Autonomic Nervous System Overview
Question 1:
Identify the component parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system, and state their functions.
The component part of central nervous and the peripheral nervous system as a flow diagram has been given below and its components are given in the said flow chart.


b) Describe the autonomic nervous system

The autonomic nervous system mainly acts on the automatic movement of internal organs without prior intervention into their functional activities (Fox, 2015). They comprise of three set of nerves are described below:
Sympathetic nervous system: It plays key role to connect the brain by nerves from the spinal cord with internal organs. This response is termed as flight or fight. Its function is to produce adjustment to the body which is localized, for example the sweating rate increases as the body temperature enhanced. This will prepare an individual from looming danger. In the stress condition this nervous system gets activated and hormone adrenalin will get released from adrenal gland that will ultimately increase the heart rate. (Kreibig, 2010)
Continue your exploration of Function of the Brain and Nervous System with our related content.
Parasympathetic nervous system: This part of nervous system regulates the activity of visceral parts of organs such as glands. It also provides the control of many tissues but to be noted that it is not meant to regulate crucial parts of life. The nerve fibres for parasympathetic nervous system is cranial nerves. The nature of organization of parasympathetic nerve are almost similar to sympathetic nerve. It has two motor component one is preganglionic and other is postganglionic neurons. The preganglionic neurons stay at brainstem within the specific group of cell (nuclei). These neurons secrets neurotransmitter acetylcholine for signal transmission. (Kreibig, 2010)
Enteric nervous system: They are the group of nerves which is in the form of mesh-like networking and regulate the function of the gastrointestinal tract in human body. These nerves though clubbed with both other nervous system sympathetic and parasympathetic but can act independently. This nervous system even can be operated without the dependence of brain and spine. Apart from the acetylcholine this nervous system also secretes dopamine and serotonin. (Kreibig, 2010)

Question 2:
Describe the structure of a sensory neurone and a motor neurone, and explain their functions in a reflex arc.
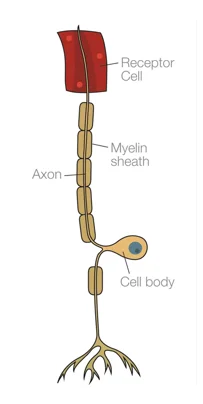

Sensory neurons are connected from the receptor cell to its point of action through intervening axon, cell body and dendrons. Whereas motor neuron which don’t need any receptor organ, are connected directly to the point of action. The sensory response moves through sensory nerve and goes to brain via spinal cord whereas motor response goes from brain to the corresponding organ. Figure 1 demonstrates the variation of structure of the both neurons. (Power, et al, 2011)
Question 3:
Explain, using illustrations, the function of a motor neuron and a sensory neuron in a reflex arc using the example of a knee jerk (patellar) reflex.
Function of Sensory and motor neuron in reflex arc: The act of sensory neuron and motor neuron are concomitant. Sensory neuron bring the nerve impulse from the receptor (skin, eye) to the central nervous system and the motor neuron bring the nerve response to the effector to do the resultant action. This is termed as the reflex arc (McArdle, et al, .2010).
Looking for further insights on Foundations of Nursing and Evidence Based Healthcare? Click here.
For example knee jerk reflex or patellar reflex is the sudden movement of kicking happens in the lower leg upon sharp tap on the patellar tendon. Patellar tendon lies exactly below the knee cap. (O'Brien, 2010)
Question 4 (2.1)
2.1 Describe and explain the transmission of an action potential in a myelinated neurone:

