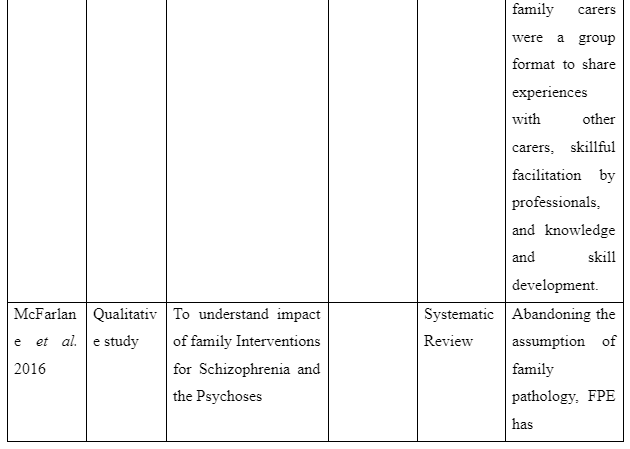
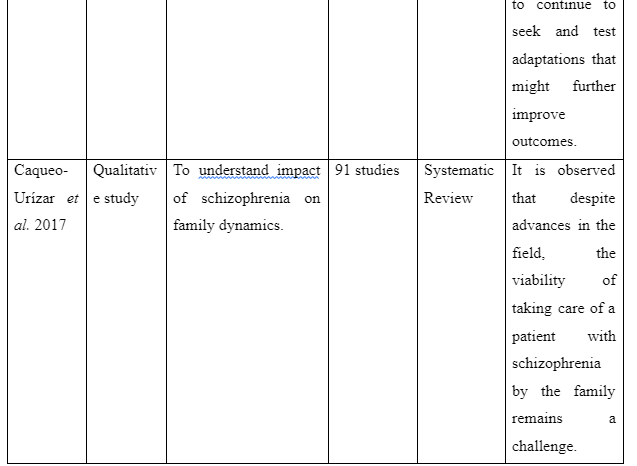
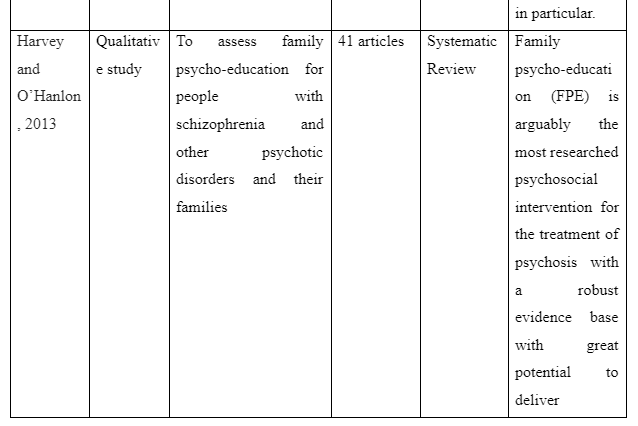
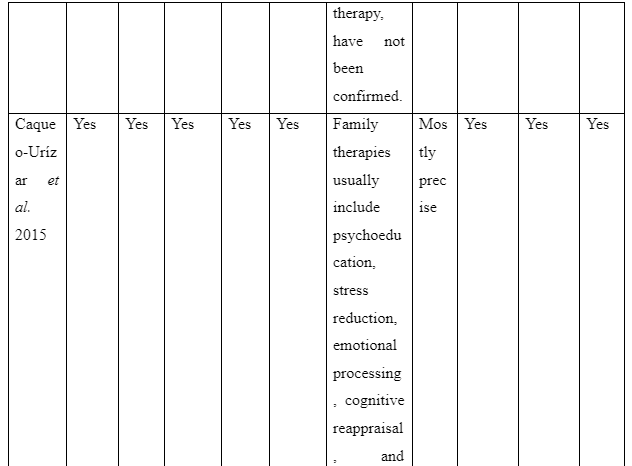
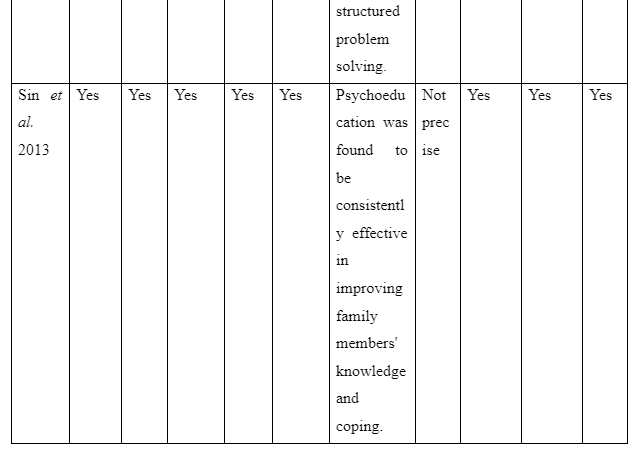
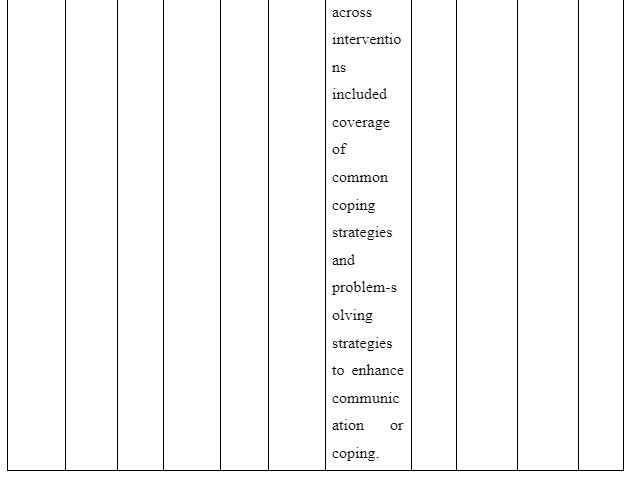
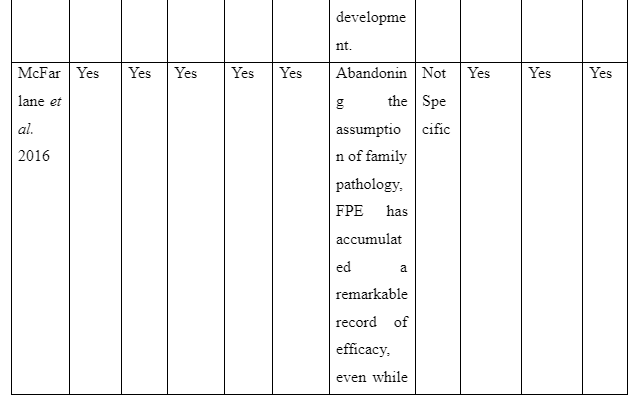
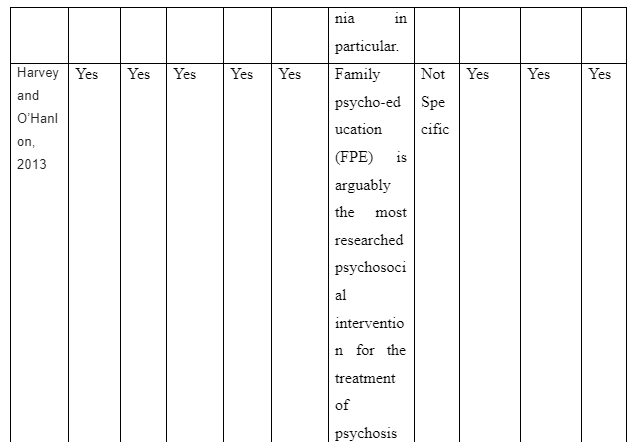
The way family intervention is to be provided by including family members of patients suffering from schizophrenia is presented in the theme. The study by Harvey and O’Hanlon (2013) informs that to provide family intervention for assisting schizophrenia patients the family members are to be included in the assessment and treatment process of the patients. This is required so that the family members have knowledge regarding the way they can participate in care and treatment for the patients to avoid relapse of the disease. In contrast, the study Sin and Norman (2013) mentions that psychoeducation of family members are needed to provide family intervention for schizophrenia patients as it educates the family members regarding the way to manage their psychological health while offering care to patients. It also educates them about the myths as well as negative beliefs regarding schizophrenia to be avoided to offer effective care to the patients suffering from schizophrenia in the family. Moreover, the basic information about schizophrenia and impact of medical treatment for schizophrenia on the patients is the basic concept educated through psychoeducation to family members for providing family intervention in assisting patients with schizophrenia. In comparison, the study by McFarlane (2016) informs that to provide family intervention for schizophrenia patients the communication training is to be implemented for their family members to improve interpersonal skills of each family member. In the study by Caqueo-Urízar et al. (2017), it is reported that structured problem-solving one of the way to provide family intervention as it let the family members talk about the negative emotions they are experiencing and the way to cope them to ensure proper assistance and well-being to the patients suffering from schizophrenia in the family. Thus, the theme mentions that to provide family intervention the psychoeducation, inclusion of family members in patient’s treatment and assessment, structured problem-solving and communication training are required to help the family member successfully assist in the recovery of schizophrenia patients in the community.
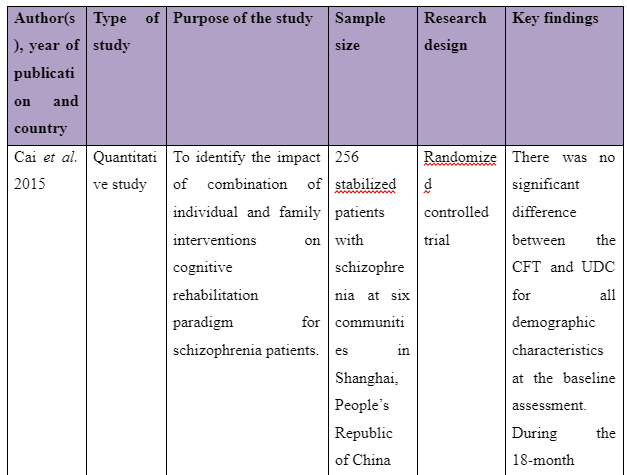
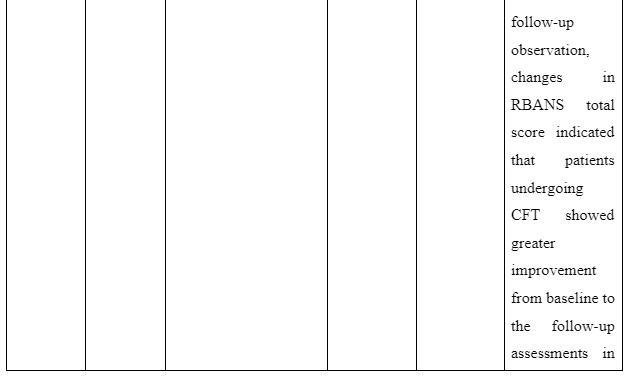
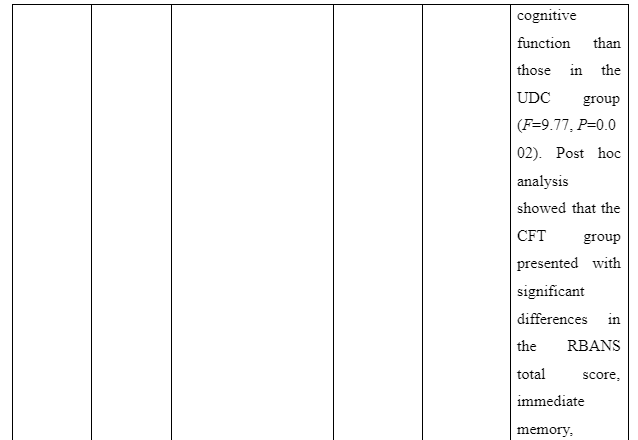
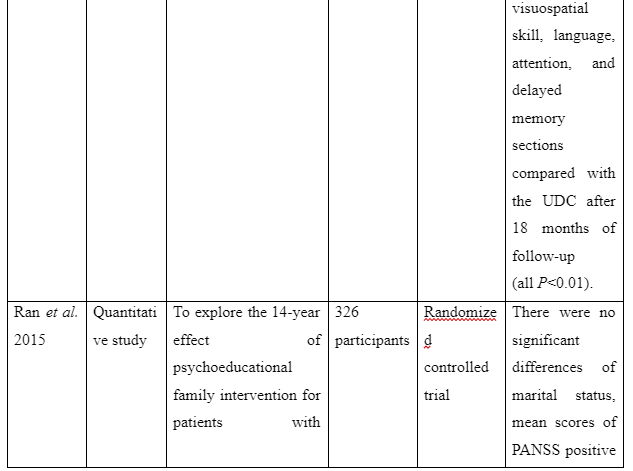
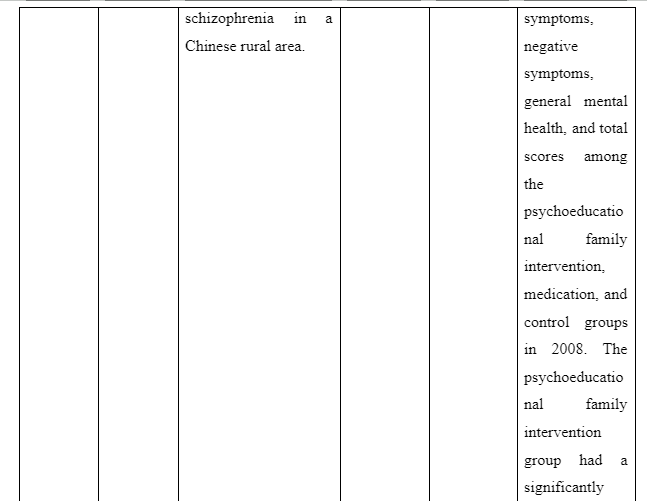
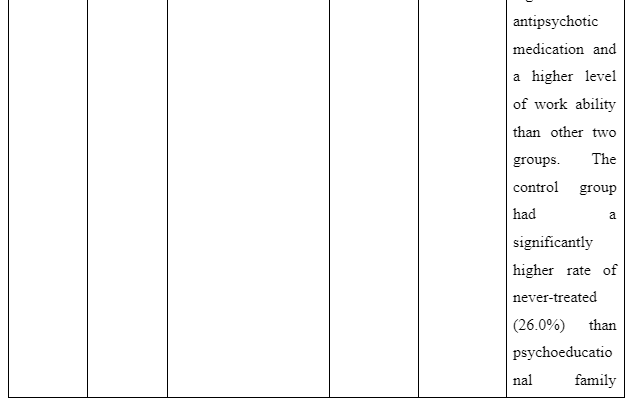
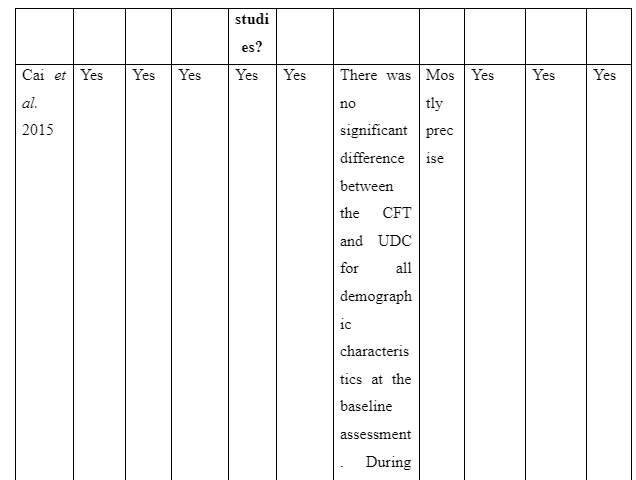
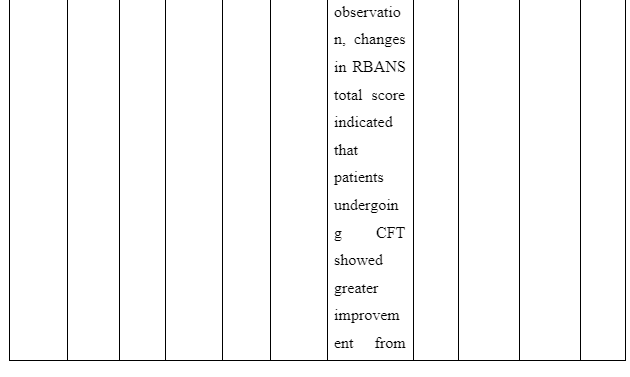
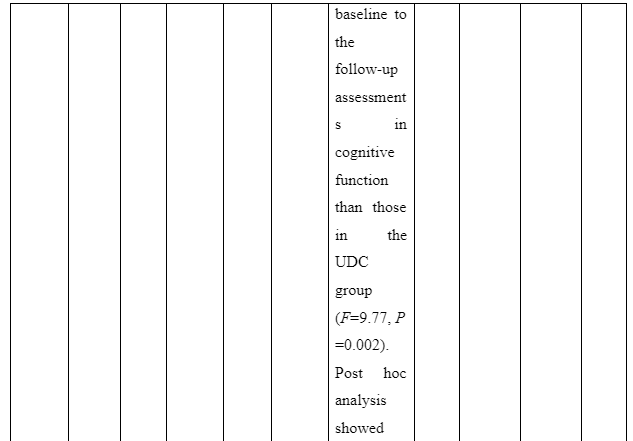
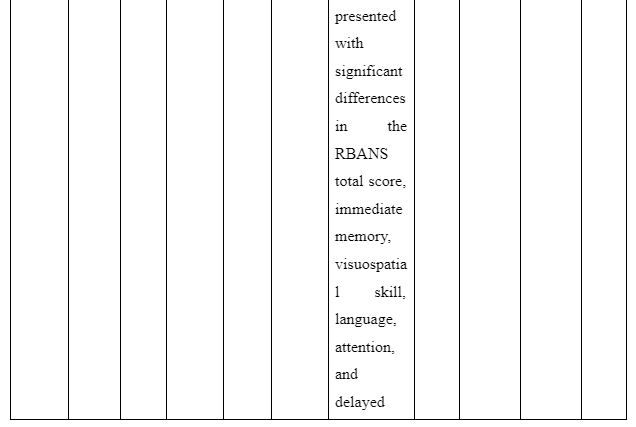
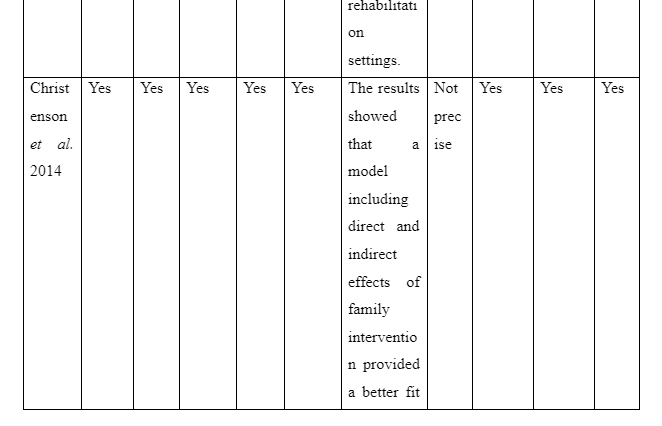
The theme is developed to present information whether or not family intervention actually works in assisting the recovery of patients suffering from schizophrenia in the community. In the study of Cai et al. (2015), a total of 256 patients who are suffering from schizophrenia are selected and divided into two groups of which one of the groups is provided comprehensive family therapy (CFT) and the other group is provided usual daily care (USD). The Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) used for checking the severity of symptoms of the illness in patient with schizophrenia and Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS) that checks cognitive functioning are implemented to collect data about the patient’s performance after 18 months. The score for group with CFT showed 211.83±35.84 after 18 months follow-up compared to 183.87±37.32 score on pretest whereas the group provided with UDC showed 189.23±36.19 score on follow-up compared to 178.55±32.95 received during the pretest. In another study by Ran et al. (2015), it is reported that increased work efficiency of schizophrenia patients who are under family intervention is seen compared to the patients present in the control group. It is evident as full-time workability scores for group who were under family intervention was 25.6 compared to control group which has 15.4 scores. Thus, scores informed that family intervention is effective to ensure better recovery of patients suffering from schizophrenia in the community compared to others provided with usual care.