A neuron receives input from its neighbouring neuron with the help of a chemical termed as neurotransmitter. If the signal is intense the neuron will pass it to the adjacent neuron. The signal is transmitted from dendrite to axon end by simultaneous on and off of ion channels which are regulated by potential difference and this results a brief setback of the resting membrane potential resulting the creation of an action potential. This action potential when moves down to the axon the membrane changes its polarity (Ford, et al, 2015). Sodium and potassium ion and the associated pump play an important role to generate action potential. When stimulus is received by the nerve cell then the sodium channel gets open and the three sodium ion which is positively charged with enter to the nerve cell by diffusion and two potassium ion will diffuse out from the cell. This sodium potassium pump induce the imbalance which will lead to the separation of charge cross the membrane, so the resting membrane potential will be converted to action potential (Lacroix, et al, 2013).
The transmission of an action potential to make a communication it is necessary that the potential should travel along the axon. When it reach the terminus of axon it releases neurotransmitter. This speed of action potential conduction is dependent both on the diameter of axon and its resistance towards leakage of potential. Here myelin plays the role of insulator which stops the leaking of current and increase the speed for conduction of action potential. In multiple sclerosis disease this myelin layer get degraded and as a result the action potential conduction slows down due to current leakage. (O'Brien, 2010)
Question 5 (2.2)
2.2 Describe the all-or-nothing nature of nerve impulses
All or nothing principle is such that the strength of response by which nerve response to a stimulus is quantised or rather it is independent of the intensity of stimulus. If the stimulus goes out of the potential threshold the response will be there, otherwise there will be zero response (Tasaki, 2012). The individual nerve fibre respond to stimulation based on this principle. It has been found in the nerve fibre response. If a stimulus is above threshold value an action potential is generated and the neuron then set out information through its axon from a cell body to the synapse then changes in the polarization of cell result the propagation of signal through the length of axon. The action potential gives always a complete response. There is no strong or weak action potential or rather there is an all or nothing response. This lowers the possibility of information to be lost along the path. It’s like a gun firing process. A very slight push on trigger will not be good enough and the shooting will not be possible. If the push is above a particular strength the gun will fire the bullet. Moreover, the speed of the bullet is not dependent on the strength above a minimum value of shooting. (McComas, 2011)
Question 6 (2.3)
2.3 Explain the importance of the myelin sheath and the refractory period in determining the speed of nervous impulses.
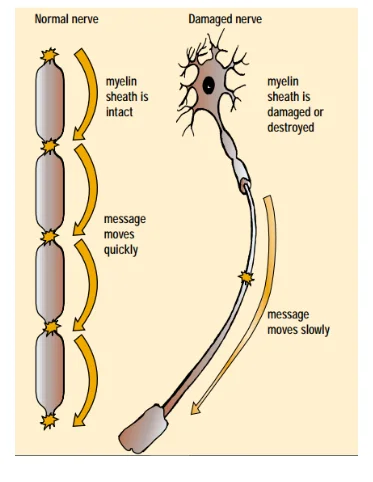
Nerve fibres are coated with a non-conducting layer of fat called myelin sheath. Nerve fibres present in the gray matter do not have myelin sheath, as soon as neuron comes into white matter it gets it covering, myelin sheath. When it comes out of central nervous system it gets another cover the neurolemma. When nerve fibres end at the peripheral region first neurolemma is lost and then myelin sheath and at last the axis cylinder. Then the nerve ends as nacked. This layer promotes the movement of impulse through its leak proof activity and acts as insulator. There are gaps in this layer called nodes of Ranvier (Ford, et al, 2015). The impulse can move quickly by hopping from one node to another and in this way the movements become quicker if it would travel through entire length of fibre. The transmission speed is very high like 100mt/sec, as high as a formula one racing car. The loss of this fatty layer leads to severe ailment because mow the potential can no longer jump rather it has to travel a continuous long distance. So, the whole process of electric potential transfer becomes short-circuited. Also, there is a high rate of leakage of potential this kind of damage of myelin sheath is called multiple sclerosis and the symptoms can include sensory impairment like blurred vision, difficulties in controlling the body movement like failure to control urination.

Opening of Na+ channels instantly leads to inactivation of them. Therefore, at the apex of the action potential every Na+ ion channel gets deactivated. When they are inactivated they cannot get activated instantly and they remain closed for a particular time period. The recovery of activated state from its inactivated counterpart is a voltage dependent procedure and the generation of this voltage needs time of about 3-4 millisecond. Hence, after each inactivation cycle at least 3-4 millisecond is needed for all Na+ ion channels to work again. The time period from start of the action potential to just after the peak is termed as absolute refractory period see figure 4. This is the period of time during which the second stimulus provided (no matter how strong is it) does not lead to second set of action potential. The absolute refractory period is 1-2 millisecond. After this absolute refractory time period Na+ ion channels start to come back from inactivation and if then strong enough stimuli are given, it may work again by generation of action potentials. However, this time the given stimuli needs to be much stronger than originally needed when the neuron is at rest. This kind of situation will be continued till all of the Na+ ion channels have recovered from the state of inactivation. The time period during which the stronger stimuli (stronger with respect to normally needed) is given is called relative refractory period. (McComas, 2011)
Question 7 (3.1)
Describe the structure of a cholinergic synapse, and explain how it functions

This kind of synapses use acetylcholine as neurotransmitter. This is the most important kind of synapse in the body as it transmit the signal into neuromuscular junctions. The transmission of synaptic impulse begins when the action potential travels presynaptic neuron’s synaptic knob. With this impulse the Ca2+ ion channels open up. Then the Ca2+ from the outside fluid comes into presynaptic knob (Picciotto, et al, 2012). This influx causes synaptic vesicles containing acetylcholine to fuse into the presynaptic membrane. Then the acetylcholine get released into the inter synaptic cleft. This acetylcholine through diffusion process goes into the acetylcholine receptor of postsynaptic neuron. (DeFeudis, 2012)
Question 8 (3.2)
The illustration below explains the role of synapses. Explain the role of the synapse in the nervous system in determining the direction of nerve impulse transmission, allowing the interconnection of nerve pathways.