Benefit of Family Intervention in assisting patients to recover from Schizophrenia
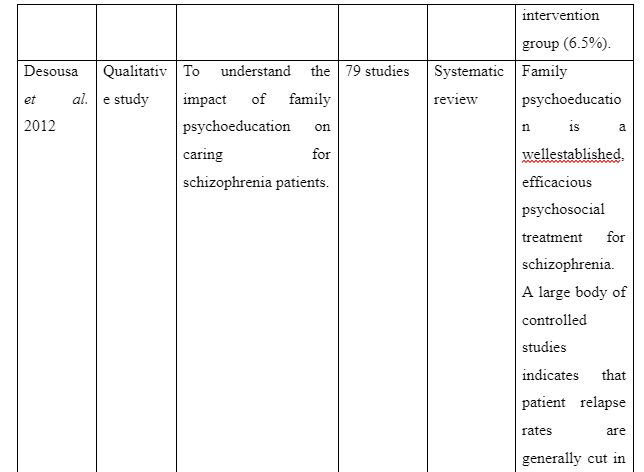
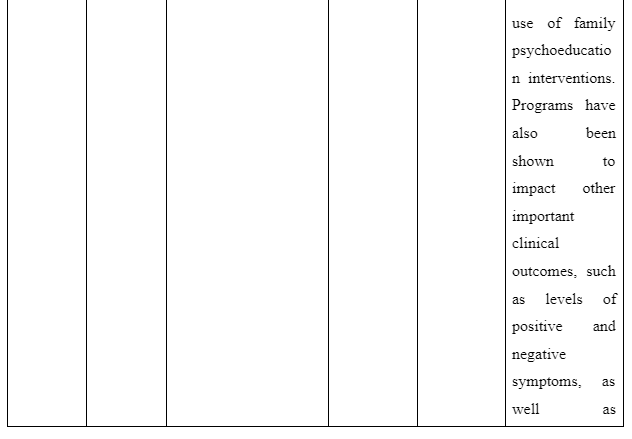
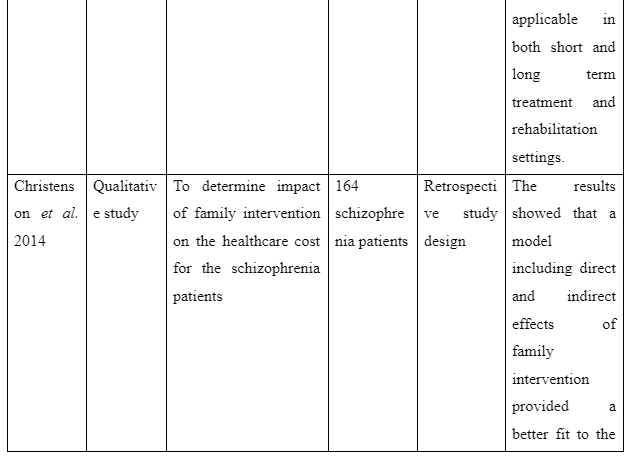
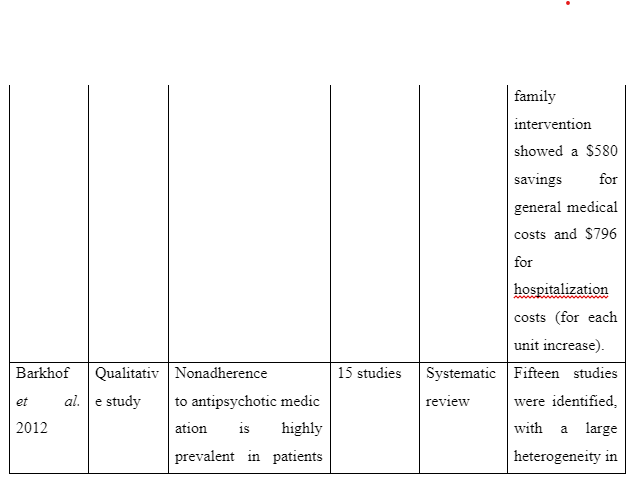
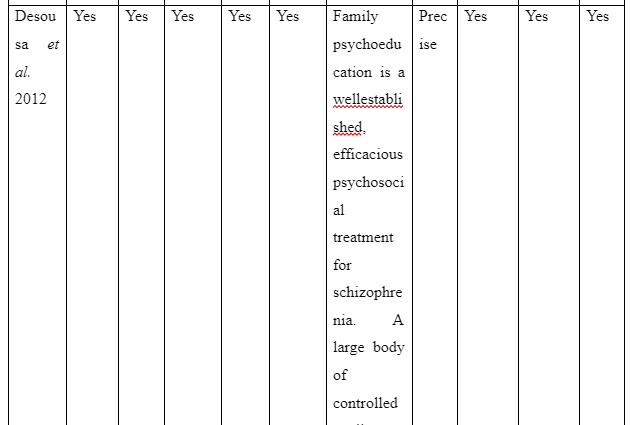
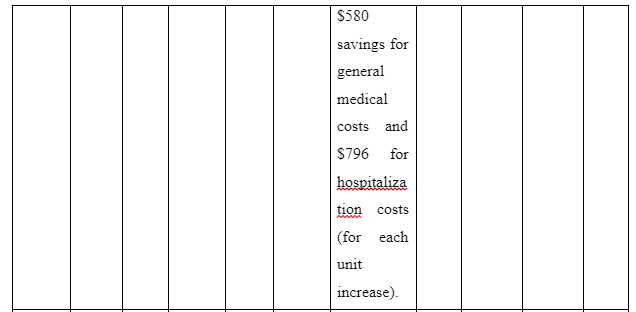
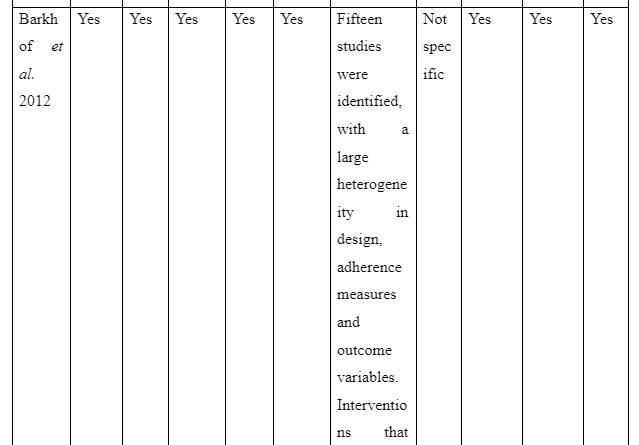
The theme informs about the advantages to be accessed on providing family intervention to assist patients for recovering from schizophrenia in the community. The study Desousa et al. (2012) refers that family intervention is effective to reduce frequent relapses of symptoms among the schizophrenia patients. However, the study by Christenson et al. (2014) which gathered information from Kansas Medicaid system mentions that due to family intervention for the schizophrenia patients a direct saving of $586 (average) is experienced in general medicine cost of each individual. Moreover, $796 (average) was considered to be saved directly for hospitalisation costs of patients suffering from schizophrenia on the implication of family intervention per individual. In contrast, the study of Barkhof et al. (2012) mentions including family supports for patient with schizophrenia showcased instance of positive adherence of the patients to take medication. Thus, it can be concluded that benefit of family intervention for recovery of schizophrenia patients is that it acts to reduce treatment cost, hospitalisation cost, increase medication compliance of the patients and avoid relapse of symptoms of the illness.
Challenges to be experienced in delivering Family Intervention for assisting patients to recover from Schizophrenia
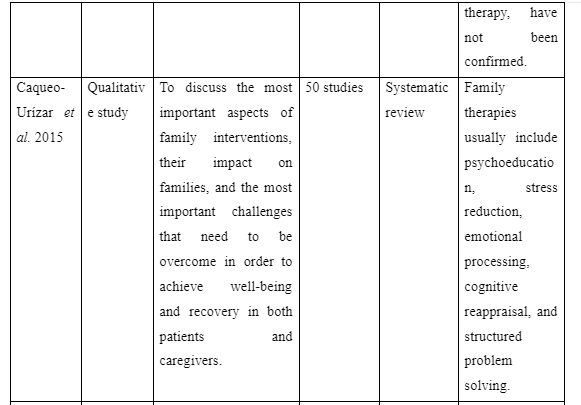
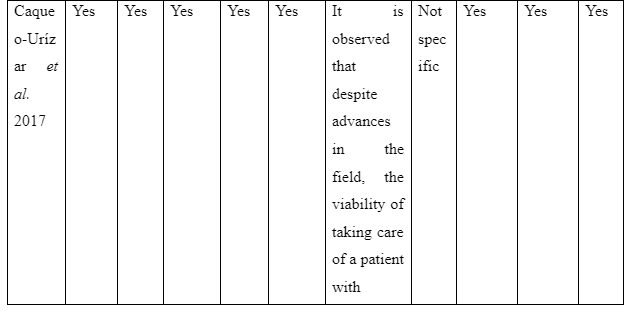
The challenges faced by health professionals and group leaders to execute family intervention for assisting recovery of schizophrenia patients in the community are to be mentioned in the theme. In the study of Caqueo-Urízar et al. (2015), it is mentioned that motivating patients to participate in multi-family intervention is difficult as well as time-consuming. This is because while many family members were motivated to join the patients showed anxiousness regarding the intervention. The study also explains that maintaining the autonomy of the patients posed as a challenge for implementing family intervention of patients as the intervention leads the family to restrict certain activities of the patients irrespective of their opinions to ensure their recovery. Thus, it indicates that time-consumption and maintaining the autonomy of patients are the two challenges experienced in implementing family intervention for assisting recovery of schizophrenic individual in the community.
Summary
The resulted gathered informs that ways to provide family intervention include psychoeducation, inclusion of family members in patient’s treatment and assessment, structured–problem-solving and communication training for successfully allowing the family members to participate in care for schizophrenia patients to ensure their recovery from the illness in the community. The results also mentioned that benefit of the family intervention is that it reduces medication and hospitalisation costs as well as effective in avoiding relapse of symptoms related to schizophrenia ensuring effective recovery of the individuals. However, increased time and hindrance in ensuring the autonomy of the patients during family intervention are the challenges experiences in delivering the family intervention to assist recovery of schizophrenia patients.
Discussion of Findings
The study is organised to understand the way of delivering family intervention along with its impact and challenges to be faced in providing it to assist in the recovery of schizophrenia patients. The results gathered informed that the first theme mentions the ways family intervention can be provided by including family members in assisting patients to recover from schizophrenia. It is evident as it has highlighted that inclusion of family members during treatment and assessment process of the patient is mandatory and an effective step to provide family intervention. This is because inclusion of family members in the assessment of patients makes them aware of the current risk and health condition of the patient as well as their inclusion in treatment makes the family members aware about the role and responsibilities which they have to play to offer continuous care to the patients to ensure their proper recovery (Harvey and O’Hanlon, 2013). The fact is supported by the study of Asmal et al. (2014) where it is mentioned that to execute family intervention the researchers ensured that family members attend each clinical assessment of the schizophrenic patients and their treatment. This is required so that the family members are aware of the progress in health of the patients as well as the role and responsibilities to be played by them to ensure better well-being of schizophrenia individuals in the family. The first theme also mentions that psychoeducation of the family members along with communication training and structured problem-solving are the ways to be considered in successfully implementing family intervention for recovering patients with schizophrenia (Sin and Norman, 2013; McFarlane, 2016; Caqueo-Urízar et al. 2017). In order to provide family intervention, the psychoeducation is required as it leads to resolve different myths and misconception related to schizophrenia as well as provide basic information about cause and impact of different medication of schizophrenia to family members so that they have knowledge regarding the misconceptions to be avoided and activities to be taken for the patients to ensure their recovery. Thus, psychoeducation is one of the ways to be followed in offering family therapy as it helps to educate the family members regarding the role and concepts to be developed as well as myths and negative beliefs to be avoided to ensure better care delivery to the patients for their proper recovery. Therefore, psychoeducation one another way of family intervention as it makes the family members develop proper mental ability to support and care for schizophrenia patients in the family (Sin and Norman, 2013).
The fact is supported by the study of Desousa et al. (2012) where the researchers have mentioned that psychoeducation being one of the ways of family intervention helps the family members develop better concept regarding the way to control the stressors faced while providing care to the patients. This, in turn, helps them to provide better support and care to the schizophrenic individuals helping to lower relapse of the condition and future hospitalisation. The communication training is another way to be considered in providing family intervention for schizophrenia recovery because it leads the family to understand the way interaction is to be made with the schizophrenia patients so that the person's symptoms can be controlled and proper care is delivered (McFarlane, 2016). The fact is similar to the information presented by Girón et al. (2015) where it is mentioned that schizophrenic patients due to impaired cognitive ability shows inability to communicate normally and shows inappropriate behaviour. The family members by understanding the fact accordingly required to changes their way of interaction with the individuals by maintain positive expression and active listening attitude along with showing negotiations to effectively interact and support caring for the patients to ensure their recovery. Thus, communication training would be an effective way of providing proper family intervention as in the process the family would know regarding the way they are express and interact with schizophrenic patients so that their care needs and demands are properly fulfilled to ensure their better health. The first theme also mentions that problem-solving is one of the ways to ensure successful implementation of family intervention in schizophrenia (Caqueo-Urízar et al. 2017). The fact is supported by the study of Edge et al. (2016) where it is informed that stressor and problems within the family are to be resolved so that the family tension can be reduced. This is because tension-free family members would be able to flow proper rules and actions required in family intervention for successfully assisting in the recovery and management of schizophrenia individuals. The second theme mentions through Ran et al. (2015) and Cai et al. (2015) that family intervention is actually effective in patients with schizophrenia to initiate their better recovery compared to usual care provided to patients. This is because family intervention provided to schizophrenic patients showed better work efficiency and relapse of negative symptoms related to the illness ensure better health progress is made through the approach. The fact is similar to the study of Girón et al. (2015) where it mentioned that effective family intervention leads to control and better care of patients suffering from schizophrenia in turn
supporting their better health improvement. The third theme mentions that benefit of family intervention for assisting the recovery of schizophrenia patients is reduction of treatment cost and hospitalisation cost, increase medication compliance of the patients and avoid relapse of symptoms of the illness. The family intervention does reduce the medicine and hospitalisation cost because with the effective participation of the family members finances required to be spent in arranging hired caregivers can be avoided. Moreover, family members offer care to patients at home thus reducing the cost of their hospitalisation (Desousa et al. 2012; Christenson et al. 2014; Barkhof et al. 2012). The study by Barkhof et al. (2012) supported that family intervention helps to improve medical compliance among the schizophrenic patients as in the process family members takes active part to ensure medication for schizophrenia is taken by the patient on regular basis without skipping. The study by Schennach et al. (2012) informs that family intervention is beneficial for schizophrenic patients as it helps to reduce the relapse rate of symptoms. This is because family members in the intervention taken an active part to ensure proper care as per the needs and demands of the patients are provided so that they orient towards better health recovery through controlling the symptoms of the illness. The study by Phanthunane et al. (2011) mentioned that the addition of family intervention along with medication treatment of schizophrenia patients has a cost-effective impact. Thus, the facts presented about the benefit of family intervention that it ensures cost-effective care along with avoiding relapse of the illness is also supported by other studies by Schennach et al. (2012) and Phanthunane et al. (2011). The last theme mentioned that increased time consumption along with the assurance of proper autonomy of the patients is seen as challenge in implementing family intervention for the recovery of schizophrenic patients. The increased time is taken in family intervention as all the family members are to be individually assessed and then are to be made to work collectively and empathetically with the patient. Moreover, in many cases, patients show hindrance to show participation in family intervention and thus more time is taken to convince them in creating the intervention (Caqueo-Urízar et al. 2015). The fact of time consumption is supported by the study of Chakrabarti (2011) where it is mentioned that family intervention is costly, labour-intensive and needs increased time for its implementation to offer care to the schizophrenia patients to ensure their recovery. However, no other studies have been found which mentions that the autonomy of patients is challenging the
implementation of family intervention for assisting recovery of schizophrenia patients. Thus, it cannot be assured that the autonomy of patients is hindered while implementing family intervention to ensure recovery of schizophrenic individuals in the community.