The illustration describes the pathway of neurotransmission from transmission through neuronal network. The incoming impulse travels from one neuron cell to another neuron cell. The first cell is called presynaptic cell and the second one is postsynaptic cell. In the illustration marker 1 shows that the nerve impulse travels from axon to the presynaptic knob (Choquet, et al, 2013).
Marker 2: Upon travelling of this impulse the synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitter molecules (indicated in the illustration as blue particles), move and fuse to the presynaptic membrane (Choquet, et al, 2013).
Marker 3: Upon fusion of the synaptic vesicles into the presynaptic membrane the neurotransmitter molecules are released into the interstitial space called synaptic cleft (Choquet, et al, 2013).
Marker 4: The neurotransmitter molecule released into synaptic cleft goes to the post synaptic membrane, containing the neurotransmitter receptor molecules. This receptor molecules are basically ion channel proteins. Upon binding of the neurotransmitter the ion channel gets opened and Na+ ion passes through them. Afterword enzymes break the neurotransmitter molecules into their precursors, which are finally reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron (Choquet, et al, 2013). The pink arrow shows the transmission of impulse.
Question 9 (3.3)
Describe the role and effect of synaptic inhibition.
Synaptic inhibition is very important and it happens all around brain and nerves. This process is as important as the excitation pathway. This happens by the action of a chemical transmitter substance which pushes neuron towards the backway from firing. The most common de-excitation neurotransmitter is GABA (gamma amino butyric acid). Another important neurotransmitter is glycine. Lack of this inhibitors the opposing muscle present in our body like biceps and triceps would not work properly, as a result convulsion occurs. In case of strychnine poisoning this glycine is knocked out and the patient undergoes death due to rapid convulsion. (Andersen et. al. 2006)

Reflections
Can you identify specific learning points? If so tell us about these.
Answer: The assignment contains a complete guide to the action of nervous system including its components. The important point associated with this assignment is, it is a point by point approach towards learning of the complete scenario.
Were the materials and assessment clear? If not, can you identify areas for improvement?
Answer: They were very much clear.
Did the topic inspire you to further reading? Please share any relevant/interesting links.
Answer: Yes. It indulge my curiosity of anatomy and physiology of nervous system.
Reference
Andersen, P., Morris, R., Amaral, D., Bliss, T. and O'Keefe, J. eds., 2006. The hippocampus book. Oxford university press.
Brodal, P., 2004. The central nervous system: structure and function. oxford university Press
Choquet, D. and Triller, A., 2013. The dynamic synapse. Neuron, 80(3), pp.691-703.
DeFeudis, F.V., 2012. Central cholinergic systems and behaviour. Elsevier.
Esquenazi, A., Talaty, M., Packel, A. and Saulino, M., 2012. The ReWalk powered exoskeleton to restore ambulatory function to individuals with thoracic-level motor-complete spinal cord injury. American journal of physical medicine & rehabilitation, 91(11), pp.911-921.
Ford, M.C., Alexandrova, O., Cossell, L., Stange-Marten, A., Sinclair, J., Kopp-Scheinpflug, C., Pecka, M., Attwell, D. and Grothe, B., 2015. Tuning of Ranvier node and internode properties in myelinated axons to adjust action potential timing. Nature communications, 6(1), pp.1-14.
Lacroix, J.J., Campos, F.V., Frezza, L. and Bezanilla, F., 2013. Molecular bases for the asynchronous activation of sodium and potassium channels required for nerve impulse generation. Neuron, 79(4), pp.651-657.
Nelson, A.B. and Kreitzer, A.C., 2014. Reassessing models of basal ganglia function and dysfunction. Annual review of neuroscience, 37, pp.117-135.
Power, J.D., Cohen, A.L., Nelson, S.M., Wig, G.S., Barnes, K.A., Church, J.A., Vogel, A.C., Laumann, T.O., Miezin, F.M., Schlaggar, B.L. and Petersen, S.E., 2011. Functional network organization of the human brain. Neuron, 72(4), pp.665-678.
Tasaki, I., 2012. Physiology and electrochemistry of nerve fibers. Elsevier.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