Application of Findings
In the context of practice where proper care for individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia is arranged, the above findings are effective to be implemented. This is evident as the findings mentioned that family intervention in recovery from patients suffering from schizophrenia in the community helps in reducing relapse of the symptoms as well as arranges cost-effective care (Desousa et al. 2012; Christenson et al. 2014; Barkhof et al. 2012). In England, it is reported that to arrange cognitive behavioural therapy for schizophrenia patients £250-£300 is required initially and £100 is required for further follow-up (NICE, 2014). However, the family intervention would require must less finance to be spent as the key part of counselling and caring for the patients with schizophrenia are to be done personally by the family members who do not require any payment. Further, continuous and effective care of the family members towards the patient suffering from schizophrenia ensure avoiding relapse of the symptoms of the illness as well as shows better medical compliance Schennach et al. (2012). Therefore, implementing the family intervention in caring for schizophrenia patients would be beneficial to avoid relapse of the symptoms making schizophrenic individuals lead their life normally and improve their cognitive ability to interact effectively with others in the society. However, the increased time-consumption in application of family intervention as mentioned is regarded to pose hindrance for it to be implemented as sole care support for schizophrenia patients. This is because early intervention is suggested to treat schizophrenia patients as late intervention worsens the symptoms of mental illness making the patients, as well as their family members, suffer stress, depression and anxiety (Kahn and Sommer, 2015). Further, delay in care leads patients with schizophrenia show increased negative symptoms that lead them to show poor response to recovery (Üçok et al. 2015). Thus, the family intervention is to be applied but it is kept in mind that it is implemented at the earliest to ensure effective recovery of schizophrenia patients.
Reflection
The assignment led me to develop knowledge regarding the way schizophrenia individuals create stress and depression for the family members as helped me to understand the way family intervention can act to resolve emotional burden on the family members regarding the presence of individuals affected with the illness in their surroundings. It also led me to understand the aspects to be focussed on to provide family intervention in assisting recovery of schizophrenia patients in the community. I also develop knowledge regarding the importance of psychoeducation along with communication training in establishing family intervention. The study led me to develop knowledge regarding the way family intervention impacts on the performance and health of the schizophrenia patients during their recovery. I also understood the benefits of family intervention as the challenges to be experienced during its implementation to assist the recovery of patients suffering from schizophrenia in the community.
Achievement of aims and Objectives
To identify the way of providing family intervention for schizophrenia patients The first objective is achieved through theme 1. This is because ideas regarding the way family intervention are provided for delivering care support to schizophrenia patient is mentioned. It is evident as, under the theme inclusion of family members in patient assessment and treatment, psychoeducation and communication training along with structured problem-solving are referred to the way to be followed in which family intervention can be achieved. It is also mentioned under the results that psychoeducation and communication training are ways for family intervention as it helps the family members avoid wring beliefs and promote better efficiency to communicate as well as understand needs of the schizophrenic patients to fulfil them so as to assist them in proper recovery.
To analyse the impact of family intervention for assisting recovery of schizophrenia patients in the community The second objective is achieved through theme 2 and 3 as the way family interventions are acting for schizophrenia patients to ensure their recovery is properly analysed. This is evident as statistical data presented in theme 2 informs the family intervention is actually effective for the schizophrenia patients compared to those who are provided usual care to assist them in recovery from the illness. Further, in theme 3 the benefits of family intervention such as better medical compliance, lower hospitalisation and treatment cost for schizophrenia patients are mentioned through analysis of various studies indicating how the family intervention are positively impacting the care process and patients.
To evaluate the challenges faced in providing family intervention to assist recovery of schizophrenia patients in the community The third objective is achieved through theme 4 where the challenges faced in providing family intervention for recovery of schizophrenia patients are mentioned. There it is informed that increased time consumption along with hindrance in managing autonomy of the patients is seen as challenge in applying the intervention. The increased time-consumption is a challenge because it leads to create delay in treatment for the schizophrenia patients which raises the issue of facing deteriorated symptoms portrayal by the patients.
Research Limitations
The study is mainly done through the literature review process in which different existing articles and journals are analysed and evaluated to develop information. However, the limitation is that no real-life data or new information that can be gathered through primary research in which personal experiences of the individuals regarding family intervention could be explained is able to be collected. The time provided to execute the study is short which acted as limitation as it resulted to avoid fulfilling in executing better in-depth research. Moreover, due to financial constraints many well-informative articles and journals which can be accessed through paid mode only could not be used which resulted in lowering the scope to gather better quality information for the study.
Recommendations
The emotional distress faced by the family members of individuals suffering from schizophrenia is to be resolved first before making them consider participating in the family intervention. This is because stress and tension created by the actions of the schizophrenic individuals in the family lead the family members to lose hope of showing participation in care for the individuals. Thus, resolving the emotional distress would make the family members become able to think and judge properly to understand the actual importance and benefit of family intervention in turn showing support for its successful application.
The stigma regarding schizophrenia if present in the family are to be resolved to ensure they believe that care support is able to recover the individuals who they are thinking can never be managed to live normally. The failure to resolve stigma results the family members retain their negative attitude towards the illness which in turn lead them to avoid showing participation in family intervention as they feel it be useless. Thus, resolving the stigma is important to raise positive attitude among family members in fruitfully showing participation to execute family intervention.
The family interventions are to be made as early as possible by taking immediate steps and gathering resources for it application by the health professionals and the nurses. This is because delay in implementing would deteriorate the health condition of the patients. In addition, effective participation from the family members and patients are to be ensured by informing them about the advantages of family intervention for helping the patient recover from the illness.

References
- Amagai, M., Takahashi, M. and Amagai, F., 2016. Qualitative study of resilience of family caregivers for patients with schizophrenia in Japan. Age (Years), 63(4.9), pp.55-74.
- Ardizzi, M., Ambrosecchia, M., Buratta, L., Ferri, F., Peciccia, M., Donnari, S., Mazzeschi, C. and Gallese, V., 2016. Interoception and positive symptoms in schizophrenia. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 10, p.379.
- Asmal, L., Mall, S., Emsley, R., Chiliza, B. and Swartz, L., 2014. Towards a treatment model for family therapy for schizophrenia in an urban African setting: Results from a qualitative study. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 60(4), pp.315-320.
- Atkinson, K.M., Koenka, A.C., Sanchez, C.E., Moshontz, H. and Cooper, H., 2015. Reporting standards for literature searches and report inclusion criteria: making research syntheses more transparent and easy to replicate. Research synthesis methods, 6(1), pp.87-95.
- Bademli, K. and Duman, Z.Ç., 2016. Emotions, ideas and experiences of caregivers of patients with schizophrenia about" family to family support program". Archives of psychiatric nursing, 30(3), pp.329-333.
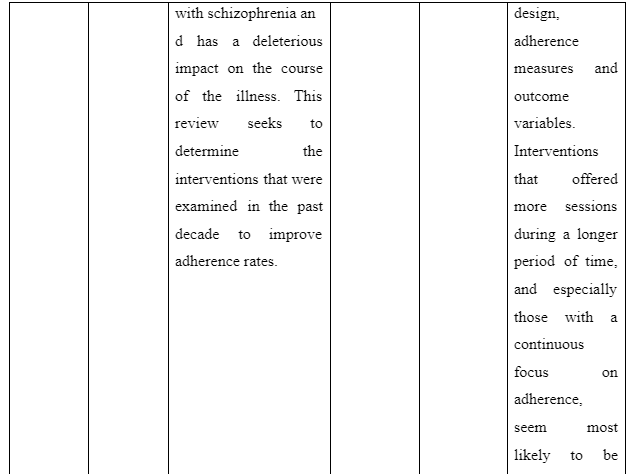
- Barkhof, E., Meijer, C.J., de Sonneville, L.M., Linszen, D.H. and de Haan, L., 2012. Interventions to improve adherence to antipsychotic medication in patients with schizophrenia–a review of the past decade. European Psychiatry, 27(1), pp.9-18.
- Bishop, M. and Greeff, A.P., 2015. Resilience in families in which a member has been diagnosed with schizophrenia. Journal of psychiatric and mental health nursing, 22(7), pp.463-471. Cai, J., Zhu, Y., Zhang, W., Wang, Y. and Zhang, C., 2015. Comprehensive family therapy: an effective approach for cognitive rehabilitation in schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment, 11, p.1247.
- Campellone, T.R., Sanchez, A.H. and Kring, A.M., 2016. Defeatist performance beliefs, negative symptoms, and functional outcome in schizophrenia: a meta-analytic review. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 42(6), pp.1343-1352. Caqueo-Urízar, A., Rus-Calafell, M., Urzúa, A., Escudero, J. and Gutiérrez-Maldonado, J., 2015. The role of family therapy in the management of schizophrenia: challenges and solutions. Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment, 11, p.145.
- Caqueo-Urízar, A., Rus-Calafell, M., Craig, T.K., Irarrazaval, M., Urzúa, A., Boyer, L. and Williams, D.R., 2017. Schizophrenia: impact on family dynamics. Current psychiatry reports, 19(1), p.2. Carvalho, D.P., Azevedo, I.C., Cruz, G.K., Mafra, G.A., Rego, A.L., Vitor, A.F., Santos, V.E., Cogo, A.L. and Júnior, M.A.F., 2017. Strategies used for the promotion of critical thinking in nursing undergraduate education: a systematic review. Nurse education today, 57, pp.103-107.
- Cella, M., Preti, A., Edwards, C., Dow, T. and Wykes, T., 2017. Cognitive remediation for negative symptoms of schizophrenia: a network meta-analysis. Clinical psychology review, 52, pp.43-51. Chakrabarti, S., 2011. Family interventions in schizophrenia: Issues of relevance for Asian countries. World journal of psychiatry, 1(1), p.4.
- Chan, C.K.P. and Ho, R.T.H., 2016. Discrepancy in spirituality among patients with schizophrenia and family care-givers and its impacts on illness recovery: a dyadic investigation. British Journal of Social Work, 47(1), pp.28-47. Chrastina, J., 2016. PICO (T) and PCD formats of clinically relevant questions in the conceptualization of special education research. J Except People, 1(8), pp.32-40.
- Christenson, J.D., Crane, D.R., Bell, K.M., Beer, A.R. and Hillin, H.H., 2014. Family intervention and health care costs for Kansas Medicaid patients with schizophrenia. Journal of marital and family therapy, 40(3), pp.272-286. Desousa, A., Kurvey, A. and Sonavane, S., 2012. Family psychoeducation for schizophrenia: a clinical review. Malaysian Journal of Psychiatry, 21(2). pp.29-34. Desousa, A., Kurvey, A. and Sonavane, S., 2012. Family psychoeducation for schizophrenia: a clinical review. Malaysian Journal of Psychiatry, 21(2). pp.1-12.
- Eichner, C. and Berna, F., 2016. Acceptance and efficacy of metacognitive training (MCT) on positive symptoms and delusions in patients with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis taking into account important moderators. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 42(4), pp.952-962. Fiorillo, A., Del Vecchio, V., Luciano, M., Sampogna, G., Sbordone, D., Catapano, F., De Rosa, C., Malangone, C., Tortorella, A., Veltro, F. and Nicolò, G., 2016. Feasibility of a psychoeducational family intervention for people with bipolar I disorder and their relatives: results from an Italian real-world multicentre study. Journal of affective disorders, 190, pp.657-662.
- Foster, K., Maybery, D., Reupert, A., Gladstone, B., Grant, A., Ruud, T., Falkov, A. and Kowalenko, N., 2016. Family-focused practice in mental health care: An integrative review. Child & Youth Services, 37(2), pp.129-155. Girón, M., Nova-Fernández, F., Mañá-Alvarenga, S., Nolasco, A., Molina-Habas, A., Fernández-Yañez, A., Tabarés-Seisdedos, R. and Gómez-Beneyto, M., 2015. How does family intervention improve the outcome of people with schizophrenia?. Social psychiatry and psychiatric epidemiology, 50(3), pp.379-387.
- Harvey, C. and O’Hanlon, B., 2013. Family psycho-education for people with schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders and their families. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 47(6), pp.516-520.
- health.ebsco.com 2019, CINHAL, Available at: https://health.ebsco.com/products/the-cinahl-database [Accessed on: 19th October 2019] Kahn, R.S. and Sommer, I.E., 2015. The neurobiology and treatment of first-episode schizophrenia. Molecular psychiatry, 20(1), p.84. Kangasniemi, M., Pakkanen, P. and Korhonen, A., 2015. Professional ethics in nursing: an integrative review. Journal of advanced nursing, 71(8), pp.1744-1757.
- Koivunen, M. and Saranto, K., 2018. Nursing professionals' experiences of the facilitators and barriers to the use of telehealth applications: a systematic review of qualitative studies. Scandinavian journal of caring sciences, 32(1), pp.24-44. Köpke, S., Giordano, A., Veronese, S., Christin Rahn, A., Kleiter, I., Basedow‐Rajwich, B., Fornari, A., Battaglia, M.A., Drulovic, J., Kooij, L. and Koops, J., 2019. Patient and caregiver
- involvement in the formulation of guideline questions: findings from the European Academy of Neurology guideline on palliative care of people with severe multiple sclerosis. European journal of neurology, 26(1), pp.41-50. Lasebikan, V.O. and Ayinde, O.O., 2013. Family burden in caregivers of schizophrenia patients: Prevalence and socio-demographic correlates. Indian journal of psychological medicine, 35(1), p.60.
- Leonardo, R., 2018. PICO: Model for Clinical Questions. Evid Based Med Pract, 3(115), p.2. livingwithschizophreniauk 2019, Schizophrenia: Facts and Figures, Available at: https://www.livingwithschizophreniauk.org/facts-and-figures/ [Accessed on: 19th October 2019] Marder, S.R. and Galderisi, S., 2017. The current conceptualization of negative symptoms in schizophrenia. World Psychiatry, 16(1), pp.14-24.
- McFarlane, W.R., 2016. Family interventions for schizophrenia and the psychoses: A review. Family Process, 55(3), pp.460-482. McGowan, J., Sampson, M., Salzwedel, D.M., Cogo, E., Foerster, V. and Lefebvre, C., 2016. PRESS peer review of electronic search strategies: 2015 guideline statement. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 75, pp.40-46.
- NICE 2014, Costing statement: Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: treatment and management Implementing the NICE guideline on Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults, Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg178/resources/costing-statement-191763901 [Accessed on: 19th October 2019]
- NICE 2015, NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE, https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg155/update/CG155/documents/psychosis-and-schizophrenia-in-children-and-young-people-final-scope2 [Accessed on: 19th October 2019] Okpokoro, U. and Sampson, S., 2014. Brief family intervention for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia bulletin, 40(3), p.497.
- Phanthunane, P., Vos, T., Whiteford, H. and Bertram, M., 2011. Cost-effectiveness of pharmacological and psychosocial interventions for schizophrenia. Cost Effectiveness and Resource Allocation, 9(1), p.6.
- psychiatry.cam.ac.uk 2014, Systematic Review of the Incidence and Prevalence of Schizophrenia and Other Psychoses in England, Available at: https://www.psychiatry.cam.ac.uk/files/2014/05/Final-report-v1.05-Jan-12.pdf [Accessed on: 19th October 2019]
- Ran, M.S., Chan, C.W., Ng, S.M., Guo, L.T. and Xiang, M.Z., 2015. The effectiveness of psychoeducational family intervention for patients with schizophrenia in a 14-year follow-up study in a Chinese rural area. Psychological medicine, 45(10), pp.2197-2204.
- Remington, G., Foussias, G., Fervaha, G., Agid, O., Takeuchi, H., Lee, J. and Hahn, M., 2016. Treating negative symptoms in schizophrenia: an update. Current treatment options in psychiatry, 3(2), pp.133-150.
- Ribé, J.M., Salamero, M., Pérez-Testor, C., Mercadal, J., Aguilera, C. and Cleris, M., 2018. Quality of life in family caregivers of schizophrenia patients in Spain: caregiver characteristics, caregiving burden, family functioning, and social and professional support. International journal of psychiatry in clinical practice, 22(1), pp.25-33. Rouleau, G., Gagnon, M.P., Côté, J., Payne-Gagnon, J., Hudson, E., Bouix-Picasso, J. and Dubois, C.A., 2017. Effects of e-learning in a continuing education context on nursing care: a review of systematic qualitative, quantitative and mixed studies reviews (protocol). BMJ open, 7(10), p.e018441.
- Scells, H., Zuccon, G., Koopman, B., Deacon, A., Azzopardi, L. and Geva, S., 2017, November. Integrating the framing of clinical questions via PICO into the retrieval of medical literature for systematic reviews. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (pp. 2291-2294). ACM. Schennach, R., Riedel, M., Musil, R. and Möller, H.J., 2012. Treatment response in first-episode schizophrenia. Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience, 10(2), p.78.
- Sekar, A., Bialas, A.R., de Rivera, H., Davis, A., Hammond, T.R., Kamitaki, N., Tooley, K., Presumey, J., Baum, M., Van Doren, V. and Genovese, G., 2016. Schizophrenia risk from complex variation of complement component 4. Nature, 530(7589), p.177. Sin, J. and Norman, I., 2013. Psychoeducational interventions for family members of people with schizophrenia: a mixed-method systematic review. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 74(12), pp.e1145-62.
- Tas, C., Danaci, A.E., Cubukcuoglu, Z. and Brüne, M., 2012. Impact of family involvement on social cognition training in clinically stable outpatients with schizophrenia—a randomized pilot study. Psychiatry research, 195(1-2), pp.32-38. Üçok, A., Çikrikçili, U., Karabulut, S., Salaj, A., Öztürk, M., Tabak, Ö. and Durak, R., 2015. Delayed initiation of clozapine may be related to poor response in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. International clinical psychopharmacology, 30(5), pp.290-295.
- van Os, J., 2016. “Schizophrenia” does not exist. BMJ, 352, p.375. Von Kardorff, E., Soltaninejad, A., Kamali, M. and Eslami Shahrbabaki, M., 2016. Family caregiver burden in mental illnesses: The case of affective disorders and schizophrenia–a qualitative exploratory study. Nordic journal of psychiatry, 70(4), pp.248-254.
- hen, Q. and Yang, M., 2017. Effect of caregivers’ expressed emotion on the care burden and rehospitalization rate of schizophrenia. Patient preference and adherence, 11, p.1505. Burbach, F.R., 2018. Family therapy and schizophrenia: a brief theoretical overview and a framework for clinical practice. BJPsych Advances, 24(4), pp.225-234.

























Dig deeper into A Holistic Exploration from Origins to Contemporary with our selection of articles.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



